Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: agricultural-biotechnology
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Agricultural Biotechnology market, encompassing insights, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It delves into market size, segment performance, technological advancements, regional dynamics, and profiling of leading companies in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
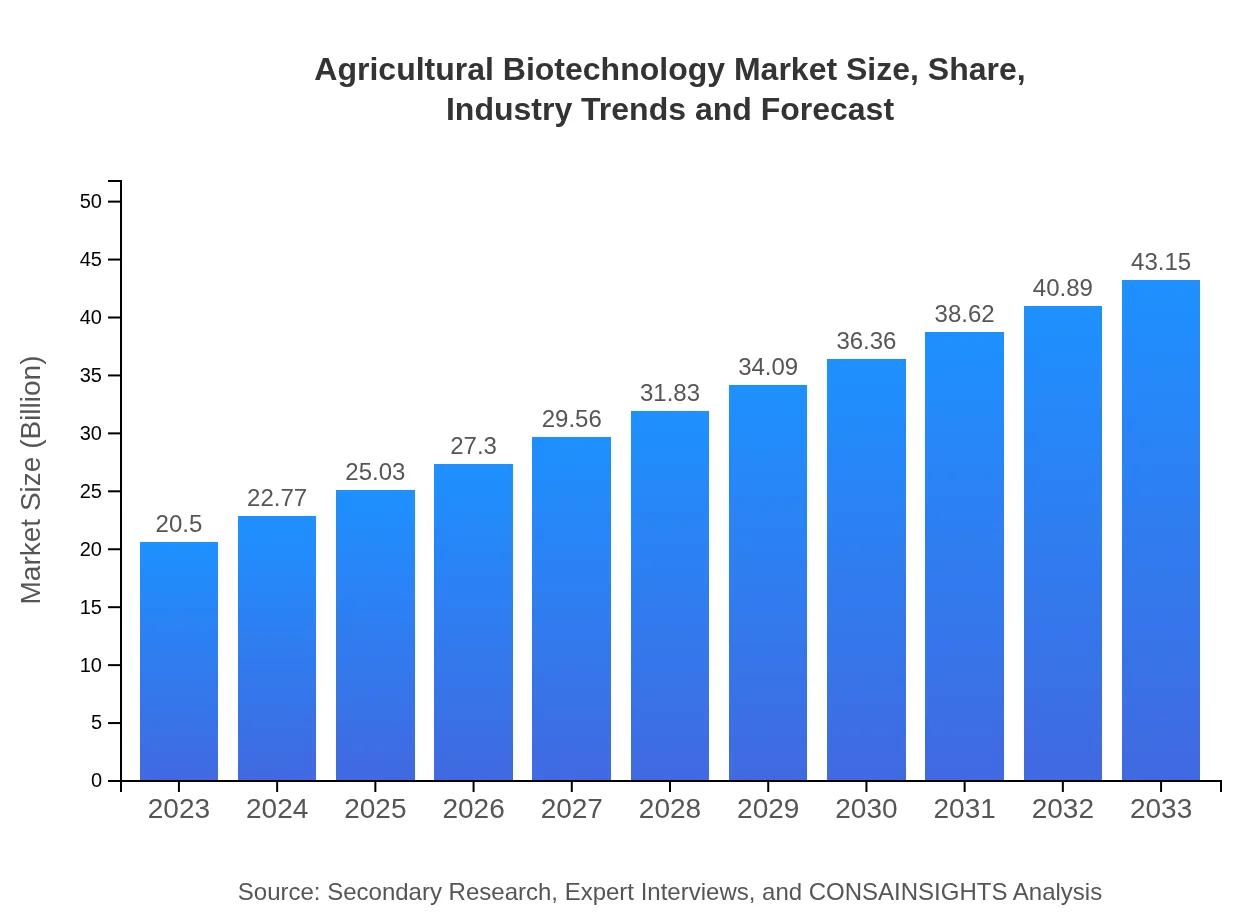
| 2023 Market Size | $20.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $43.15 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Overview
Customize Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Agricultural Biotechnology market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Agricultural Biotechnology's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Agricultural Biotechnology
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Agricultural Biotechnology market in 2023?
Agricultural Biotechnology Industry Analysis
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report:
The European market for Agricultural Biotechnology stands at USD 6.96 billion in 2023, with an anticipated growth to USD 14.64 billion by 2033. Europe is experiencing a slow but steady acceptance of biotech crops, prompted by changing consumer preferences and rising regulatory support for sustainable agricultural practices.Asia Pacific Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report:
In 2023, the Agricultural Biotechnology market in the Asia Pacific region is valued at USD 3.46 billion, with projections to reach USD 7.29 billion by 2033, driven largely by a growing population, enhancing food security, and increasing adoption of agricultural technologies. Countries like India and China are leading the charge, investing heavily in biotech crops and innovative farming practices.North America Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report:
North America, particularly the U.S., is the largest market, with a size of USD 7.05 billion in 2023 and projections of USD 14.84 billion by 2033. The region's advanced research capabilities, large-scale agricultural operations, and widespread acceptance of GM technology substantially contribute to its market dominance.South America Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report:
The South American market is expected to grow from USD 1.87 billion in 2023 to USD 3.94 billion by 2033. The adoption of genetically modified crops, particularly in Brazil and Argentina, is a critical factor in this growth. Favorable climatic conditions and supportive government policies are essential elements fueling expansion.Middle East & Africa Agricultural Biotechnology Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market will reach USD 1.16 billion in 2023, and it is expected to double to USD 2.44 billion by 2033. Investments in biotechnology are tagged as key to addressing climate change impacts, increasing food production, and improving nutrition quality across the regions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
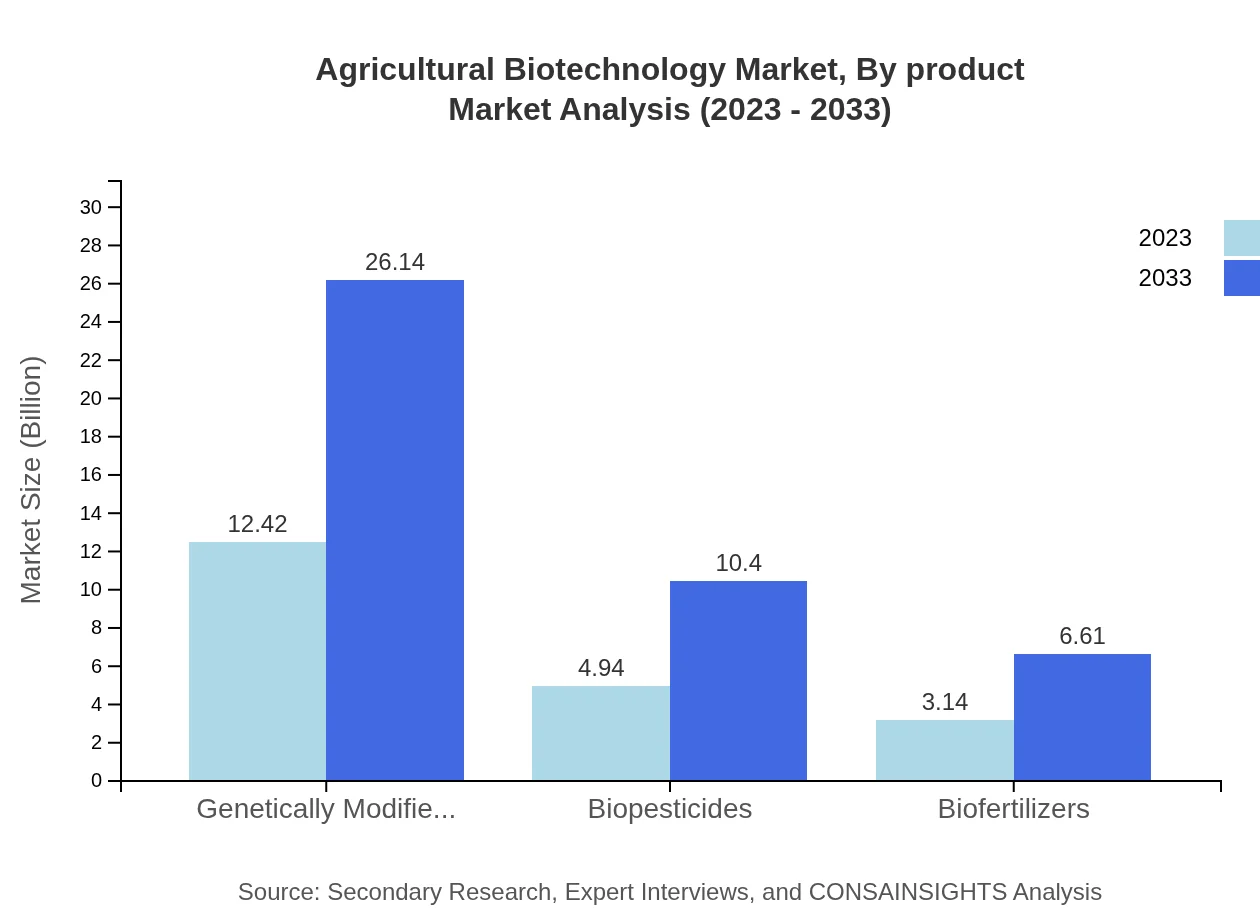
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis By Product
By 2033, the market for genetically modified crops is expected to reach USD 26.14 billion from USD 12.42 billion in 2023, representing a 60.57% share of the market. Biopesticides and biofertilizers also demonstrate robust growth, with sizes predicted to reach USD 10.40 billion and USD 6.61 billion by 2033 respectively.
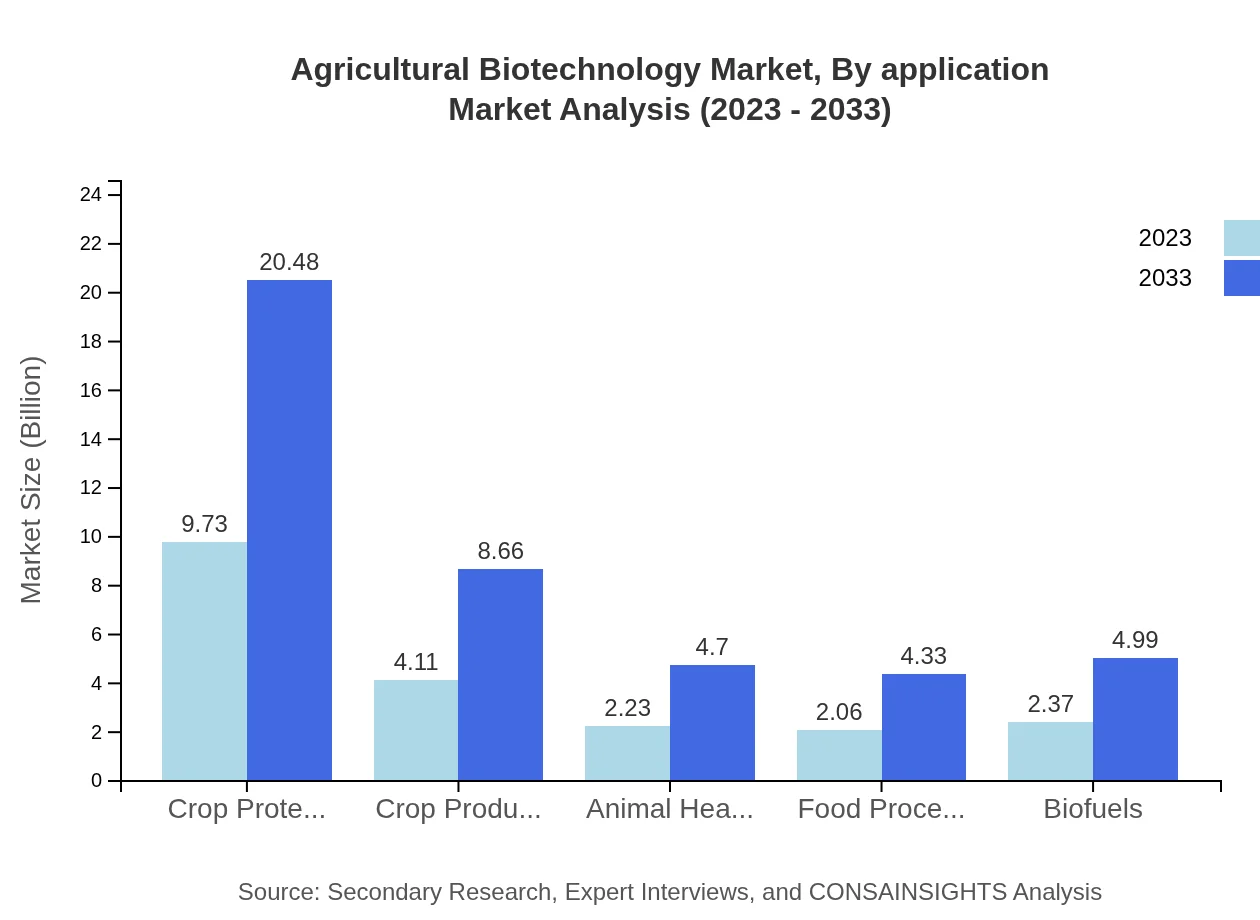
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis By Application
Usage of genetic engineering and biotechnology primarily targets crop protection and production. Crop Protection accounts for a 47.45% market share in 2023, equating to USD 9.73 billion, while Crop Production is anticipated to grow to USD 8.66 billion by 2033.
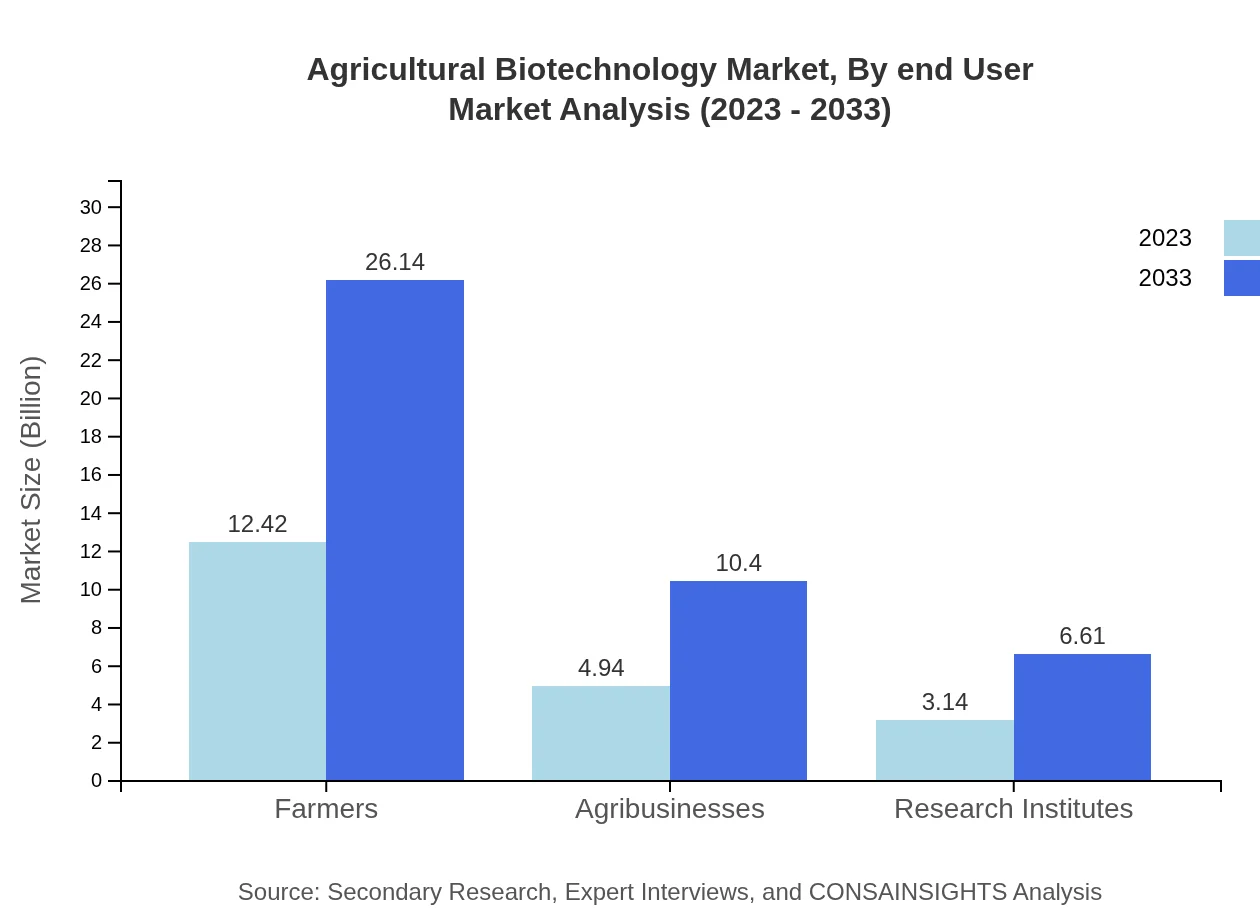
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis By End User
The primary end-users within this market include farmers, agribusinesses, and research institutions. Farmers lead the market share with significant investments in biotechnology, while agribusinesses and research institutions drive innovation and product development.
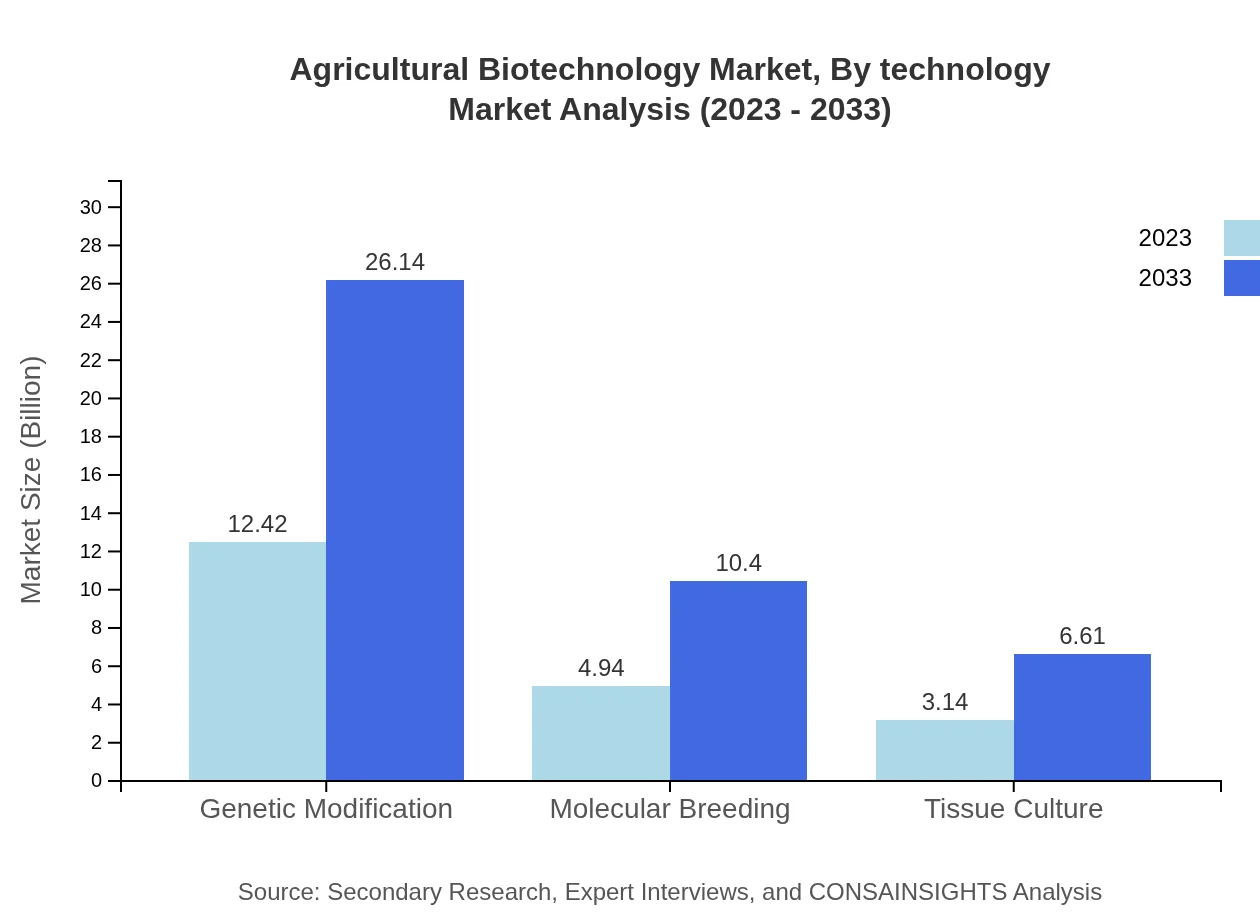
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis By Technology
Technologies such as genetic modification, molecular breeding, and tissue culture contribute prominently. Genetic modification captures a significant market share, reflecting its importance in developing resilient crops that can withstand climate change effects.
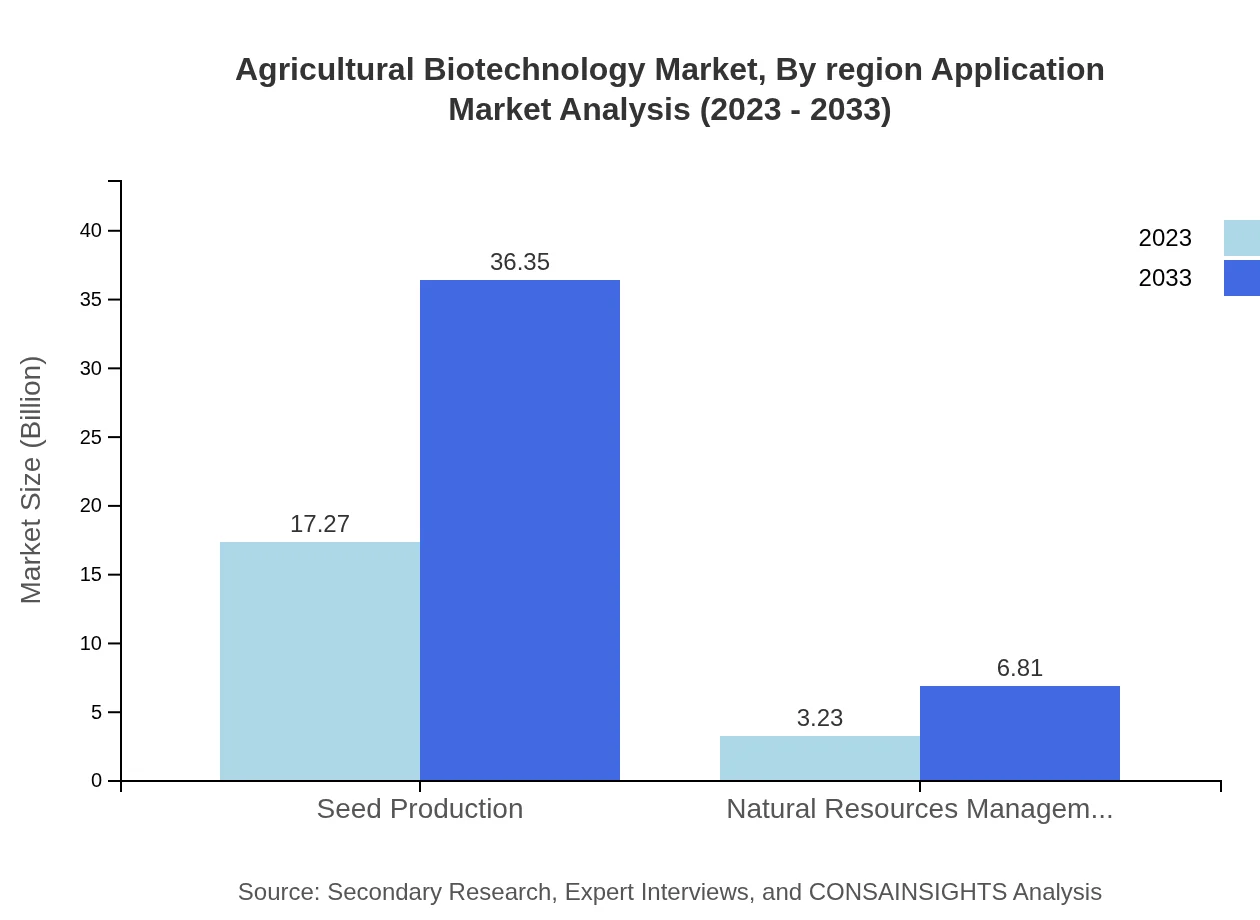
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Analysis By Region Application
Major applications include biofuels, animal health, and food processing, with biofuels projected to grow significantly due to a rising global demand for renewable energy sources.
Agricultural Biotechnology Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Agricultural Biotechnology Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leader in agricultural biotechnology, known for its development of genetically modified seeds and crop protection products.Bayer AG:
Significant in crop science and biotechnology products, Bayer focuses on sustainable agriculture and solutions to enhance crop yields and protection.Syngenta AG:
A global company dedicated to sustainable agriculture, offering innovations in seeds and crop protection technologies.DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
With a long-standing commitment to agriculture, DuPont specializes in environmental stewardship through advanced biotechnological practices.Corteva Agriscience:
Corteva focuses on innovative crop protection products and genetically engineered seeds aiming for a sustainable food supply.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Agricultural Biotechnology?
The Agricultural Biotechnology market is projected to reach a market size of $20.5 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the Agricultural Biotechnology industry?
Key market players include major biotech companies, agribusiness firms, and research institutes specializing in genetic modification, crop protection, and biofertilizer development, contributing to advancements in agricultural output and sustainability.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Agricultural Biotechnology industry?
The growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for food due to population growth, the need for sustainable agricultural practices, and advancements in genetic research that enhance crop resilience against pests and adverse climate conditions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Agricultural Biotechnology market?
The Asia Pacific region is one of the fastest-growing markets, projected to grow from $3.46 billion in 2023 to $7.29 billion by 2033, reflecting a significant compound annual growth rate.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Agricultural Biotechnology industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the Agricultural Biotechnology sector, providing insights into market dynamics, competitive landscape, and growth opportunities.
What deliverables can I expect from this Agricultural Biotechnology market research project?
From the Agricultural Biotechnology market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports featuring market size data, segment analysis, trends, forecasts, and competitive analysis, ensuring well-rounded insights for strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of Agricultural Biotechnology?
Current trends in agricultural biotechnology include increasing adoption of genetically modified organisms, sustainable farming practices, investment in biopesticides, and advancements in molecular breeding technologies aimed at improving crop yields.