3d Metrology Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-metrology
3d Metrology Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 3D Metrology market, including insights into market size, growth rates, segmentation, and regional dynamics from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
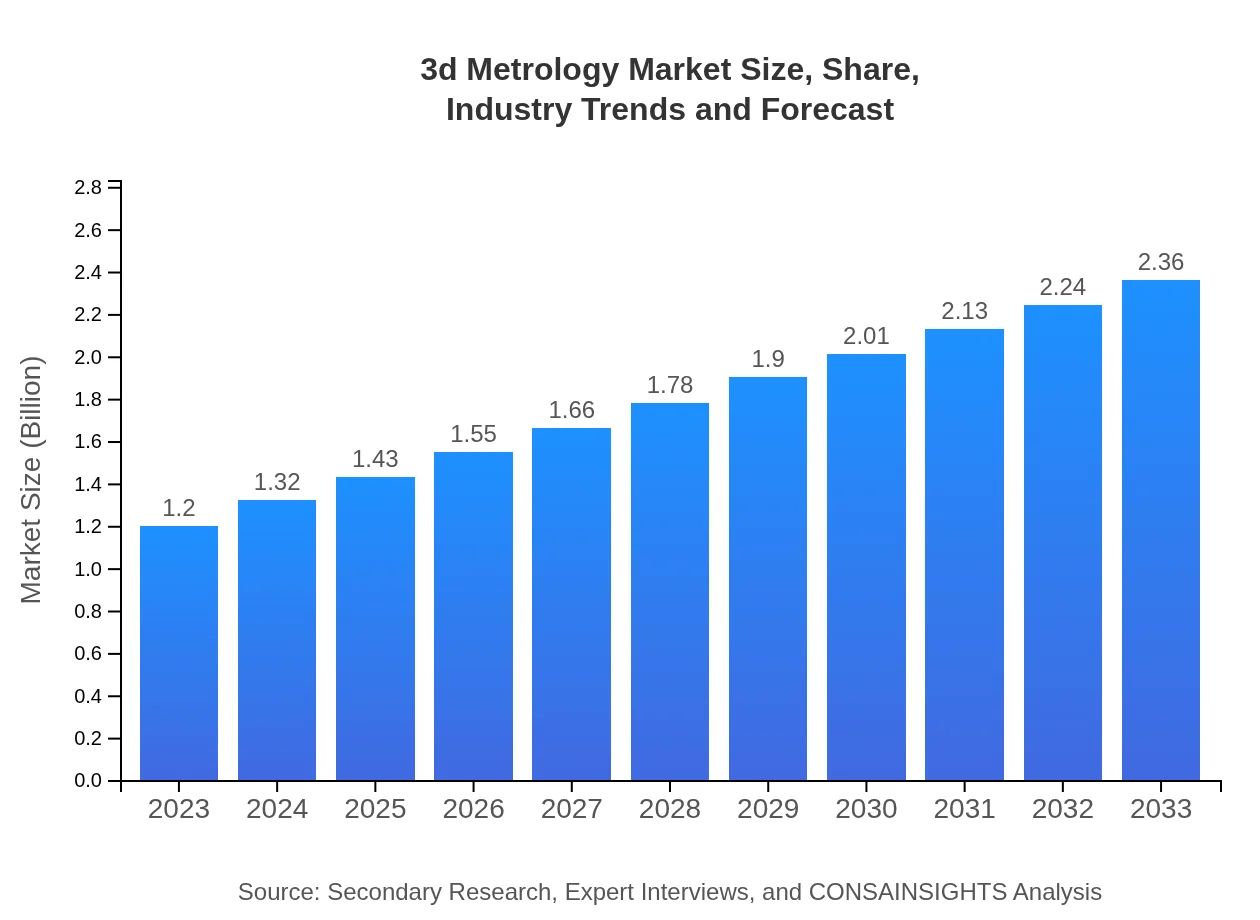
| 2023 Market Size | $1.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.36 Billion |
| Top Companies | Hexagon AB, Carl Zeiss AG, FARO Technologies, Renishaw plc |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3d Metrology Market Overview
Customize 3d Metrology Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Metrology market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Metrology's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Metrology
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the 3D Metrology market in 2023?
3d Metrology Industry Analysis
3d Metrology Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3d Metrology Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Metrology Market Report:
The European market for 3D Metrology is expected to experience growth from $0.31 billion in 2023 to $0.61 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by stringent quality control regulations in the automotive and aerospace industries. Additionally, Europe’s focus on smart manufacturing practices enhances demand for advanced metrology solutions.Asia Pacific 3d Metrology Market Report:
The Asia Pacific 3D Metrology market is forecasted to grow from $0.26 billion in 2023 to $0.51 billion by 2033. The growth is primarily driven by burgeoning automotive and electronics industries in countries like China, Japan, and India. The rising demand for precise manufacturing practices and smart factories are key factors boosting this market.North America 3d Metrology Market Report:
North America stands as a significant market, from $0.42 billion in 2023 to $0.82 billion by 2033. The presence of major automotive manufacturers and a strong aerospace sector are major contributors to market expansion. The region is characterized by advanced manufacturing technologies and high adoption rates of metrology solutions.South America 3d Metrology Market Report:
In South America, the market size is projected to reach $0.11 billion by 2033, up from $0.05 billion in 2023. Growth here is fueled by increased investment in infrastructure and industrial sectors with a focus on modernization and quality control processes.Middle East & Africa 3d Metrology Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is anticipated to grow from $0.16 billion in 2023 to $0.31 billion by 2033. Key drivers include rising investments in manufacturing and infrastructure projects, as well as the growing focus on quality and standards in industries such as oil & gas and construction.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
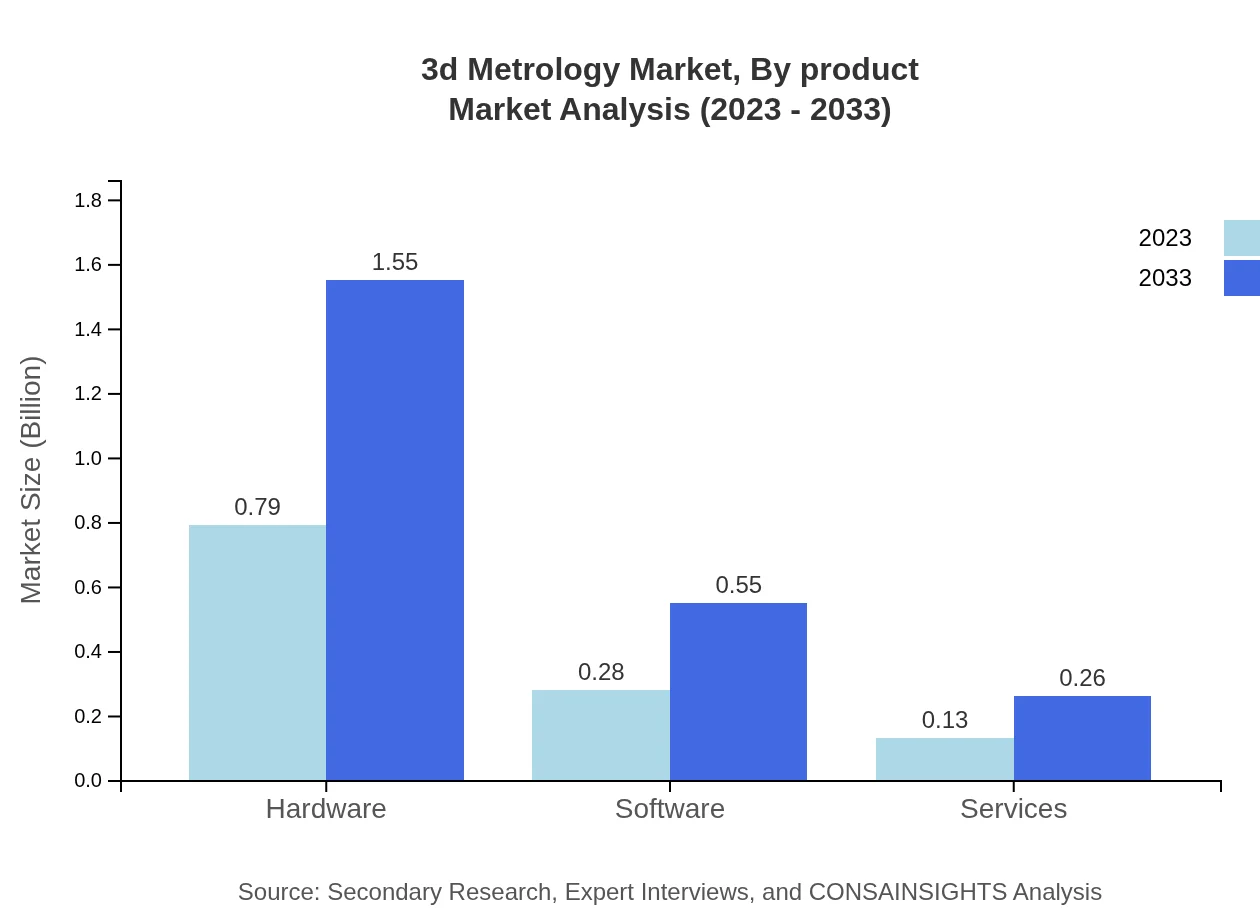
3d Metrology Market Analysis By Product
In 2023, hardware segment dominates the 3D Metrology market with a size of $0.79 billion and a market share of 65.55%. By 2033, it is projected to reach $1.55 billion, maintaining its share. The software segment is expected to grow from $0.28 billion in 2023, with a 23.3% market share, to $0.55 billion in 2033. Services, although a smaller segment at $0.13 billion in 2023 (11.15% market share), are projected to grow to $0.26 billion by 2033 due to increasing customer demands for support.
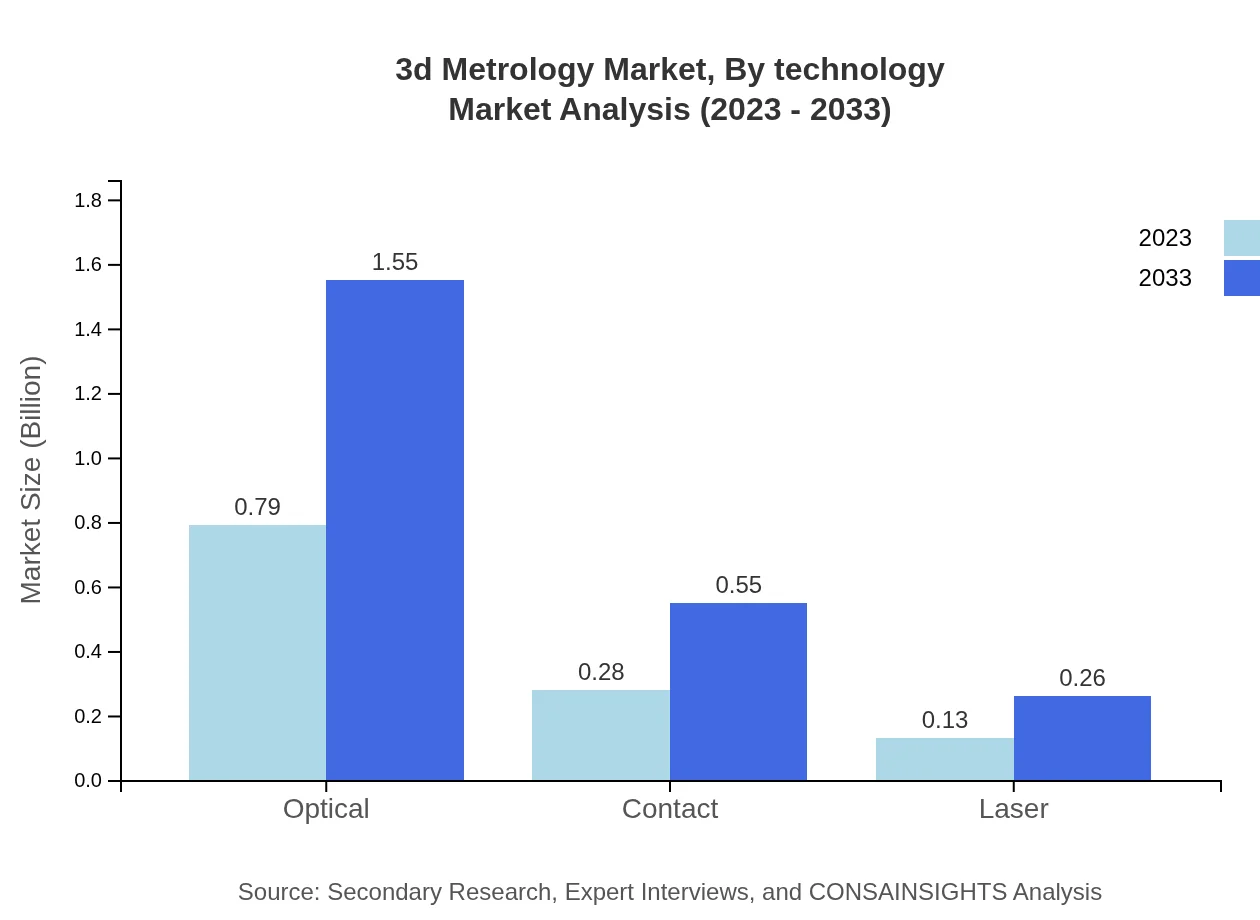
3d Metrology Market Analysis By Technology
The technological landscape of 3D Metrology includes innovations like laser scanning and optical measurement systems. By 2033, laser technologies are expected to account for a significant share as they become more prevalent in industrial applications.
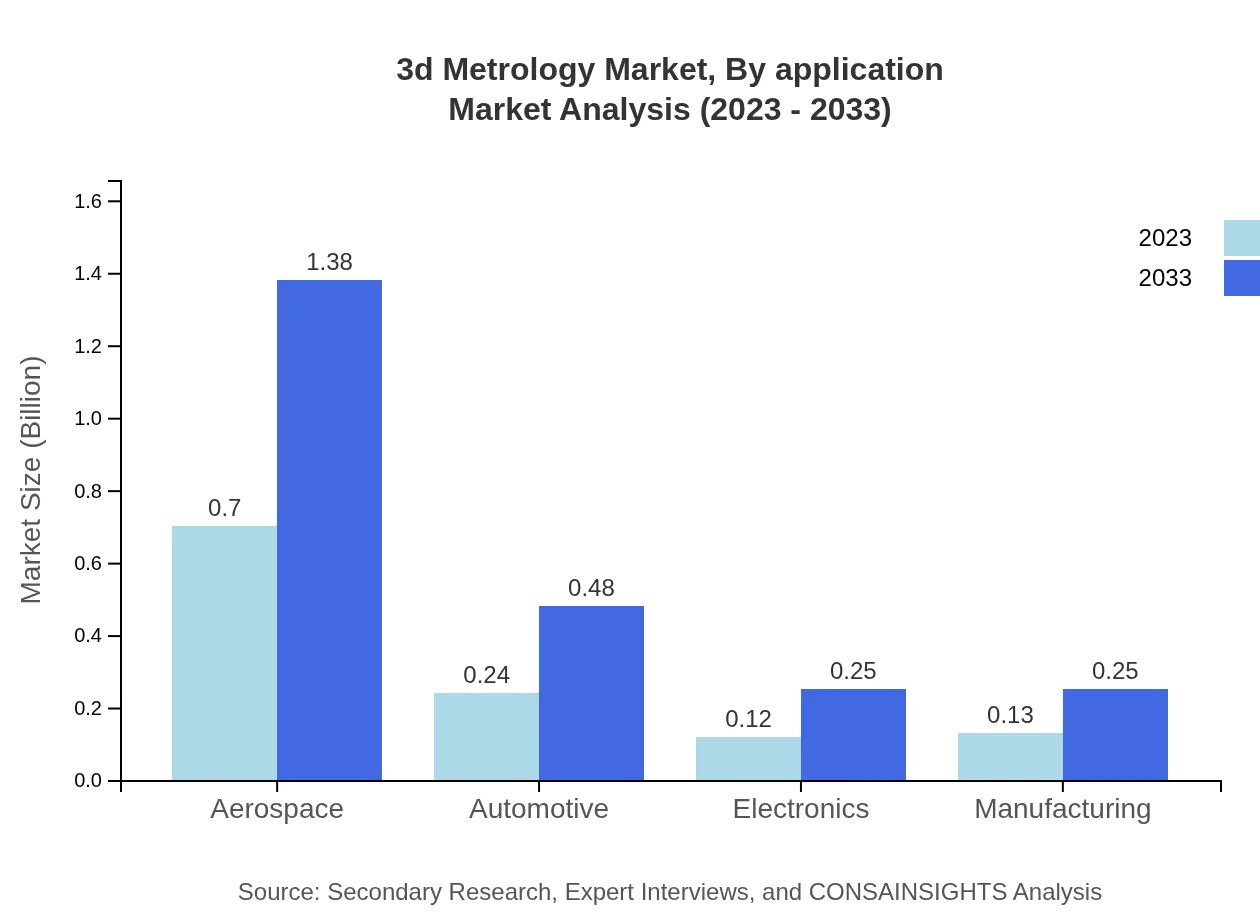
3d Metrology Market Analysis By Application
Aerospace is projected to remain a leading application for 3D metrology, expanding from $0.70 billion in 2023 to $1.38 billion in 2033, while automotive applications are also significant at $0.24 billion in 2023.
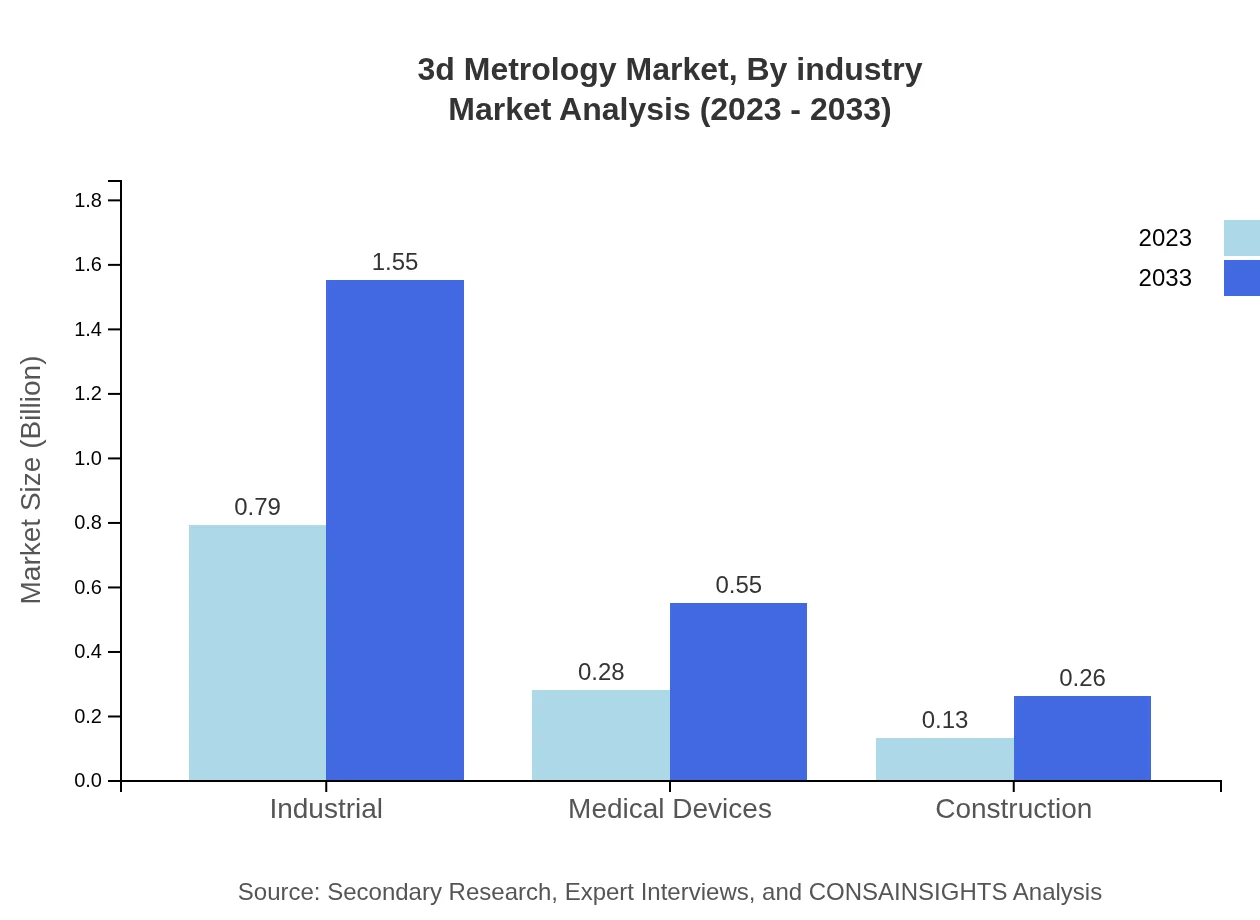
3d Metrology Market Analysis By Industry
Industries such as healthcare are becoming critical segments, with expected growth in medical devices utilizing 3D Metrology to ensure high-quality standards. This industry is projected to grow from $0.28 billion (2023) to $0.55 billion (2033).
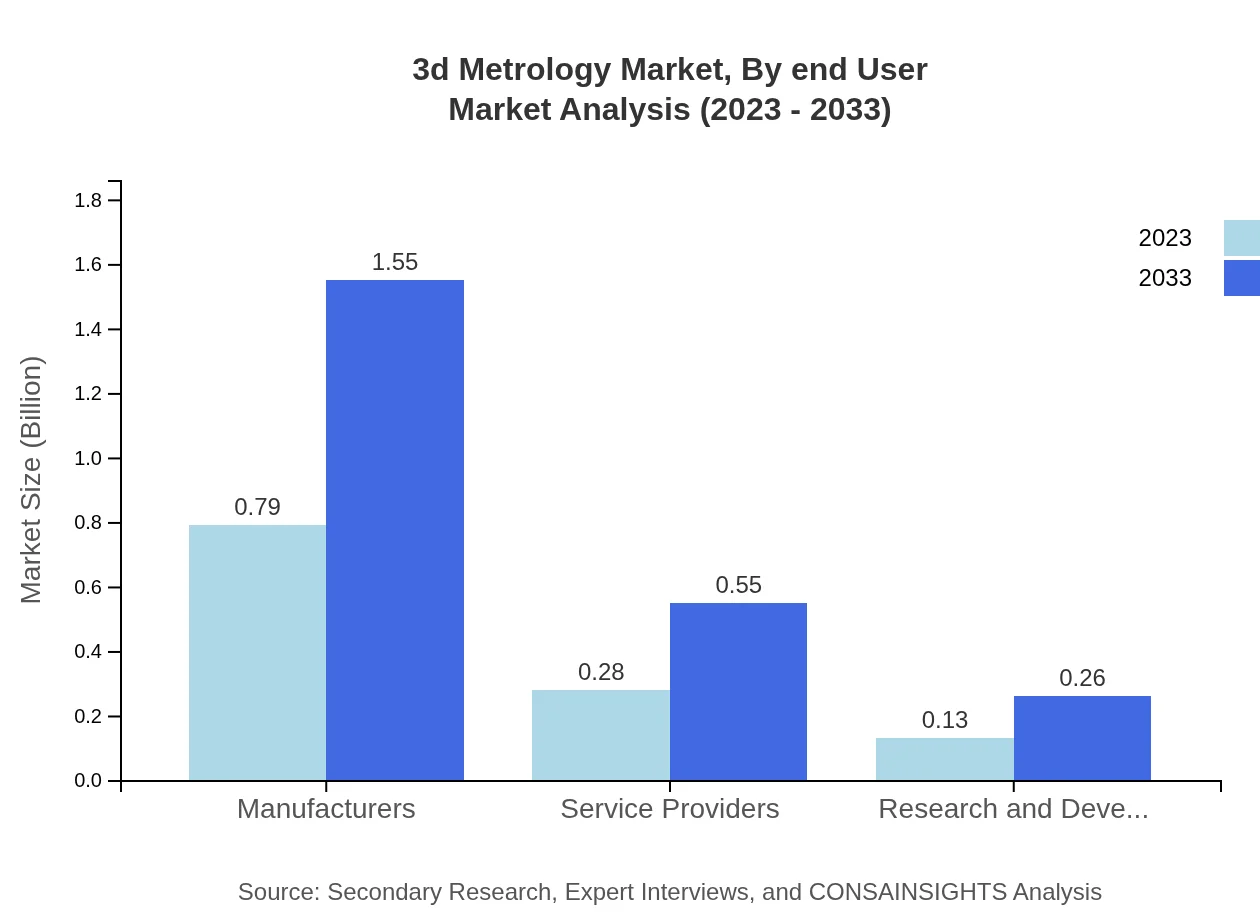
3d Metrology Market Analysis By End User
End users in sectors like manufacturing and construction are expected to adopt 3D Metrology solutions as standards for quality assurance and compliance in production processes continue to increase.
3d Metrology Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3D Metrology Industry
Hexagon AB:
Hexagon offers a wide range of solutions including measurement systems and software, leading the market in advanced 3D Metrology applications.Carl Zeiss AG:
A highly recognized name in precision measurement technologies, Carl Zeiss provides innovative solutions, including optical and laser measurement tools.FARO Technologies:
FARO specializes in 3D measurement and imaging solutions, advancing the capabilities of industries such as manufacturing and construction.Renishaw plc:
Renishaw focuses on metrology solutions, providing smart measurement tools for quality control in various manufacturing sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3d Metrology?
The global 3D metrology market is valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2023, with a projected growth rate of 6.8% CAGR, indicating robust demand and expansion potential in the coming years.
What are the key market players or companies in this 3d Metrology industry?
Key players in the 3D metrology market include major companies such as Hexagon AB, Carl Zeiss AG, and Faro Technologies, Inc., which drive innovation and technological advancements, maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3d Metrology industry?
Growth in the 3D metrology industry is primarily driven by increasing automation in manufacturing processes, rising demand for quality assurance, and advancements in metrology technology ensuring higher precision and efficiency in measurements.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3d Metrology?
The fastest-growing region in the 3D metrology market is Asia Pacific, with market growth from $0.26 billion in 2023 to $0.51 billion in 2033, reflecting a significant increase in manufacturing activities and investment in technology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 3d Metrology industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients within the 3D metrology industry, providing in-depth insights and analysis to support informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3d Metrology market research project?
Deliverables from the 3D metrology market research include comprehensive market analysis reports, forecast studies, segmentation insights, competitive landscape assessments, and actionable recommendations for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of 3d Metrology?
Current market trends in 3D metrology focal on increased integration of artificial intelligence, expansion of automation technologies, and the growing adoption of portable measurement systems, enhancing operational efficiency and versatility.