3d Laser Scanner Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-laser-scanner
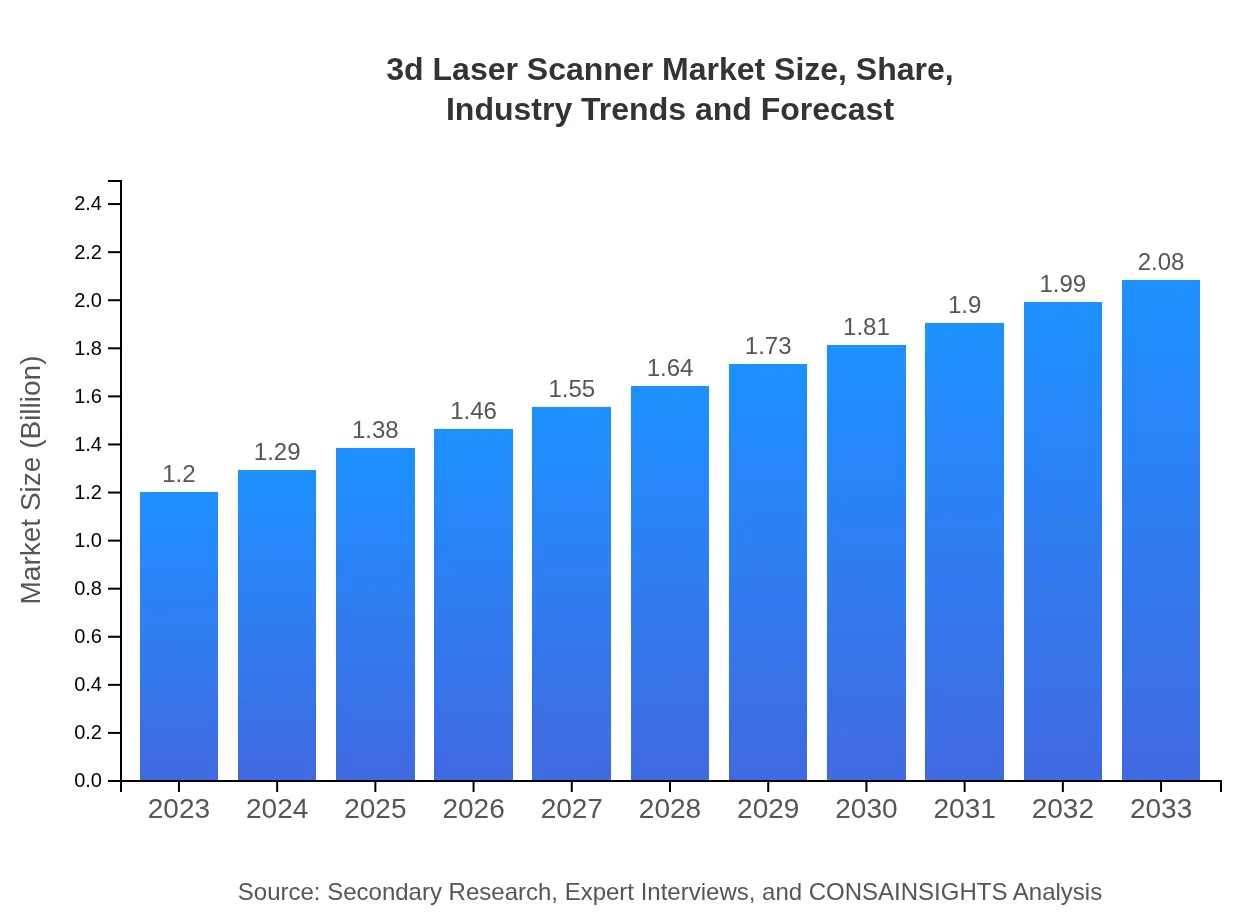
3d Laser Scanner Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 3D Laser Scanner market from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, growth trends, regional insights, and competitive landscape, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions in this evolving industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $1.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.08 Billion |
| Top Companies | Faro Technologies, Leica Geosystems, Trimble Inc., Zoller + Fröhle GmbH |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3d Laser Scanner Market Overview
Customize 3d Laser Scanner Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Laser Scanner market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Laser Scanner's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Laser Scanner
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 3d Laser Scanner market in 2023?
3d Laser Scanner Industry Analysis
3d Laser Scanner Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3d Laser Scanner Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Laser Scanner Market Report:
Europe's market is projected to expand from $0.29 billion in 2023 to $0.50 billion by 2033. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are leading due to strong regulations around construction standards and technological innovations. The rise in historic preservation efforts is also contributing significantly to this growth.Asia Pacific 3d Laser Scanner Market Report:
The 3D laser scanner market in Asia Pacific is growing rapidly, projected to reach $0.40 billion by 2033 from $0.23 billion in 2023. Contributions from emerging economies such as China and India are significant, with increased investments in infrastructure development driving demand. Additionally, technology adoption in sectors like manufacturing and construction is expected to enhance market dynamics.North America 3d Laser Scanner Market Report:
North America maintains a prominent position in the global market, expected to rise from $0.42 billion in 2023 to $0.72 billion by 2033. The presence of key market players and led technology-driven industries like automotive and aerospace emphasize advanced scanning solutions. The integration of 3D scanning with digital twins is a notable trend here.South America 3d Laser Scanner Market Report:
The South American market is anticipated to grow from $0.12 billion in 2023 to $0.20 billion by 2033. The mining and construction industries in countries like Brazil and Argentina are key contributors. However, the market is challenged by economic fluctuations and limited technological adoption.Middle East & Africa 3d Laser Scanner Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to grow from $0.15 billion in 2023 to $0.25 billion by 2033. Countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) are adopting 3D laser technologies for urban development projects. However, challenges such as budget constraints and economic dependence on oil affect overall growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
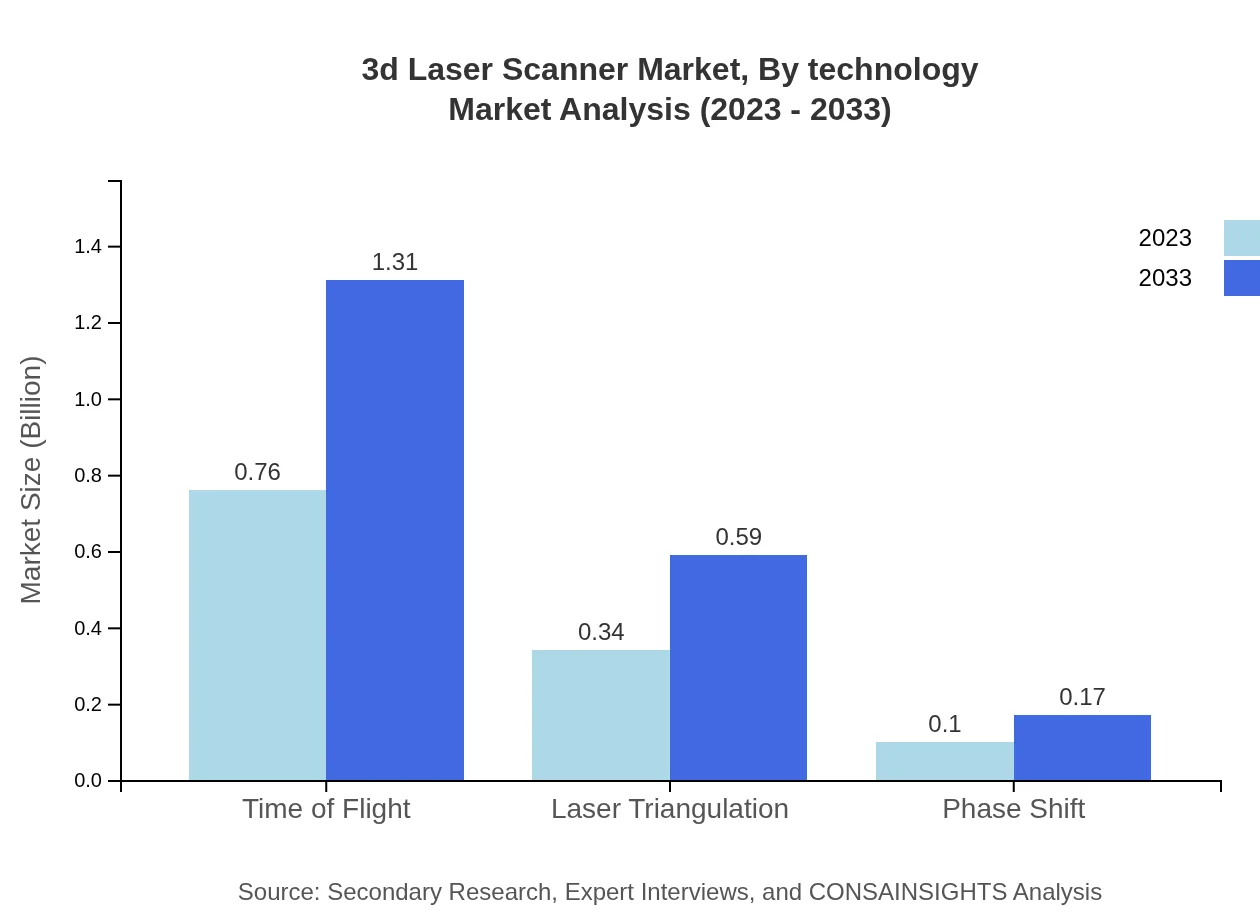
3d Laser Scanner Market Analysis By Technology
The market is predominantly driven by the Time of Flight technology, accounting for a sizeable portion of the overall market share due to its efficiency in large-scale applications. Laser triangulation and phase shift technologies also contribute significantly but have narrower application scopes. Time of Flight was valued at $0.76 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow at a strong pace, reflecting the trend towards more versatile and effective scanning solutions.
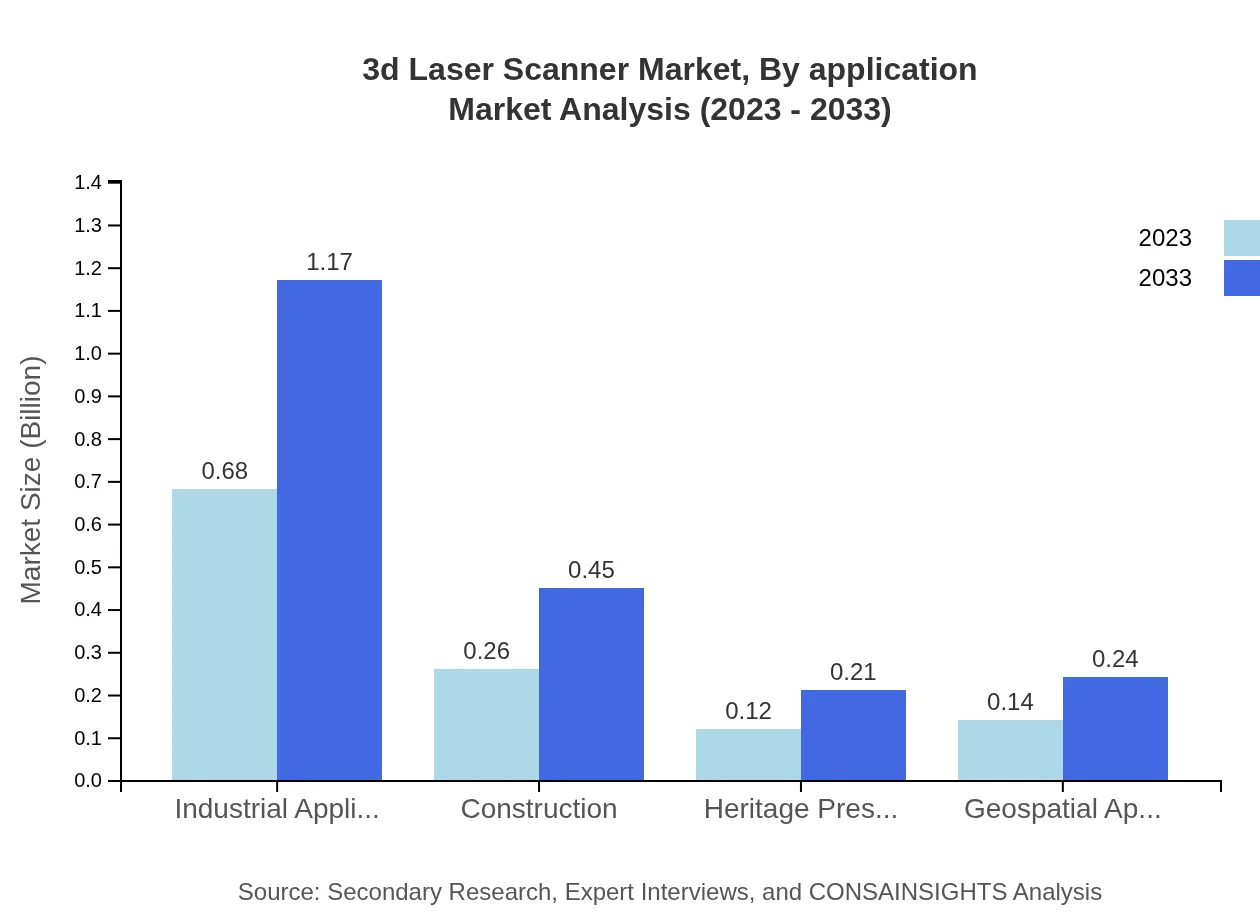
3d Laser Scanner Market Analysis By Application
Architecture and industrial applications dominate the 3D laser scanner market, with architecture showcasing a market size of $0.68 billion in 2023 and $1.17 billion by 2033. Increasing demand for precise measurements in construction projects is driving this growth. Manufacturing and automotive sectors also play significant roles, witnessing growing adoption of 3D technology for quality control processes.
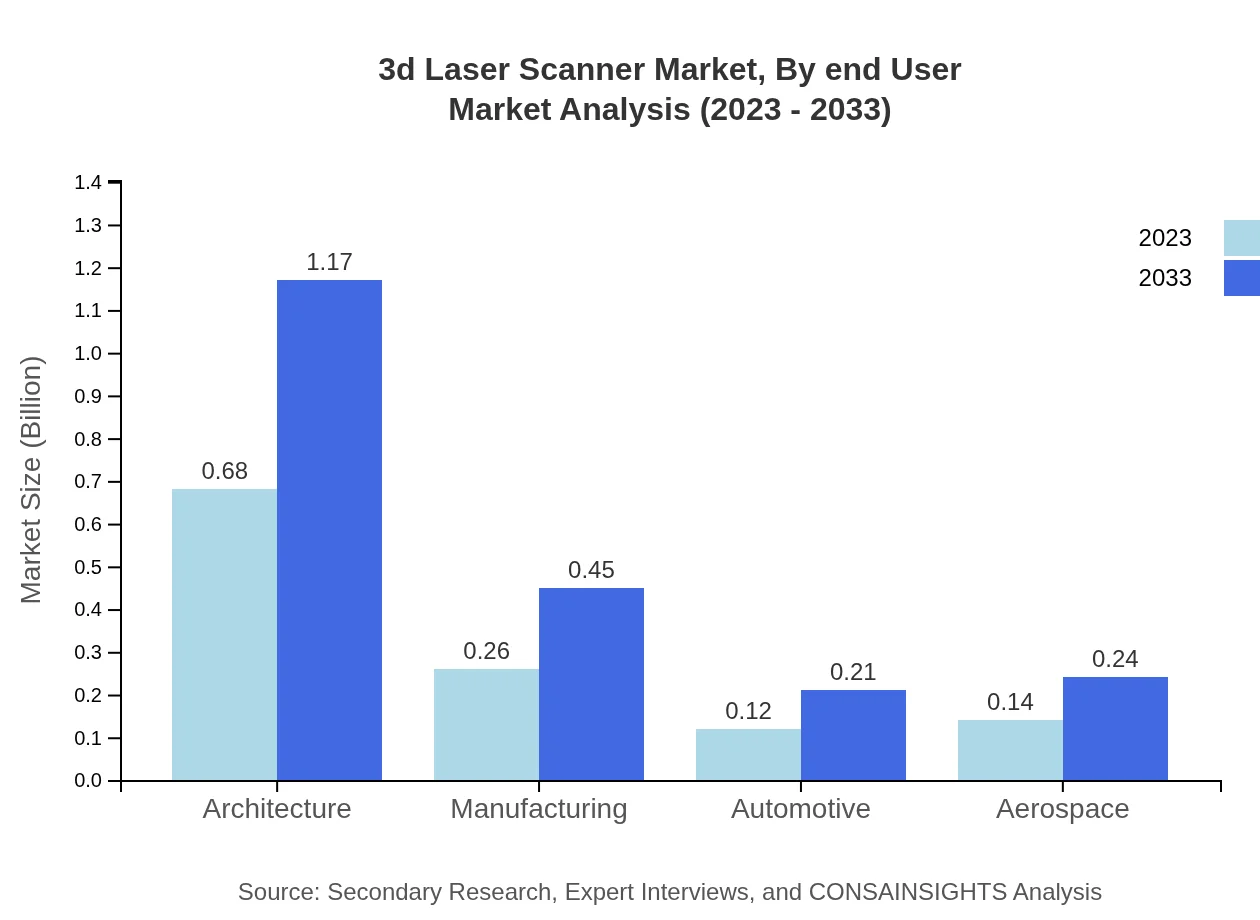
3d Laser Scanner Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment includes construction firms, historical preservation units, and geospatial technology firms, with construction representing a considerable market share of 21.81%. As more construction firms leverage 3D laser scanning for BIM applications, this trend is expected to rise, ensuring accuracy and minimizing errors in project execution.
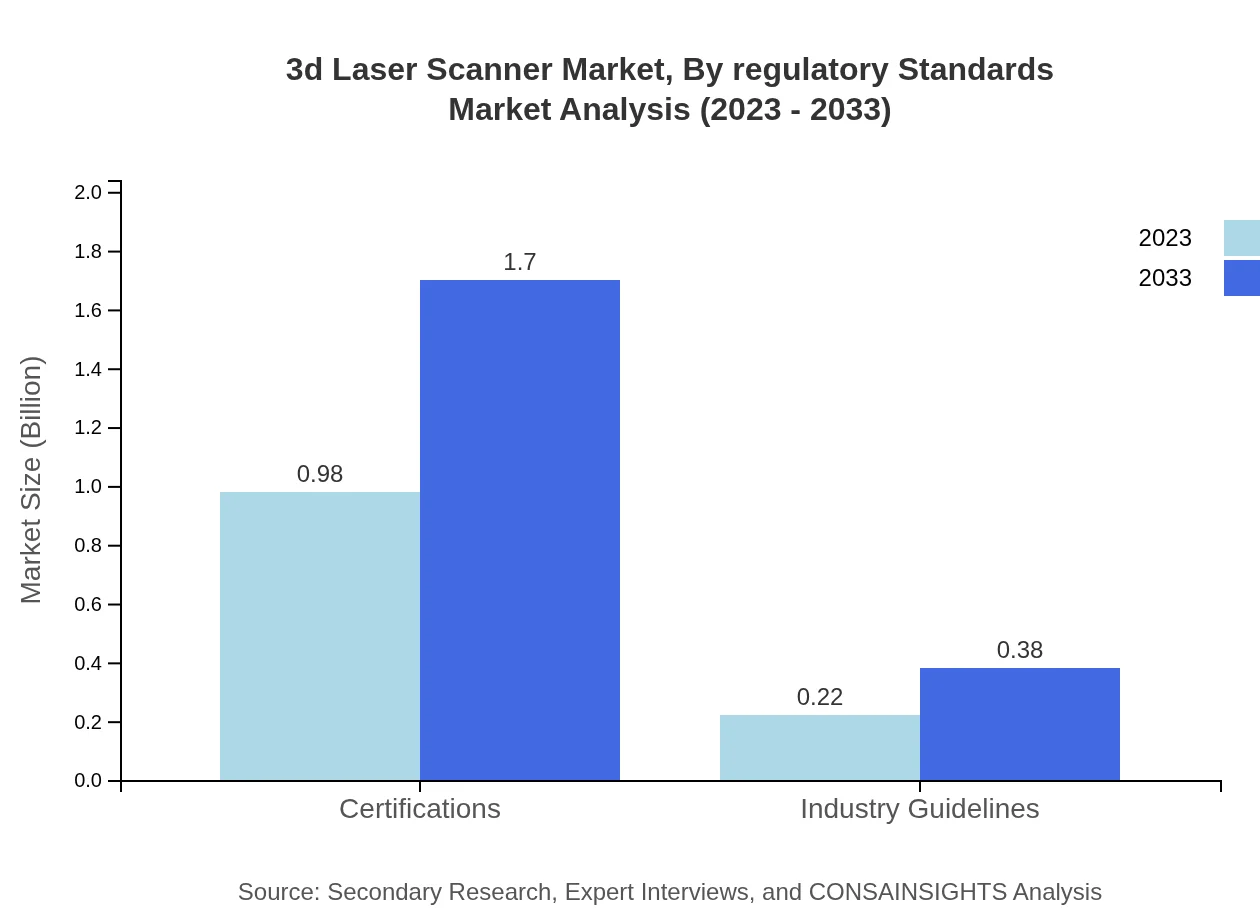
3d Laser Scanner Market Analysis By Regulatory Standards
Regulatory standards are influencing the adoption of 3D laser technology in various regions. The demand for certification compliance in construction projects is a major driving force. The certification segment is projected to sustain a dominant share, growing from $0.98 billion in 2023 to $1.70 billion by 2033, reflecting industry's commitment to maintaining quality and safety in operations.
3d Laser Scanner Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3d Laser Scanner Industry
Faro Technologies:
A leading provider of 3D laser scanner technology, Faro Technologies offers innovative solutions for industries such as construction, aerospace, and manufacturing. Their focus on precision and reliability has established them as industry leaders.Leica Geosystems:
Part of Hexagon, Leica Geosystems is renowned for its advanced laser scanning technology and software solutions. The company serves various sectors including surveying, engineering, and construction with a commitment to enhancing productivity through innovative measurement solutions.Trimble Inc.:
Trimble is a technology company focusing on the connected construction ecosystem, providing 3D laser scanners that align with building information modeling (BIM) workflows for improved planning and execution.Zoller + Fröhle GmbH:
Zoller + Fröhle specializes in 3D measurement technology, focusing on high precision and quality. They provide solutions for all sectors that require accurate data capture, enhancing productivity and workflow efficiency.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3D laser scanners?
The global 3D laser scanner market is valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 5.5% extending to 2033, indicating steady growth driven by advancements in technology and rising applications across multiple sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the 3D laser scanner industry?
Key players in the 3D laser scanner market include major companies renowned for innovation and technology, such as Faro Technologies, Leica Geosystems, Topcon, and Trimble. These companies play pivotal roles in shaping market dynamics and driving competition.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3D laser scanner industry?
The growth of the 3D laser scanner industry is driven by increasing demand across sectors like construction, manufacturing, and architecture, technological advancements, and the growing need for precision measurements in industrial applications.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3D laser scanner market?
The fastest-growing region in the 3D laser scanner market is North America, projected to grow from $0.42 billion in 2023 to $0.72 billion by 2033, fueled by technological advancements and widespread adoption in various industries.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 3D laser scanner industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client requirements within the 3D laser scanner industry, providing in-depth insights and analysis to help organizations strategize effectively.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3D laser scanner market research project?
Deliverables from the 3D laser scanner market research project include comprehensive reports, detailed market analysis, regional insights, segment data, and strategic recommendations to aid decision-making.
What are the market trends of 3D laser scanners?
Current market trends in 3D laser scanners include the increased adoption of handheld devices, integration with software solutions, and a focus on environmental sustainability, ensuring relevance in a rapidly evolving technology landscape.