Agrigenomics Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: agrigenomics
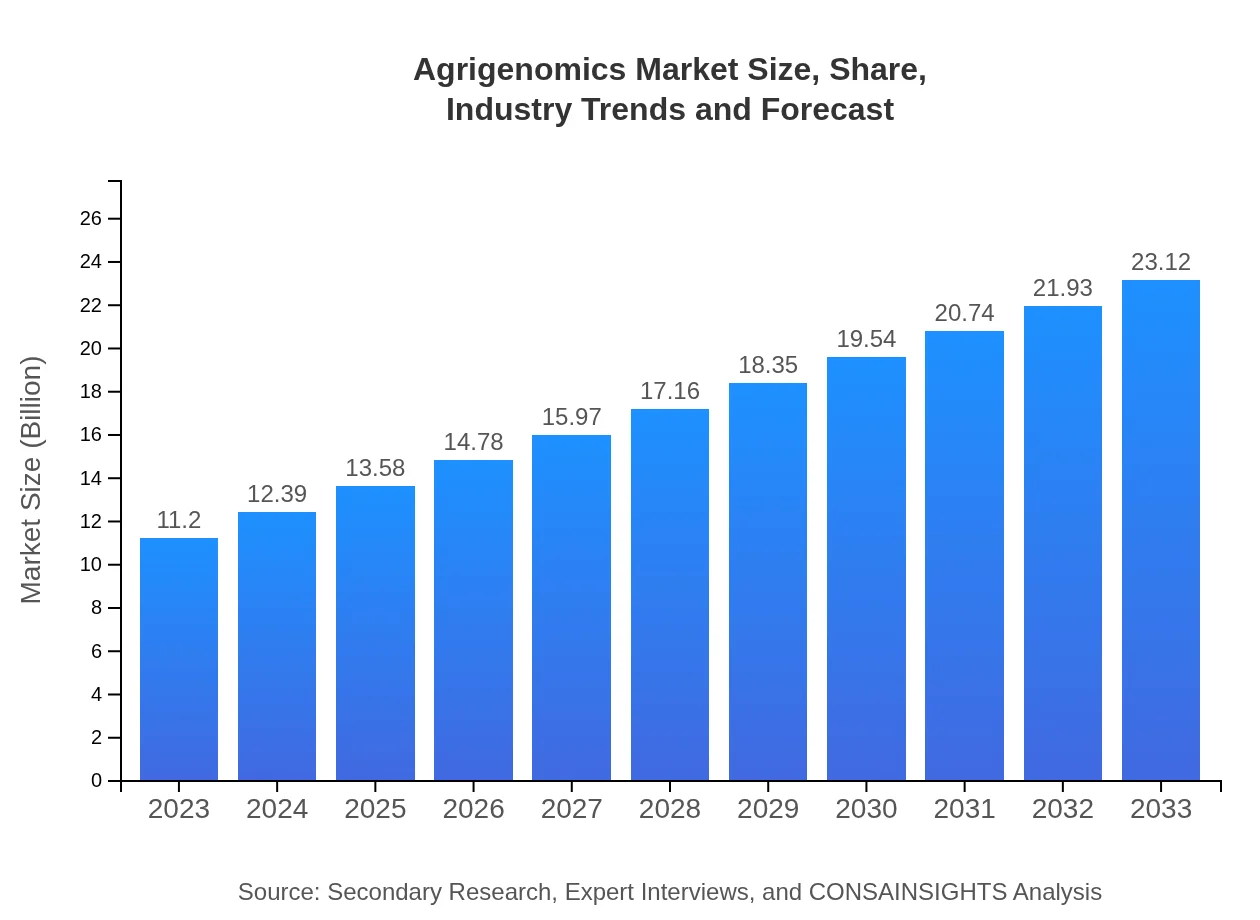
Agrigenomics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Agrigenomics market, covering insights on market size, growth trends, industry segmentation, and regional dynamics, with forecasts extending from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $11.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $23.12 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, Syngenta AG, Agilent Technologies, Illumina, Inc., Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Agrigenomics Market Overview
Customize Agrigenomics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Agrigenomics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Agrigenomics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Agrigenomics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Agrigenomics market in 2023?
Agrigenomics Industry Analysis
Agrigenomics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Agrigenomics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Agrigenomics Market Report:
Europe’s Agrigenomics market was valued at $2.72 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $5.61 billion by 2033, driven by regulatory frameworks that promote innovative agricultural practices and consumer demand for sustainable products.Asia Pacific Agrigenomics Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Agrigenomics market was valued at $2.20 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $4.55 billion by 2033, driven by rising population and food demand. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in agricultural genomics.North America Agrigenomics Market Report:
The North American market, valued at $3.89 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $8.02 billion by 2033. The United States leads in agrigenomics research, with significant investments from major biotech firms.South America Agrigenomics Market Report:
South America’s Agrigenomics market stands at $0.99 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $2.05 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by the region’s focus on enhancing crop yields and developing disease-resistant varieties.Middle East & Africa Agrigenomics Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market size is currently $1.40 billion (2023) and is forecasted to reach $2.89 billion by 2033. Increased adoption of advanced farming techniques and government support initiatives contribute to this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
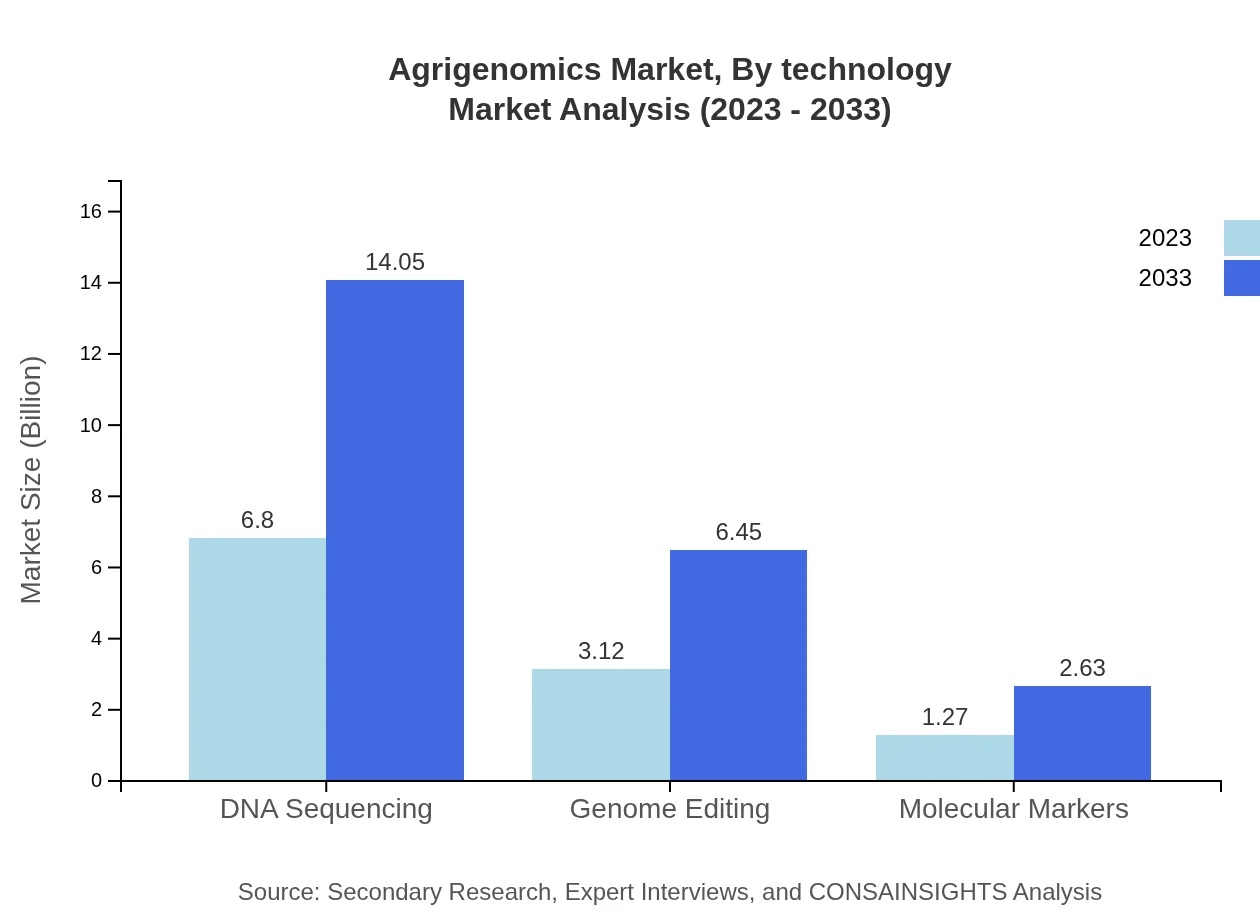
Agrigenomics Market Analysis By Technology
The Agrigenomics market by technology is led by DNA sequencing, which represented $6.80 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $14.05 billion by 2033. Genome editing and molecular markers follow closely, collectively advancing agricultural practices. The share of technology types indicates a robust focus on genomic technologies across various agricultural segments.
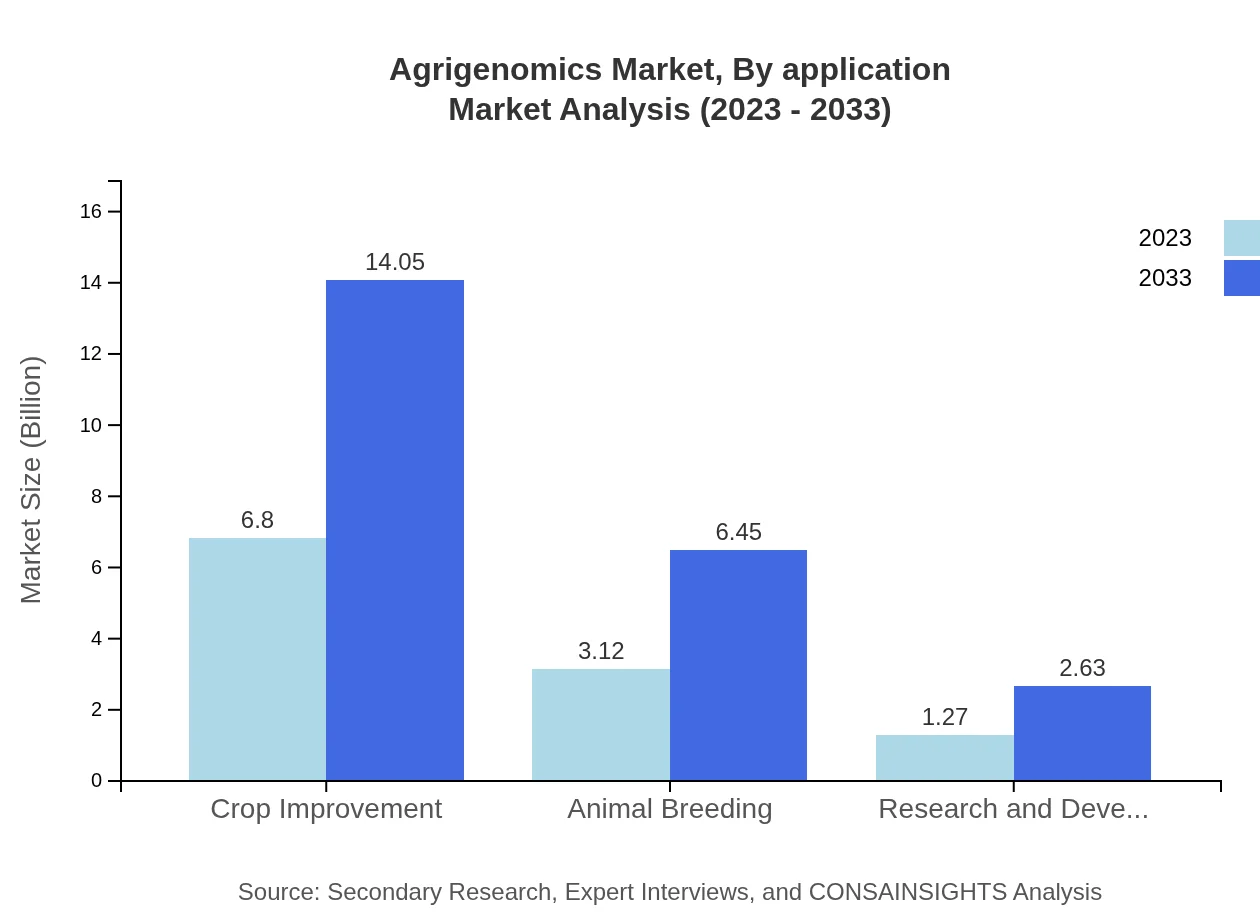
Agrigenomics Market Analysis By Application
The application analysis reveals crop improvement as the dominant segment, significantly impacting market dynamics with a size of $6.80 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $14.05 billion by 2033. Animal breeding and research & development also represent valuable segments, highlighting the multidimensional approach of agrigenomics towards boosting productivity.
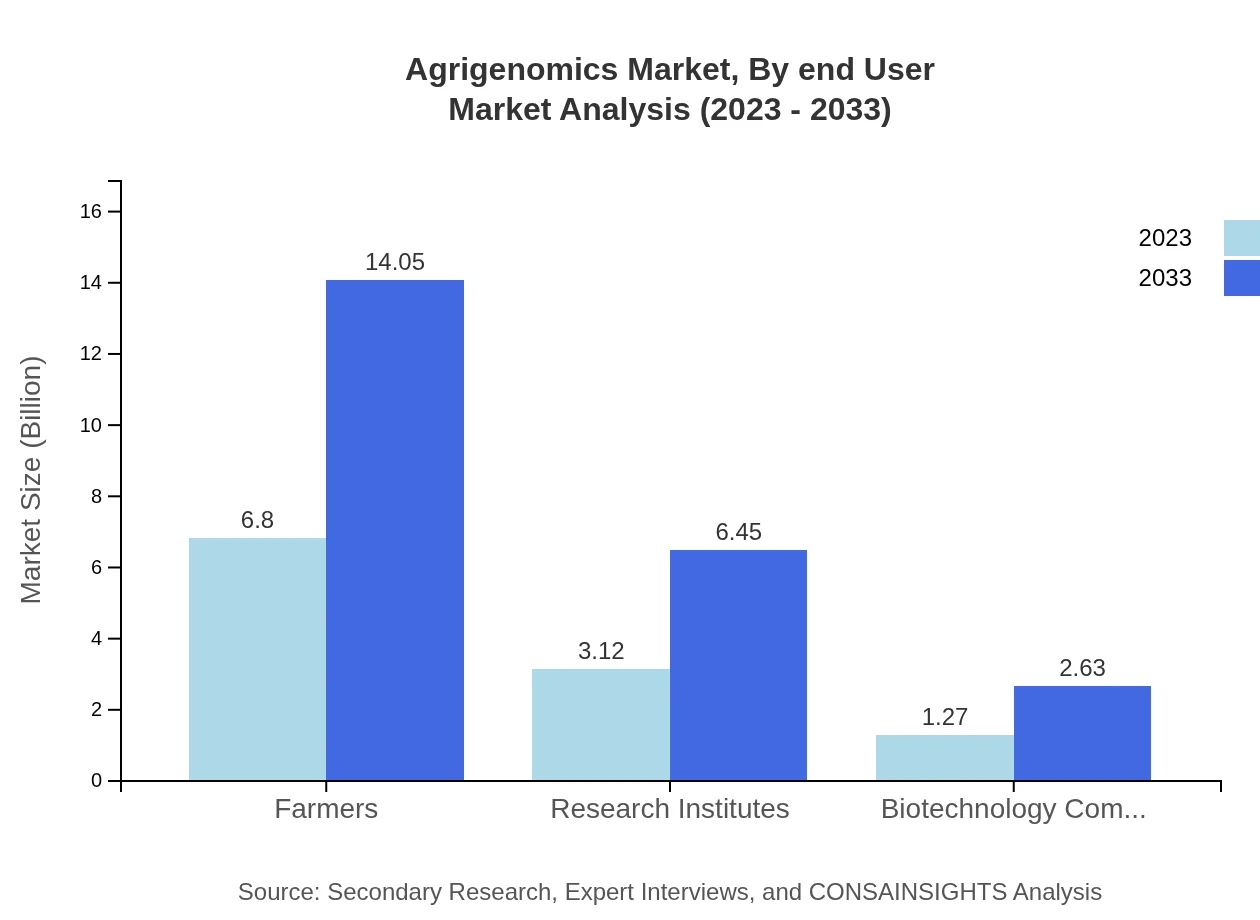
Agrigenomics Market Analysis By End User
Farmers are the largest end-users in the Agrigenomics market, commanding a market size of $6.80 billion in 2023, growing to $14.05 billion by 2033. Research institutes and biotechnology companies are vital contributors, emphasizing collaborative efforts towards enhancing agricultural outcomes.
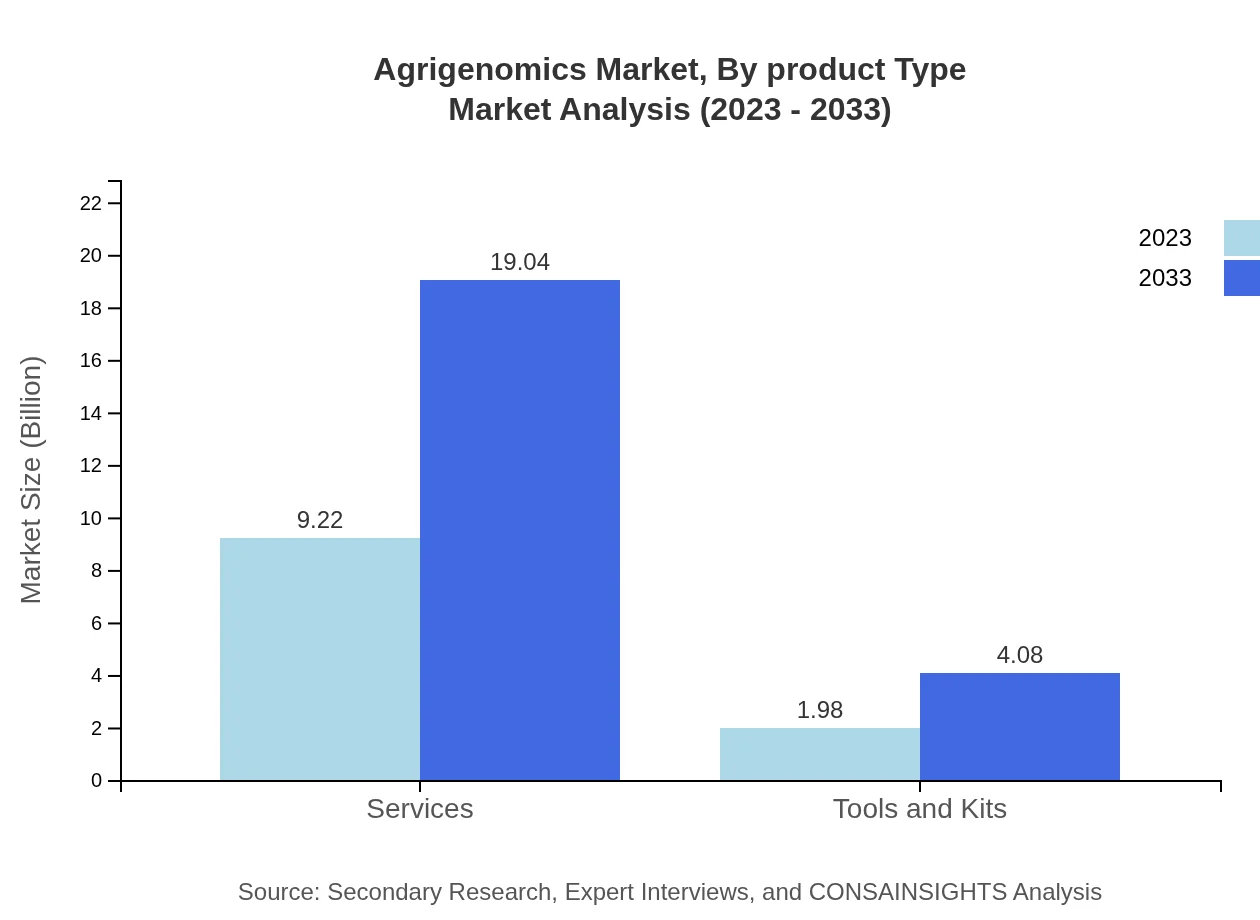
Agrigenomics Market Analysis By Product Type
The analysis by product type identifies services as the primary segment, with a market size of $9.22 billion in 2023, projected to double by 2033. Tools and kits, although smaller, exhibit a growing trend toward personalized agrigenomic solutions.
Agrigenomics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Agrigenomics Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leader in genetically modified seeds, focusing on biotechnology and agricultural solutions aimed at enhancing crop yields and sustainability.Syngenta AG:
Specializes in sustainable agriculture and crop protection, integrating advanced technologies to innovate in seed development and agricultural practices.Agilent Technologies:
Provides comprehensive solutions in genomics and proteomics, facilitating research and applications in agriculture through advanced analytical tools.Illumina, Inc.:
A prominent supplier of next-generation sequencing platforms that drive the advancement of genomic analysis within agrigenomics.Corteva Agriscience:
Focuses on the global agricultural market by leveraging integrated seed and crop protection technologies to enhance food production.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of agrigenomics?
The agrigenomics market is currently valued at approximately $11.2 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% over the next decade. This growth indicates a robust demand for advanced genomic techniques in agriculture.
What are the key market players or companies in the agrigenomics industry?
Key market players in agrigenomics include major firms such as Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and DuPont. These companies are leading in innovative genomic technologies, critical for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the agrigenomics industry?
Primary growth drivers in agrigenomics include increasing demand for food security, advancements in genomic technologies, and the rising importance of sustainable agricultural practices. Additionally, increased investment in R&D fuels innovation in the field.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the agrigenomics market?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the agrigenomics market, with projections showing growth from $3.89 billion in 2023 to $8.02 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also demonstrate significant growth opportunities.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the agrigenomics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the agrigenomics industry. This includes detailed analysis on market trends, forecasts, competitive landscapes, and segmentation.
What deliverables can I expect from this agrigenomics market research project?
Deliverables from the agrigenomics market research project include comprehensive market analysis reports, detailed segmentation insights, future growth projections, competitive landscape evaluations, and tailored recommendations for strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of agrigenomics?
Key trends in agrigenomics include an increasing focus on precision agriculture, the integration of biotechnology with traditional farming practices, and the growing use of big data analytics for crop management. These trends are crucial for enhancing agricultural outcomes.
What are the market segments in agrigenomics?
Market segments for agrigenomics include farmers, research institutes, and biotechnology companies. Farmers hold a significant share, constituting 60.75% of the market, highlighting their pivotal role in adopting genomic solutions for crop improvement.