Aquaculture Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: aquaculture
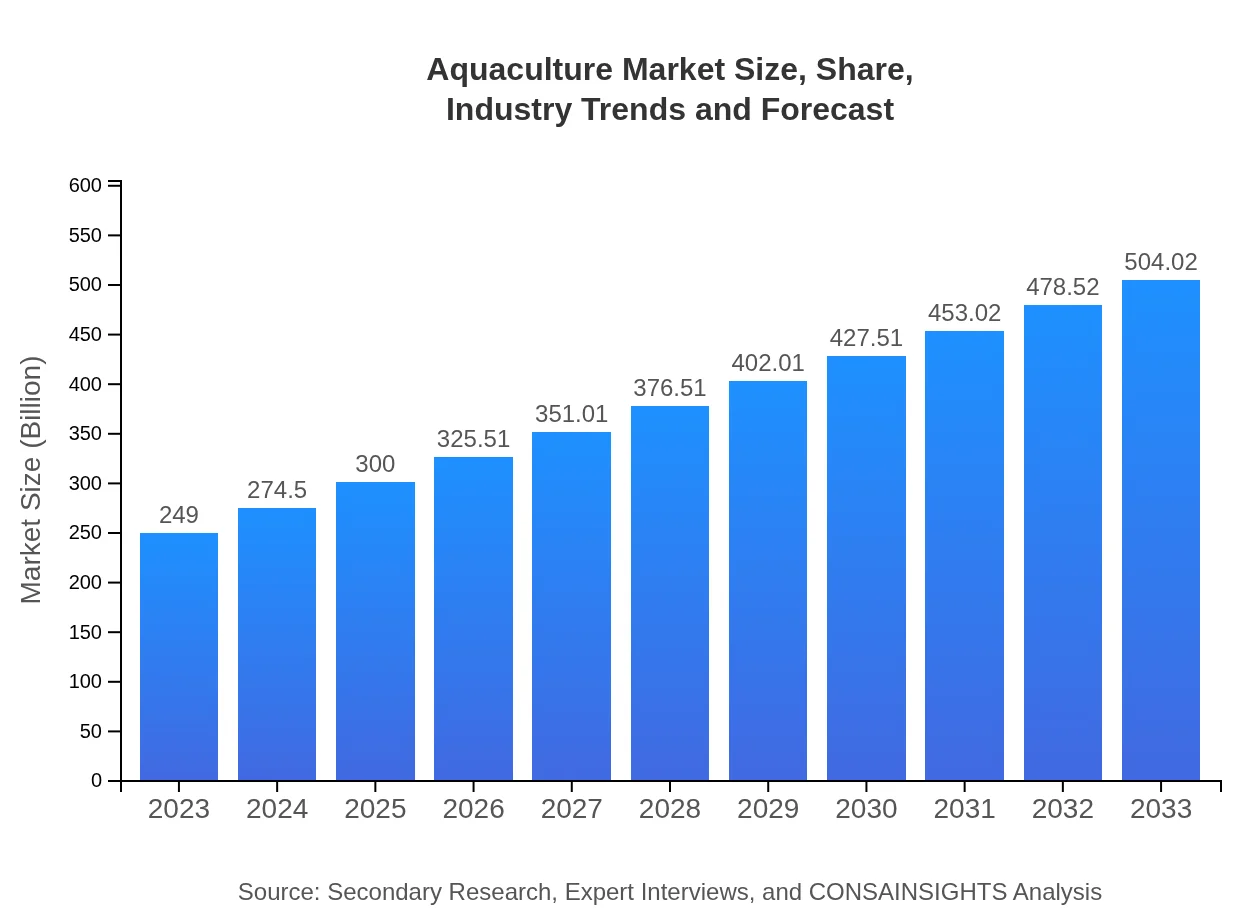
Aquaculture Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the Aquaculture market, including insights into market size, growth trends, technology advancements, and key players for the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $249.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.1% |
| 2033 Market Size | $504.02 Billion |
| Top Companies | Marine Harvest ASA, Thai Union Group PCL, Cermaq Group AS, Cooke Aquaculture Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Aquaculture Market Overview
Customize Aquaculture Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Aquaculture market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Aquaculture's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Aquaculture
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Aquaculture market in 2033?
Aquaculture Industry Analysis
Aquaculture Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Aquaculture Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Aquaculture Market Report:
Europe's aquaculture market was valued at USD 84.21 billion in 2023, expected to grow to USD 170.46 billion by 2033. Regulatory standards regarding sustainability and environmental impact drive innovations in the sector, making Europe a leader in responsible aquaculture practices.Asia Pacific Aquaculture Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the aquaculture market, accounting for significant production volumes. In 2023, the market was valued at USD 43.77 billion and is projected to reach USD 88.61 billion by 2033. Leading countries such as China and India are major contributors, focusing on sustainable practices to meet the rising local and global seafood demand.North America Aquaculture Market Report:
The North American aquaculture market, valued at USD 85.11 billion in 2023, is anticipated to achieve USD 172.27 billion by 2033. The United States and Canada are focusing increasingly on local seafood production to reduce dependency on imports, ensuring quality and sustainability in their offerings.South America Aquaculture Market Report:
In South America, the aquaculture market was valued at USD 24.33 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 49.24 billion by 2033. Countries like Brazil and Chile are investing in technologies to enhance aquaculture practices and productivity, tapping into both domestic consumption and export opportunities.Middle East & Africa Aquaculture Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the aquaculture market is smaller, valued at USD 11.58 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 23.44 billion by 2033. Countries are increasingly exploring aquaculture as a means to enhance food security and economic growth, leveraging their coastal resources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
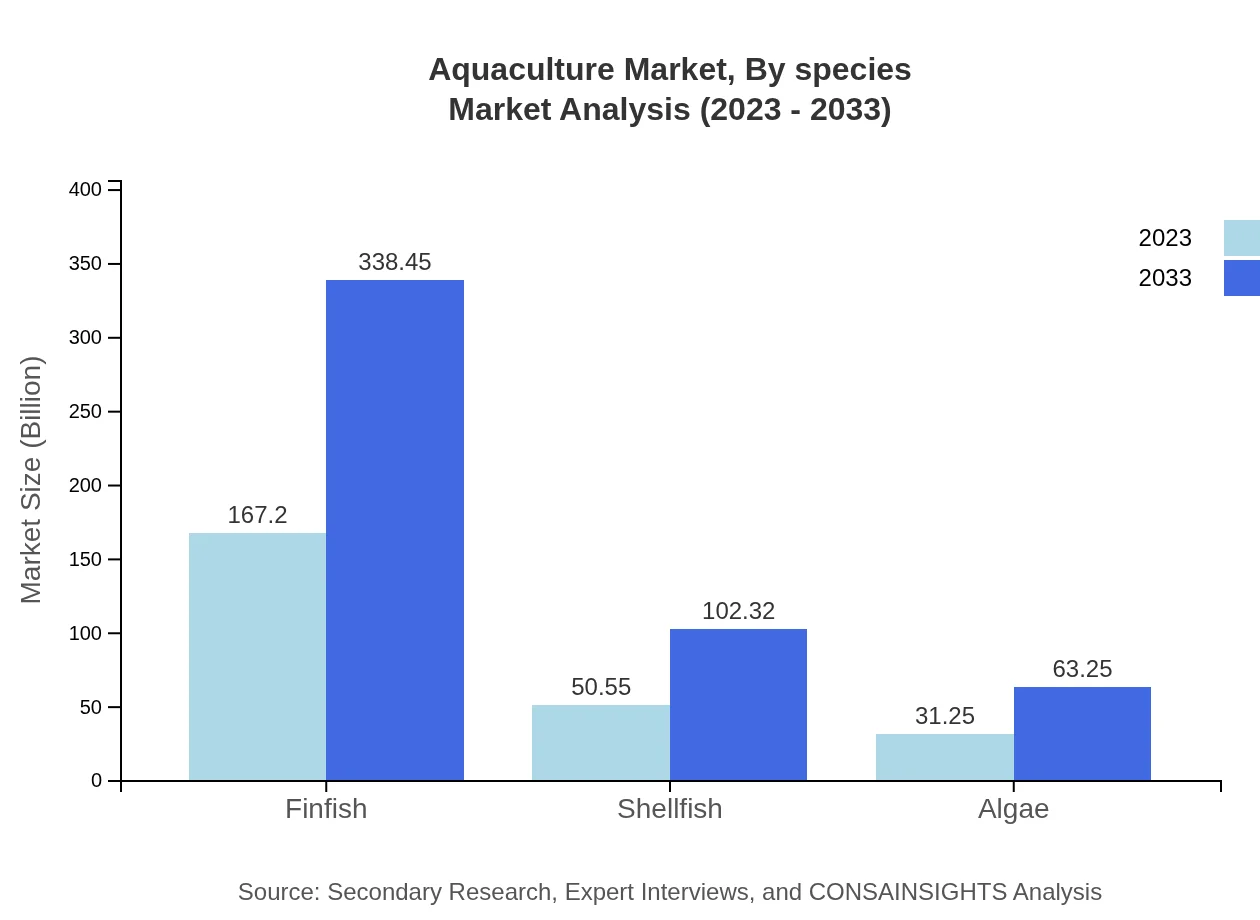
Aquaculture Market Analysis By Species
In terms of species, the finfish segment is the largest contributor to the market, valued at USD 167.20 billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 338.45 billion by 2033. Shellfish follows with a market size of USD 50.55 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 102.32 billion by 2033. Algae is emerging as a significant player, with a market valuation of USD 31.25 billion in 2023 and projected growth to USD 63.25 billion by 2033 due to increasing demand for health supplements and biofuels.
Aquaculture Market Analysis By Production Method
The production method segmentation highlights the prominence of extensive and intensive aquaculture systems. The extensive system is valued at USD 167.20 billion, while the intensive system accounts for USD 50.55 billion in 2023. Innovations like Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (USD 50.55 billion in 2023) and biosecure aquaculture practices are expected to enhance productivity and ensure sustainable practices in the growing market.
Aquaculture Market Analysis By End User
The retail sector is a major end-user of aquaculture products, valued at USD 167.20 billion in 2023 and expected to maintain this share through 2033. Foodservice also plays a critical role, with a market size of USD 50.55 billion in 2023, which is projected to increase significantly due to the growing trend of seafood consumption in restaurants and food outlets. The export market, showing potential, had a size of USD 31.25 billion in 2023.
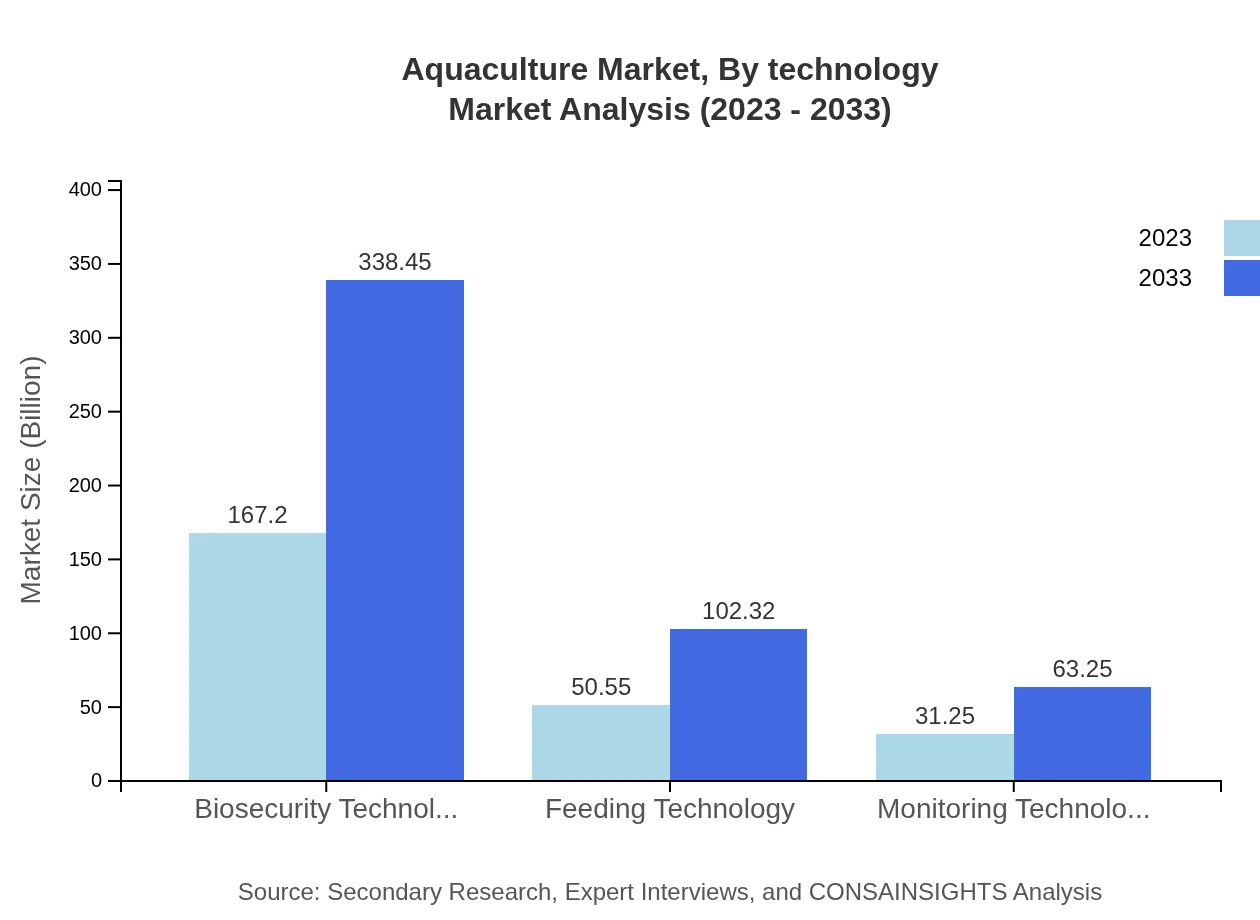
Aquaculture Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are reshaping aquaculture practices, with Biosecurity Technology leading at a market size of USD 167.20 billion in 2023. Feeding Technology (USD 50.55 billion) and Monitoring Technology (USD 31.25 billion) are vital for improving production efficiency and maintaining fish health. Innovations in aquaponics are attracting attention as sustainable farming practices gain momentum.
Aquaculture Market Analysis By Geography
Regional analysis highlights that different geographical areas focus on specific species and production techniques, with North America and Europe leading in advanced sustainable practices. Asia-Pacific dominates overall production due to favorable climatic conditions and growing demand. The Middle East and Africa require further development but show promising potential as they explore aquaculture as part of strategies toward food security.
Aquaculture Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Aquaculture Industry
Marine Harvest ASA:
A leading global seafood company, Marine Harvest specializes in sustainable fishing practices and is a significant player in the salmon farming sector.Thai Union Group PCL:
One of the world’s largest producers of seafood products, Thai Union focuses on innovations and sustainable practices to ensure its leading position in the global aquaculture industry.Cermaq Group AS:
Cermaq is recognized for its commitment to responsible aquaculture principles and is a leading producer of salmon and trout.Cooke Aquaculture Inc.:
Cooke Aquaculture is known for its vertically integrated aquaculture practices, focusing on environmental stewardship and quality seafood production.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of aquaculture?
The global aquaculture market is projected to reach approximately $249 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% from its current valuation. This expansion reflects increasing demand for aquaculture products driven by dietary shifts towards seafood.
What are the key market players or companies in this aquaculture industry?
Major players in the aquaculture industry include multinational corporations contributing to different segments, like Marine Harvest, Thai Union Group, and Regal Springs. These companies focus on sustainable aquaculture practices and innovation in technology to enhance production.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the aquaculture industry?
Key drivers of growth include rising global seafood demand, advancements in aquaculture technologies, and increasing awareness of sustainable food sourcing. Additionally, shifting consumer preferences for high-protein diets and eco-friendly practices further bolster market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the aquaculture?
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to grow from $43.77 billion in 2023 to $88.61 billion by 2033. North America and Europe are also significant markets witnessing substantial growth due to increased fish consumption and sustainable practices.
Does ConsainInsights provide customized market report data for the aquaculture industry?
Yes, ConsainInsights offers customized market report data for the aquaculture industry, tailoring insights specific to client needs. This includes market size, trends, competitive landscape, and future forecasts tailored for targeted decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this aquaculture market research project?
Deliverables include detailed analysis reports, market size data, forecasts, competitive intelligence, and insights on market trends. Clients will receive actionable insights that can inform strategic decisions and investment opportunities within the aquaculture industry.
What are the market trends of aquaculture?
Current trends in the aquaculture market include increasing adoption of technology for monitoring and biosecurity, growth in organic aquaculture practices, and expanding algae farming. Additionally, there's a significant shift towards sustainable practices and regulatory compliance.