3d Printing Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-printing
3d Printing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 3D printing market, including market size, industry trends, segmentation, and regional insights. It covers projected growth from 2023 to 2033 and highlights key technology advancements shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
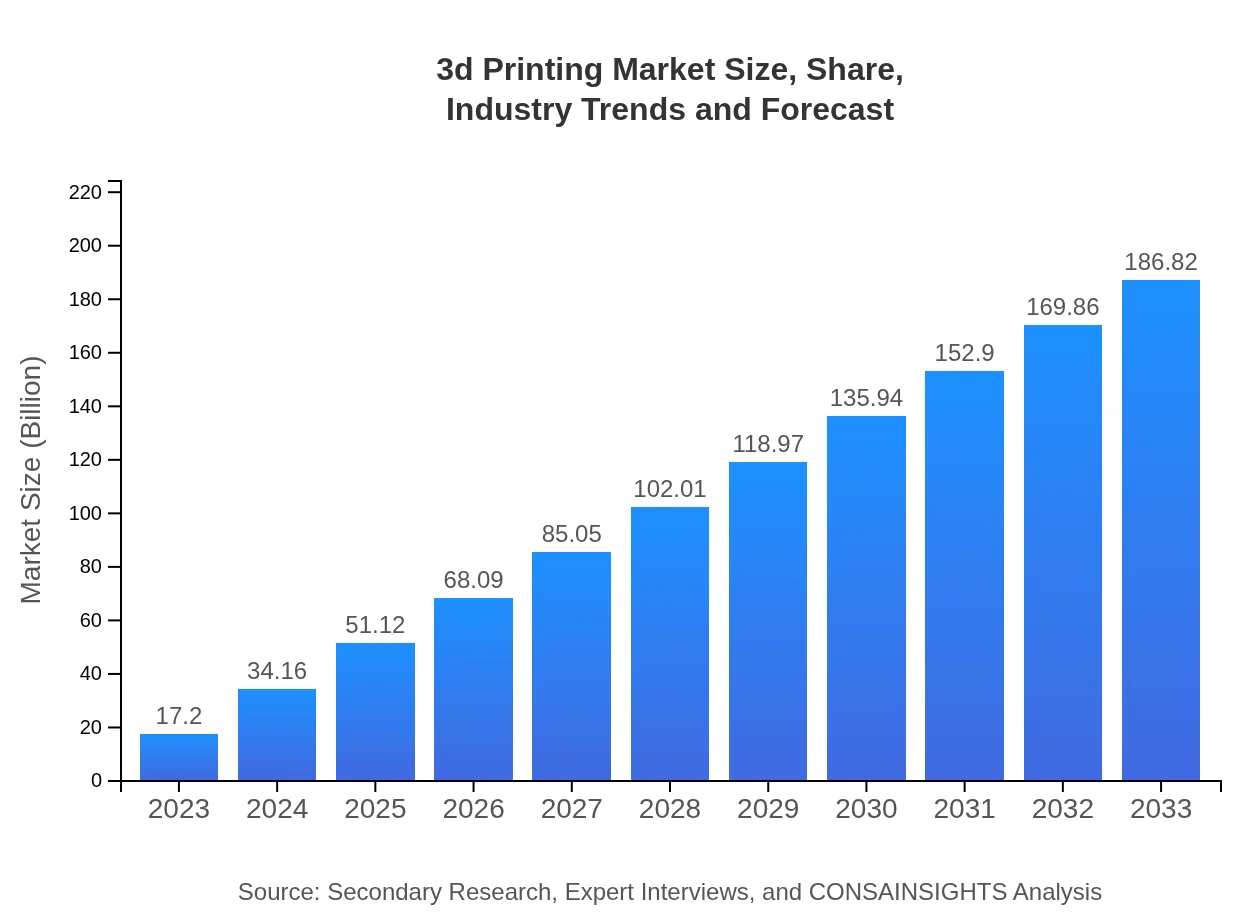
| 2023 Market Size | $17.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 25.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $186.82 Billion |
| Top Companies | Stratasys, 3D Systems, HP Inc., EOS GmbH, Materialise |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3D Printing Market Overview
Customize 3d Printing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Printing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Printing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Printing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 3D Printing market in 2023?
3D Printing Industry Analysis
3D Printing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3D Printing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Printing Market Report:
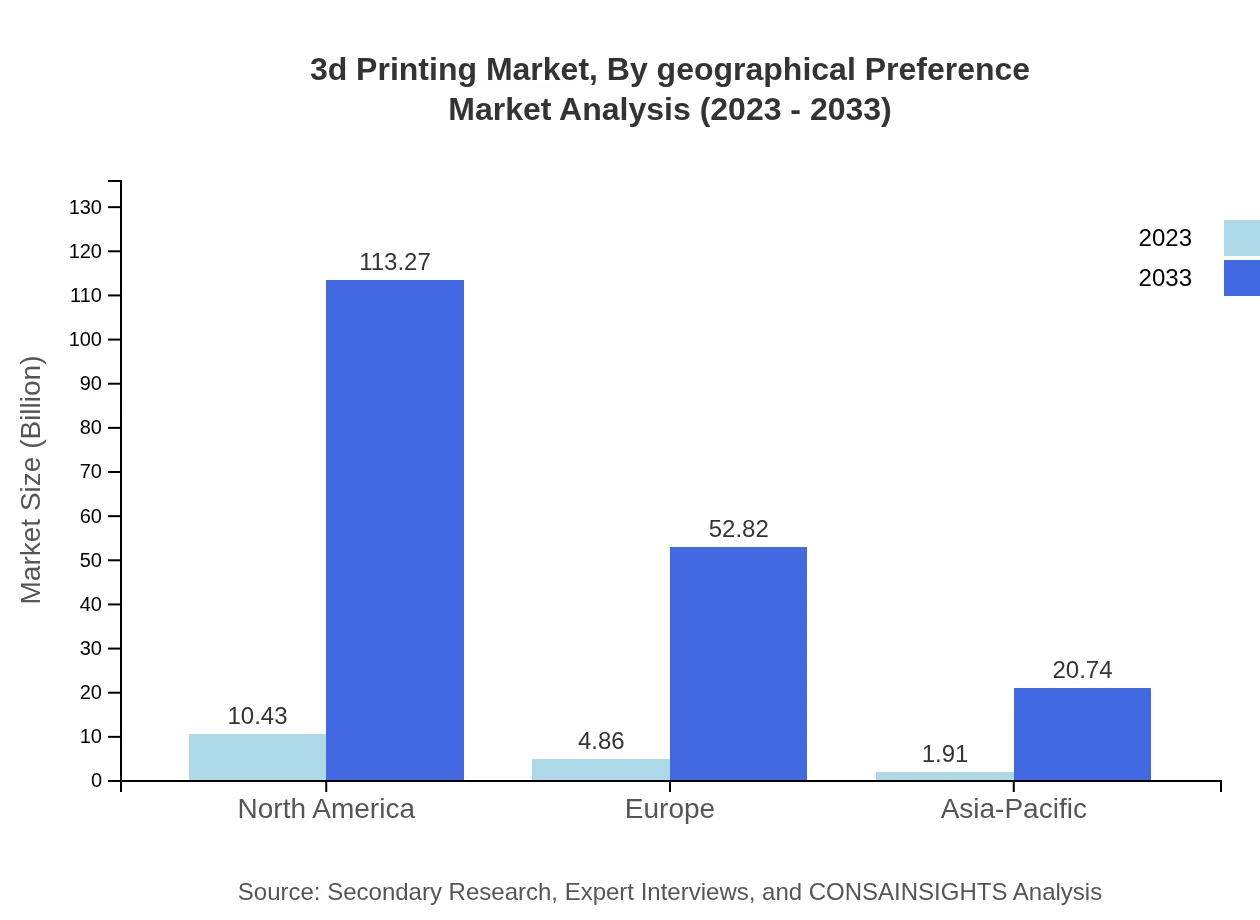
The European 3D printing market was valued at $5.29 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $57.47 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a mature manufacturing base and a focus on sustainability, leading to increased integrations of 3D printing into manufacturing processes. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are at the forefront of these developments.Asia Pacific 3d Printing Market Report:
In 2023, the 3D printing market in the Asia Pacific region is valued at approximately $2.73 billion and is expected to reach around $29.63 billion by 2033. Rapid industrialization, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on manufacturing flexibility drive demand in countries like China, Japan, and India. Strategic government initiatives to promote 3D printing technology further enhance growth prospects.North America 3d Printing Market Report:
North America remains a leading region for the 3D printing market, with a size of $6.60 billion in 2023 projected to soar to approximately $71.70 billion by 2033. Strong adoption of 3D printing technologies in aerospace, automotive, and healthcare sectors, combined with significant investments in R&D, are substantial contributors to its robust growth.South America 3d Printing Market Report:
For South America, the 3D printing market was valued at $0.28 billion in 2023, with a forecasted growth to $3.01 billion by 2033. The demand in this region is rising, particularly in industries such as healthcare and automotive, where 3D printing is being utilized for prototyping and customized manufacturing.Middle East & Africa 3d Printing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's 3D printing market stood at $2.30 billion in 2023, with anticipated growth to $25.02 billion by 2033. Increasing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies and expanding applications within industries such as healthcare and construction are prominent drivers in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
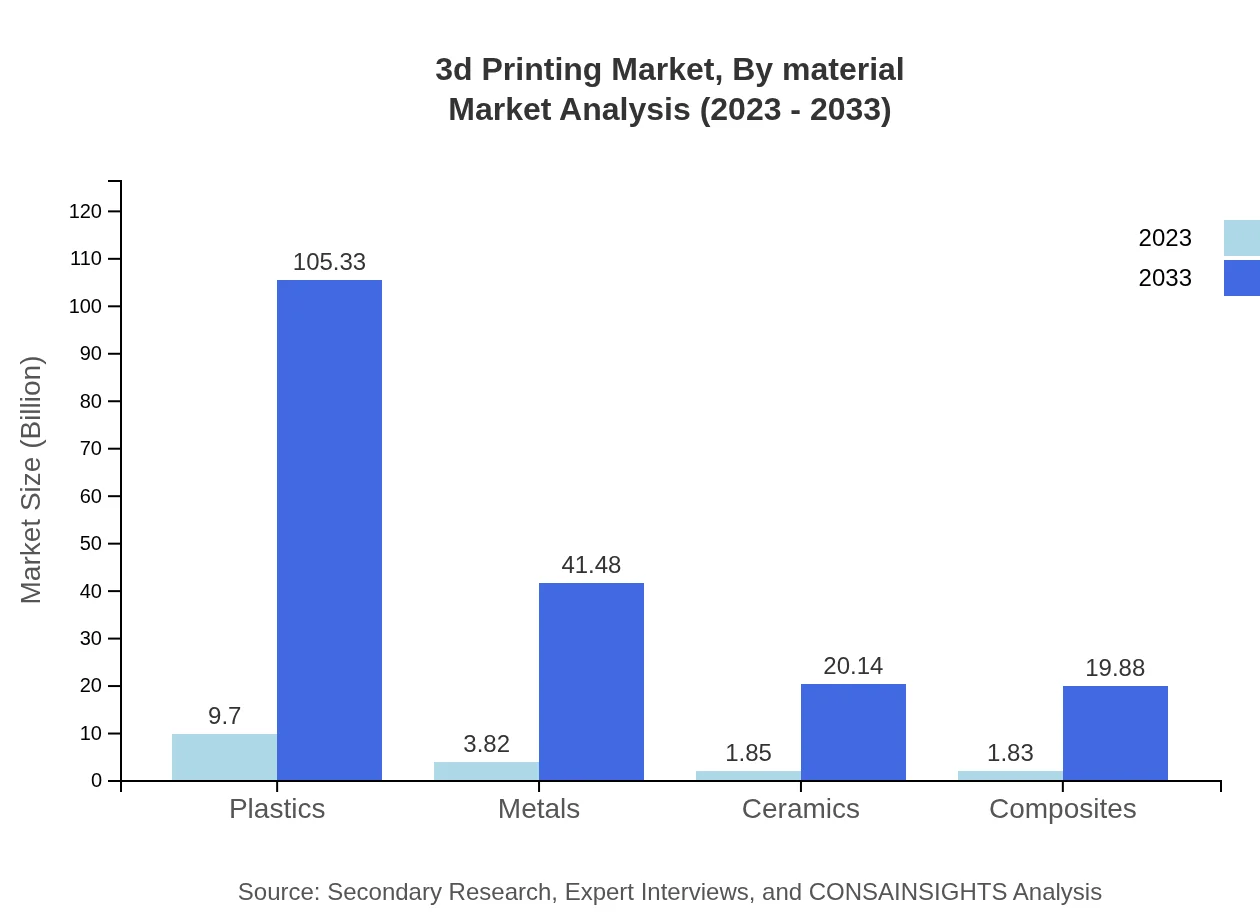
3d Printing Market Analysis By Material
The 3D printing market is segmented by materials, which include plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. Plastics currently dominate the market, accounting for approximately 56.38% of market share. Metal 3D printing is gaining traction due to its applications in aerospace and automotive industries, while ceramics and composites are carving out niches in specialized areas.
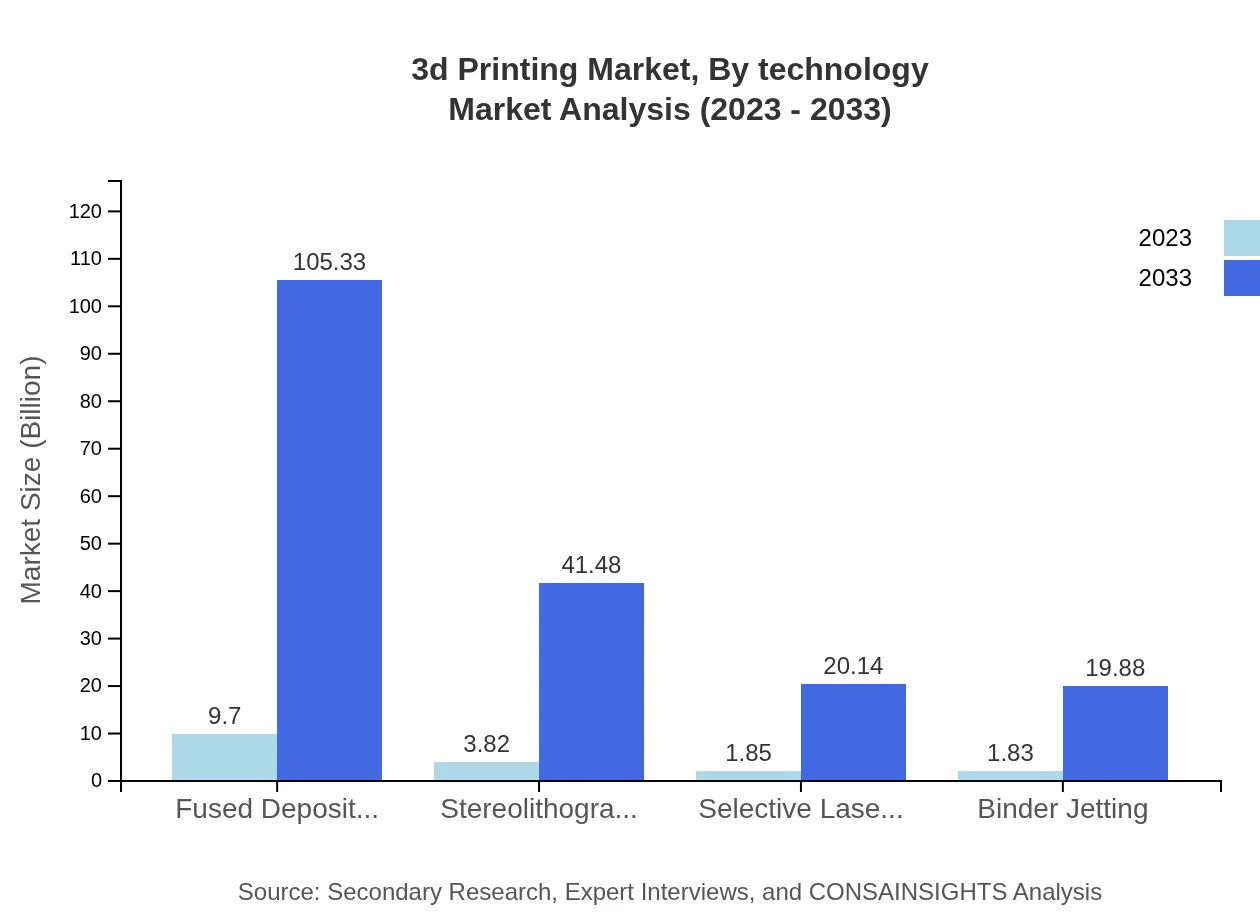
3d Printing Market Analysis By Technology
Technology-wise, the market spans FDM, SLA, SLS, and Binder Jetting. FDM technology holds the largest market share (56.38%), favored for its ease of use among hobbyists and businesses alike. SLA provides high precision for applications in medical and dental fields, whereas SLS is utilized predominantly in industrial applications for creating functional parts.
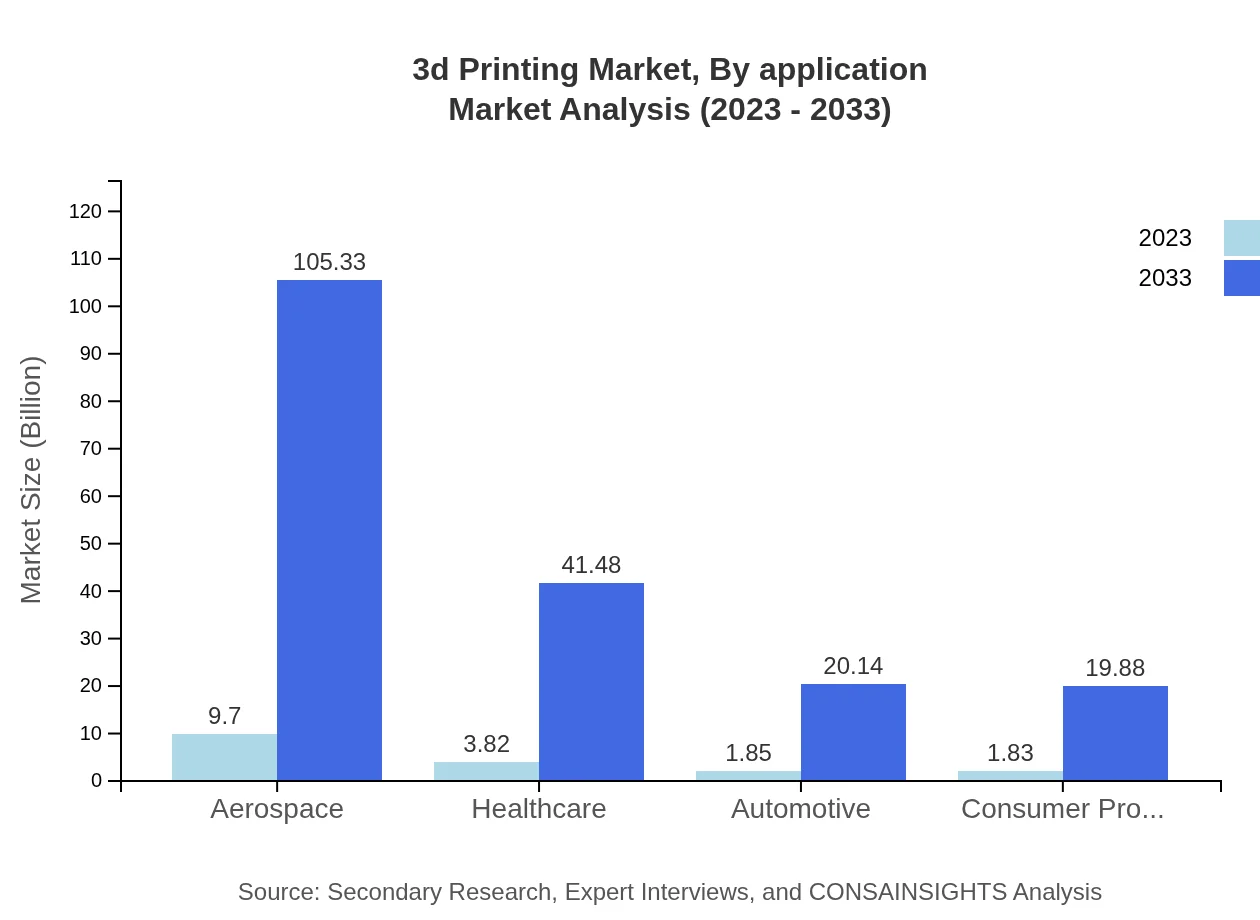
3d Printing Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, major sectors include aerospace, healthcare, automotive, consumer products, and education. Aerospace leads with a market share of 56.38% in 2023, attributed to the demand for lightweight components, while healthcare grows significantly for bioprinting solutions.
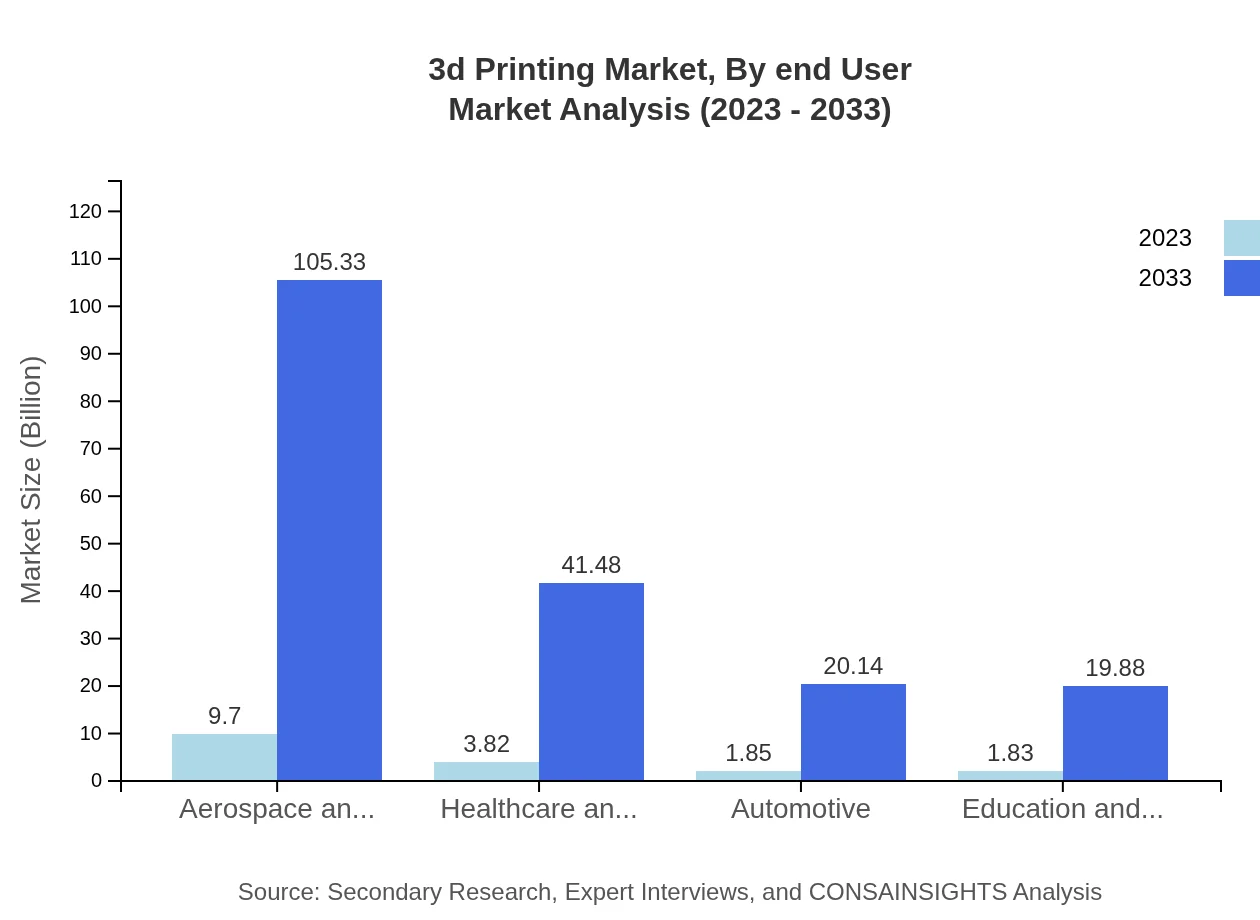
3d Printing Market Analysis By End User
The end-user market for 3D printing includes sectors like aerospace, healthcare, and automotive. Aerospace holds a substantial portion of the market, taking advantage of 3D printing for rapid prototyping and production of complex components. Healthcare is increasingly using 3D printing for implants and surgical tools, while the automotive sector leverages it for prototyping and manufacturing customized parts.
3d Printing Market Analysis By Geographical Preference
Geographically, North America is leading, emphasizing advanced manufacturing and robust technology adoption. Europe follows due to its strong industrial base and innovation focus, while Asia Pacific shows significant growth potential owing to industrial expansion and government initiatives supporting 3D printing technologies.
3D Printing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3D Printing Industry
Stratasys:
Stratasys is a leading provider of 3D printing and additive manufacturing solutions. Renowned for its FDM and PolyJet technologies, it serves various industries, driving innovation and efficiency in product development.3D Systems:
3D Systems is an early pioneer in the 3D printing industry, offering comprehensive 3D printing solutions, including systems, materials, and software. It plays a vital role in advancing metal and bioprinting technologies.HP Inc.:
HP is known for its Jet Fusion technology, revolutionizing polymer 3D printing with faster production speeds and reduced costs. The company continues to push boundaries with innovations catering to industrial applications.EOS GmbH:
EOS specializes in industrial 3D printing solutions, particularly metal 3D printing technologies. Their systems are widely adopted in aerospace and automotive sectors for producing high-quality, functional parts.Materialise:
Materialise offers integrated software and 3D printing solutions, facilitating the production of medical devices, automotive parts, and consumer products, emphasizing complex, data-driven designs.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3D Printing?
The 3D-printing market is projected to reach approximately $17.2 billion by 2033, growing at a significant CAGR of 25.2% from 2023. This growth is driven by increasing adoption across various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in this 3D Printing industry?
Key market players in the 3D-printing industry include renowned companies that specialize in additive manufacturing technologies, materials production, and service provisions. They vary across sectors such as aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer products.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3D Printing industry?
Key factors driving growth include technological advancements in printing materials and methods, increasing demand for customized products, and the ability to reduce production costs and time across multiple industries.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3D Printing?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the 3D-printing market, forecasted to reach approximately $71.70 billion by 2033, with a significant increase from $6.60 billion in 2023, reflecting a strong CAGR.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 3D Printing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the 3D-printing industry, providing insights on specific segments, regional data, and competitive analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3D Printing market research project?
Clients can expect detailed reports including market size forecasts, trends analysis, competitive landscape evaluations, and insights on various segments tailored to their specific inquiries.
What are the market trends of 3D Printing?
Current trends in the 3D-printing market include increasing reliance on additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping, advancements in bioprinting technologies, and integration of AI and IoT for enhanced production processes.