Autonomous Tractors Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: autonomous-tractors
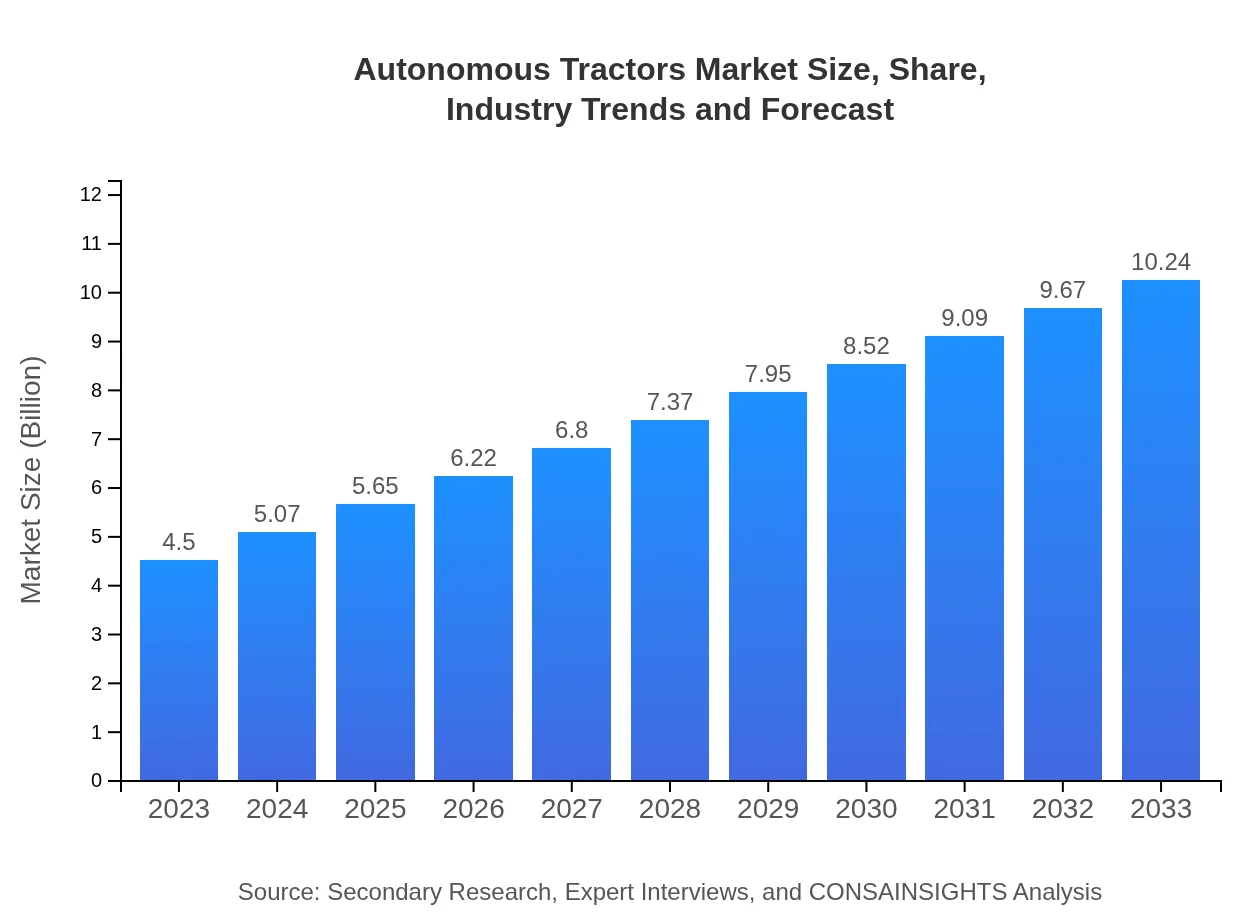
Autonomous Tractors Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the global Autonomous Tractors market, providing insights into market trends, size, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It covers segmentation, regional analysis, industry trends, and major players, offering a comprehensive overview of the evolving landscape of autonomous agriculture.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $10.24 Billion |
| Top Companies | John Deere, AG Leader Technology, Case IH, Trimble, Kubota |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Autonomous Tractors Market Overview
Customize Autonomous Tractors Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Autonomous Tractors market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Autonomous Tractors's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Autonomous Tractors
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Autonomous Tractors market in 2023?
Autonomous Tractors Industry Analysis
Autonomous Tractors Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
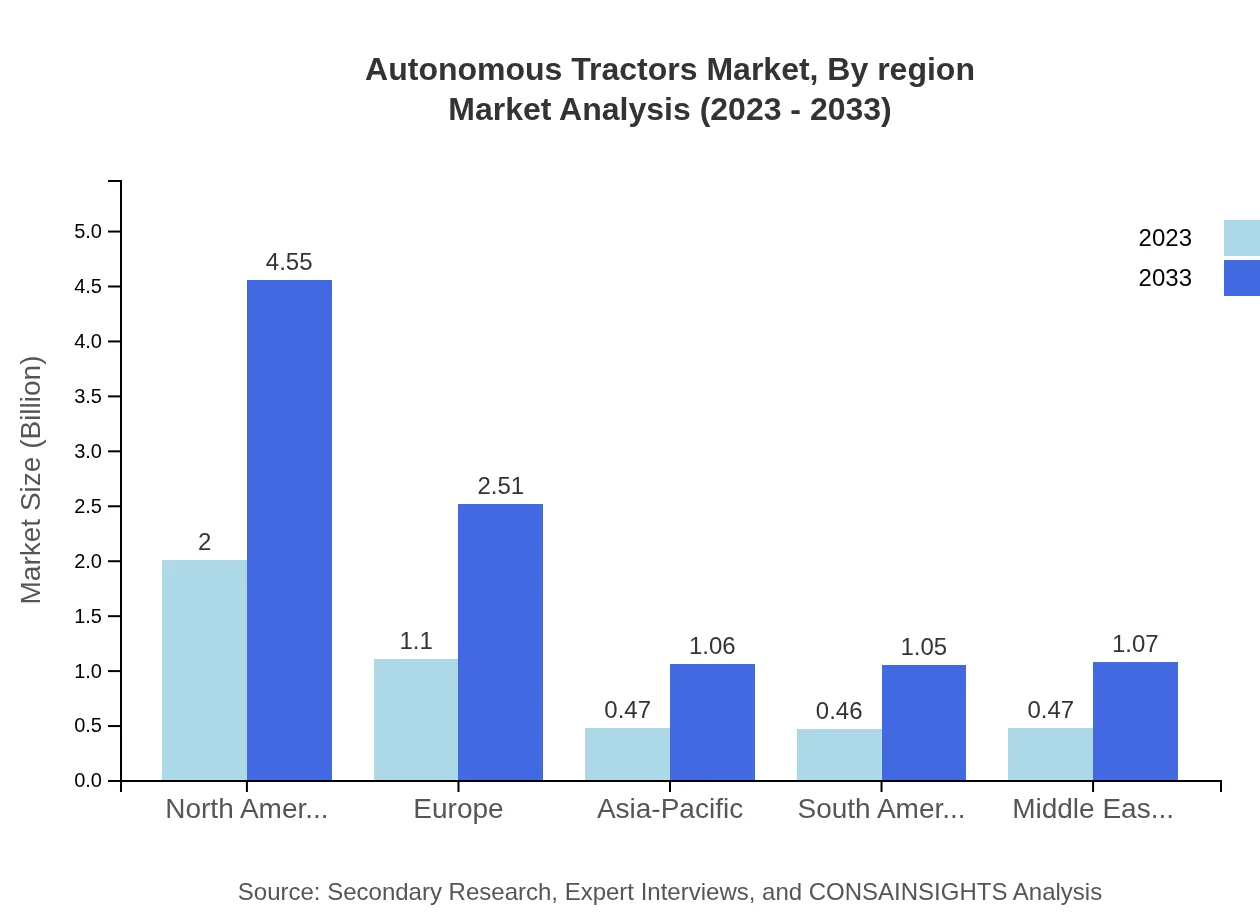
Autonomous Tractors Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Autonomous Tractors Market Report:
In Europe, the market is anticipated to increase from $1.40 billion in 2023 to $3.18 billion by 2033. The European Union's emphasis on sustainable agriculture practices provides a favorable environment for the adoption of autonomous tractors. Countries like Germany and France are leading in technology adoption as farmers strive to meet rising food demands ethically.Asia Pacific Autonomous Tractors Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Autonomous Tractors market is projected to grow from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.97 billion by 2033. The increasing adoption of advanced agricultural practices, combined with government initiatives to promote smart farming, will drive market growth. Countries like India and China are at the forefront of this transition, leveraging autonomous technologies to boost production.North America Autonomous Tractors Market Report:
North America leads the market, with estimates of growth from $1.55 billion in 2023 to $3.53 billion by 2033. The United States is a key market, where the integration of technology in agriculture is widespread. Farmers are increasingly adopting autonomous solutions for higher yields and reduced operational costs and sustainability initiatives are gaining traction.South America Autonomous Tractors Market Report:
South America's market is expected to rise from $0.40 billion in 2023 to $0.92 billion in 2033. The region's diverse agricultural sector benefits from autonomous tractors, especially in countries like Brazil and Argentina, where large agricultural operations can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. The region has a growing interest in sustainability, further fueling demand.Middle East & Africa Autonomous Tractors Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from $0.28 billion in 2023 to $0.64 billion by 2033. While currently smaller, the agricultural sector in these regions is gradually embracing technological advancements, particularly in irrigation-heavy farms, to improve production efficiency and food security.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
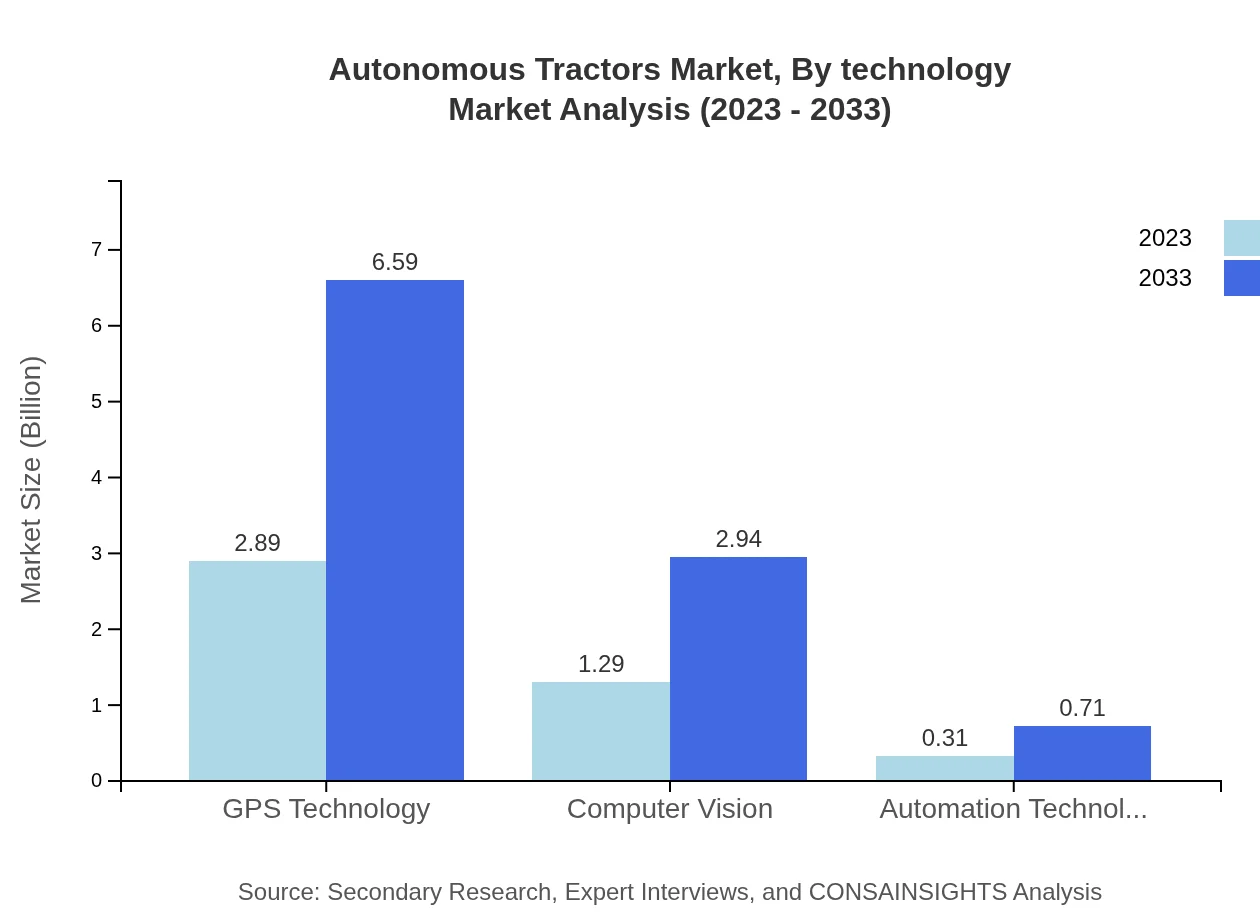
Autonomous Tractors Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment is dominated by GPS technologies, which held a market size of approximately $2.89 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $6.59 billion by 2033, reflecting a share of 64.33%. Computer vision technologies, with $1.29 billion in 2023, are expected to expand significantly, emphasizing their growing role in precision agriculture. Automation technology, while smaller at $0.31 billion, shows promise for growth as farmers seek more efficient operational frameworks.
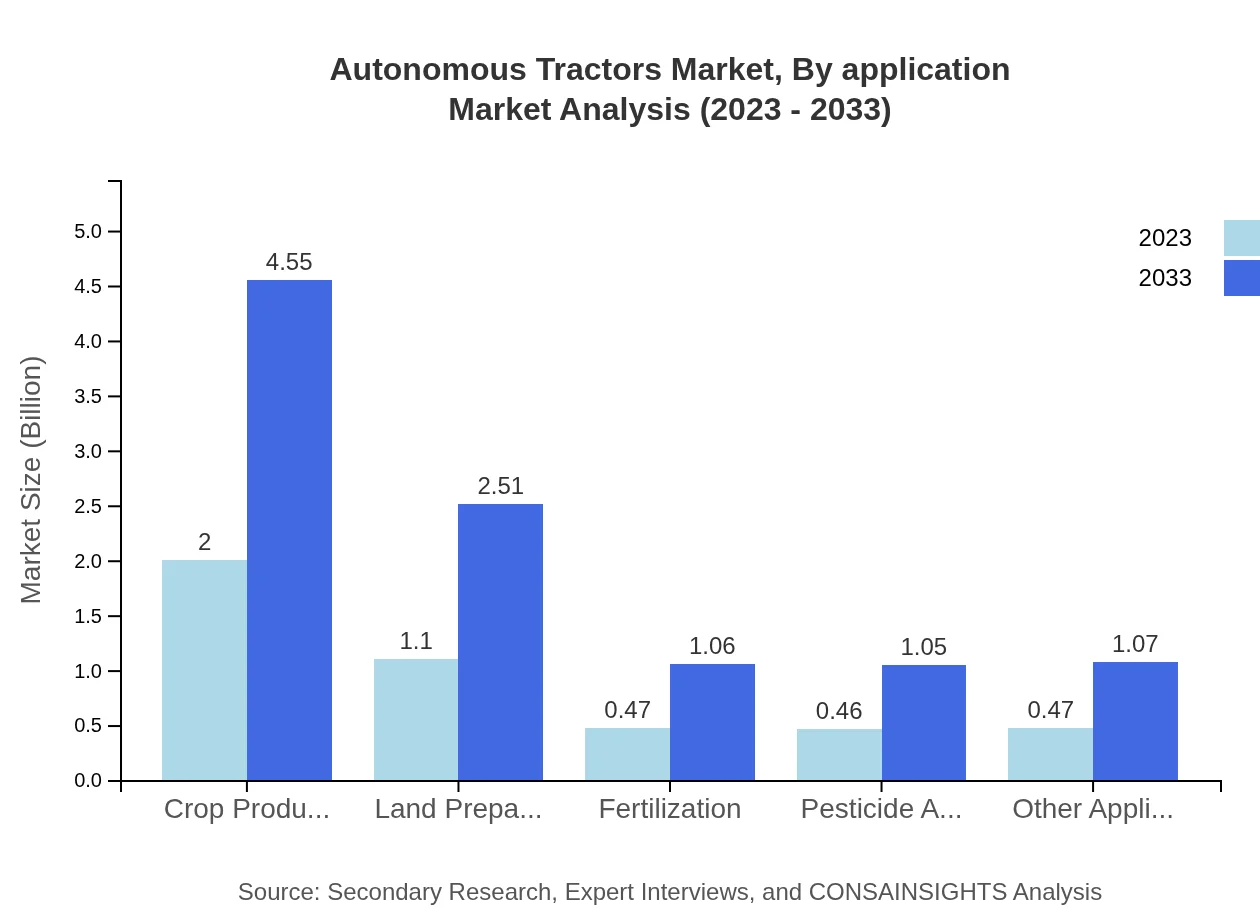
Autonomous Tractors Market Analysis By Application
In the application segment, crop production leads with a market size of $2.00 billion in 2023, projected to rise to $4.55 billion by 2033, capturing a significant share of 44.44%. Land preparation follows, currently at $1.10 billion, and expected to grow, highlighting its essential role in enhancing agricultural efficiency. Other applications, including fertilization and pesticide application, are also expanding as farmers adopt technology to maximize outputs while minimizing inputs.
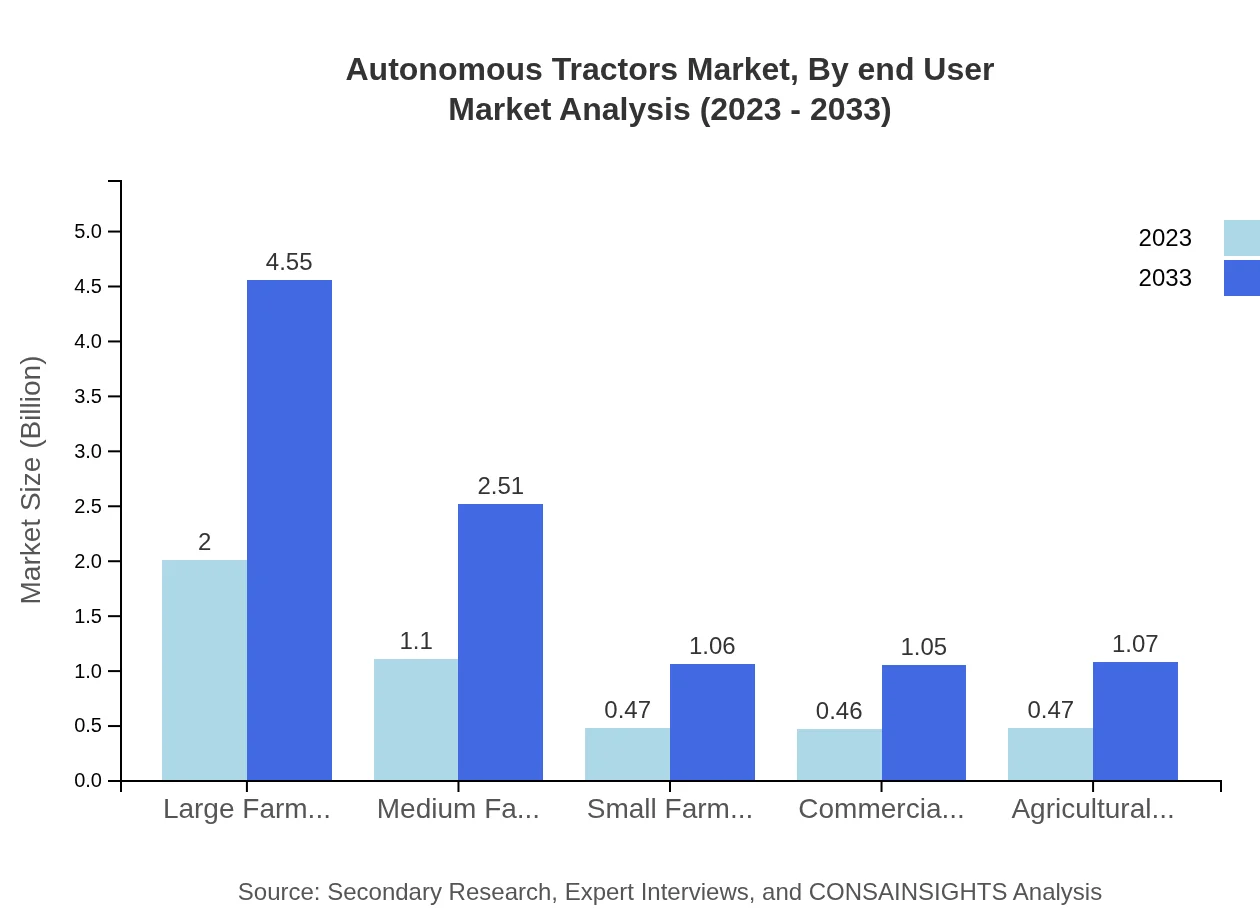
Autonomous Tractors Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment showcases large farmers, leading with a substantial market size of $2.00 billion in 2023, and forecasts to reach $4.55 billion by 2033, holding steady at 44.44% share. Medium farmers follow, emphasizing the broad applicability of autonomous solutions across farm sizes. The rise of commercial farming is notable as well, driving demand for advanced tractors to handle larger acreage efficiently.
Autonomous Tractors Market Analysis By Region
The regional market analysis highlights significant variances in adoption rates. North America demonstrates the highest market strength, leveraging advanced farming technologies. Europe follows closely, focusing on sustainability. Asia-Pacific is emerging rapidly, with governmental support for modern farming techniques while South America and the Middle East show growing adaptability to these innovations in agricultural practices.
Autonomous Tractors Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Autonomous Tractors Industry
John Deere:
A leading player in the agricultural machinery sector, John Deere focuses heavily on integrating advanced technology into farming equipment, particularly autonomous solutions.AG Leader Technology:
AG Leader develops innovative precision farming technologies and is recognized for its leadership in GPS and software systems, enhancing tractor capabilities.Case IH:
Part of CNH Industrial, Case IH offers a wide range of advanced agricultural equipment, including autonomous machinery, driven by innovation and efficiency.Trimble:
Trimble specializes in GPS technology and precision agriculture solutions, greatly influencing the adoption of autonomous tractors in various regions.Kubota:
Kubota produces powerful, versatile tractors and is increasingly investing in autonomous systems, emphasizing reliability and ease of use.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of autonomous Tractors?
The autonomous tractors market is currently valued at $4.5 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.3%. The market size is anticipated to increase significantly over the next decade, highlighting an expanding demand for automation in agriculture.
What are the key market players or companies in the autonomous Tractors industry?
Key players in the autonomous tractors market include leading agricultural machinery manufacturers such as John Deere, AGCO Corporation, and Case IH. These companies are at the forefront of technological advancements, contributing to market growth through innovation and strategic collaborations.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the autonomous tractors industry?
Several factors are driving growth in the autonomous tractors industry, including increasing labor costs, a need for efficiency in farming operations, and advances in technologies such as GPS and AI. Additionally, government incentives for modernizing agriculture further fuel market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the autonomous tractors market?
North America is recognized as the fastest-growing region in the autonomous tractors market, with a projected market size increase from $1.55 billion in 2023 to $3.53 billion by 2033. The region's strong focus on technological advancements and adoption of automation in agriculture contributes to this growth.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the autonomous tractors industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs and requirements of clients in the autonomous tractors industry. This service facilitates deeper insights and informed decision-making based on unique market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this autonomous tractors market research project?
From the autonomous tractors market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports detailing market trends, growth forecasts, detailed segment analysis, and competitor insights, as well as regional market specifics, all designed to support strategic planning.
What are the market trends of autonomous tractors?
Current market trends in autonomous tractors include increased adoption of precision agriculture techniques, rising investments in technology integration, and the development of eco-friendly tractors. These trends signal a shift towards more sustainable and efficient farming practices globally.