2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: 2g-and-3g-switch-off
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 2G and 3G switch-off market, covering insights into market size, growth forecasts, segmentation, and regional analysis from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
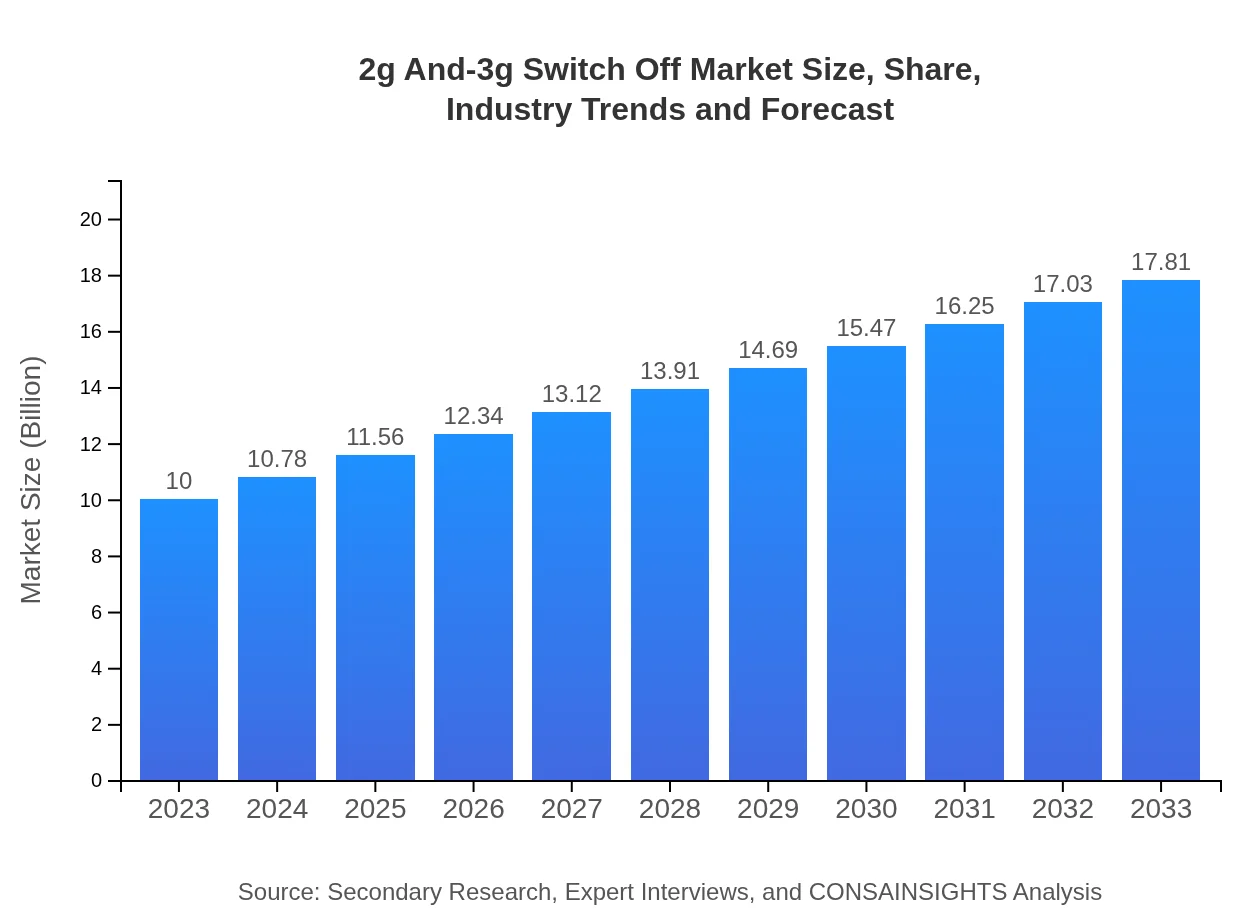
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $17.81 Billion |
| Top Companies | Vodafone, AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, Telefónica, China Mobile |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Overview
Customize 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 2g And-3g Switch Off market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 2g And-3g Switch Off's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 2g And-3g Switch Off
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 2g And-3g Switch Off market in 2023?
2g And-3g Switch Off Industry Analysis
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report:
Europe, as a mature market, is projected to grow from USD 2.97 billion in 2023 to USD 5.28 billion by 2033. The switch-off of 2G and 3G networks in various European nations is increasingly driven by regulatory mandates aiming for enhanced network efficiency.Asia Pacific 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region is valued at approximately USD 1.75 billion, projected to grow to USD 3.11 billion by 2033. The high number of mobile users and rapid technological adoption contribute significantly to this growth, along with government initiatives aiming to enhance digital infrastructure.North America 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report:
North America shows a robust market size of USD 3.88 billion in 2023, expected to rise to USD 6.90 billion by 2033. The region's advanced telecom ecosystem and high adoption rates of 4G and 5G technologies are vital contributors to this growth forecast.South America 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report:
The South American market size is relatively small, estimated at USD 0.20 billion in 2023, with a projected increase to USD 0.36 billion in 2033. Key markets like Brazil and Argentina are anticipated to drive slow but steady growth as local operators begin transitioning away from legacy networks.Middle East & Africa 2g And-3g Switch Off Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's market is valued at USD 1.21 billion in 2023, forecasting to reach USD 2.16 billion by 2033. Increasing mobile penetration and demands for better connectivity are the primary drivers of this market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
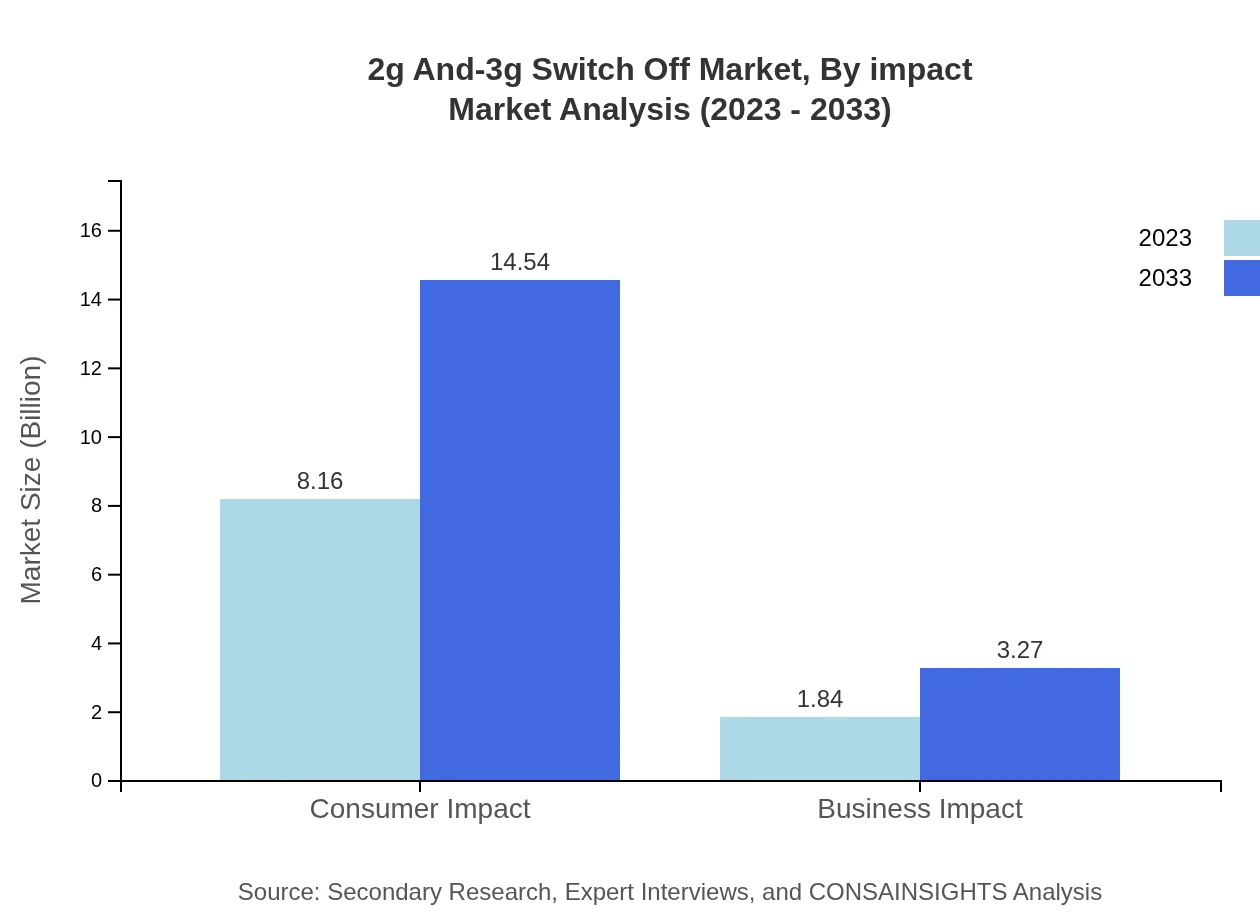
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis By Impact
Consumer Impact: In 2023, consumer impact on the market is estimated at USD 8.16 billion, projected to grow to USD 14.54 billion by 2033, showcasing significant demand for improved mobile services. Business Impact: Business impact is expected to rise from USD 1.84 billion in 2023 to USD 3.27 billion by 2033, reflecting increasing reliance on mobile connectivity for business operations.
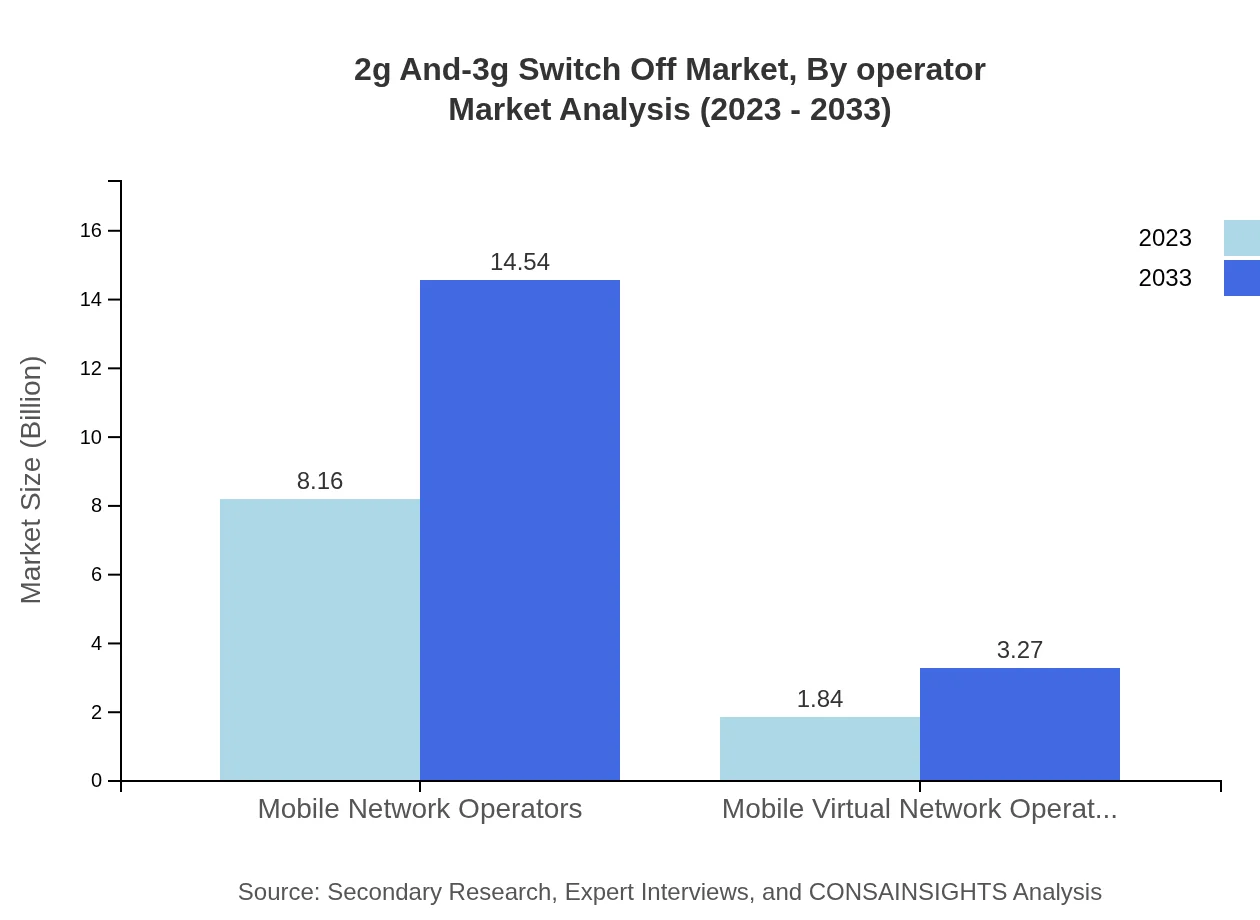
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis By Operator
Mobile Network Operators dominate the segment, with market estimates of USD 8.16 billion in 2023 and reaching USD 14.54 billion by 2033. Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) currently make up a smaller share, with projections of USD 1.84 billion in 2023 growing to USD 3.27 billion by 2033.
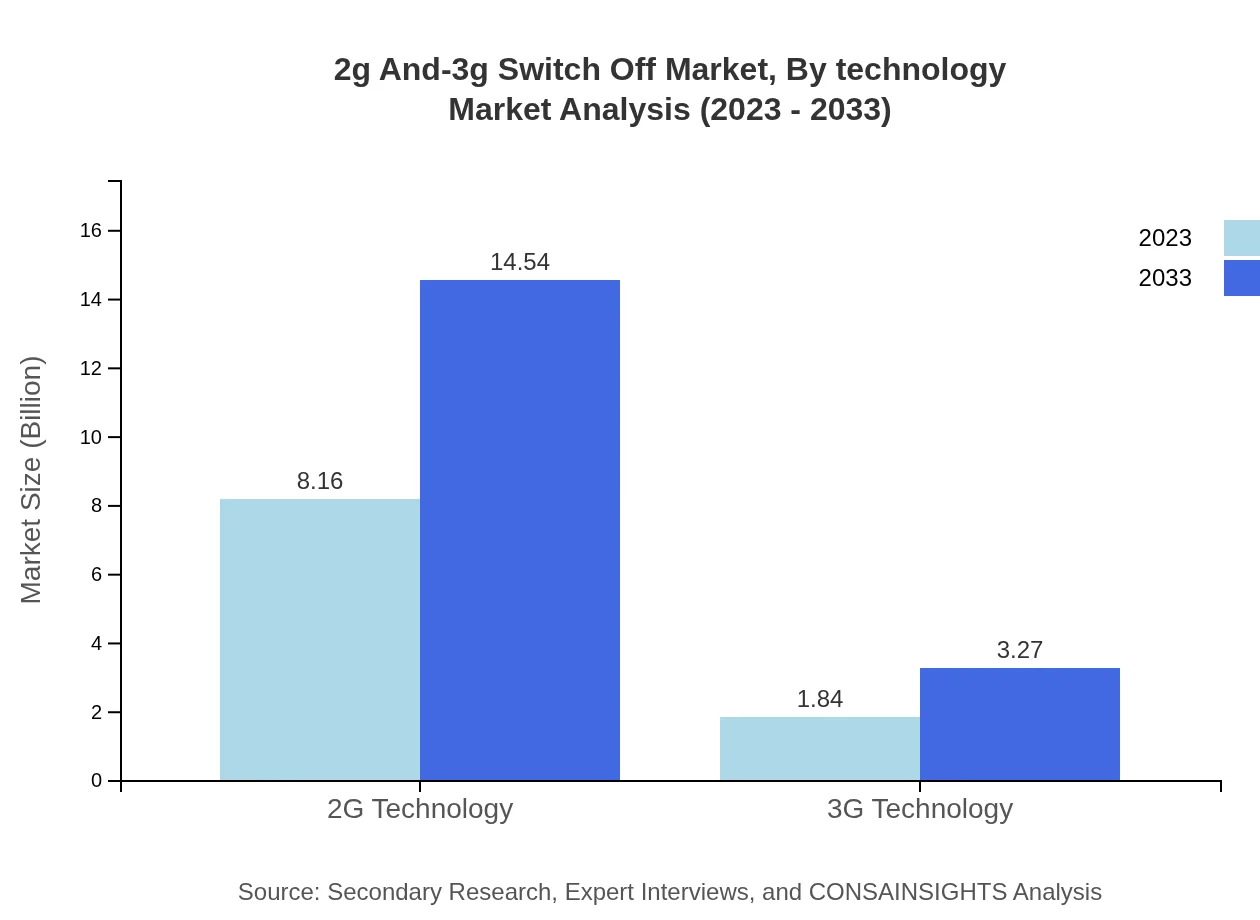
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis By Technology
In terms of technology, 2G currently holds the larger market share, with an estimated size of USD 8.16 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 14.54 billion by 2033. 3G technology, while diminishing, still plays a part with a market size of USD 1.84 billion in 2023 growing to USD 3.27 billion by 2033.
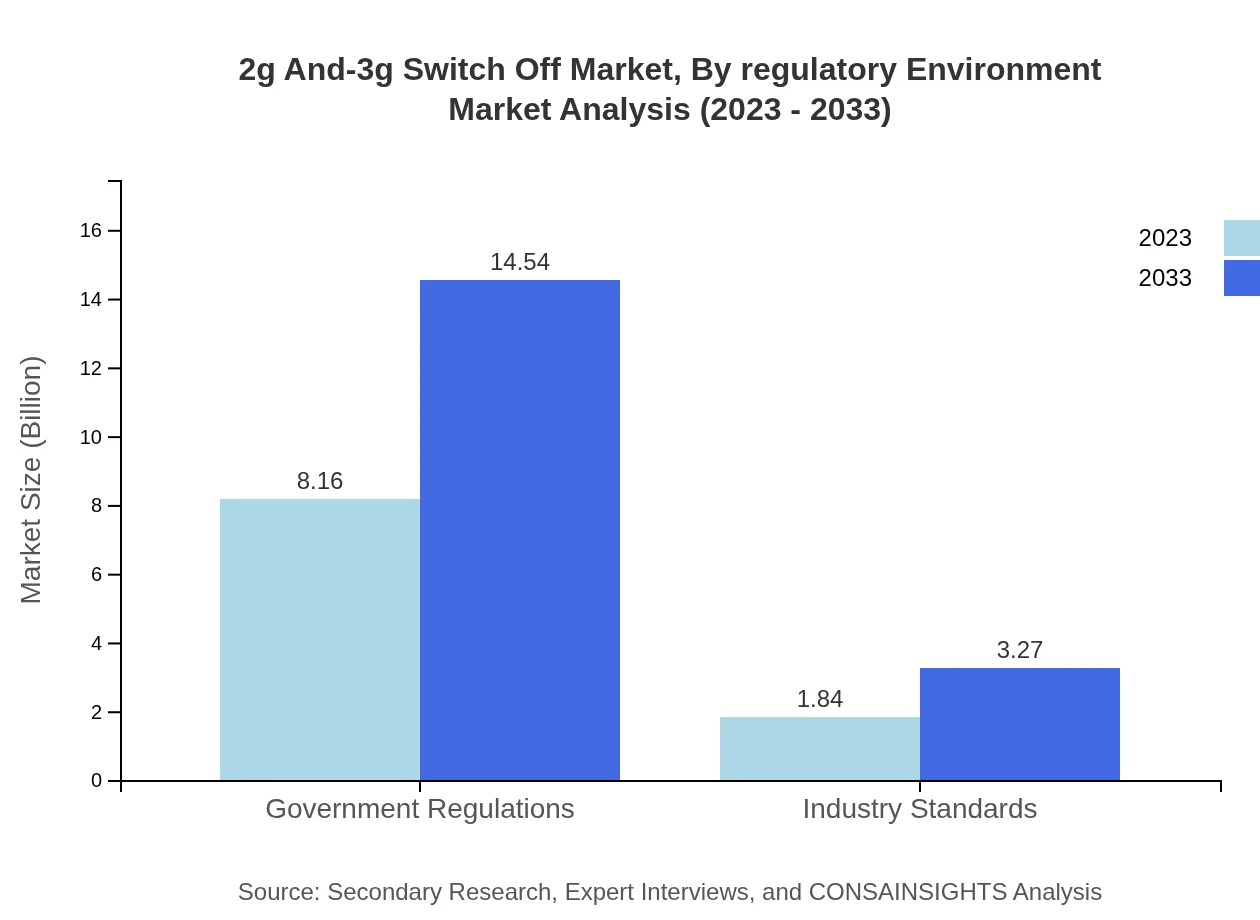
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis By Regulatory Environment
Government regulations significantly shape the market, valued at USD 8.16 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to USD 14.54 billion by 2033, indicating strong regulatory support for the transition to advanced technologies.
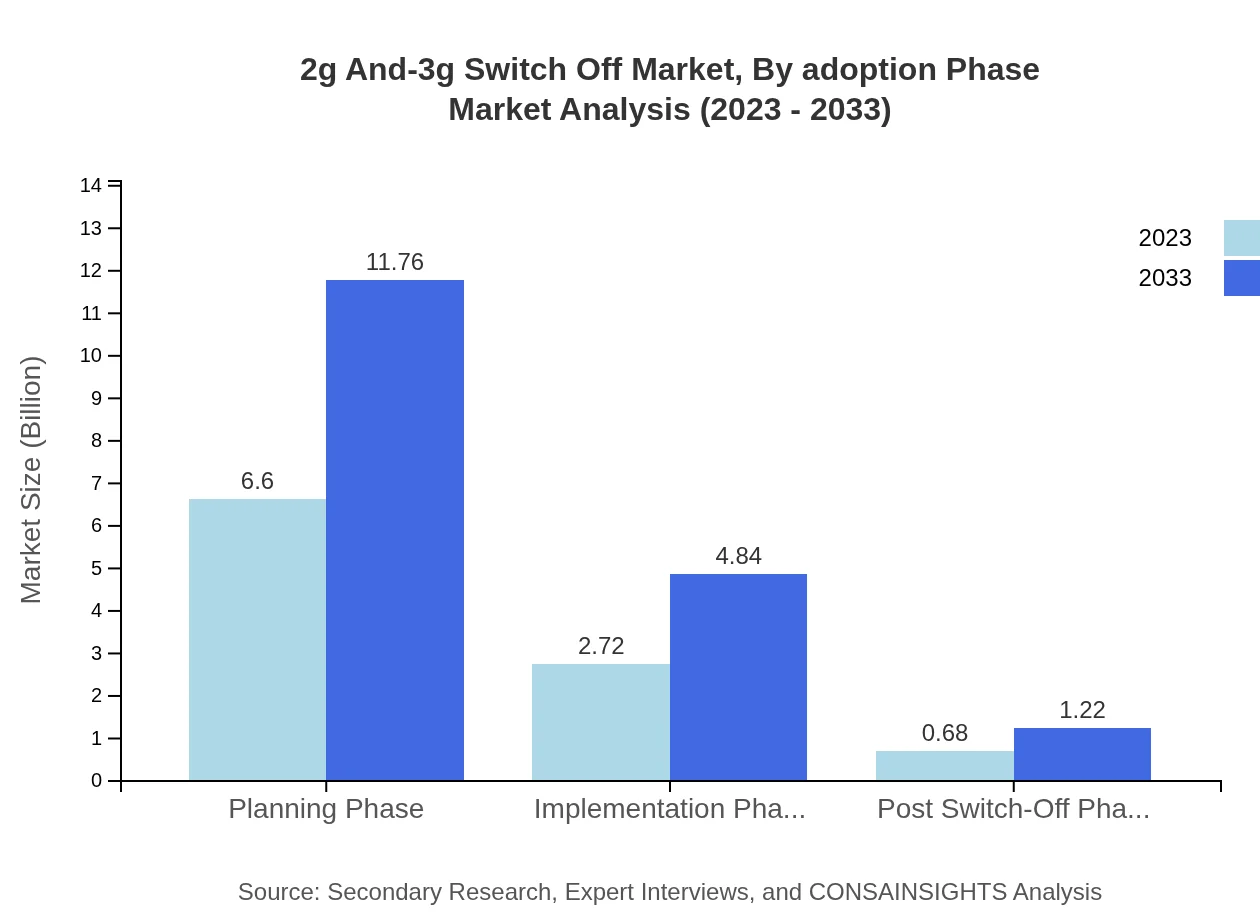
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Analysis By Adoption Phase
Market dynamics vary across adoption phases. The Planning Phase is projected to hold a market size of USD 6.60 billion in 2023, increasing to USD 11.76 billion in 2033, while the Implementation Phase sees projections from USD 2.72 billion growing to USD 4.84 billion during the same timeframe.
2g And-3g Switch Off Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 2g And-3g Switch Off Industry
Vodafone:
Vodafone is a leading player with significant investments in transitioning its services to 4G and 5G, known for its proactive approach in phasing out older networks.AT&T:
AT&T is at the forefront of the 2G and 3G switch-off, actively restructuring its technology stacks to provide enhanced connectivity and user experiences.Deutsche Telekom:
Deutsche Telekom has been a pioneer in the switch-off movement in Europe, leading initiatives to manage the network transition effectively.Telefónica:
Telefónica is dedicated to advancing its network capabilities, including the decommissioning of legacy technologies to serve its customers better.China Mobile:
China Mobile controls a significant share of the Asian market and is transitioning its operations from older mobile technologies to newer, more efficient standards.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 2g And-3g Switch Off?
The global market size for the 2G and 3G switch-off is projected to reach $10 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This reflects a significant shift towards advanced mobile technology as telecom operators phase out older networks.
What are the key market players or companies in this 2g And-3g Switch Off industry?
Key players in the 2G and 3G switch-off industry include major telecommunications companies, mobile network operators, and vendors of telecommunication equipment. These companies are actively involved in the transition to newer technologies and infrastructure development.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 2g And-3g Switch Off industry?
Key growth factors in the 2G and 3G switch-off industry include increasing demand for higher-speed networks, advancements in mobile technology, rising smartphone adoption, and regulatory pressures to modernize telecommunications infrastructure.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 2g And-3g Switch Off?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market, with expected market growth from $1.75 billion in 2023 to $3.11 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by rapid urbanization and increasing mobile data consumption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 2g And-3g Switch Off industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs in the 2G and 3G switch-off industry, including detailed analyses of market trends, competitive landscapes, and technology advancements.
What deliverables can I expect from this 2g And-3g Switch Off market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, growth forecasts, SWOT analysis of key players, data on regional performance, and insights into consumer and business impacts within the 2G and 3G switch-off market.
What are the market trends of 2g And-3g Switch Off?
Current market trends show a move towards 4G and 5G technologies, increasing investments in telecom infrastructure, and a growing emphasis on IoT applications, contributing to the gradual phase-out of 2G and 3G services.