3d Printing Plastics Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: 3d-printing-plastics
3d Printing Plastics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 3D printing plastics market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, trends, segmentation insights, industrial analysis, regional breakdowns, and forecasts for growth. It aims to offer valuable data and actionable insights for stakeholders and investors in this rapidly evolving industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
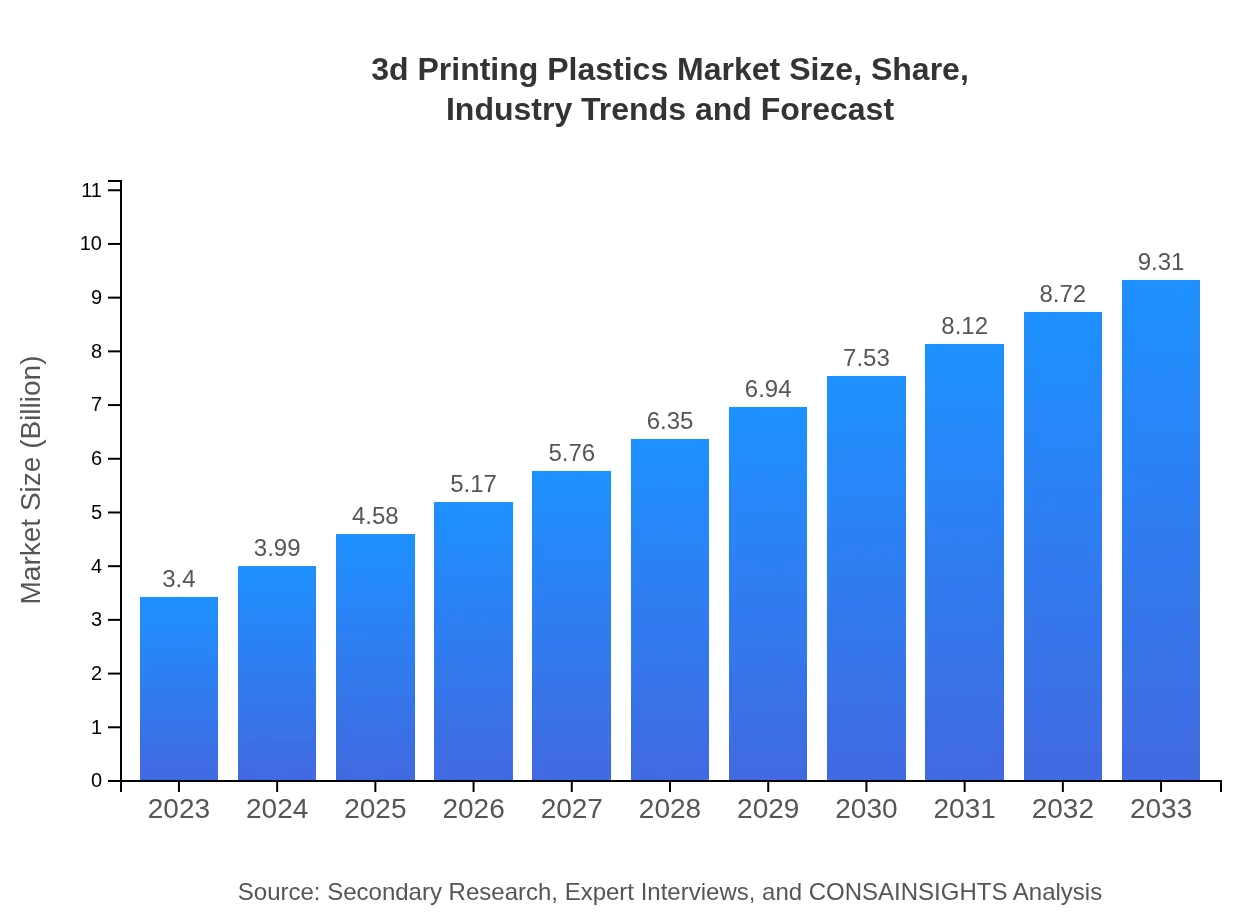
| 2023 Market Size | $3.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $9.31 Billion |
| Top Companies | Stratasys Ltd., 3D Systems Corporation, Materialise NV, MakerBot, Ultimaker |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
3d Printing Plastics Market Overview
Customize 3d Printing Plastics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 3d Printing Plastics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 3d Printing Plastics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 3d Printing Plastics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 3d Printing Plastics market in 2023?
3d Printing Plastics Industry Analysis
3d Printing Plastics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 3d Printing Plastics Market Report:
Europe is expected to reach USD 2.56 billion by 2033, up from USD 0.94 billion in 2023, driven by increasing adoption of 3D printing in industries like aerospace and medical, bolstered by supportive regulations and investments in technology.Asia Pacific 3d Printing Plastics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to showcase substantial growth, with an estimated market size of USD 0.69 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 1.89 billion by 2033. The surge in applications in manufacturing sectors alongside government initiatives promoting digital manufacturing processes significantly enhances market prospects in this region.North America 3d Printing Plastics Market Report:
North America remains the largest market, projected to grow from USD 1.24 billion in 2023 to USD 3.41 billion in 2033. The presence of numerous key players, a strong emphasis on R&D, and a robust manufacturing infrastructure contribute to this region's dominance.South America 3d Printing Plastics Market Report:
In South America, the market for 3D printing plastics is nascent but growing, with a market size of USD 0.13 billion in 2023 projected to increase to USD 0.35 billion by 2033. The demand is driven mainly by the automotive and consumer products sectors, where there is a push towards modernization in manufacturing.Middle East & Africa 3d Printing Plastics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are projected to see growth from USD 0.40 billion in 2023 to USD 1.09 billion by 2033, supported by advancements in technology and emerging applications in various sectors such as oil and gas, and construction.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
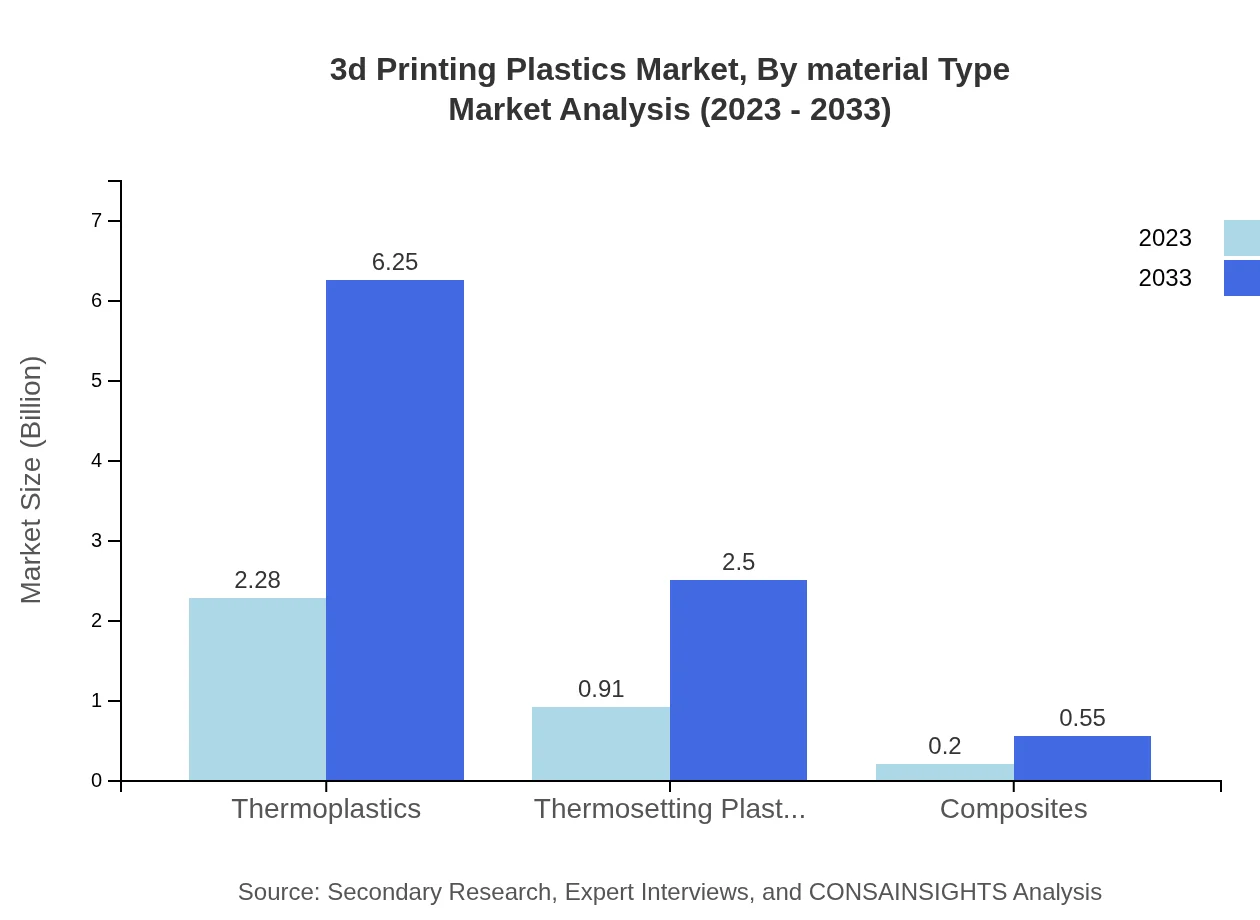
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis By Material Type
The 3D printing plastics market is prominently segmented by material type, with thermoplastics dominating the market at USD 2.28 billion in 2023 and anticipated to grow to USD 6.25 billion by 2033. Thermosetting plastics follow with a 2023 market size of USD 0.91 billion, projected to achieve USD 2.50 billion by 2033. Composites, though smaller, are growing steadily with increases from USD 0.20 billion in 2023 to USD 0.55 billion by 2033.
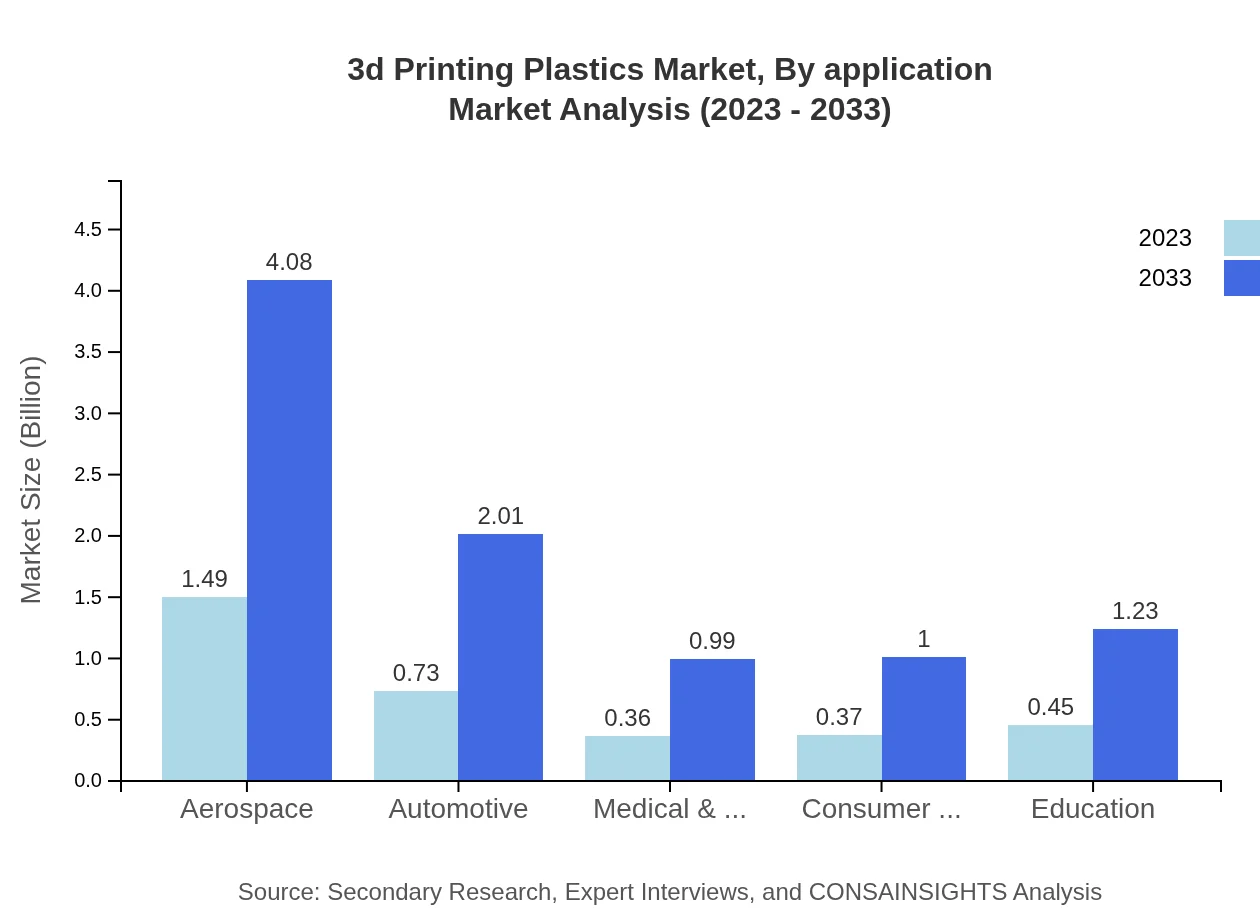
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the aerospace segment leads with market sizes of USD 1.49 billion in 2023 and USD 4.08 billion by 2033. Other significant segments include automotive at USD 0.73 billion in 2023 growing to USD 2.01 billion, and medical & dental with market sizes expanding from USD 0.36 billion to USD 0.99 billion over the same period.
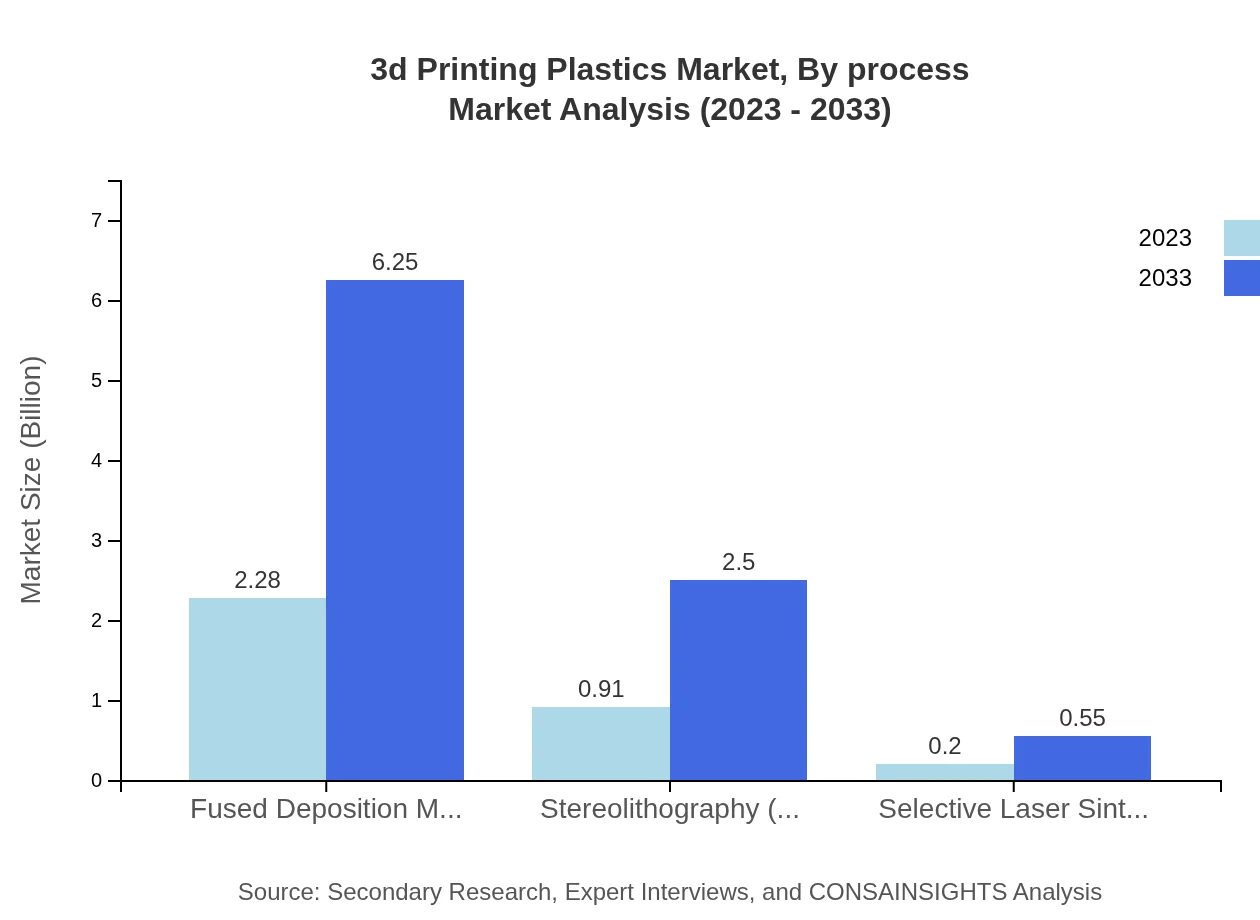
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis By Process
The market shows strong performance in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) with a market size of USD 2.28 billion in 2023, and expected growth to USD 6.25 billion by 2033. Stereolithography (SLA) is also notable, growing from USD 0.91 billion to USD 2.50 billion in the same timeframe.
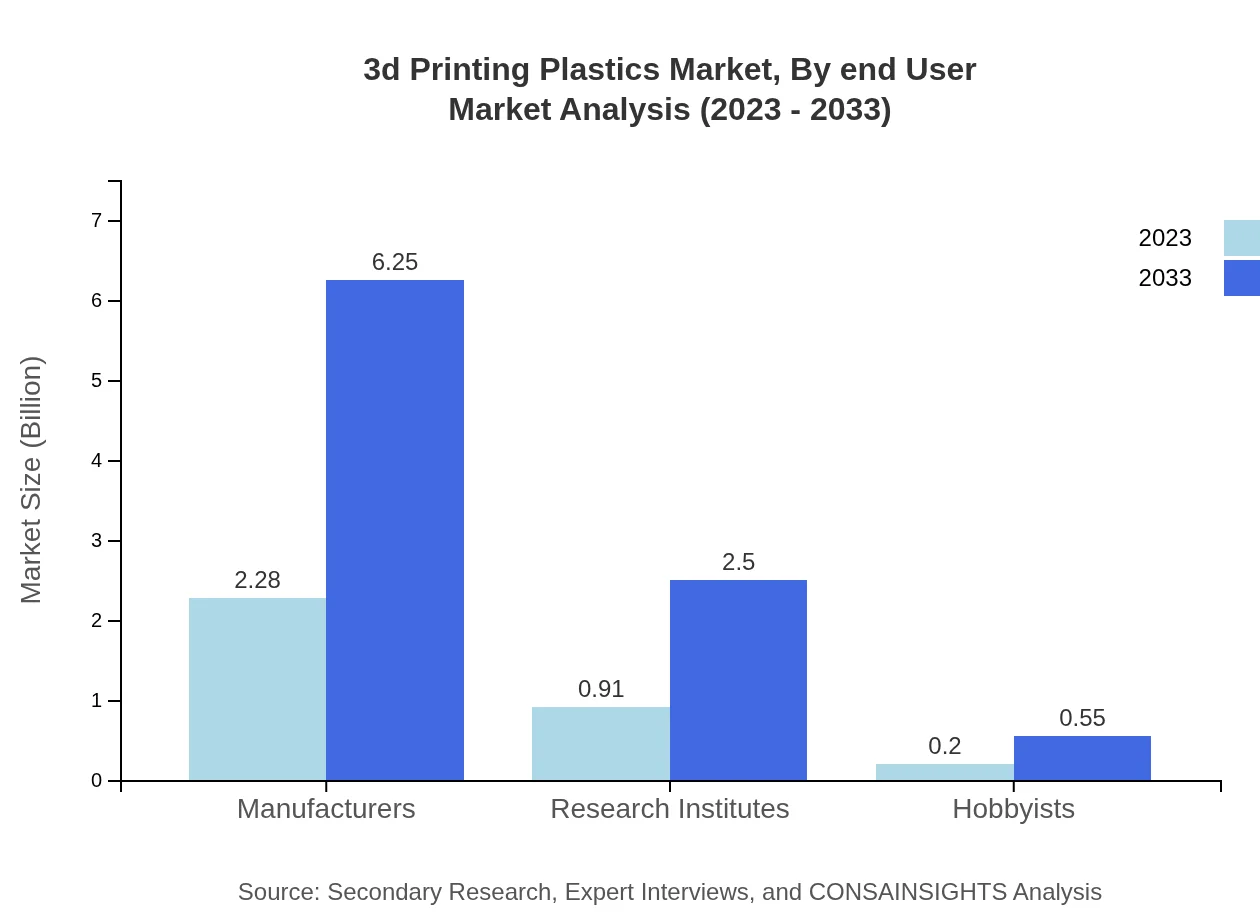
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis By End User
Key end-users include manufacturers and research institutes which hold market shares of 67.2% and 26.91% respectively in 2023. Hobbyists are emerging as potential growth areas, expanding from USD 0.20 billion to USD 0.55 billion by 2033.
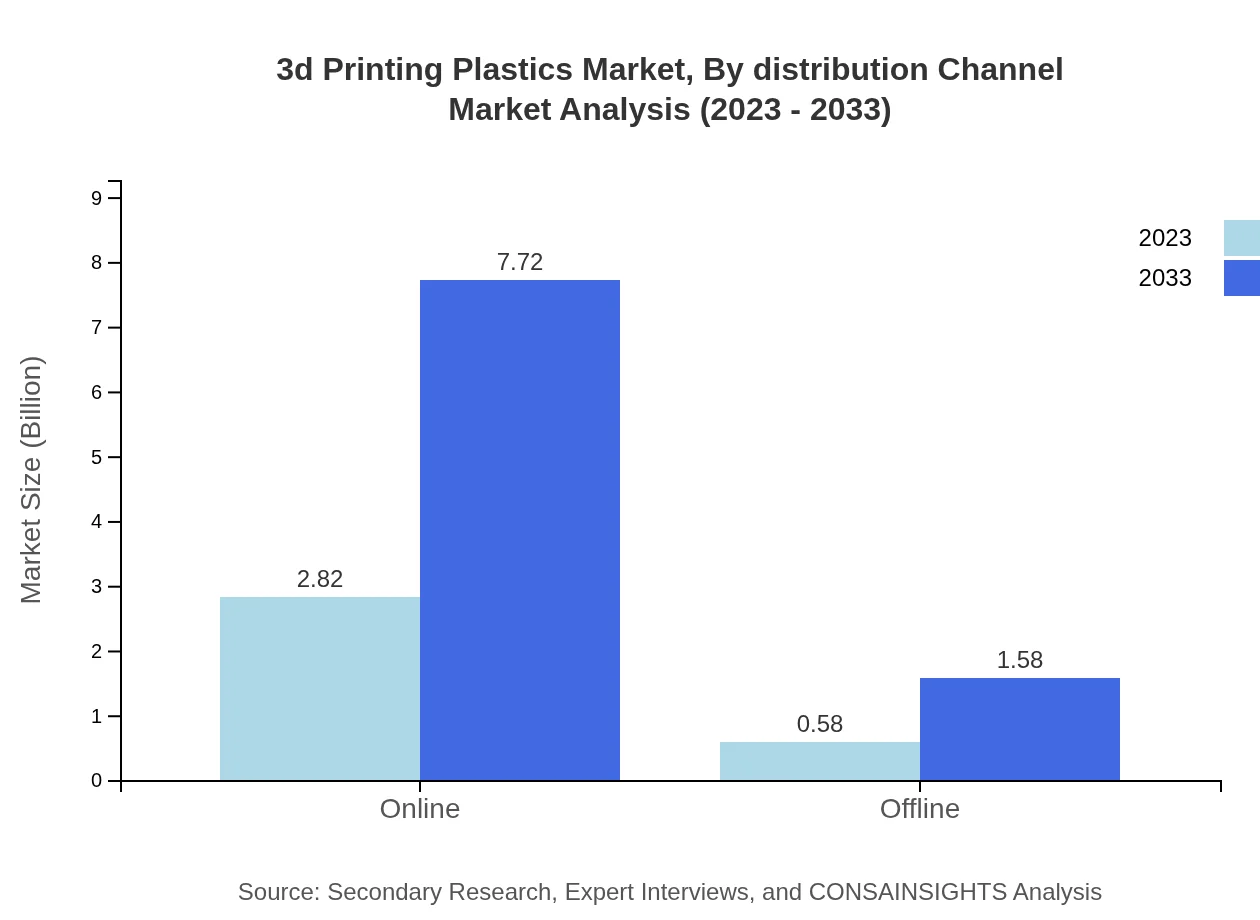
3d Printing Plastics Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The online distribution channel dominates the market with a significant share of 82.98% in 2023, whereas offline channels account for 17.02%. Market size for online channels is expected to grow from USD 2.82 billion to USD 7.72 billion by 2033.
3d Printing Plastics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 3d Printing Plastics Industry
Stratasys Ltd.:
Stratasys is a leader in polymer 3D printing technology and offers a wide range of 3D printers, materials, and services, contributing to diverse applications like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.3D Systems Corporation:
3D Systems is one of the pioneers in 3D printing technology, providing innovative solutions in plastics and metals, catering to various industries from consumer products to advanced medical applications.Materialise NV:
Materialise is a notable player known for its software solutions and services in the 3D printing space, facilitating a robust ecosystem for manufacturers and innovators.MakerBot:
MakerBot specializes in desktop 3D printers, focusing on educational and entry-level markets, successfully expanding the user base of 3D printing technology.Ultimaker:
Ultimaker is renowned for its reliable 3D printers and materials, promoting open-source solutions that cater to a diverse range of 3D printing needs, particularly in prototyping and small-scale manufacturing.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 3D Printing Plastics?
The 3D Printing Plastics market is projected to grow from $3.4 billion in 2023 to significant expansion by 2033, with a robust CAGR of 10.2%, indicating a strong upward trend and increasing demand.
What are the key market players or companies in the 3D Printing Plastics industry?
Key players in the 3D Printing Plastics market include major manufacturers and innovators that focus on advanced materials and technologies, contributing to the growth and diversity of the sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 3D Printing Plastics industry?
Major growth factors include technological advancements in 3D printing, a surge in demand from various sectors, and increased adoption of eco-friendly materials, all fueling market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 3D Printing Plastics?
Europe is expected to be the fastest-growing region, with market size increasing from $0.94 billion in 2023 to $2.56 billion by 2033, reflecting substantial growth potential.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the 3D Printing Plastics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the 3D Printing Plastics industry, providing detailed insights and analytics.
What deliverables can I expect from this 3D Printing Plastics market research project?
You can expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape insights, and segmented data for informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of 3D Printing Plastics?
Current trends include a shift towards sustainable materials, increased customization in production, and advancements in production technologies to meet diverse industry needs.