5g Core Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: 5g-core
5g Core Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the 5G Core market, highlighting current insights, market dynamics, and trends for the forecast period from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, growth potential, regional analysis, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
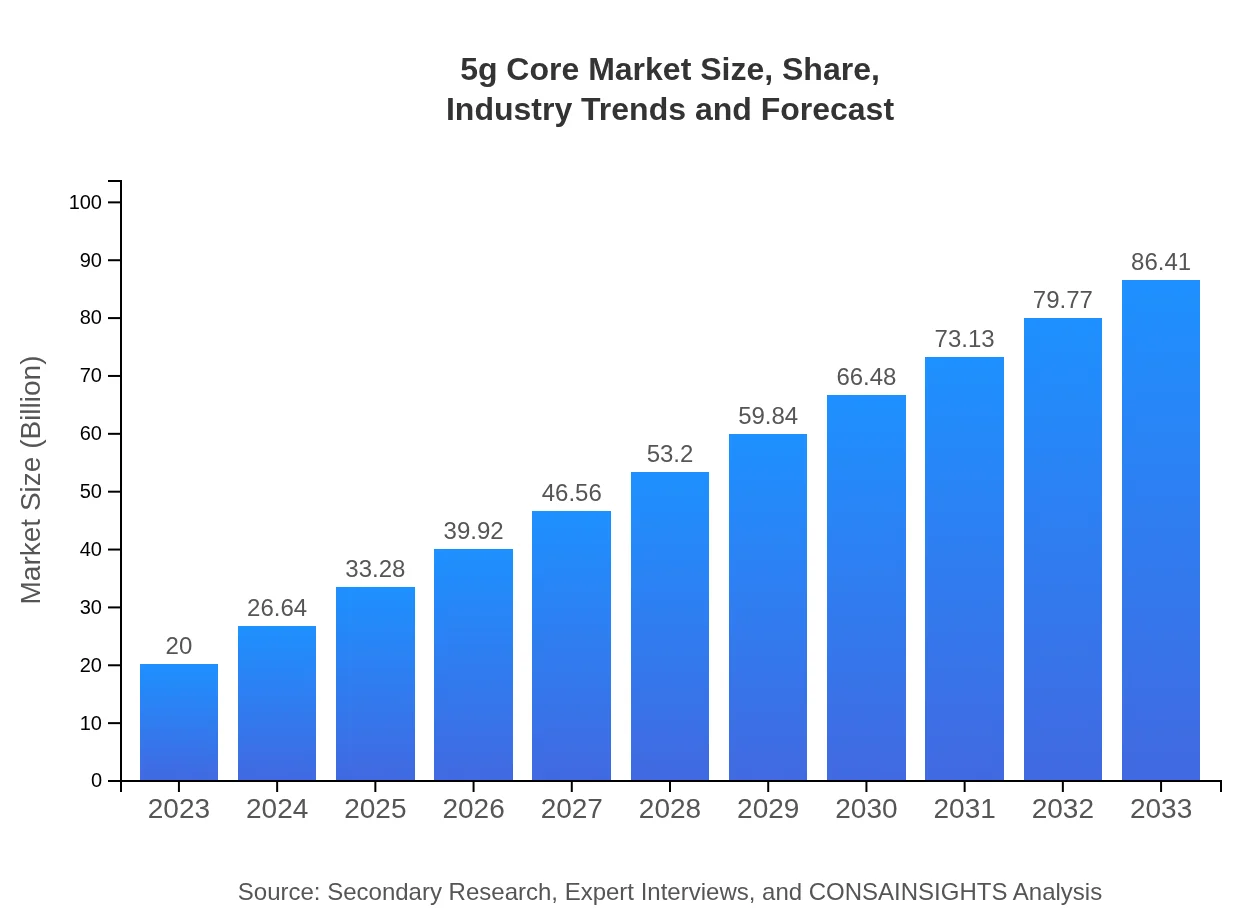
| 2023 Market Size | $20.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 15% |
| 2033 Market Size | $86.41 Billion |
| Top Companies | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson , Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics, Cisco Systems, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
5g Core Market Overview
Customize 5g Core Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of 5g Core market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand 5g Core's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in 5g Core
What is the Market Size & CAGR of 5g Core market in 2023 and 2033?
5g Core Industry Analysis
5g Core Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
5g Core Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe 5g Core Market Report:
Europe's 5G Core market is expected to grow substantially, from $6.83 billion in 2023 to $29.53 billion by 2033. Demand for advanced telecommunications solutions and a strong push towards sustainability and digital transformation are key drivers. European governments are pushing for ambitious 5G implementation plans, leading to accelerating investments in related infrastructure and services.Asia Pacific 5g Core Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is poised for substantial growth, with the market expected to increase from $3.78 billion in 2023 to approximately $16.32 billion by 2033. Countries like China and Japan are leading in 5G implementation, driven by government support and heavy investments in telecom infrastructure. The burgeoning demand for IoT applications and smart city projects is also propelling market growth in this region.North America 5g Core Market Report:
North America presents a significant market, with expectations for growth from $6.94 billion in 2023 to $29.97 billion by 2033. Major telecom companies are investing aggressively in 5G technologies to remain competitive. The region’s strong focus on technological innovation, coupled with the integration of advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning into telecommunications, is also underpinning this growth.South America 5g Core Market Report:
The 5G Core market in South America, while currently smaller, is projected to experience growth from $0.02 billion in 2023 to $0.08 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing government initiatives to expand telecommunications infrastructure and enhance connectivity, particularly in rural areas. However, economic challenges and regulatory barriers may hinder faster adoption.Middle East & Africa 5g Core Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's market is projected to grow from $2.43 billion in 2023 to $10.52 billion by 2033. The expansion is driven by increasing mobile data traffic, rapid urbanization, and government projects aimed at enhancing digital services. However, challenges such as investment costs and regulatory hurdles may impede swift progress.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
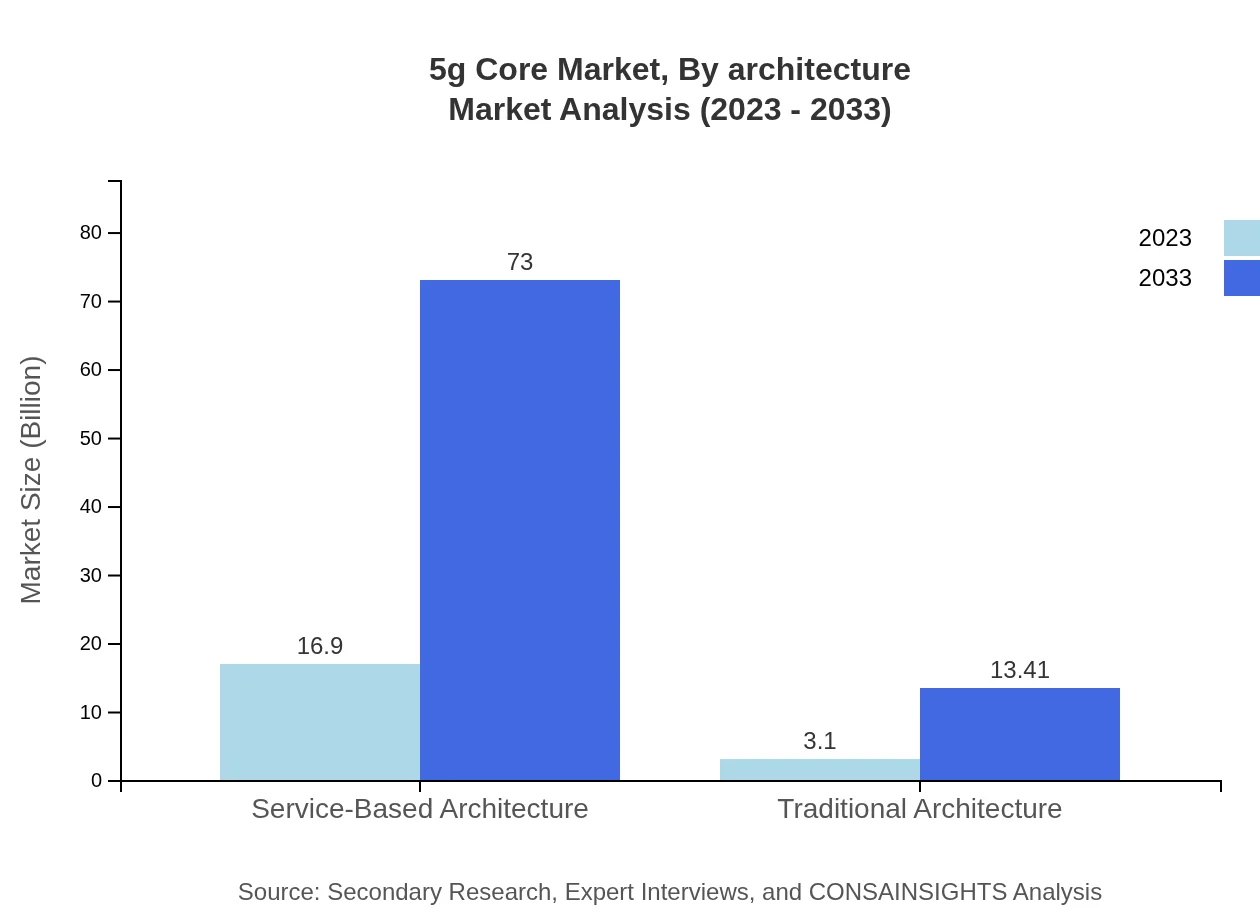
5g Core Market Analysis By Architecture
The 5G Core market by architecture is dominated by Service-Based Architecture (SBA), which is anticipated to grow from $16.90 billion in 2023 to $73.00 billion by 2033, retaining a dominance in market share at 84.48%. In contrast, Traditional Architecture is expected to increase from $3.10 billion in 2023 to $13.41 billion by 2033, holding 15.52% of the market share.
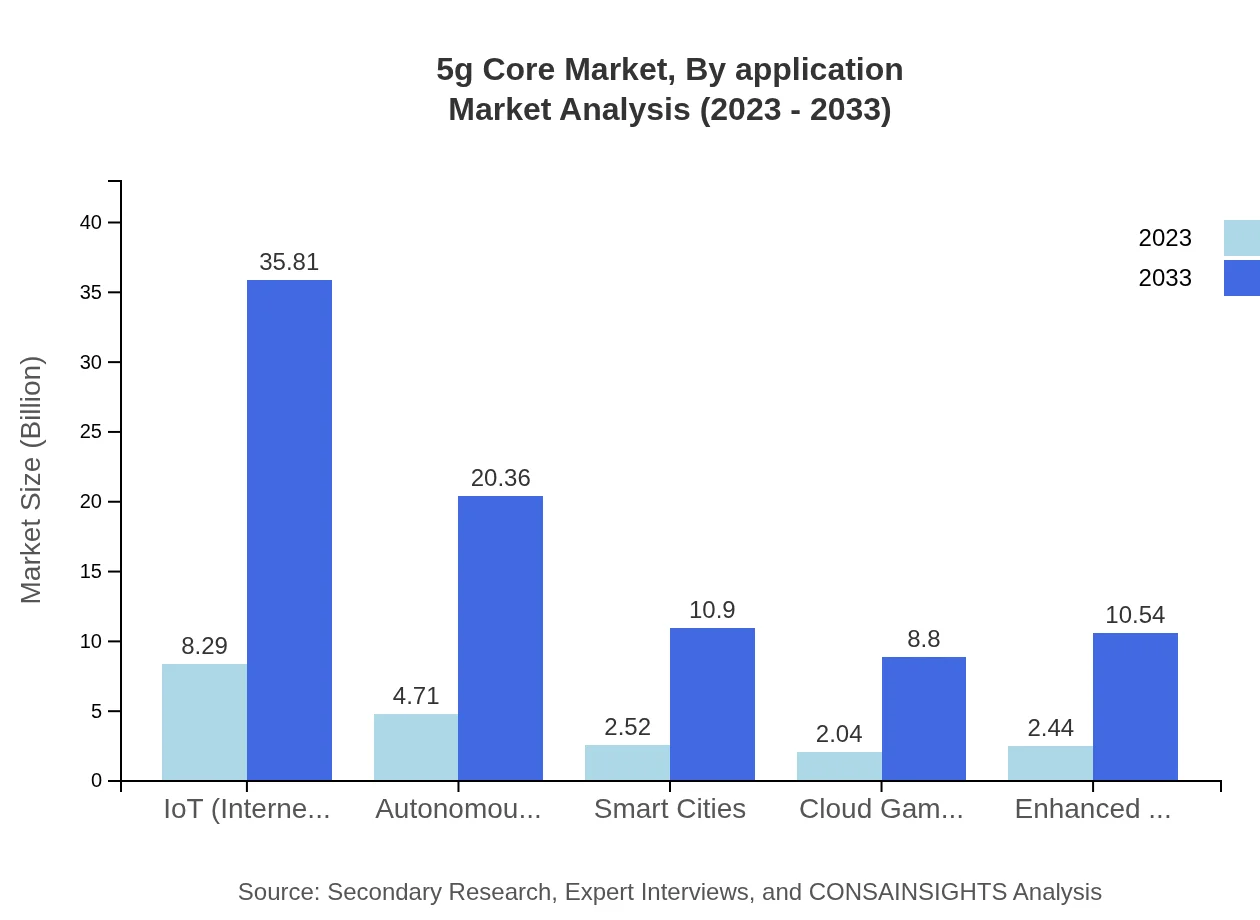
5g Core Market Analysis By Application
Applications in the 5G Core market showcase significant growth in segments like Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and IoT, with eMBB expected to climb from $12.48 billion in 2023 to $53.94 billion by 2033, capturing 62.42% of the market share. IoT will also mirror this trend with growth from $8.29 billion in 2023 to $35.81 billion by 2033.
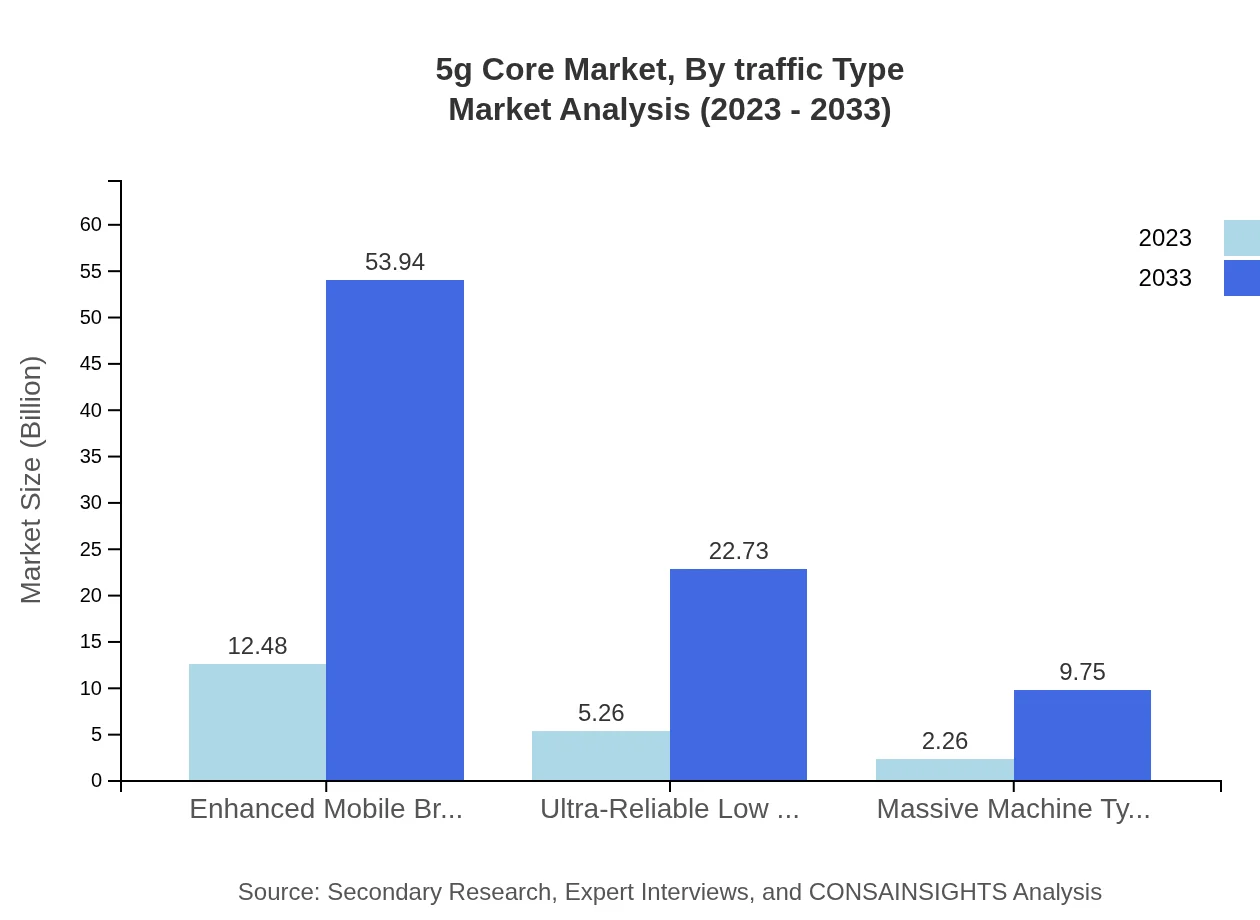
5g Core Market Analysis By Traffic Type
Traffic types in the 5G Core market reveal a key trend towards Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), projected to grow from $5.26 billion in 2023 to $22.73 billion by 2033. Other segments like Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC) and traditional traffic types are also expected to grow, indicating a shift towards more reliable communication methods across sectors.
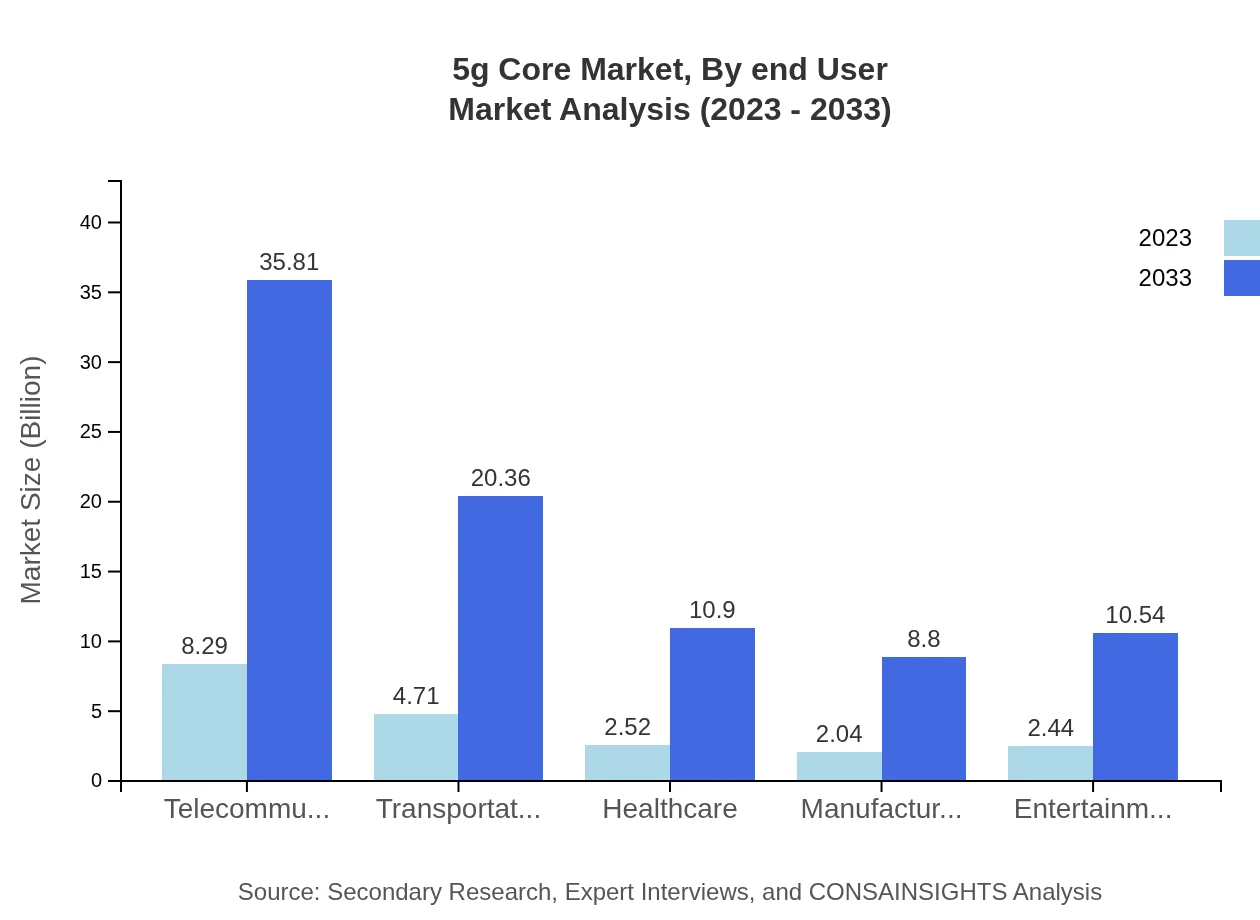
5g Core Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment of the 5G Core market shows telecommunications as the largest contributor with market size rising from $8.29 billion in 2023 to $35.81 billion by 2033. Other significant industries include transportation and healthcare, illustrating the vast applicability of 5G technology across diverse sectors.
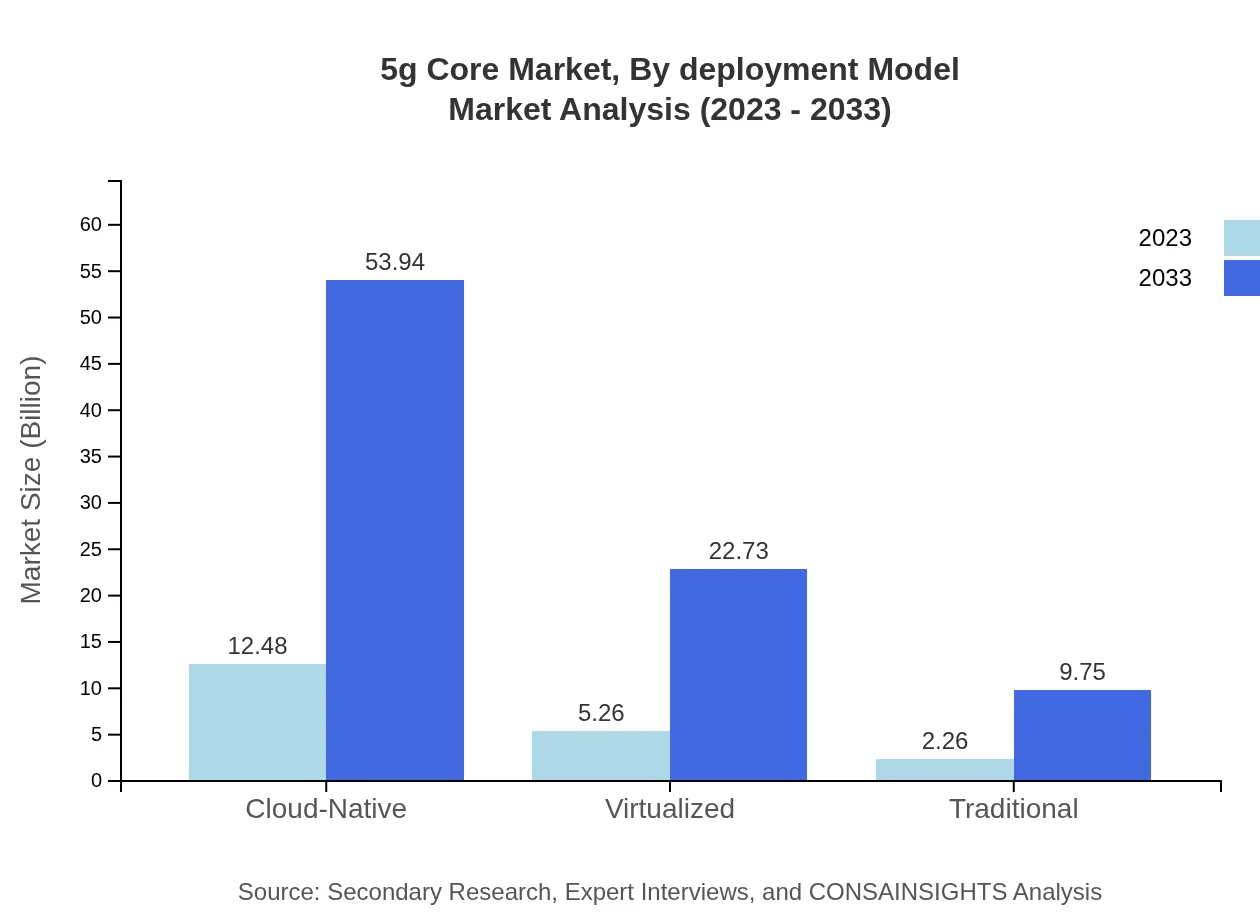
5g Core Market Analysis By Deployment Model
The market by deployment model is divided into cloud-native and virtual deployment models, with cloud-native expected to dominate, reflecting a transition to more adaptive network solutions. Growth in this segment signifies broader acceptance of cloud services in telecommunications, reflecting the industry's shift towards scalable, flexible infrastructures.
5g Core Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in 5g Core Industry
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.:
Huawei is a leading global provider of information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure and smart devices, heavily investing in 5G technology development and infrastructure.Ericsson :
Ericsson is a key player committed to the advancement of telecommunications technology, providing innovative solutions that enhance network efficiency, particularly in the 5G Core space.Nokia Corporation:
Nokia is a pioneer in the telecommunications industry, delivering high-performance network equipment and solutions critical to 5G core deployment.Samsung Electronics:
Samsung is significantly investing in 5G technologies and infrastructure, focusing on delivering cutting-edge solutions that address the needs of modern telecommunications.Cisco Systems, Inc.:
Cisco is a leader in networking technologies and services, providing solutions that support the complexity of 5G implementations across various sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of 5G Core?
The global 5G Core market is projected to reach $20 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 15%. The expansion reflects increasing investments in telecom infrastructure and demand for enhanced data services.
What are the key market players or companies in this 5G Core industry?
Key players in the 5G Core industry include Ericsson, Nokia, Huawei, Samsung, and ZTE. These companies are leading the charge in developing cutting-edge 5G technologies and solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the 5G Core industry?
The growth in the 5G Core industry is driven by increasing demand for high-speed internet, advancements in IoT technology, and the need for faster, more reliable connections in various sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the 5G Core?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the 5G Core market, expected to rise from $6.94 billion in 2023 to $29.97 billion by 2033, fueled by technological advancements and heavy investments.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the 5G Core industry?
Yes, Consainsights provides customized market reports tailored to client specifications in the 5G Core industry, offering detailed insights and data analysis to support strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this 5G Core market research project?
Expected deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, regional insights, competitive landscape assessments, trend identification, and actionable recommendations tailored to specific business needs.
What are the market trends of 5G Core?
Trends in the 5G Core market include a shift towards cloud-native solutions, increased focus on service-based architectures, and the growing importance of ultra-reliable low latency communications.