As Interface Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: as-interface
As Interface Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a thorough analysis of the As Interface market, detailing insights on market size, growth potential, trends, and competitive landscape from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
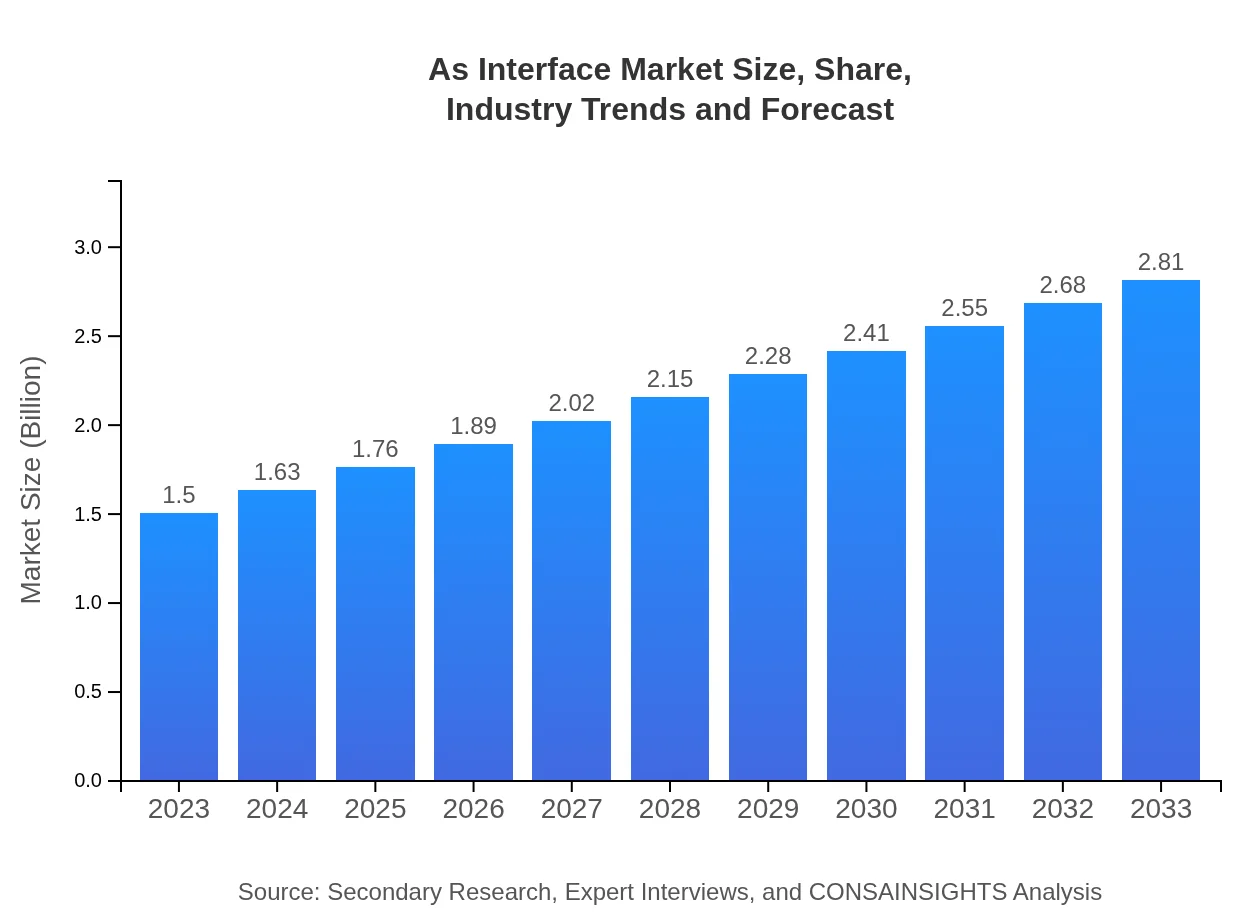
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.81 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, IFM Electronic |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
As Interface Market Overview
Customize As Interface Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of As Interface market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand As Interface's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in As Interface
What is the Market Size & CAGR of As Interface market in 2023?
As Interface Industry Analysis
As Interface Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
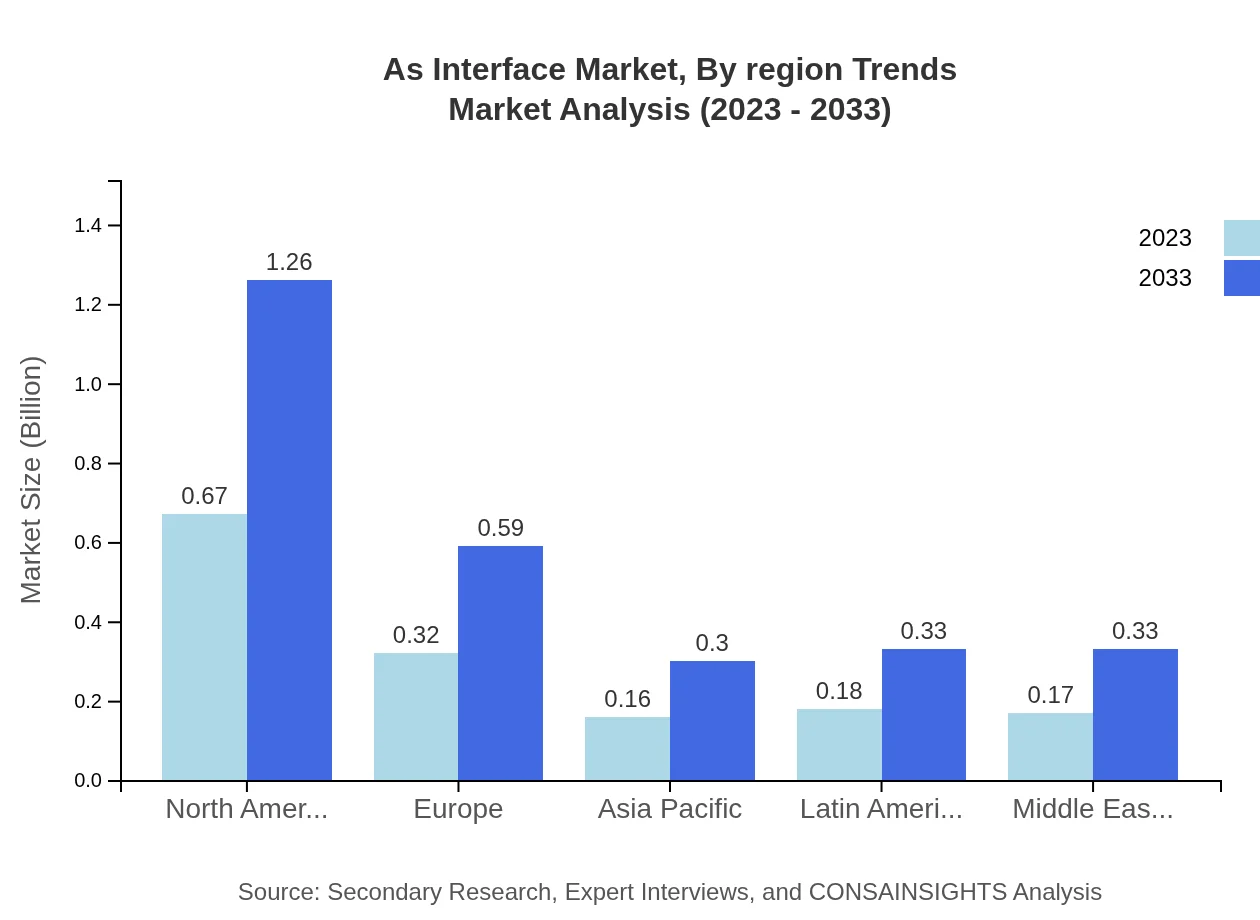
As Interface Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe As Interface Market Report:
The European market is expected to grow from $0.39 billion in 2023 to $0.73 billion by 2033. The push for carbon neutrality and sustainable manufacturing practices in Europe significantly increases the demand for effective automation solutions, including As Interface.Asia Pacific As Interface Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is predicted to experience substantial growth in the As Interface market, with its market size projected to grow from $0.29 billion in 2023 to $0.54 billion by 2033. Rapid industrialization and a focus on advancements in IoT and smart manufacturing drive this growth.North America As Interface Market Report:
North America leads the market, with a size projected to expand from $0.56 billion in 2023 to $1.04 billion by 2033. The region's emphasis on technological innovations and the advancement of the manufacturing landscape are critical growth drivers.South America As Interface Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to double from $0.13 billion in 2023 to $0.24 billion in 2033. Increased investment in automation technologies within the manufacturing sector is anticipated to boost the adoption of As Interface solutions.Middle East & Africa As Interface Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market size is anticipated to rise from $0.14 billion in 2023 to $0.26 billion by 2033. Growth is stimulated by expanding manufacturing and industrial sectors, which are increasingly seeking efficient communication protocols.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
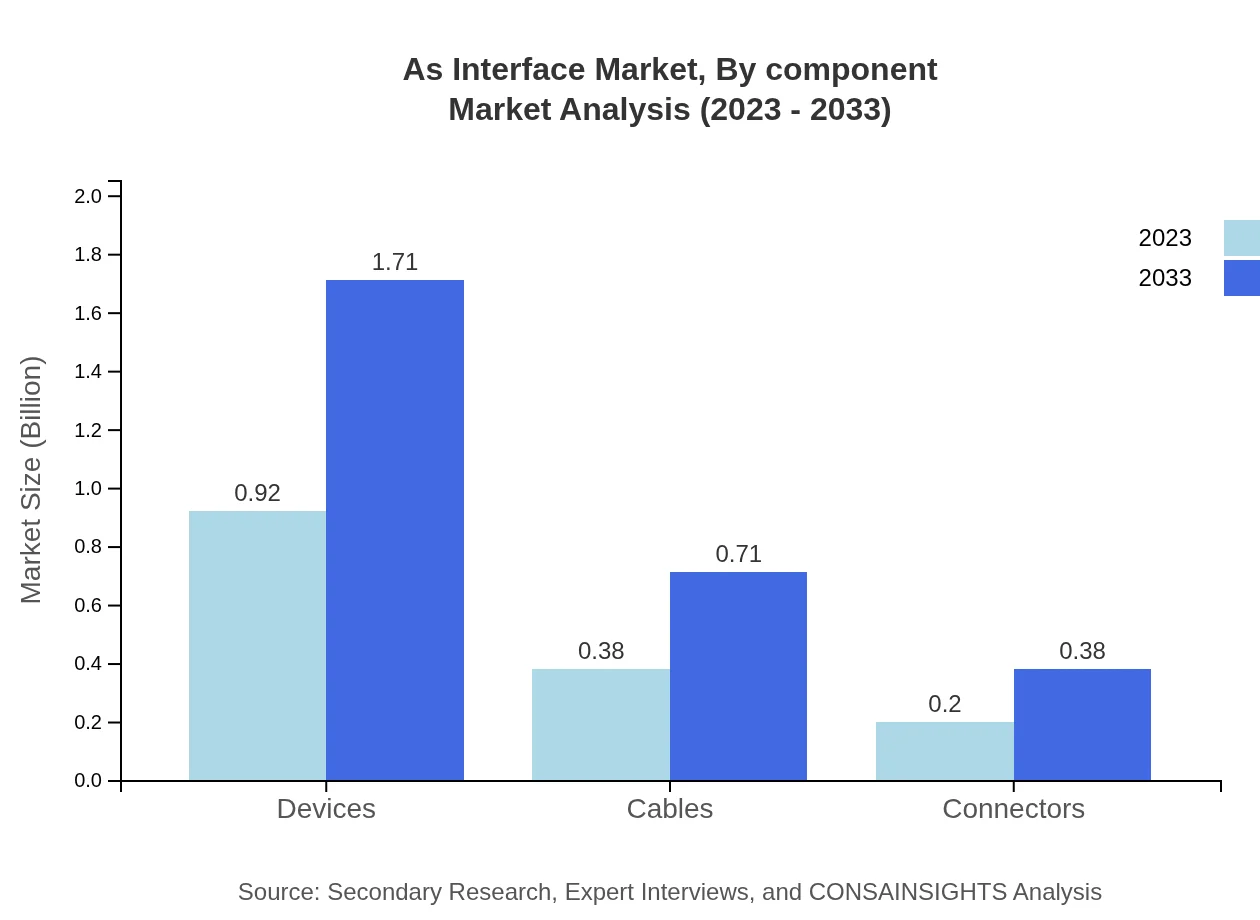
As Interface Market Analysis By Component
The devices segment remains the most significant in the As Interface market, accounting for a market size of $0.92 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $1.71 billion by 2033, representing a robust share while other components such as cables and connectors also support the network architecture.
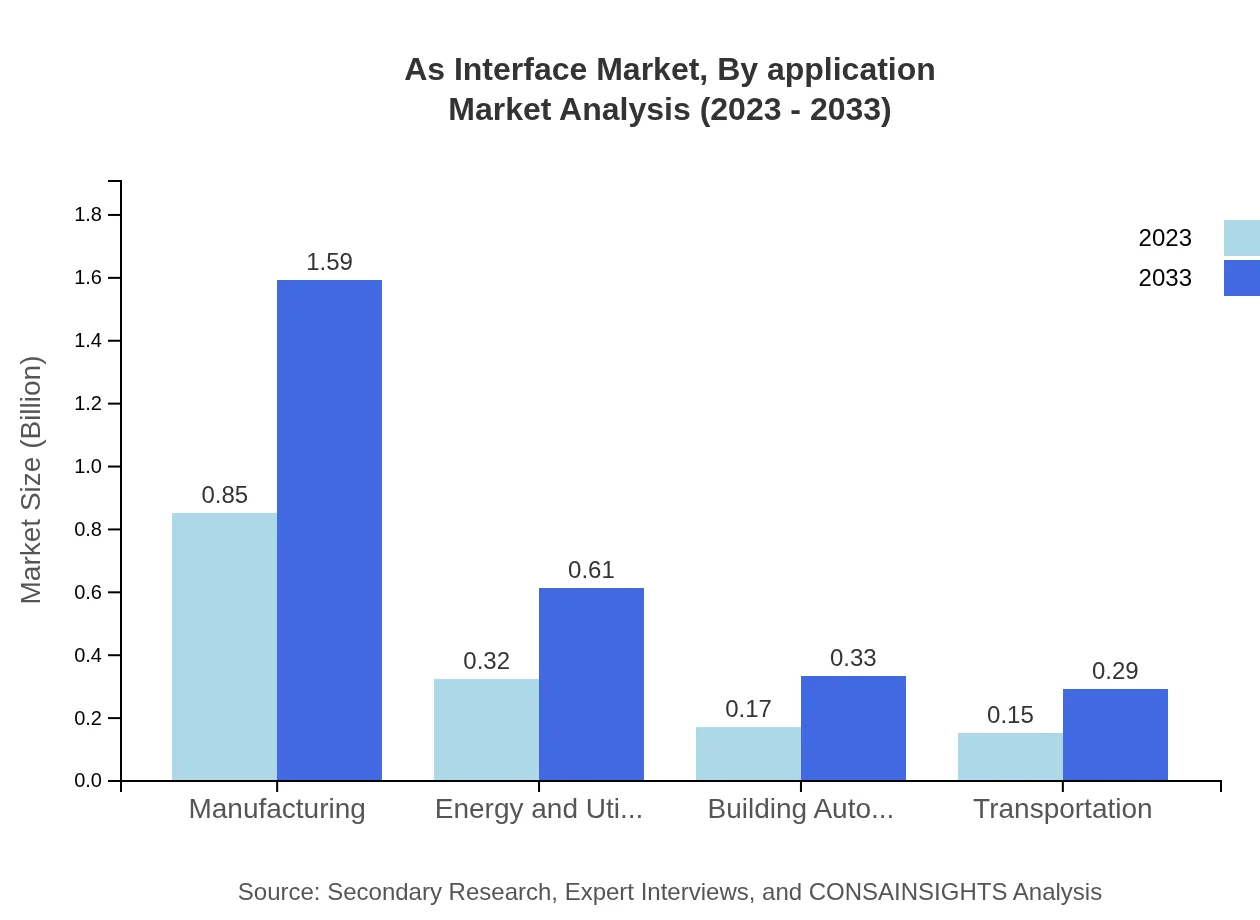
As Interface Market Analysis By Application
Applications in manufacturing and energy utilities show enormous potential, with manufacturing contributing significantly to the market size. This sector is growing from $0.85 billion in 2023 to $1.59 billion by 2033, influenced by the increasing synergy between IoT devices and automation technologies.
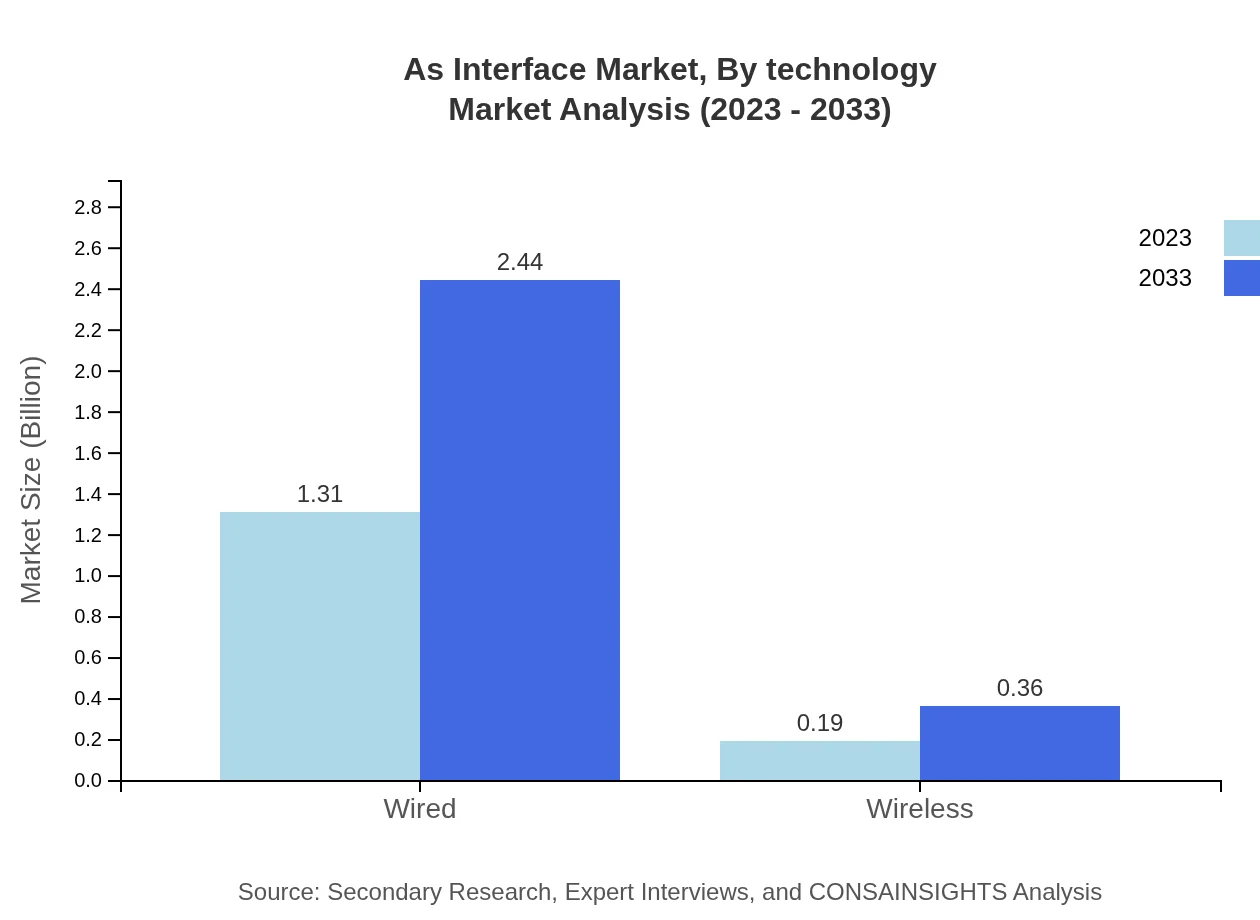
As Interface Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements in wired and wireless communication protocols are transforming the As Interface market. Wired technology currently dominates the segment, with a size of $1.31 billion expected to advance to $2.44 billion by 2033, while wireless technology also shows promising growth.
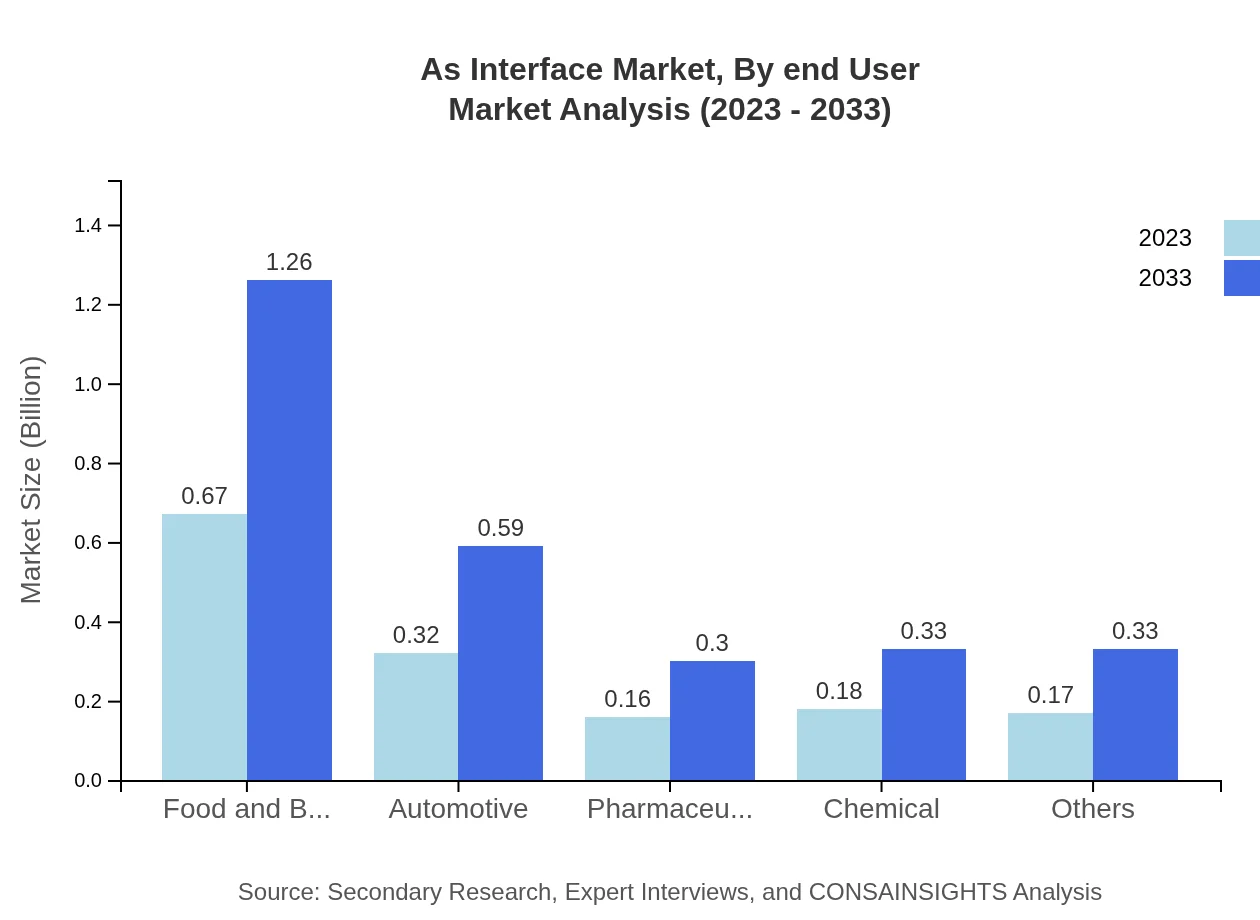
As Interface Market Analysis By End User
The automotive and manufacturing sectors are poised to drive demand, with automotive applications alone anticipating growth from $0.32 billion in 2023 to $0.59 billion by 2033, underscoring the need for efficient communication interfaces.
As Interface Market Analysis By Region Trends
Across various regions, North America exhibits a steady growth trend due to strong investments in smart factory technologies, while the Asia Pacific demonstrates rapid expansion owing to industrialization and digitalization efforts.
As Interface Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in As Interface Industry
Siemens AG:
A leading global company specializing in automation and digitalization in manufacturing industries, Siemens offers various As Interface products that enhance operational efficiency.Rockwell Automation:
A prominent player in industrial automation, Rockwell Automation provides advanced solutions in As Interface connectivity and communication protocols, primarily focusing on smart manufacturing.Schneider Electric:
Renowned for its innovative solutions in energy management and automation, Schneider Electric integrates As Interface technology into its product portfolio to offer enhanced processes to industries globally.IFM Electronic:
A key player known for its sensor technology, IFM provides various products supporting As Interface, focusing on improving communication in various industrial settings.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of as Interface?
The As Interface market is currently valued at approximately $1.5 billion, with a robust CAGR of 6.3% expected through 2033, reflecting significant growth opportunities in this sector.
What are the key market players or companies in this as Interface industry?
Key players in the As Interface market include major corporations with expertise in industrial automation and network solutions, driving innovations and competitive strategies in a rapidly evolving market.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the as Interface industry?
Growth in the As Interface industry is driven by increased automation in various sectors, the demand for real-time data exchange, and advancements in communication technologies enhancing operational efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the as Interface?
The fastest-growing region for the As Interface market is North America, expected to expand from $0.56 billion in 2023 to $1.04 billion by 2033, fueled by technological advancements and increased industrial automation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the as Interface industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the As Interface industry, providing in-depth insights and analysis to support informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this as Interface market research project?
Our As Interface market research projects deliver comprehensive reports, market forecasts, segment analyses, and insights into competitive dynamics, tailored to your strategic requirements.
What are the market trends of as Interface?
Trends in the As Interface market include increasing adoption of IoT technologies, demand for interoperability among automation systems, and significant investments in smart manufacturing solutions.