Animal Health Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: animal-health
Animal Health Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the Animal Health market, including insights into market size, growth forecasts through 2033, industry trends, and regional dynamics, along with segmentation insights and key player profiles.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
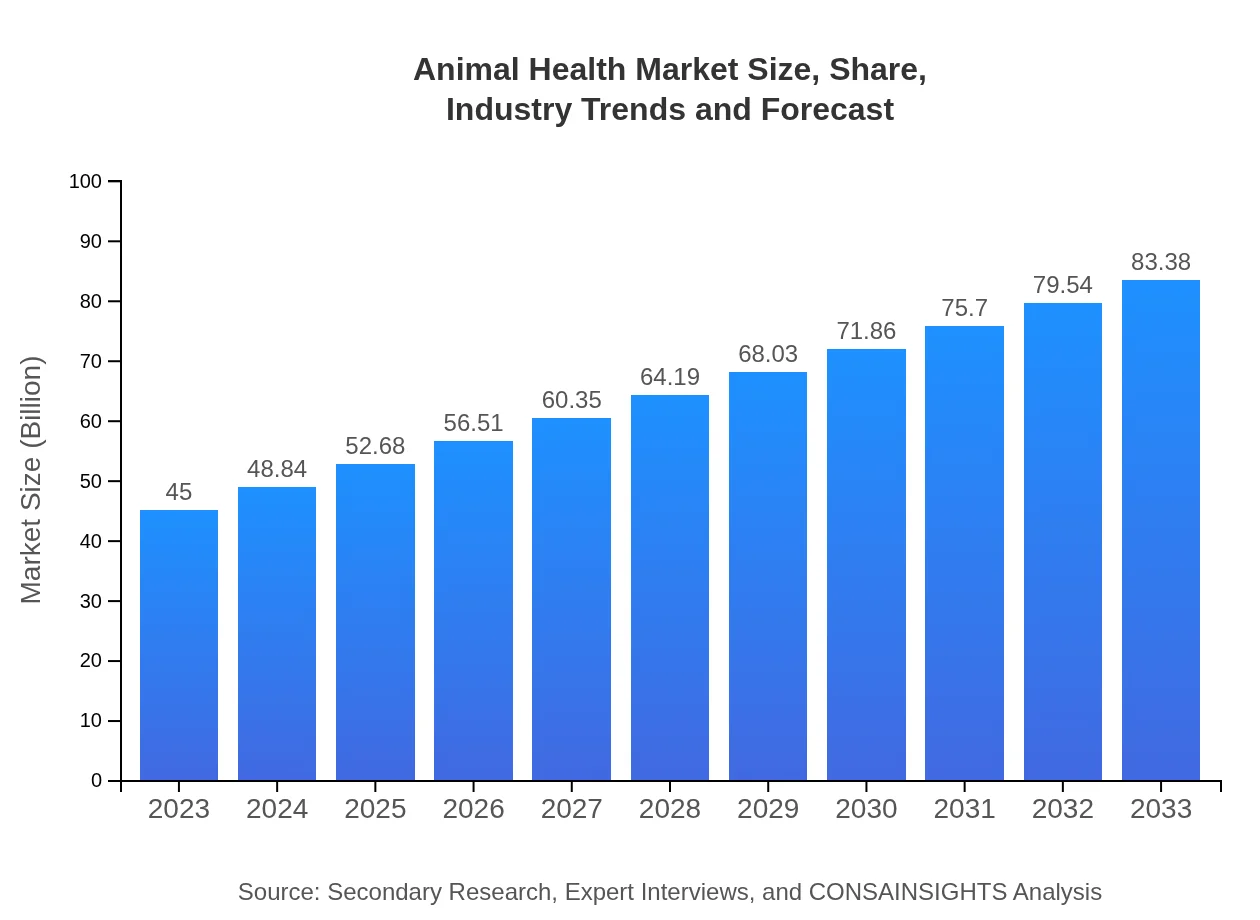
| 2023 Market Size | $45.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $83.38 Billion |
| Top Companies | Zoetis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Animal Health, Elanco |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Animal Health Market Overview
Customize Animal Health Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Animal Health market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Animal Health's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Animal Health
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Animal Health market in 2023?
Animal Health Industry Analysis
Animal Health Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Animal Health Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Animal Health Market Report:
In Europe, the market is expected to grow from $11.04 billion in 2023 to $20.46 billion by 2033. Strict regulations on animal health and welfare, coupled with heightened consumer awareness about food safety, are driving demand for Animal Health products in this region.Asia Pacific Animal Health Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing robust growth in the Animal Health sector, with a market size expected to increase from $9.14 billion in 2023 to $16.94 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by rising disposable incomes, increasing livestock production, and a growing number of pet owners in emerging economies.North America Animal Health Market Report:
The North American market, valued at $15.83 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $29.33 billion by 2033. This significant growth is fueled by advancements in technology, increasing pet healthcare expenditures, and a concerted effort towards livestock disease management.South America Animal Health Market Report:
In South America, the market is projected to grow from $3.73 billion in 2023 to $6.91 billion by 2033. The significant focus on livestock health and bolstering the agricultural sector reflects positively on the Animal Health market, driven by rising meat consumption and trade.Middle East & Africa Animal Health Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market is expected to grow from $5.25 billion in 2023 to $9.73 billion by 2033. The growth in this region is supported by an overhaul in agricultural practices, increasing livestock populations, and investment in veterinary infrastructure.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
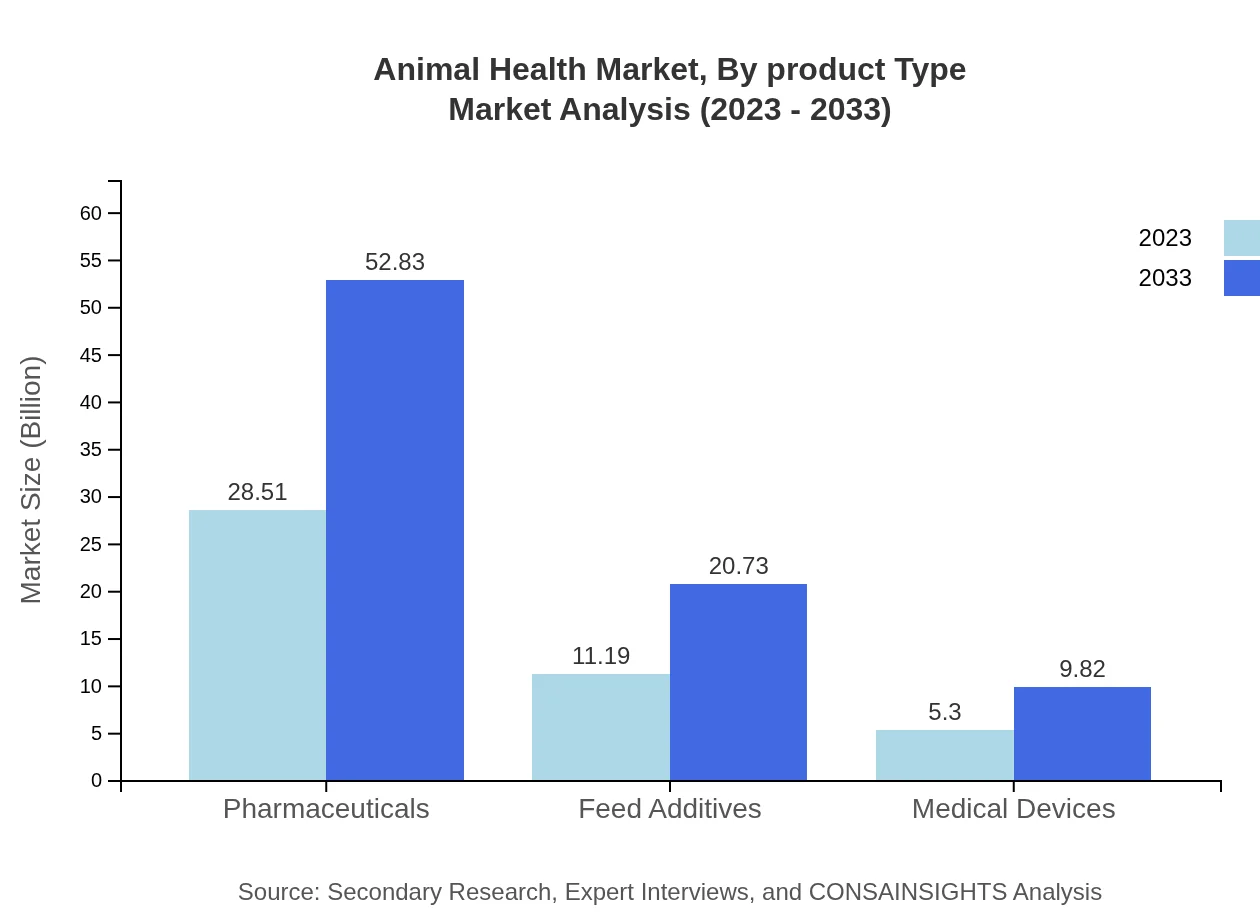
Animal Health Market Analysis By Product Type
Pharmaceuticals dominate the Animal Health market, projected to rise from $28.51 billion in 2023 to $52.83 billion by 2033. Diagnostics and vaccines are also critical, experiencing substantial growth as preventive care becomes more commonplace. Feed additives and medical devices are essential components of health management, ensuring optimal nutrition and care.
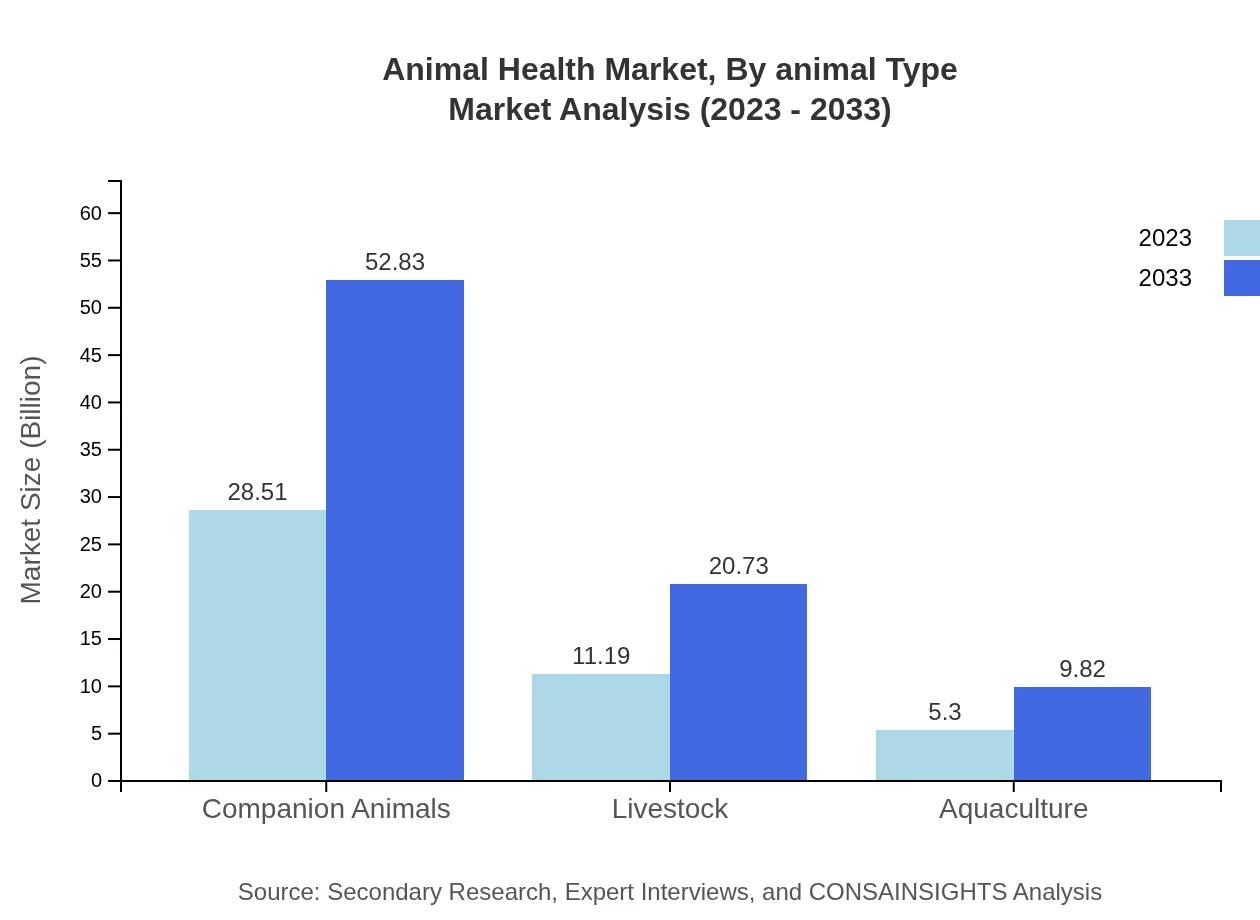
Animal Health Market Analysis By Animal Type
The companion animal segment is expected to grow significantly, projected to reach $28.51 billion in 2023 to $52.83 billion by 2033, driven by increasing spending on pet healthcare. Livestock remains a vital segment of the market, with growth encouraged by a growing demand for animal protein, while aquaculture is steadily developing with new technologies for health monitoring.
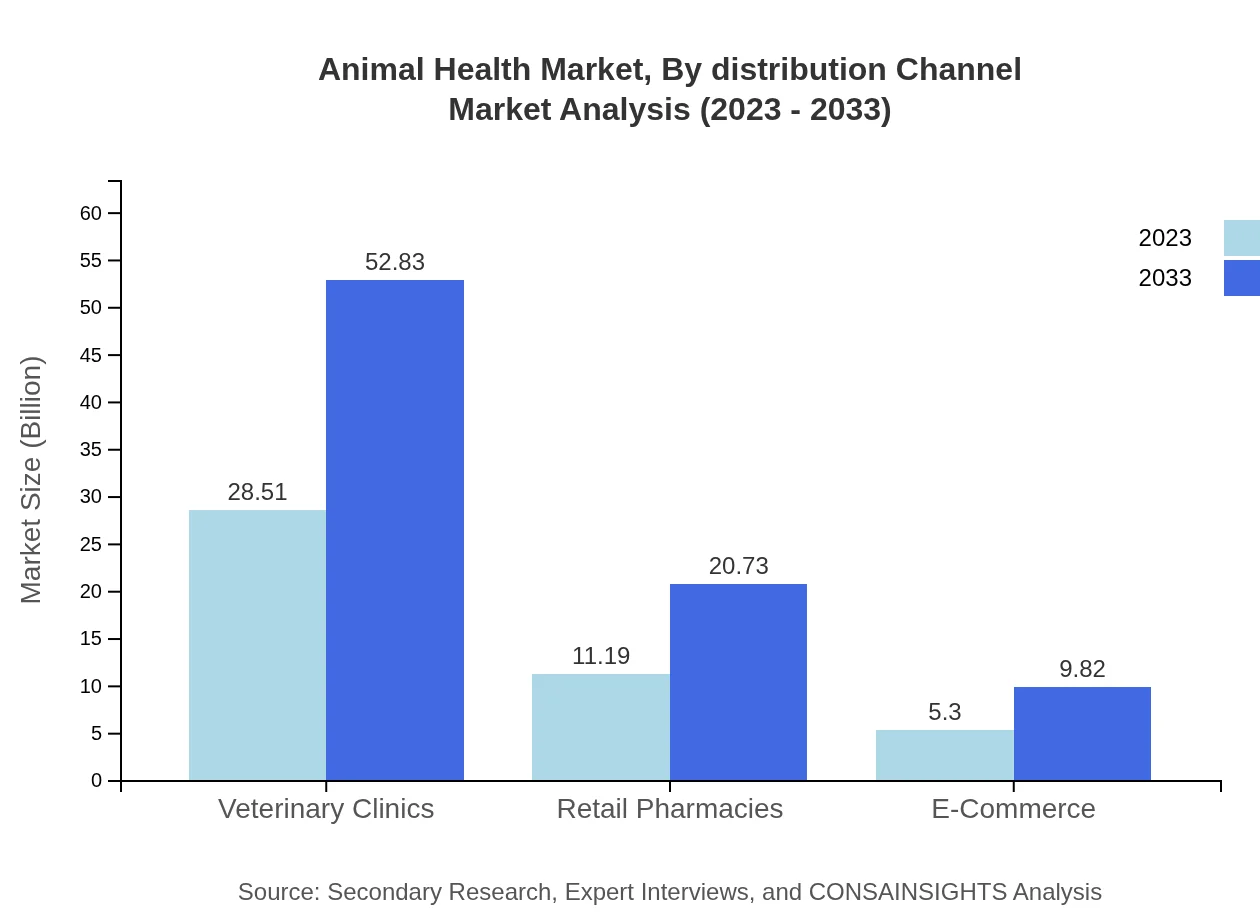
Animal Health Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Veterinary clinics continue to represent the largest distribution channel, expected to grow from $28.51 billion in 2023 to $52.83 billion by 2033. E-commerce is rapidly gaining popularity as an effective channel for accessing animal health products, with significant growth forecasted as consumers shift towards online shopping for convenience.
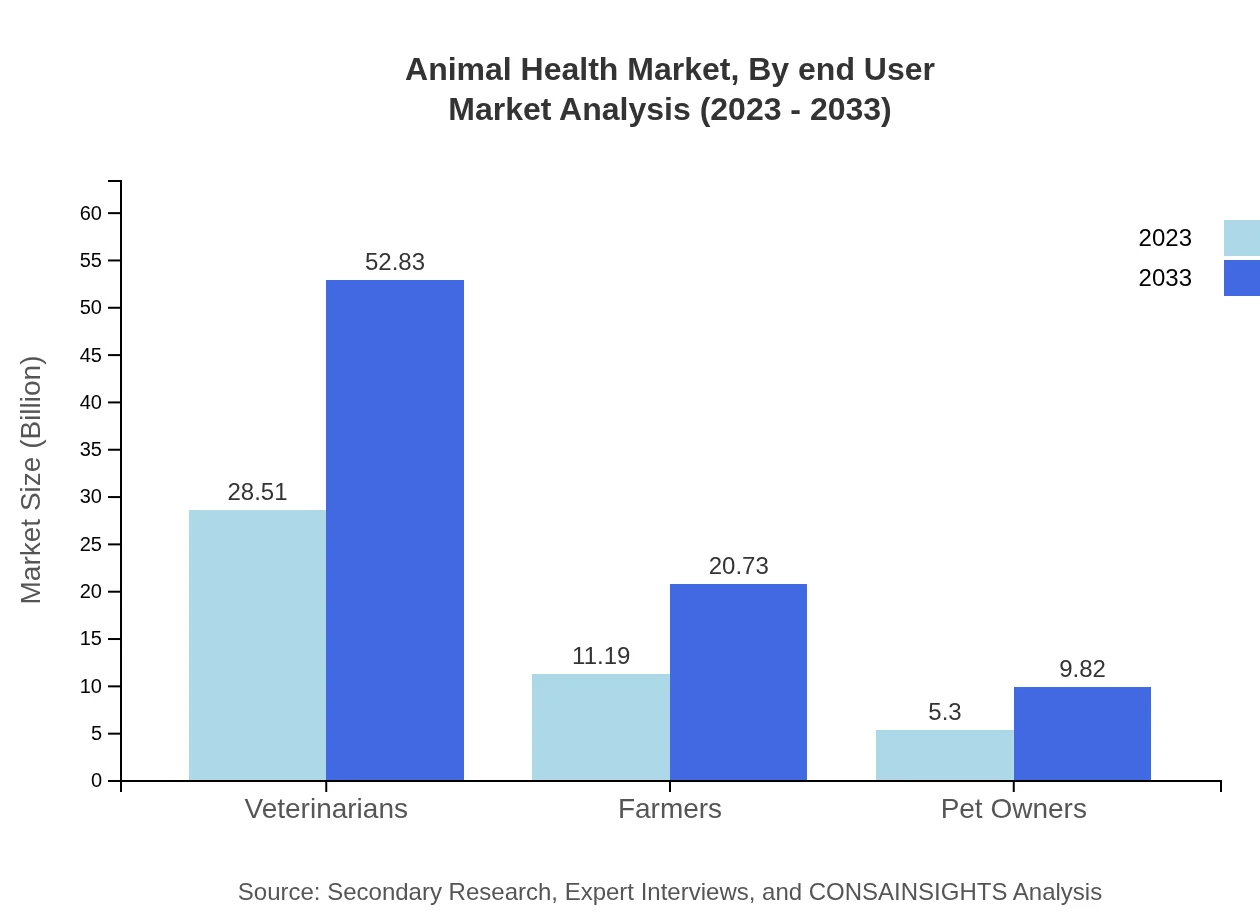
Animal Health Market Analysis By End User
Veterinarians lead as the primary end-users of animal health products, with their market share remaining stable over the forecast period. Farmers and pet owners are increasingly investing in advanced health solutions, with a projected market size of $11.19 billion for farmers growing steadily due to the rise in livestock expenditure.
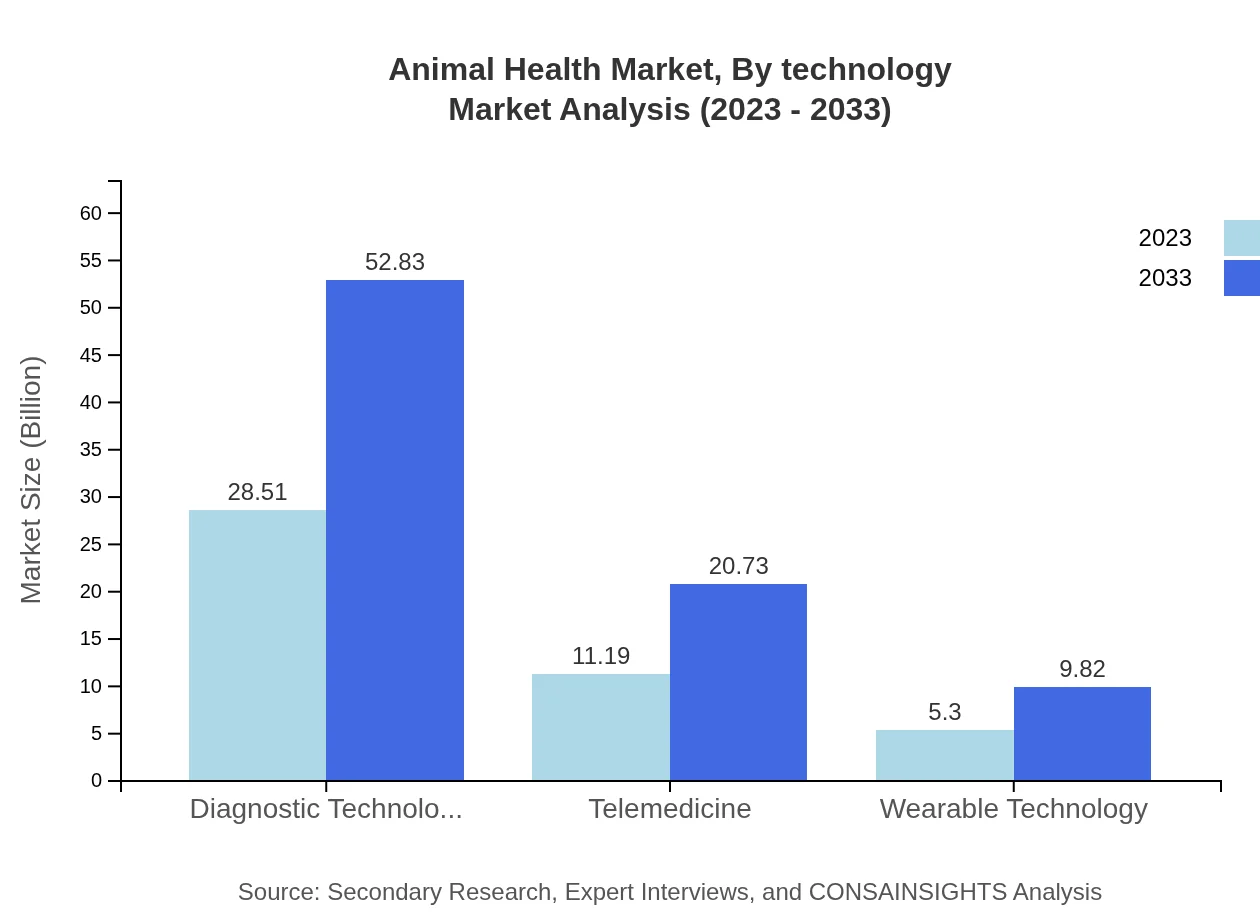
Animal Health Market Analysis By Technology
Innovations in telemedicine and wearable technologies are driving growth in the Animal Health market. Telemedicine is expected to grow from $11.19 billion in 2023 to $20.73 billion by 2033, while wearable technology is anticipated to grow from $5.30 billion to $9.82 billion, enhancing health monitoring and remote consultations for animals.
Animal Health Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Animal Health Industry
Zoetis:
As a global leader in animal health, Zoetis is known for its innovative pharmaceutical solutions and vaccines that improve the health and productivity of animals, driving industry standards forward.Boehringer Ingelheim:
Boehringer Ingelheim stands out in the Animal Health sector with a comprehensive portfolio that focuses on enhancing animal health through research and development in pharmaceuticals and vaccines.Merck Animal Health:
Merck Animal Health specializes in the research and production of vaccines and pharmaceuticals, fortifying its position as a critical player in preventive solutions for pets and livestock.Elanco:
Elanco is dedicated to developing innovative health solutions for pets and livestock, utilizing a customer-centric approach in veterinary care products.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of animal health?
The animal health market is valued at approximately $45 billion in 2023, with a projected growth rate of 6.2% CAGR, indicating robust growth potential over the coming decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the animal health industry?
Key players in the animal health sector include major firms such as Zoetis, Merck Animal Health, and Elanco, along with several other prominent organizations contributing to innovation and market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the animal health industry?
Growth factors include rising pet ownership, increasing livestock health concerns, advancements in veterinary technologies, and expanded pharmaceutical offerings that enhance treatment options for animals.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the animal health market?
The North American region exhibits the fastest growth, reflecting a market value increase from $15.83 billion in 2023 to $29.33 billion by 2033, driven by a strong focus on veterinary care.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the animal health industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the animal health industry, ensuring clients receive relevant insights and analytics.
What deliverables can I expect from this animal health market research project?
Deliverables from the animal health market research project include comprehensive reports, data analytics on segment performance, competitive analysis, and actionable insights for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of animal health?
Market trends indicate a rising demand for telemedicine and wearable technology in veterinary care, alongside increased investments in pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, signaling innovations in animal health solutions.