Bambara Beans Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: bambara-beans
Bambara Beans Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Bambara Beans market from 2023 to 2033, detailing market trends, size, and insights across various regions and segments. It also explores the technological advancements impacting the industry, key market players, and future forecasts.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
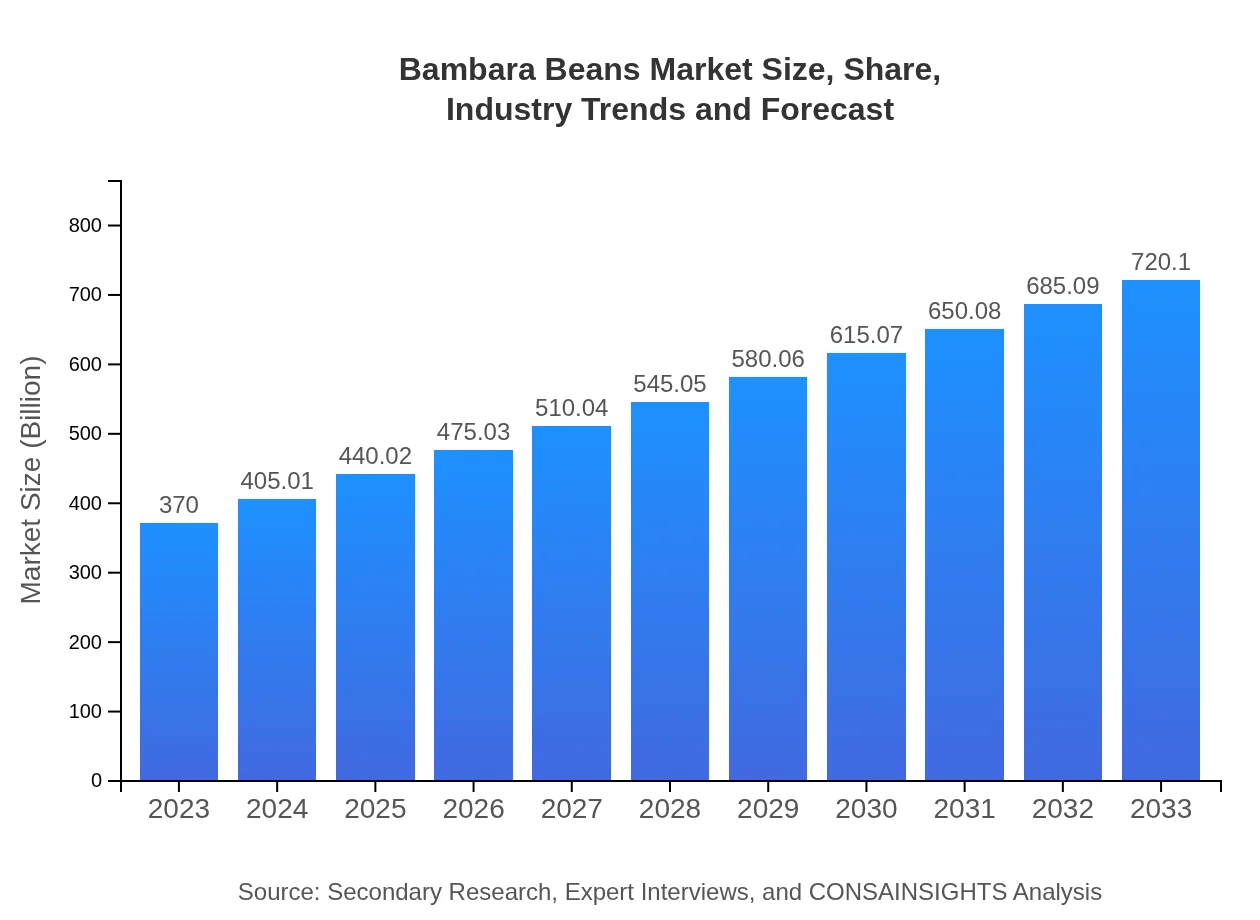
| 2023 Market Size | $370.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $720.10 Million |
| Top Companies | Agro Products and Agencies Pvt. Ltd., NutraBlend Foods, Farmland Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Bambara Beans Market Overview
Customize Bambara Beans Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Bambara Beans market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Bambara Beans's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Bambara Beans
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Bambara Beans market in 2023?
Bambara Beans Industry Analysis
Bambara Beans Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Bambara Beans Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Bambara Beans Market Report:
The European market is set to expand from $96.87 million in 2023 to $188.52 million by 2033, as consumers increasingly seek alternative protein sources and sustainable food options.Asia Pacific Bambara Beans Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Bambara Beans market is projected to grow from $81.36 million in 2023 to $158.35 million by 2033, reflecting a robust demand driven by population growth and increasing health consciousness among consumers.North America Bambara Beans Market Report:
North America, with a market size of $122.36 million in 2023, is projected to reach $238.14 million by 2033, supported by a rising trend in plant-based diets and the demand for sustainable protein sources.South America Bambara Beans Market Report:
The South American market is expected to grow from $32.63 million in 2023 to $63.51 million by 2033, primarily due to the expanding agricultural sector and the region's favorable climate for growing Bambara Beans.Middle East & Africa Bambara Beans Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to grow from $36.78 million in 2023 to $71.58 million by 2033, fueled by urbanization and a growing awareness of health benefits associated with Bambara Beans.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
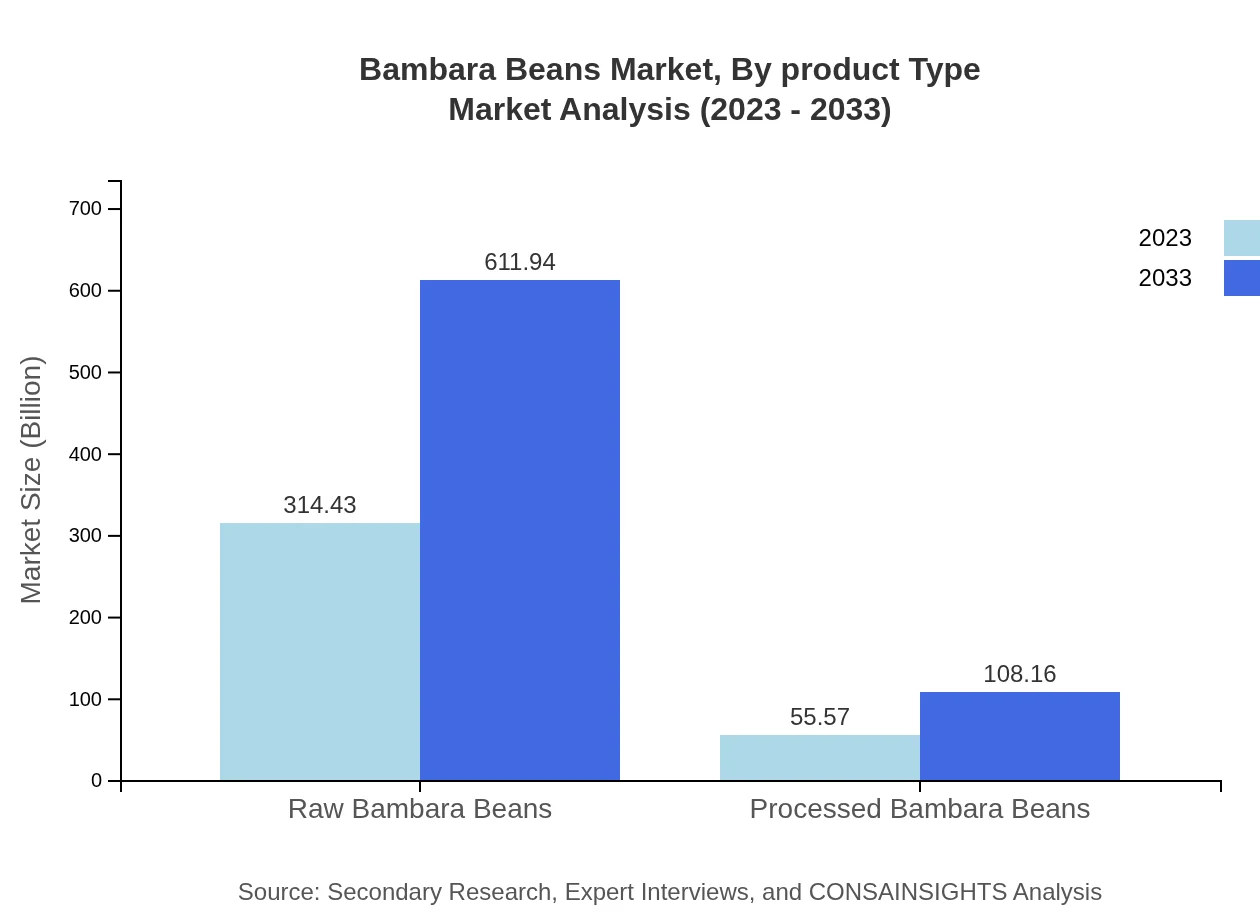
Bambara Beans Market Analysis By Product Type
The product types are divided into raw and processed Bambara Beans. Raw Bambara Beans dominate the market, projected to grow from $314.43 million in 2023 to $611.94 million by 2033, owing to their extensive application in food manufacturing and nutrition. Processed Bambara Beans are also on the rise, increasing from $55.57 million to $108.16 million over the same period.
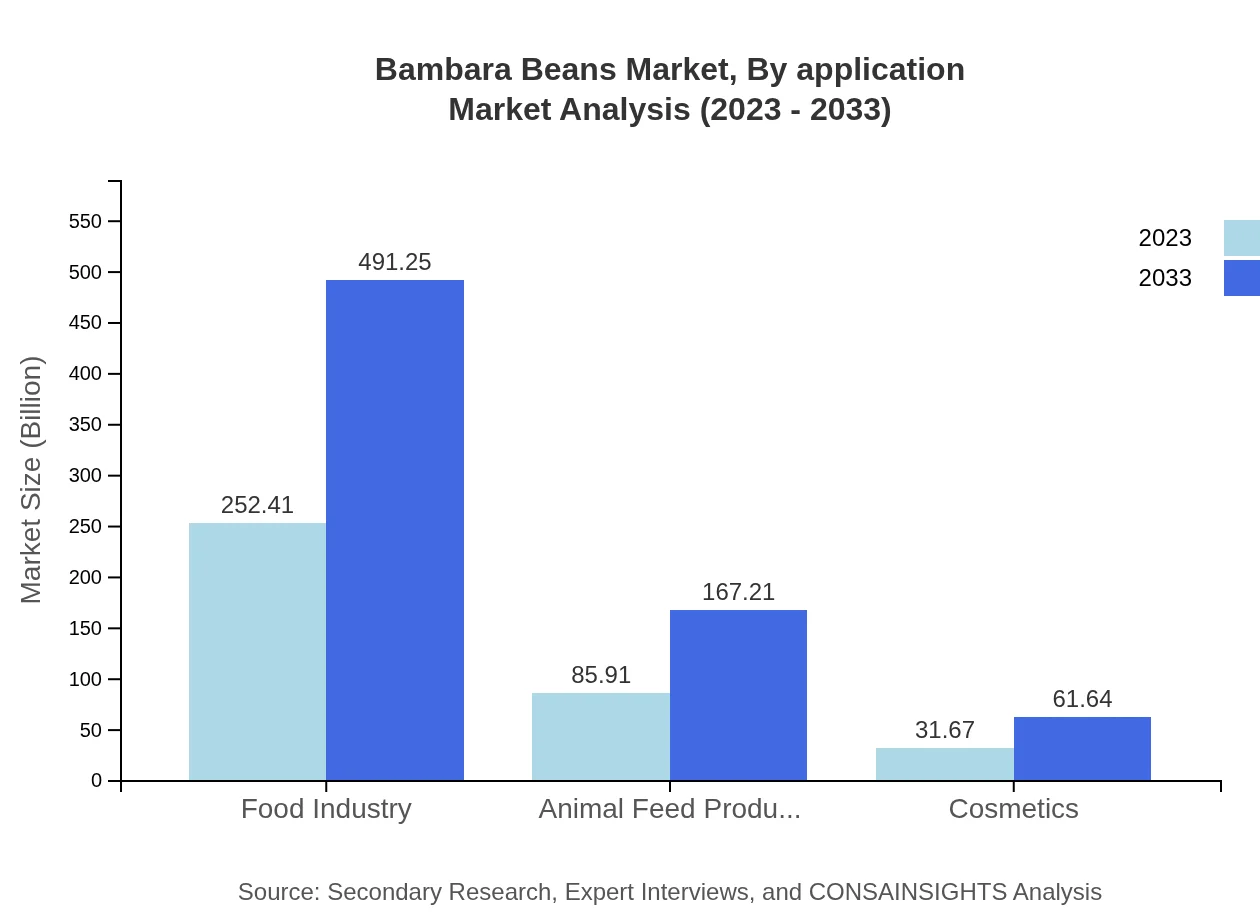
Bambara Beans Market Analysis By Application
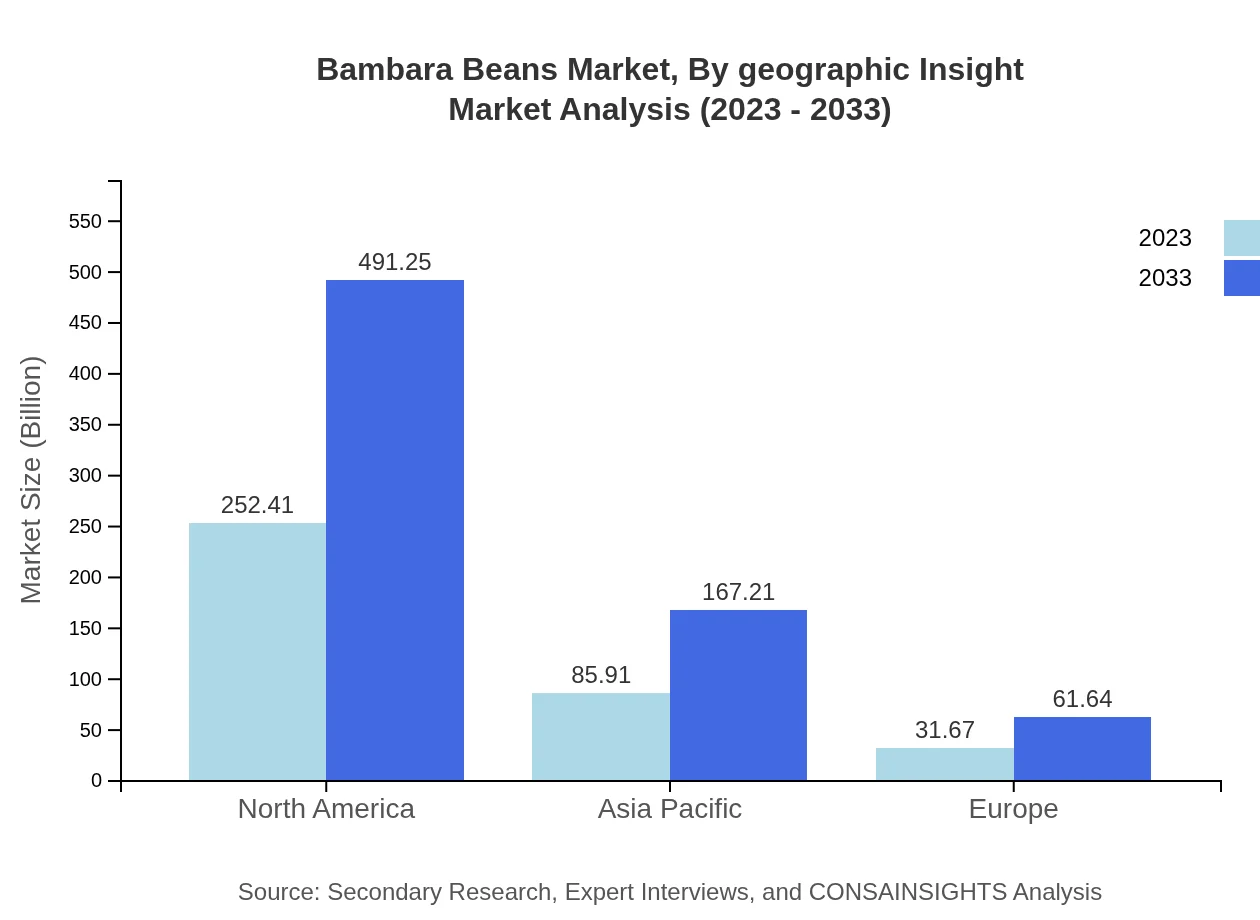
Application-wise, the food industry holds the largest share within the Bambara Beans market, expected to expand from $252.41 million in 2023 to $491.25 million by 2033. Other significant segments include animal feed production, which is forecasted to rise from $85.91 million to $167.21 million, and cosmetics, expected to grow from $31.67 million to $61.64 million.
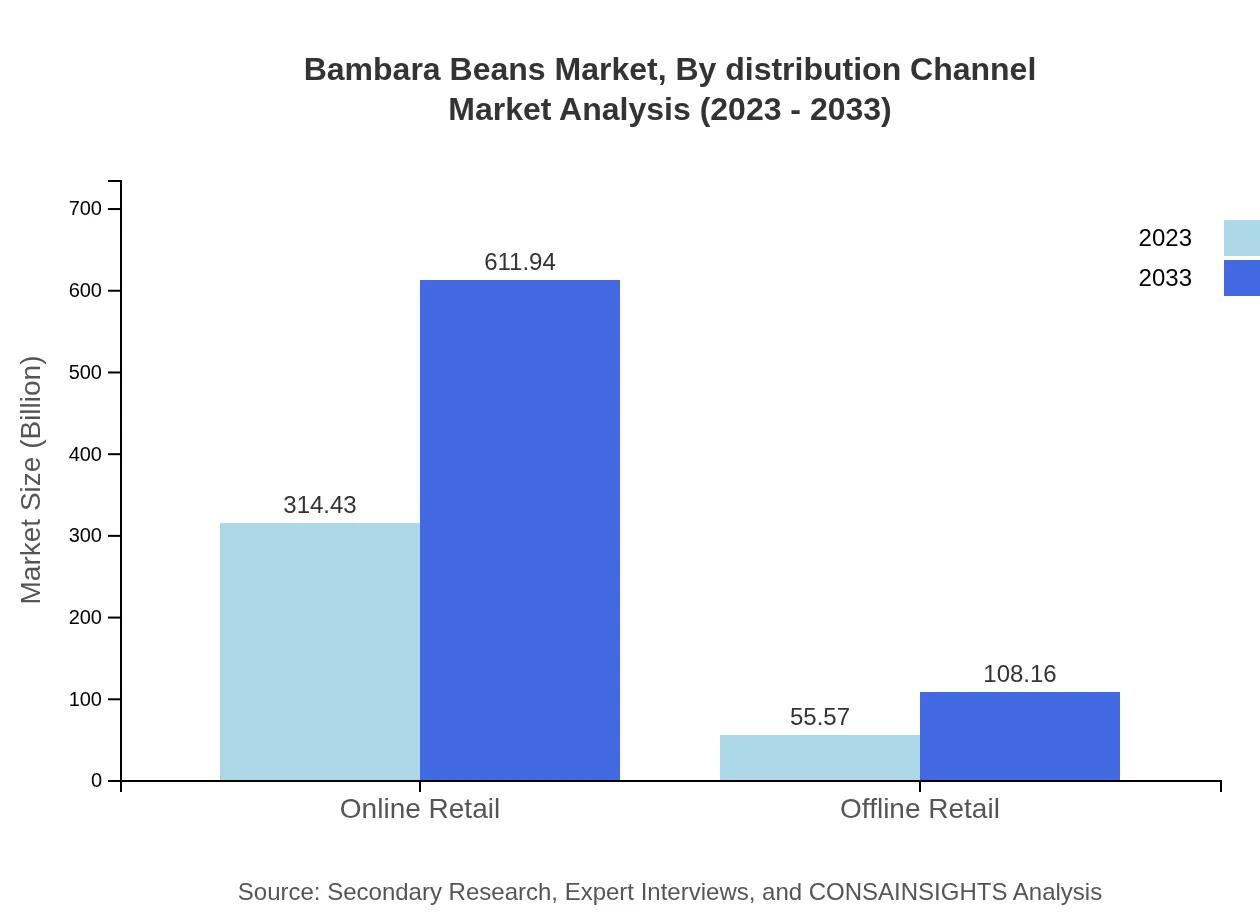
Bambara Beans Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
In distribution channels, online retail is showing substantial growth, anticipated to rise from $314.43 million in 2023 to $611.94 million in 2033. Offline retail is also growing but at a slower rate, with an increase from $55.57 million to $108.16 million, indicating a shift towards digital purchasing in consumer habits.
Bambara Beans Market Analysis By Geographic Insight
A geographic perspective indicates strong growth prospects in North America and Europe, where health trends are influencing food choices. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Africa and South America are tapping into traditional consumption and agricultural expansion.
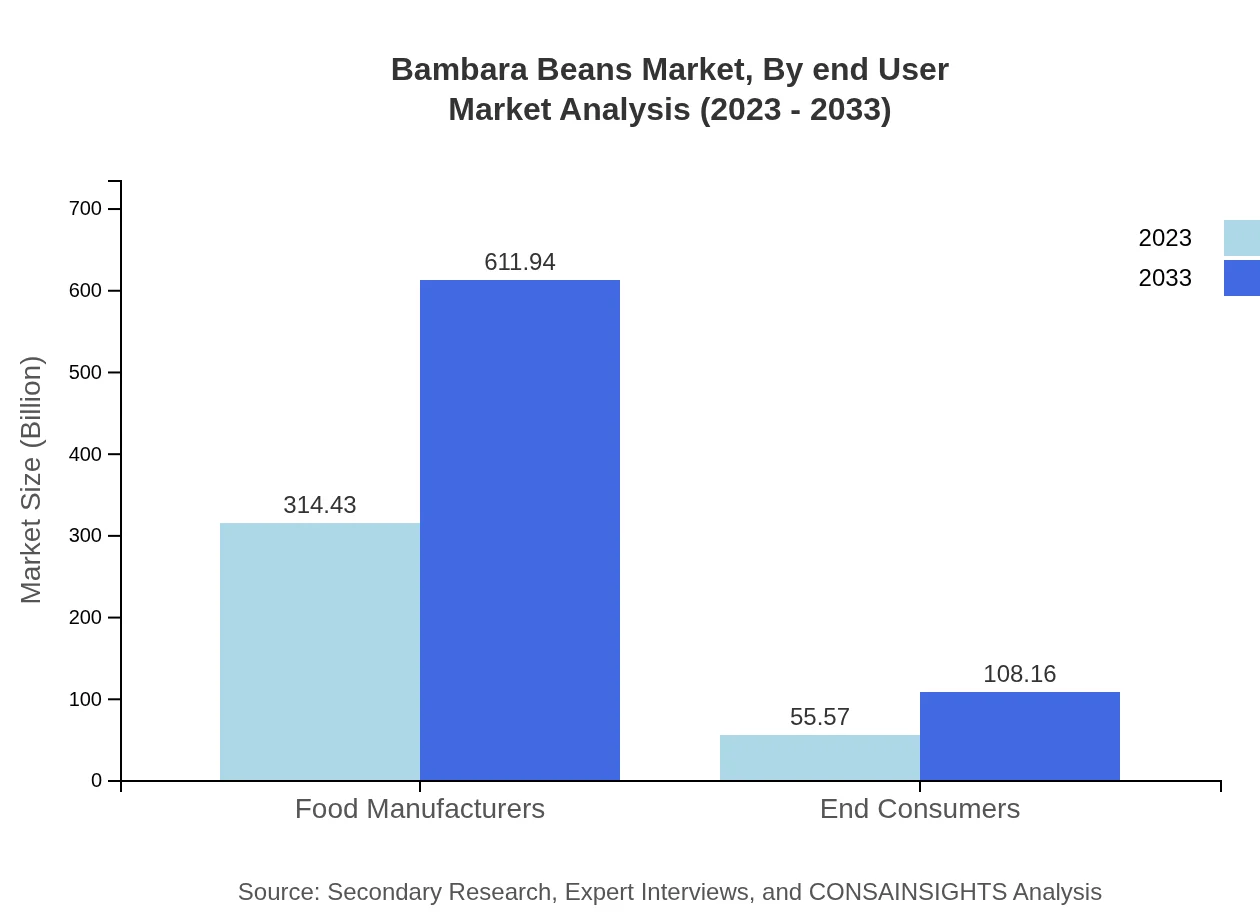
Bambara Beans Market Analysis By End User
End-users in the food manufacturing segment represent a significant market share. In 2023, food manufacturers accounted for $314.43 million, expected to grow substantially over a decade. Meanwhile, end consumers are gradually favoring Bambara Beans for their health benefits, increasing from $55.57 million to $108.16 million by 2033.
Bambara Beans Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Bambara Beans Industry
Agro Products and Agencies Pvt. Ltd.:
A leading supplier of agricultural products, they focus on sustainable practices and have introduced innovative processing techniques related to Bambara Beans.NutraBlend Foods:
Specializing in health foods, NutraBlend Foods incorporates Bambara Beans into nutritional products, targeting health-conscious consumers.Farmland Foods:
A key player in the agricultural sector, known for its commitment to organic farming of Bambara Beans and supporting local farmers.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of bambara Beans?
The global market size for bambara beans is projected at 370 million USD in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% expected through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this bambara Beans industry?
Key players in the bambara beans industry include prominent food manufacturers, agricultural processors, and retailers that focus on organic product lines, though specific names may vary based on geographical focus and market segmentation.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the bambara Beans industry?
Growth in the bambara beans market is primarily driven by rising health consciousness among consumers, increasing demand for sustainable food sources, and the expansion of the food processing industry catering to plant-based diets.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the bambara beans?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for bambara beans, projected to grow from 81.36 million USD in 2023 to 158.35 million USD in 2033, indicating robust demand and increasing cultivation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the bambara Beans industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the needs of clients in the bambara beans industry, accommodating unique business requirements and regional insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this bambara Beans market research project?
Deliverables from the bambara beans market research project typically include detailed market analysis reports, segmentation data, regional insights, and strategic recommendations to support business decision-making.
What are the market trends of bambara beans?
Current market trends for bambara beans include the increasing popularity of plant-based diets, innovation in food processing techniques, and rising consumer preference for organic and sustainable food sources.