3d Printing Construction Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-printing-construction
3d Printing Construction Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the 3D printing construction market, covering market trends, forecasts for 2023-2033, and key insights on segmentation, regional dynamics, and competitive landscape. It aims to equip readers with valuable data to navigate this rapidly evolving industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
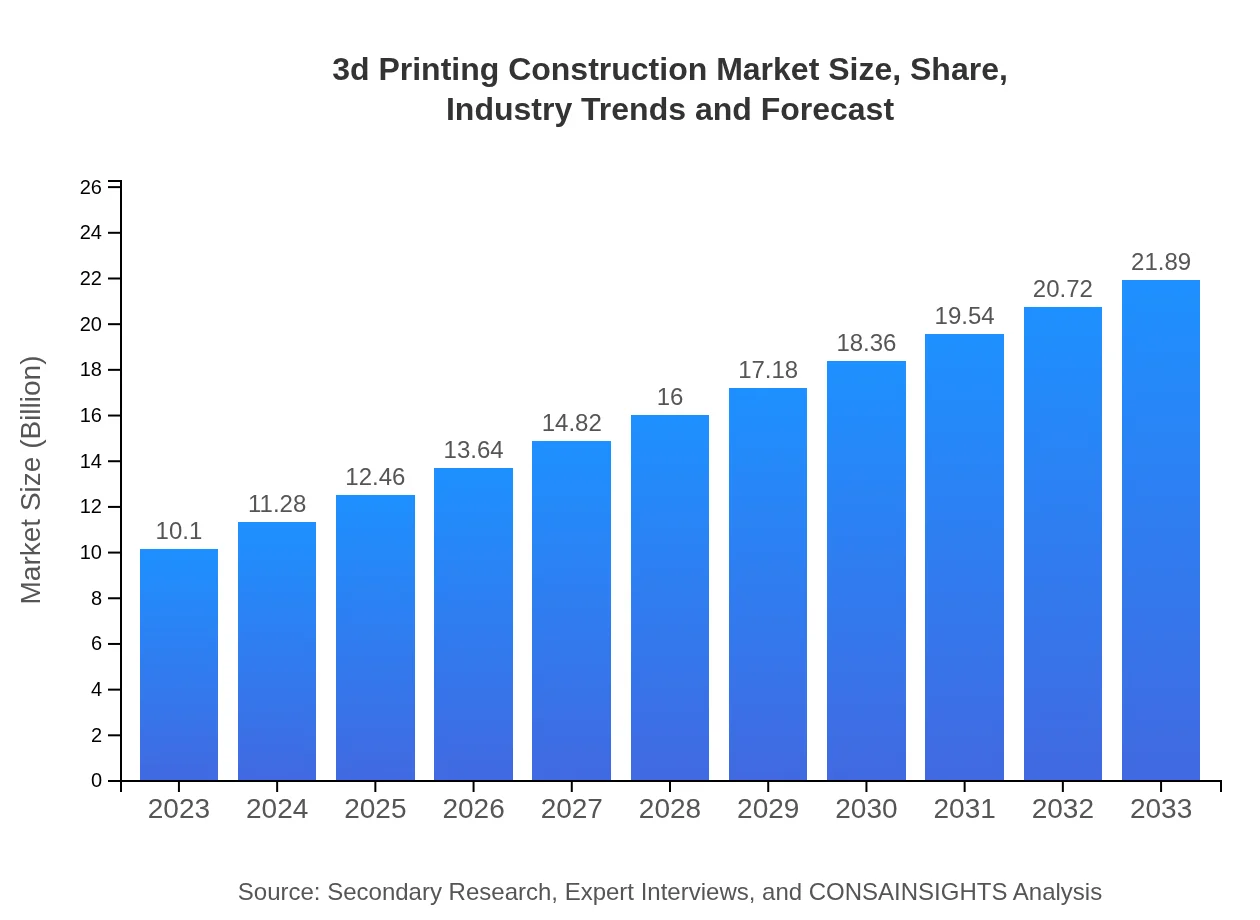
| 2023 Market Size | $10.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.89 Billion |
| Top Companies | ICON, Apis Cor, Vertico, Sika AG |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3d Printing Construction Market Overview
Customize 3d Printing Construction Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Printing Construction market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Printing Construction's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Printing Construction
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 3d Printing Construction market in 2023?
3d Printing Construction Industry Analysis
3d Printing Construction Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3d Printing Construction Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Printing Construction Market Report:
The European market for 3D printing construction is expected to grow from $3.00 billion in 2023 to $6.50 billion by 2033. The region is focused on sustainability and innovative building methodologies, with several countries, including Germany and France, investing in research and pilot projects in 3D printed homes and infrastructure.Asia Pacific 3d Printing Construction Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to witness significant growth, increasing from a market size of $2.00 billion in 2023 to $4.35 billion by 2033. Driven by rapid urbanization, changing demographics, and increased investment in smart city projects, countries such as China and India are at the forefront of adopting 3D printing technologies in construction.North America 3d Printing Construction Market Report:
North America is set to experience robust growth, with market size projected to rise from $3.58 billion in 2023 to $7.75 billion in 2033. The U.S. and Canada are leveraging advancements in technology to enhance construction efficiency while addressing labor shortages, leading organizations to invest heavily in 3D printing processes.South America 3d Printing Construction Market Report:
In South America, the market is projected to grow from $0.45 billion in 2023 to $0.98 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are leading this growth as they explore 3D printing for affordable housing solutions amidst rising construction costs and supply chain challenges.Middle East & Africa 3d Printing Construction Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from $1.07 billion in 2023 to $2.32 billion by 2033. Countries like the UAE and South Africa are pioneers in adopting 3D printing in construction, aligning with their goals for innovative infrastructure solutions and sustainable development.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
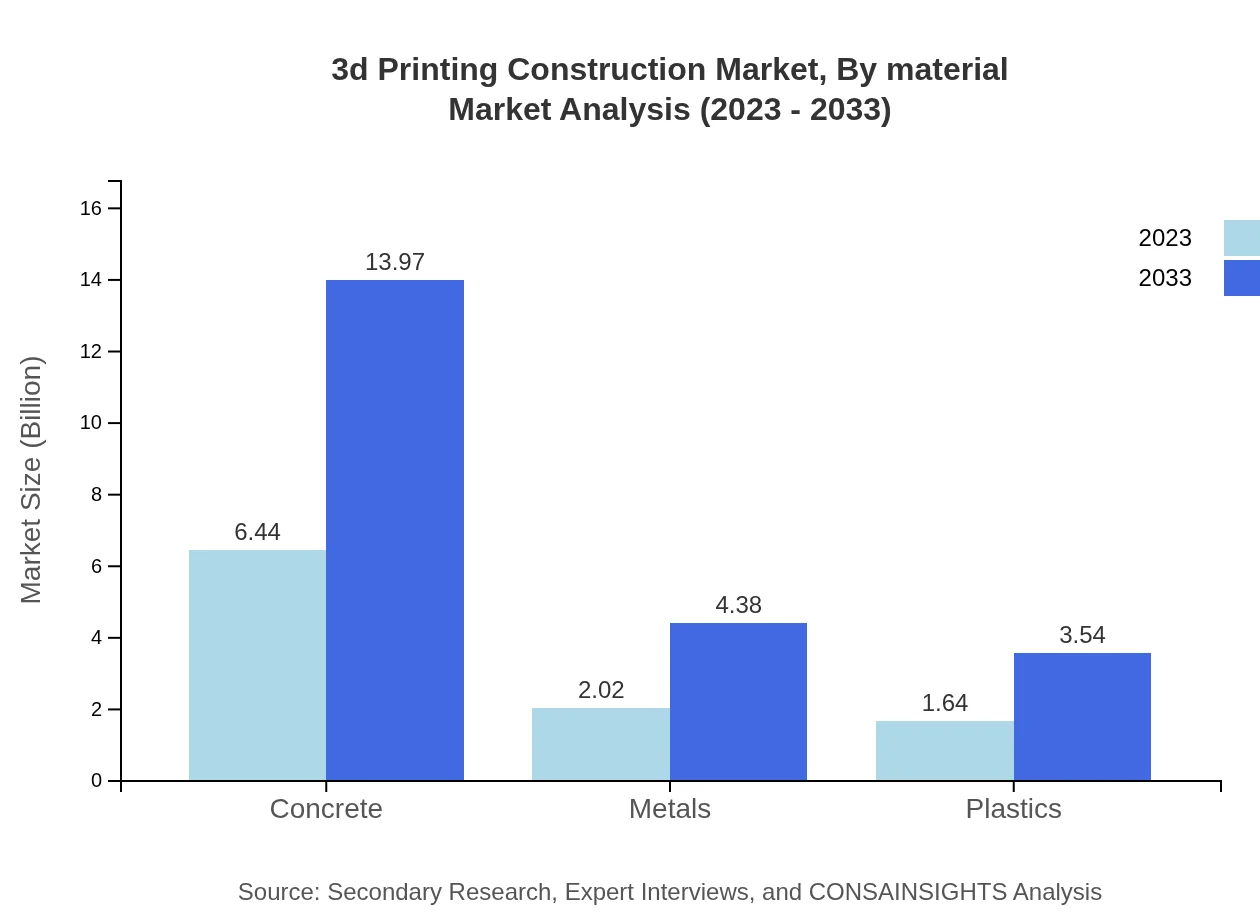
3d Printing Construction Market Analysis By Material
In the 3D printing construction sector, concrete remains the most utilized material, rising from $6.44 billion in 2023 to $13.97 billion by 2033, maintaining a 63.79% market share. Metals also have substantial traction, growing from $2.02 billion to $4.38 billion. Emerging materials, including biocomposites and plastics, are gaining popularity due to their versatility and environmental benefits, with plastics projected to grow from $1.64 billion to $3.54 billion.
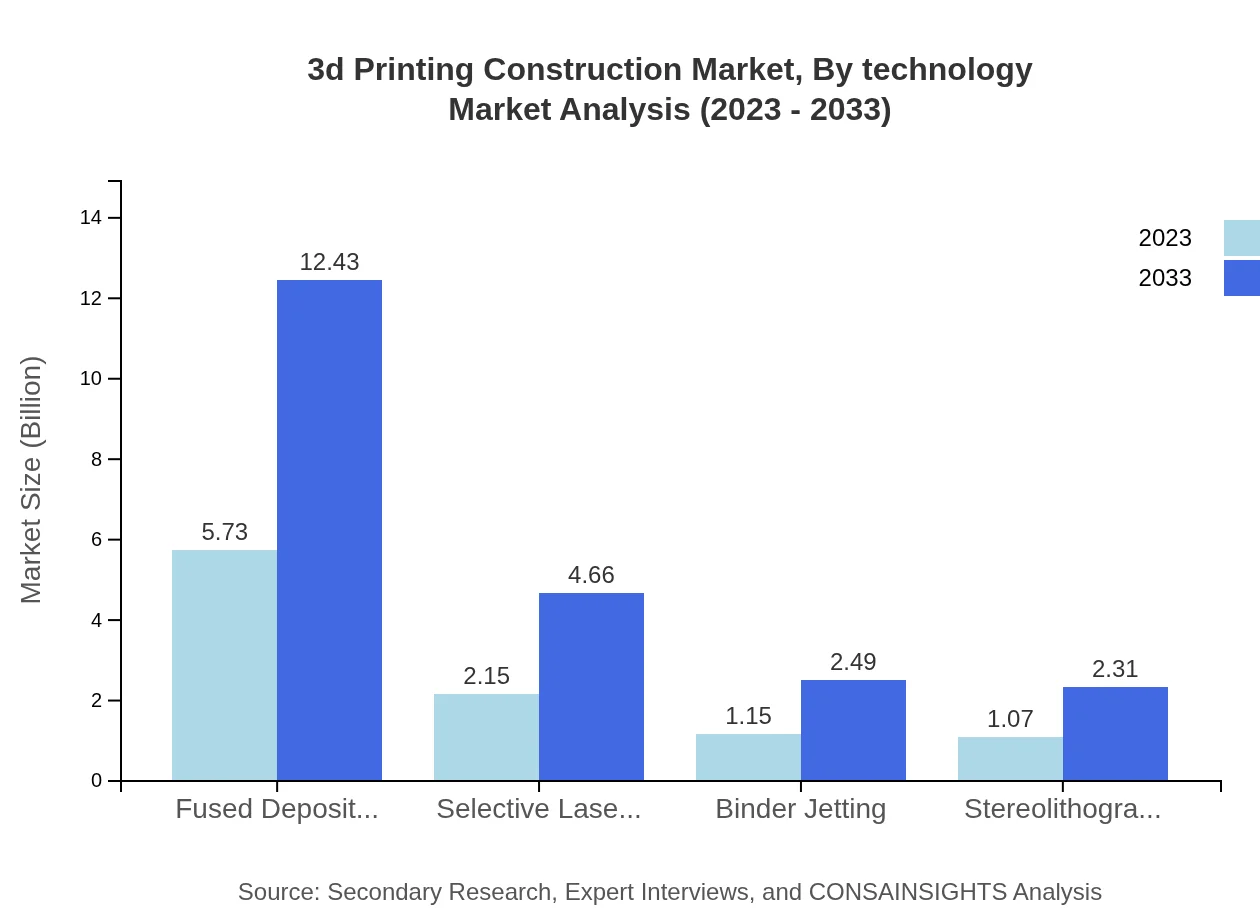
3d Printing Construction Market Analysis By Technology
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the leading technology in this market, expanding from $5.73 billion in 2023 to $12.43 billion by 2033, holding a significant market share of 56.77%. Other technologies such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Binder Jetting show growth potential, expanding from $2.15 billion to $4.66 billion and $1.15 billion to $2.49 billion, respectively, as they are increasingly adopted for specific applications that require precision and fabrication flexibility.
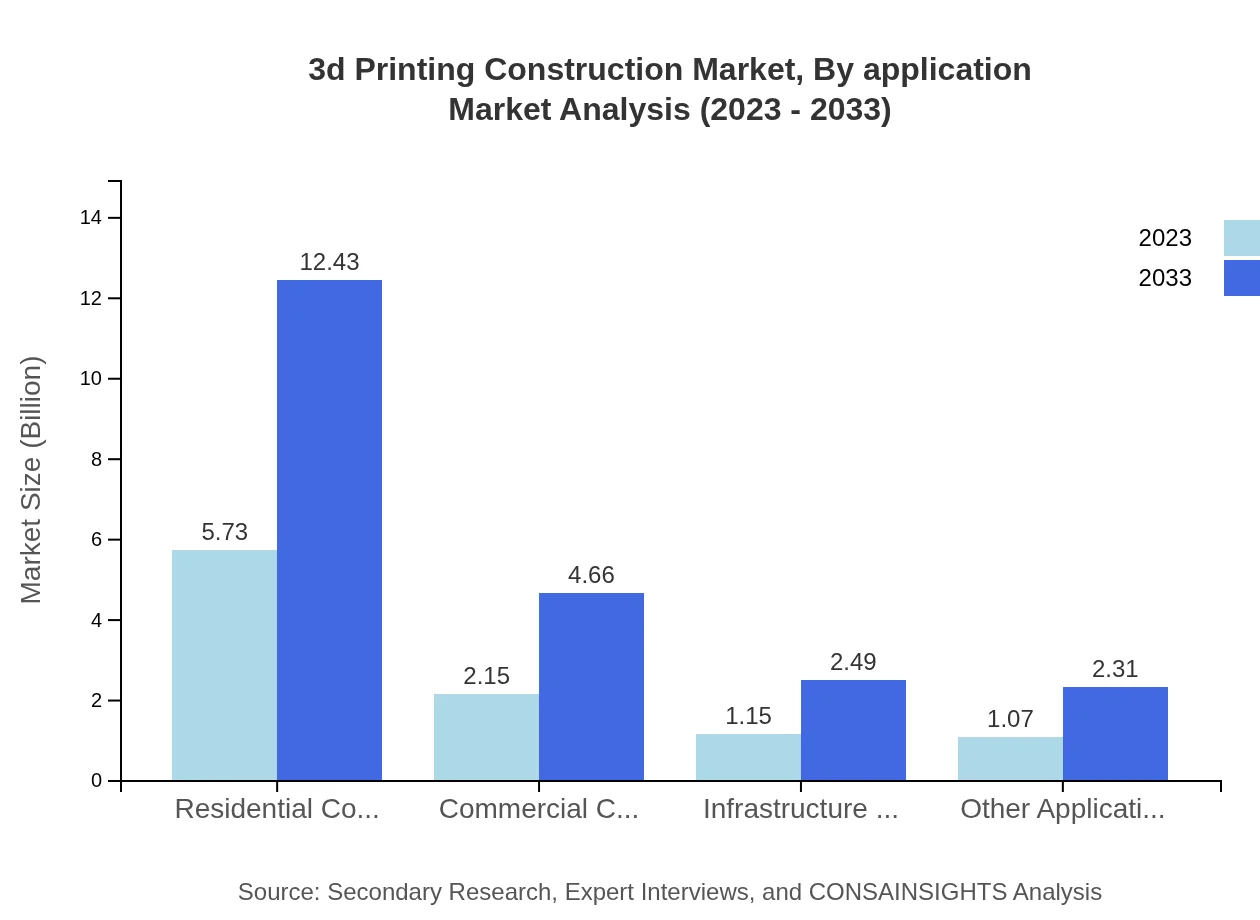
3d Printing Construction Market Analysis By Application
The residential construction segment dominates the application landscape, estimated to grow from $5.73 billion in 2023 to $12.43 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, commercial construction and infrastructure development represent important segments, growing from $2.15 billion to $4.66 billion and $1.15 billion to $2.49 billion, respectively. The utility of 3D printing for rapid prototyping and customized challenging designs is also gaining traction across various applications.
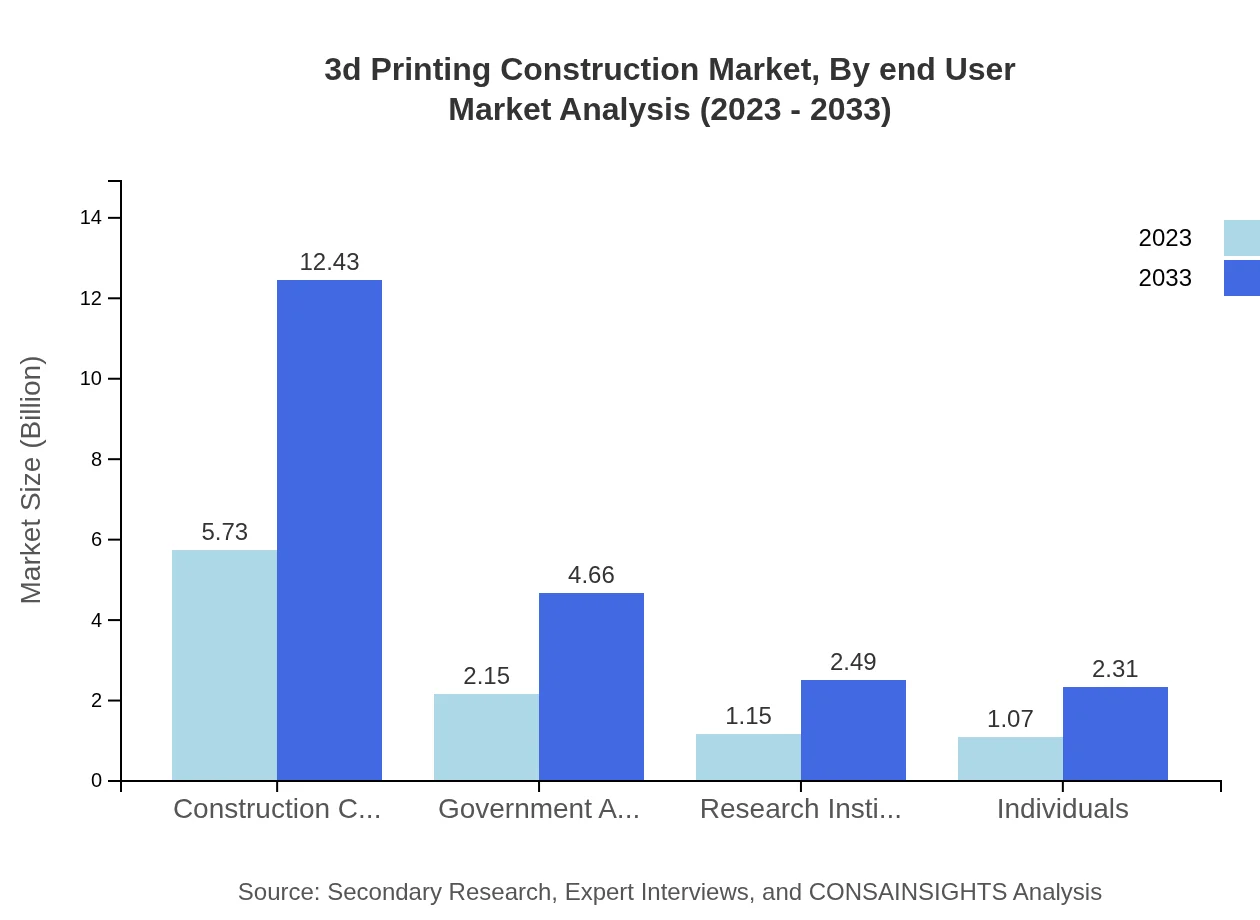
3d Printing Construction Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users in the 3D printing construction market include construction companies, government agencies, research institutions, and individual clients. Notably, construction companies dominate with a market size growing from $5.73 billion in 2023 to $12.43 billion in 2033. Government agencies are also significant, growing from $2.15 billion to $4.66 billion as they seek innovative solutions for urban development.
3d Printing Construction Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3d Printing Construction Industry
ICON:
ICON focuses on sustainable construction innovation, utilizing advanced 3D printing technology to create affordable housing solutions in vulnerable communities.Apis Cor:
Apis Cor specializes in on-site 3D printing, offering solutions that reduce the time and cost of building construction while ensuring quality and safety.Vertico:
Vertico is a leader in the development of advanced 3D concrete printing technologies, offering unique design possibilities for construction projects.Sika AG:
Sika AG provides specialty chemicals for construction and industry, contributing to concrete solutions optimized for 3D printing applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3D Printing construction?
The 3D-printing construction market is projected to reach $10.1 billion in 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.8%. This indicates significant expansion and potential investment opportunities within the industry over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the 3D Printing construction industry?
Key players include companies focused on innovation in 3D-printing technologies such as ICON, Apis Cor, and CEAD. These organizations are pioneering the advancements in materials and techniques vital for revolutionizing construction practices.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3D Printing construction industry?
Growth is driven by factors like increasing demand for affordable housing, technological advancements in printing materials, and the need for sustainable construction methods that minimize waste and reduce construction time.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3D Printing construction market?
North America is identified as the fastest-growing region, expected to increase from $3.58 billion in 2023 to $7.75 billion by 2033, leveraging advanced technologies and a rising trend towards innovative housing solutions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 3D Printing construction industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports, catering to specific business needs within the 3D-printing construction sector, ensuring clients receive tailored data and insights relevant to their strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3D Printing construction market research project?
Deliverables include detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and segment analysis, providing a comprehensive understanding of trends and forecasts within the 3D-printing construction industry.
What are the market trends of 3D Printing construction?
Current trends include the rise in eco-friendly materials, adoption in residential projects, and the use of robotics and automation to enhance efficiency. Additionally, increased collaborations among tech companies drive further innovation.