Banana Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: banana
Banana Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the banana market from 2023 to 2033, including insights into market size, growth trends, regional performance, technological advancements, segmentation, and key industry players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
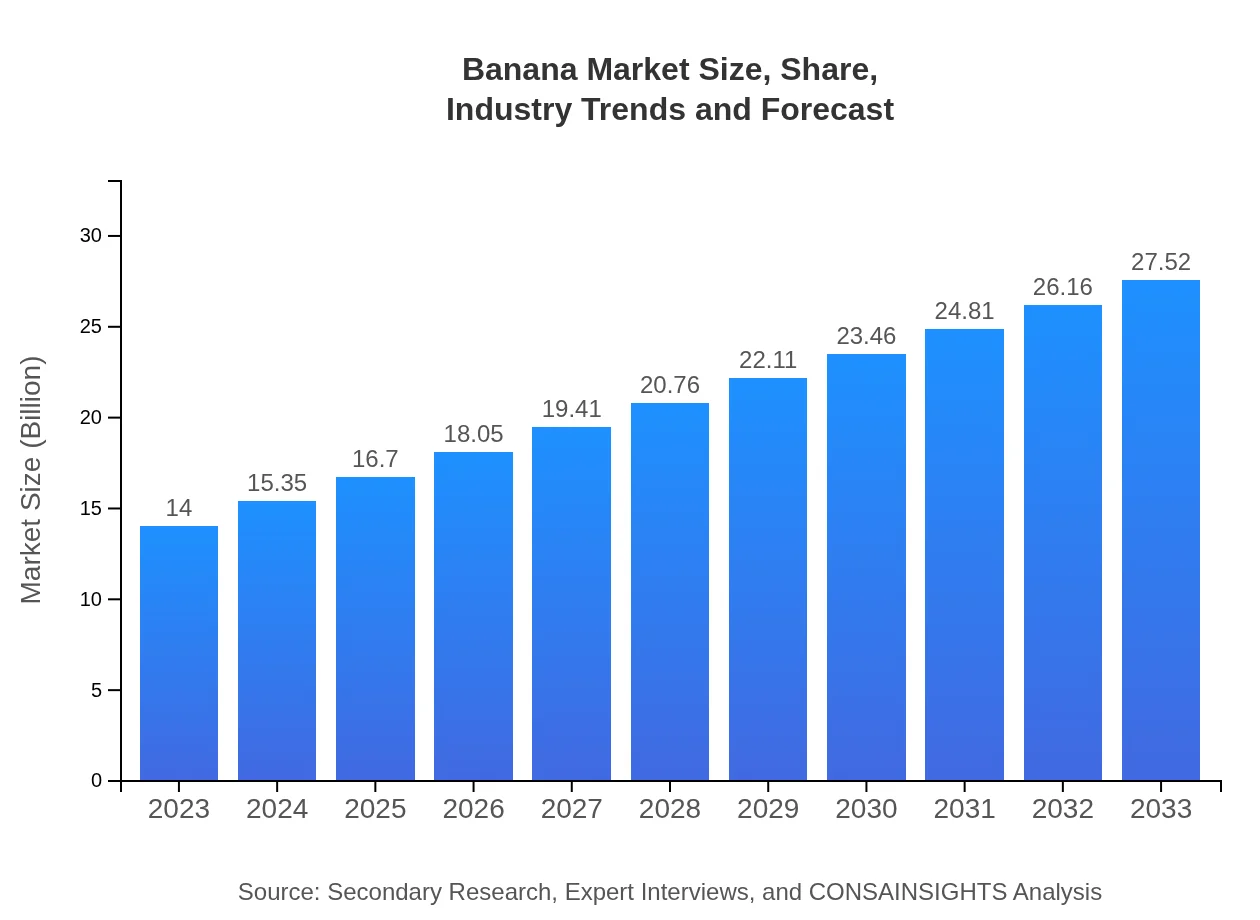
| 2023 Market Size | $14.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $27.52 Billion |
| Top Companies | Chiquita Brands International, Dole Food Company, Fyffes, Del Monte Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Banana Market Overview
Customize Banana Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Banana market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Banana's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Banana
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Banana market in 2023?
Banana Industry Analysis
Banana Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Banana Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Banana Market Report:
Europe's market size is set to grow from $4.63 billion in 2023 to $9.10 billion by 2033, largely driven by consumer trends favoring convenience and healthy snacking options. Import reliance and growing preferences for organic produce will also bolster market growth.Asia Pacific Banana Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow from a market size of $2.66 billion in 2023 to $5.23 billion by 2033. With countries like India and the Philippines being top producers, the region is seeing rising local demand and export opportunities, particularly in health-conscious markets. Innovative farming techniques are helping to improve yields and sustainability.North America Banana Market Report:
North America is projected to enhance its market from $4.62 billion in 2023 to $9.09 billion by 2033, fueled by a growing shift towards healthy eating habits and an expanding food service industry. The demand for organic bananas is particularly strong.South America Banana Market Report:
South America is a significant player in the banana market, with a market size expected to rise from $1.24 billion in 2023 to $2.44 billion by 2033. Countries like Ecuador are major exporters. The region's growth is driven by increased investments in agricultural technology and sustainable farming practices.Middle East & Africa Banana Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's market is anticipated to grow from $0.85 billion in 2023 to $1.67 billion by 2033. Increasing urbanization, along with the rising popularity of exotic fruits, particularly in the Gulf regions, supports this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
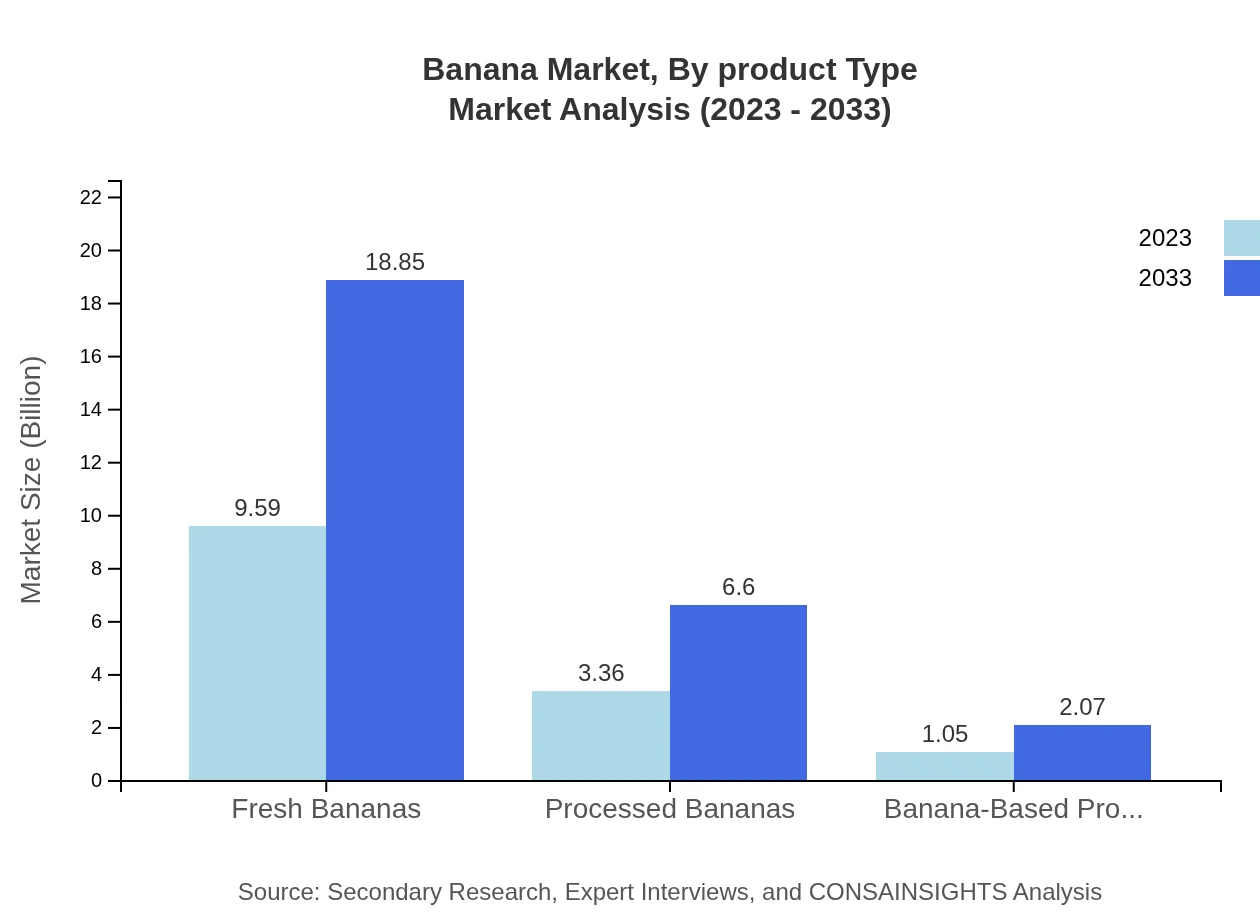
Banana Market Analysis By Product Type
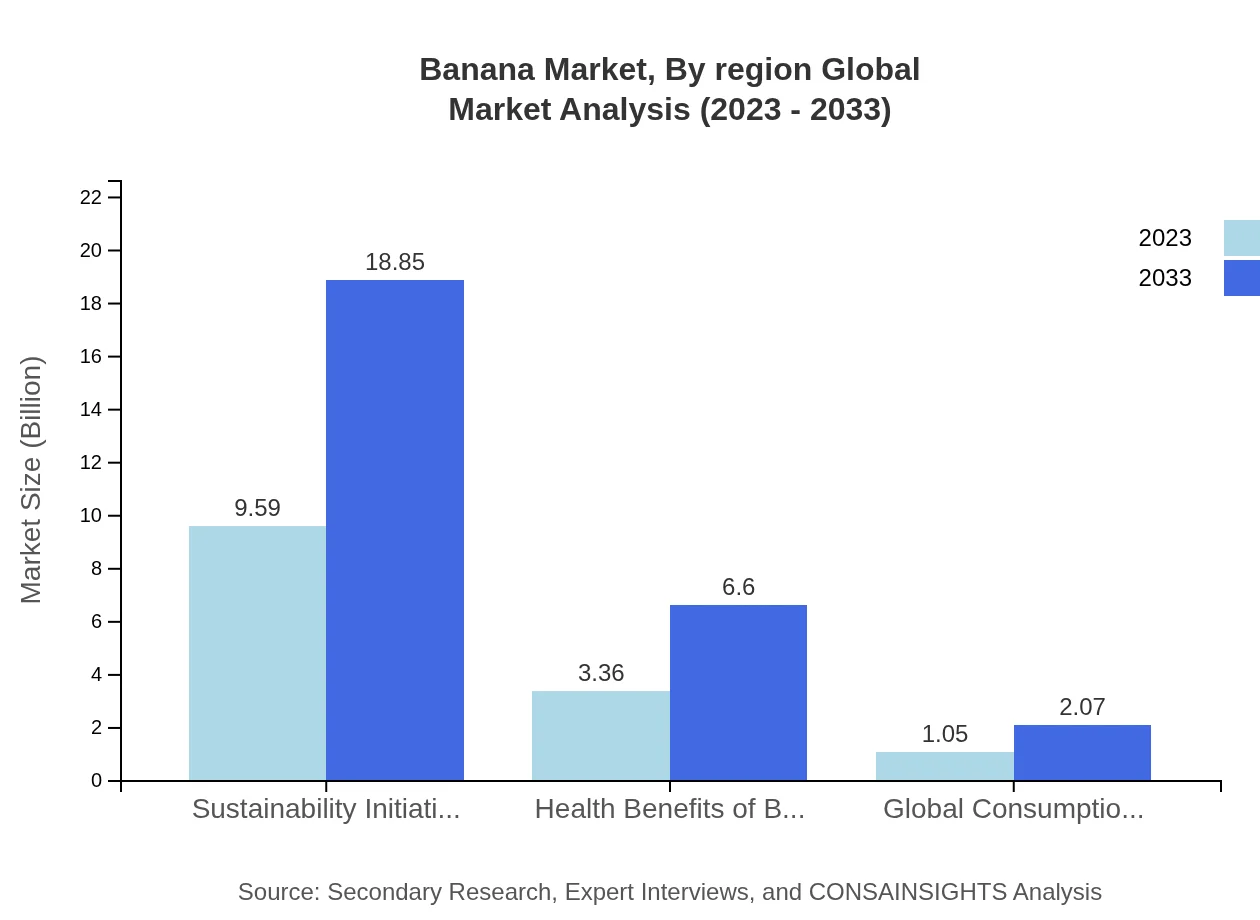
In terms of product type analysis, fresh bananas dominate the segment, generating around $9.59 billion in 2023, with an anticipated growth to $18.85 billion by 2033. Processed bananas stand at $3.36 billion in 2023, projected to reach $6.60 billion. Banana-based products contribute significantly to a diverse dietary range, with a market size of $1.05 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $2.07 billion. The shift towards healthier food options enhances the significance of these categories.
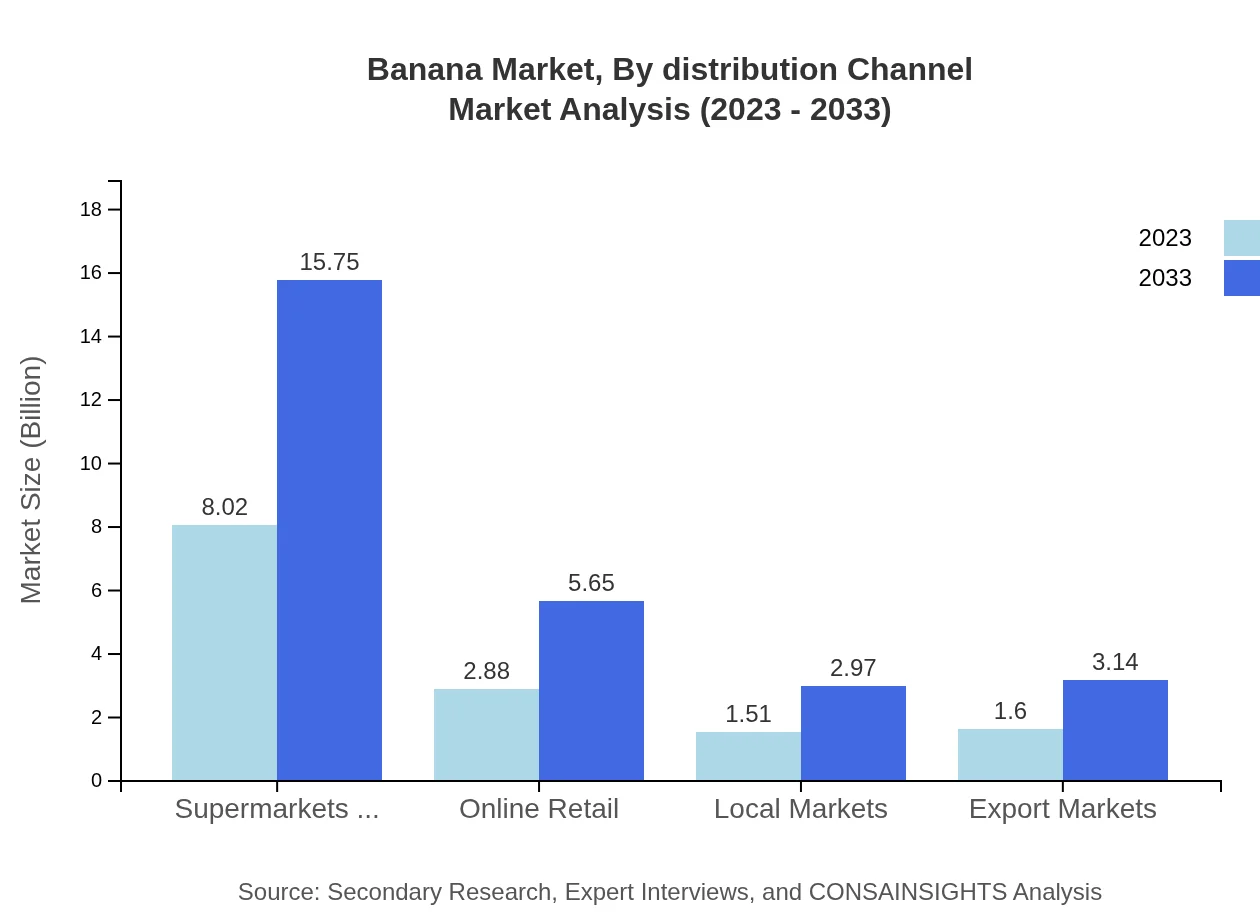
Banana Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels play a critical role in the banana market. Supermarkets and hypermarkets lead the channel distribution, with a market size of $8.02 billion projected to grow to $15.75 billion by 2033, maintaining a 57.25% market share. Online retail is also rising, anticipated to expand from $2.88 billion in 2023 to $5.65 billion, reflecting a 20.55% share. Local markets and export avenues contribute constructively, demonstrating the versatility of distribution in meeting consumer demand.
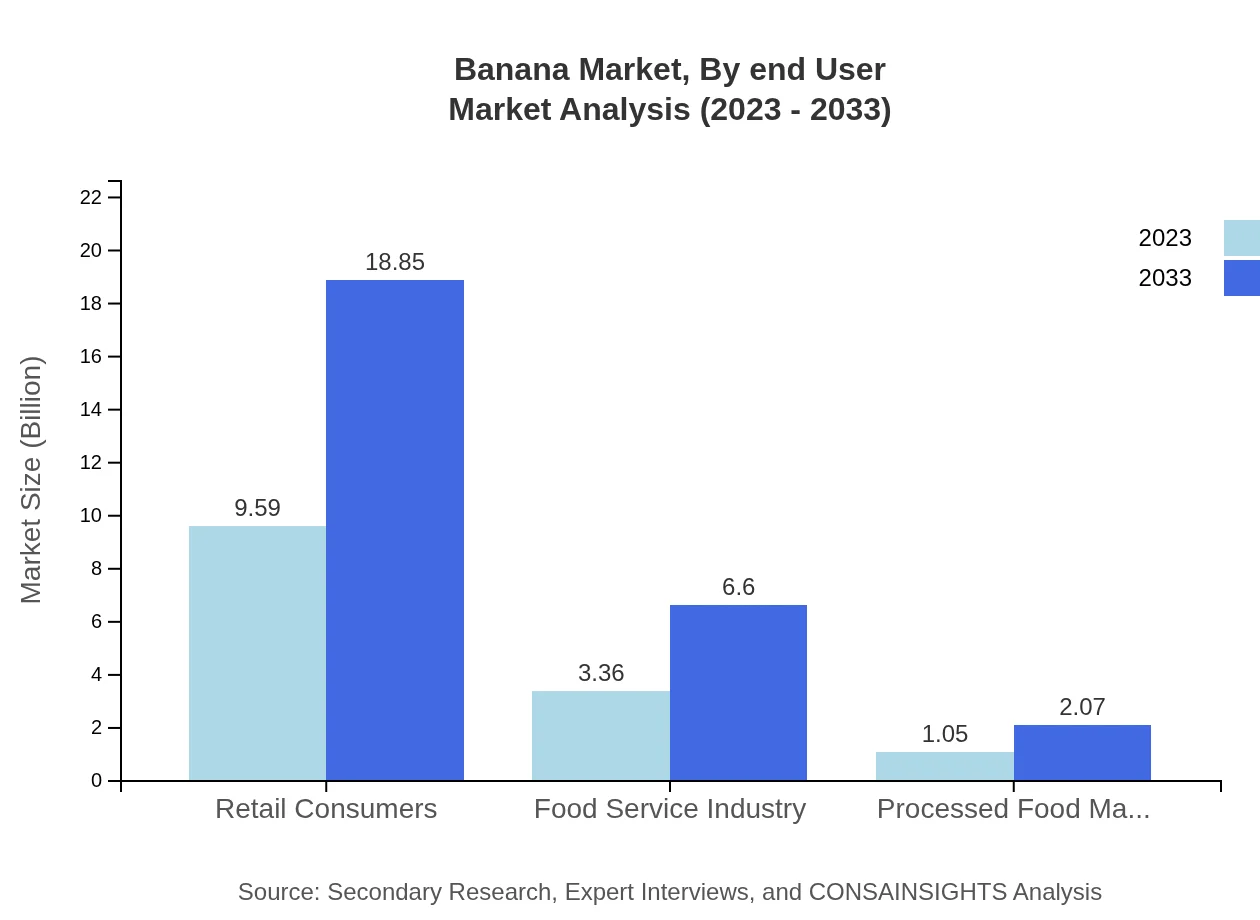
Banana Market Analysis By End User
The banana market's end-user segmentation highlights the prominence of retail consumers, accounting for a market size of $9.59 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $18.85 billion by 2033. The food service industry and processed food manufacturers represent substantial areas, with sizes of $3.36 billion and $1.05 billion respectively, underscoring the broad utility of bananas across multiple sectors that strongly influence demand.
Banana Market Analysis By Region Global
Global consumption patterns reflect an increasing trend towards health-focused diets, with the market anticipated to grow significantly due to the expanding reach of bananas as a staple food product. Sustainability initiatives resonate among consumers, promoting organic and ethically sourced bananas. This trend aligns with overall market growth, characterized by rising environmental awareness and support for local farming through fair trade practices.
Banana Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Banana Industry
Chiquita Brands International:
Chiquita is a leading producer and distributor of bananas, focusing on sustainability and high-quality products, emphasizing ethical sourcing and environmental responsibility.Dole Food Company:
Dole is another major player in the banana market, recognized for its wide range of fresh and processed fruit products, with a strong commitment to sustainability and innovation.Fyffes:
Fyffes is known for its bananas, melons, and pineapples, leading the market with a commitment to quality and sustainability, enhancing consumer health through nutritious options.Del Monte Foods:
Del Monte offers a diverse range of fruit products with a significant focus on bananas, promoting healthy eating options across various markets with a strong global presence.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of banana?
The banana market is currently valued at approximately $14 billion with a projected CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing global demand and consumption patterns favoring bananas as a staple fruit.
What are the key market players or companies in the banana industry?
Major companies in the banana industry include Chiquita Brands International, Dole Food Company, and Fresh Del Monte Produce. These players dominate production, distribution, and marketing, significantly influencing market trends and pricing strategies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the banana industry?
Key growth factors include rising health consciousness among consumers, increased popularity of bananas in smoothies and snacks, and sustainability initiatives encouraging eco-friendly farming practices. This multifaceted approach is currently reshaping the banana market.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the banana market?
Europe is the fastest-growing region in the banana market, projected to increase from $4.63 billion in 2023 to $9.10 billion by 2033. Asia Pacific follows, growing from $2.66 billion to $5.23 billion in the same period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the banana industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the banana industry. This includes in-depth analysis, forecasts, and insights for businesses seeking strategic advantages and market intelligence.
What deliverables can I expect from this banana market research project?
Deliverables from the banana market research project may include comprehensive market reports, segmentation analysis, trend forecasts, competitive analysis, and actionable insights, all aimed at supporting informed business decisions and strategies.
What are the market trends of banana?
Current market trends for bananas include a shift towards online retail, growth in supermarkets, and a focus on health benefits. Additionally, sustainability in production is becoming increasingly important to consumers, shaping future market dynamics.