Barley Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: barley
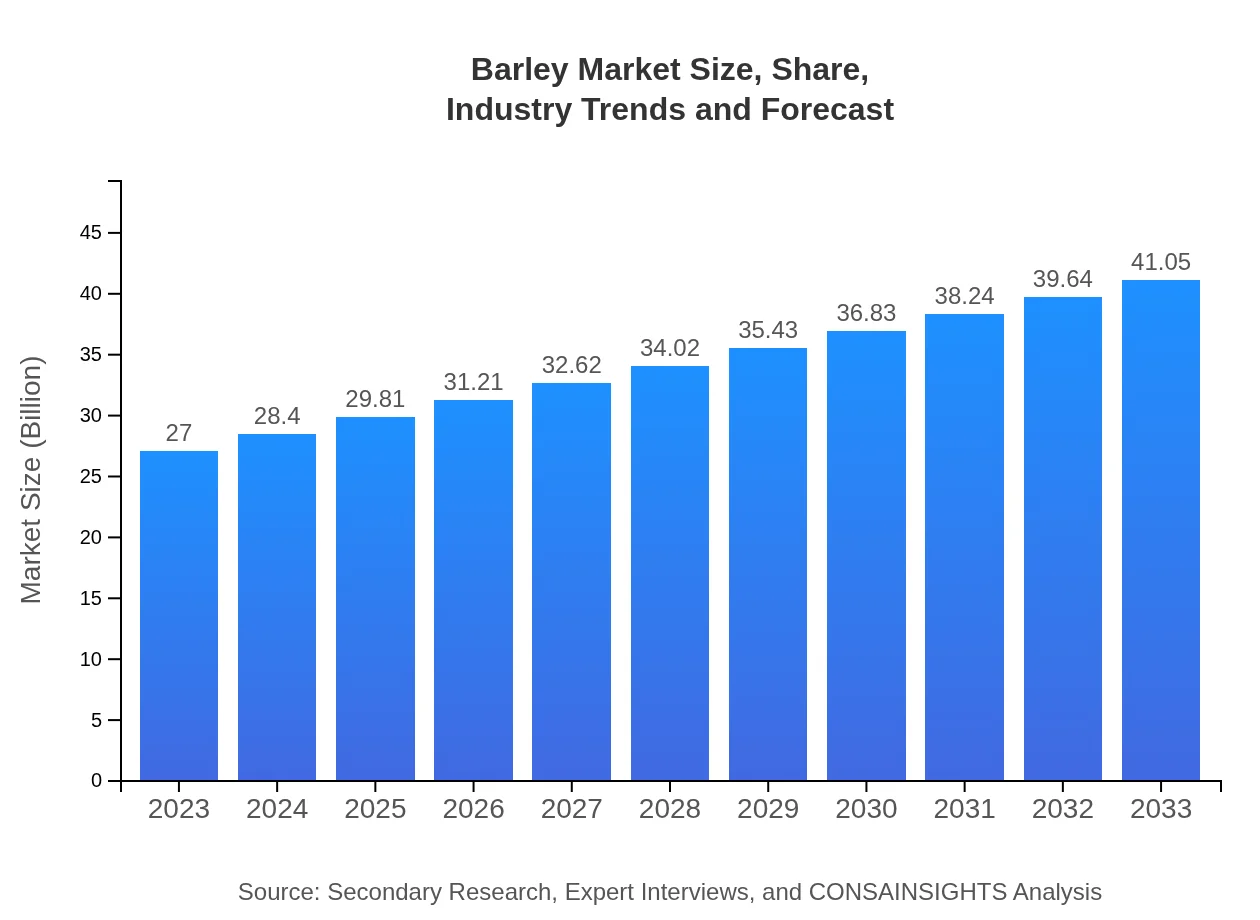
Barley Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This detailed market report examines the Barley industry, providing insights into current market conditions, growth projections, regional analysis, and key trends for the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $27.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $41.05 Billion |
| Top Companies | AB InBev, Cargill , Malteurop, Barley Farmers Federation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Barley Market Overview
Customize Barley Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Barley market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Barley's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Barley
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Barley market in 2023?
Barley Industry Analysis
Barley Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Barley Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Barley Market Report:
Europe represents one of the largest markets for barley, with a size of $6.52 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $9.90 billion by 2033. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are significant contributors, with a focus on high-quality malting barley.Asia Pacific Barley Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region exhibited a market size of $5.64 billion in 2023, expected to grow to approximately $8.57 billion by 2033. Countries such as China and Australia are prominent producers, supported by increasing awareness of barley's health benefits and its application in various cuisines.North America Barley Market Report:
North America's barley market is robust, valued at $9.25 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $14.06 billion by 2033. The United States and Canada are leading producers, primarily for the malting and animal feed industries, driven by a strong craft beer market.South America Barley Market Report:
In South America, the barley market was valued at $2.61 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $3.97 billion by 2033. Key players in Brazil and Argentina are focusing on enhancing barley production capabilities to cater to both local consumption and export markets.Middle East & Africa Barley Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's barley market was valued at $2.99 billion in 2023, projected to reach $4.54 billion by 2033. The demand in this region is influenced by agriculture and livestock farming, with countries such as Egypt and South Africa leading in production.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
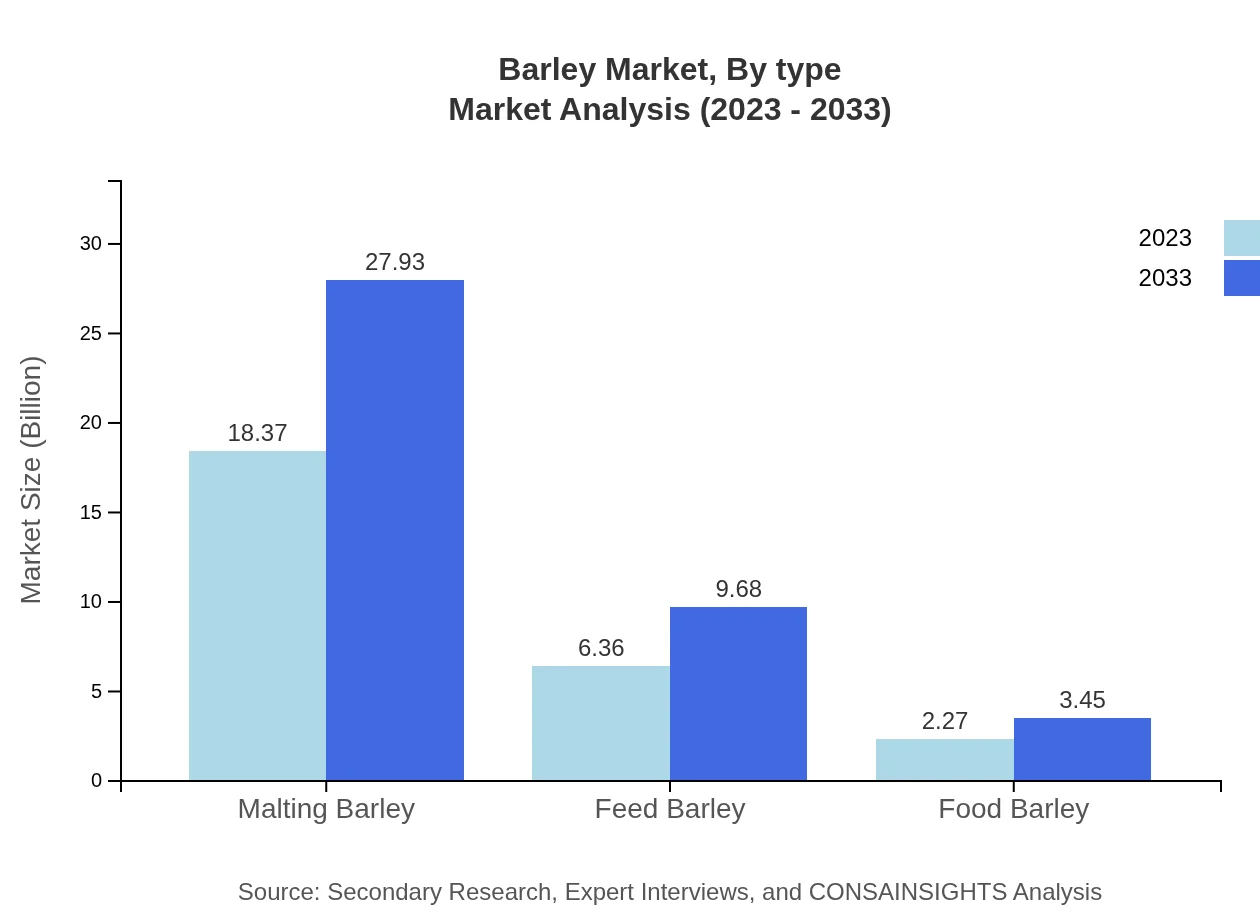
Barley Market Analysis By Type
The Barley market segments include: Malting Barley: estimated at $18.37 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $27.93 billion by 2033, constituting the largest share of the market due to rising beer production. Feed Barley: size stands at $6.36 billion in 2023, poised to reach $9.68 billion by 2033. Food Barley: valued at $2.27 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $3.45 billion by 2033.
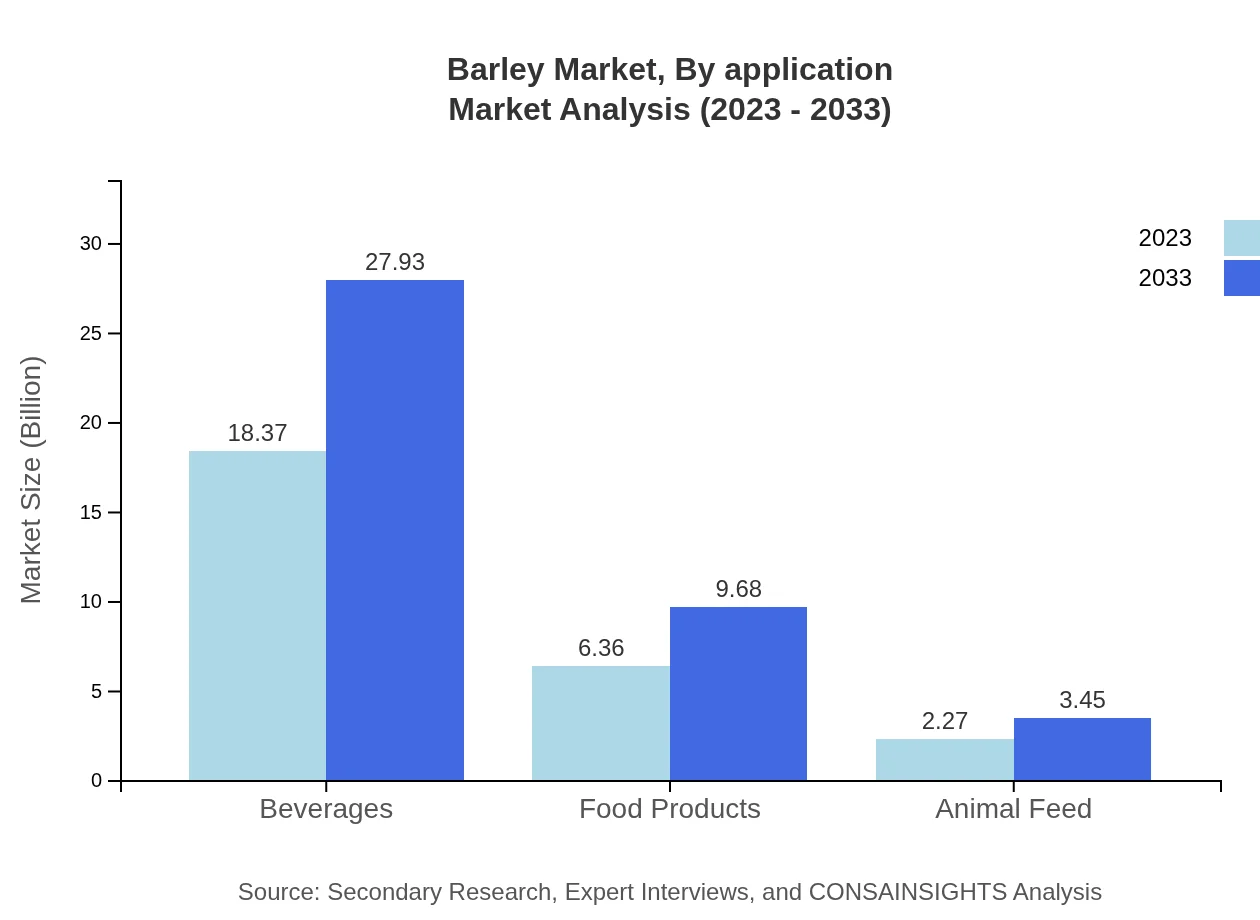
Barley Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, the market is dominated by beverages, particularly beer, with a size of $18.37 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $27.93 billion by 2033. Food products account for $6.36 billion and are expected to grow to $9.68 billion, while animal feed applications hold a market size of $2.27 billion, anticipated to increase to $3.45 billion over the forecast period.
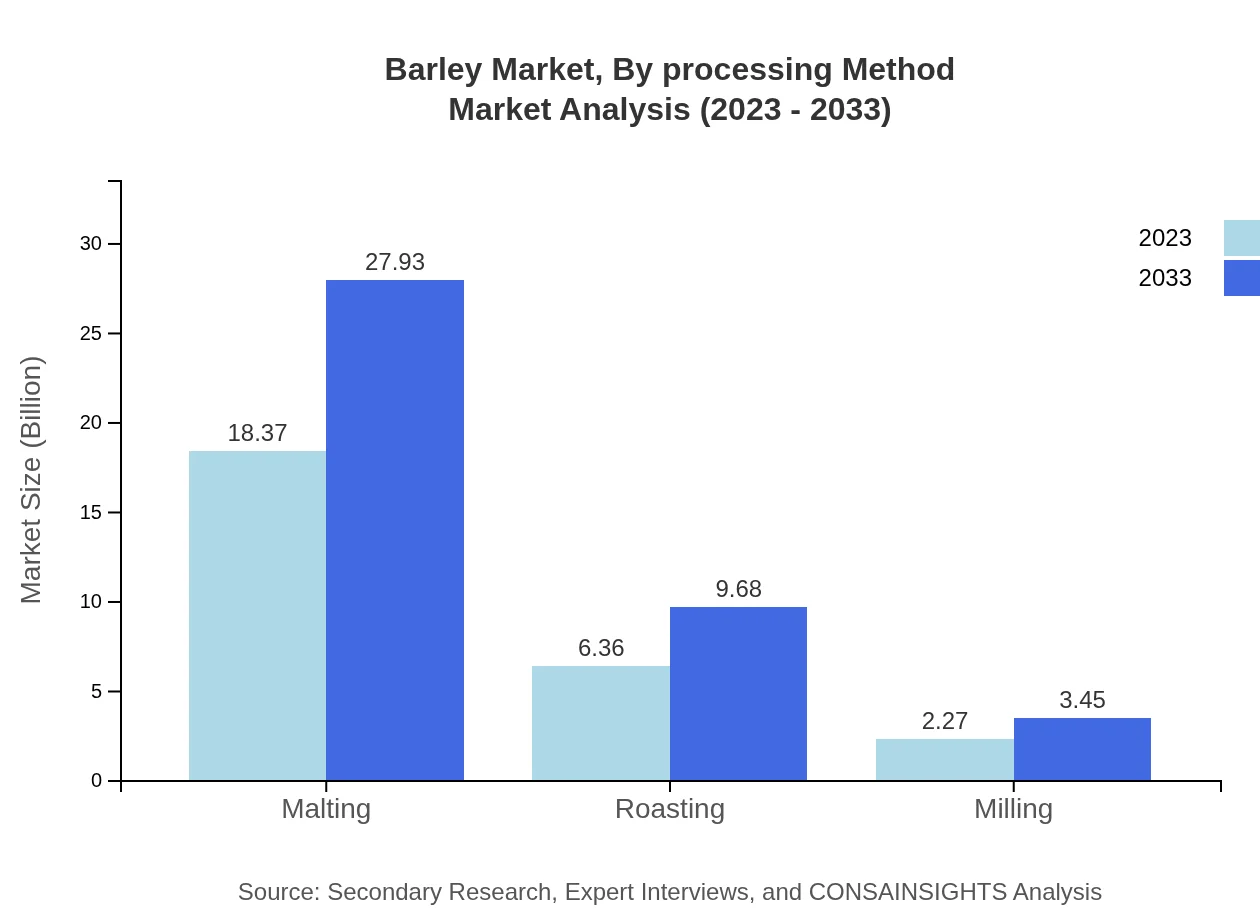
Barley Market Analysis By Processing Method
The processing methods include malting, roasting, and milling. Malting is the most significant segment, holding around 68.03% of the market share in 2023 and forecast to remain stable by 2033. Roasting holds about 23.57% share and milling about 8.4%, reflecting the growing variations in barley use in food and drink products.
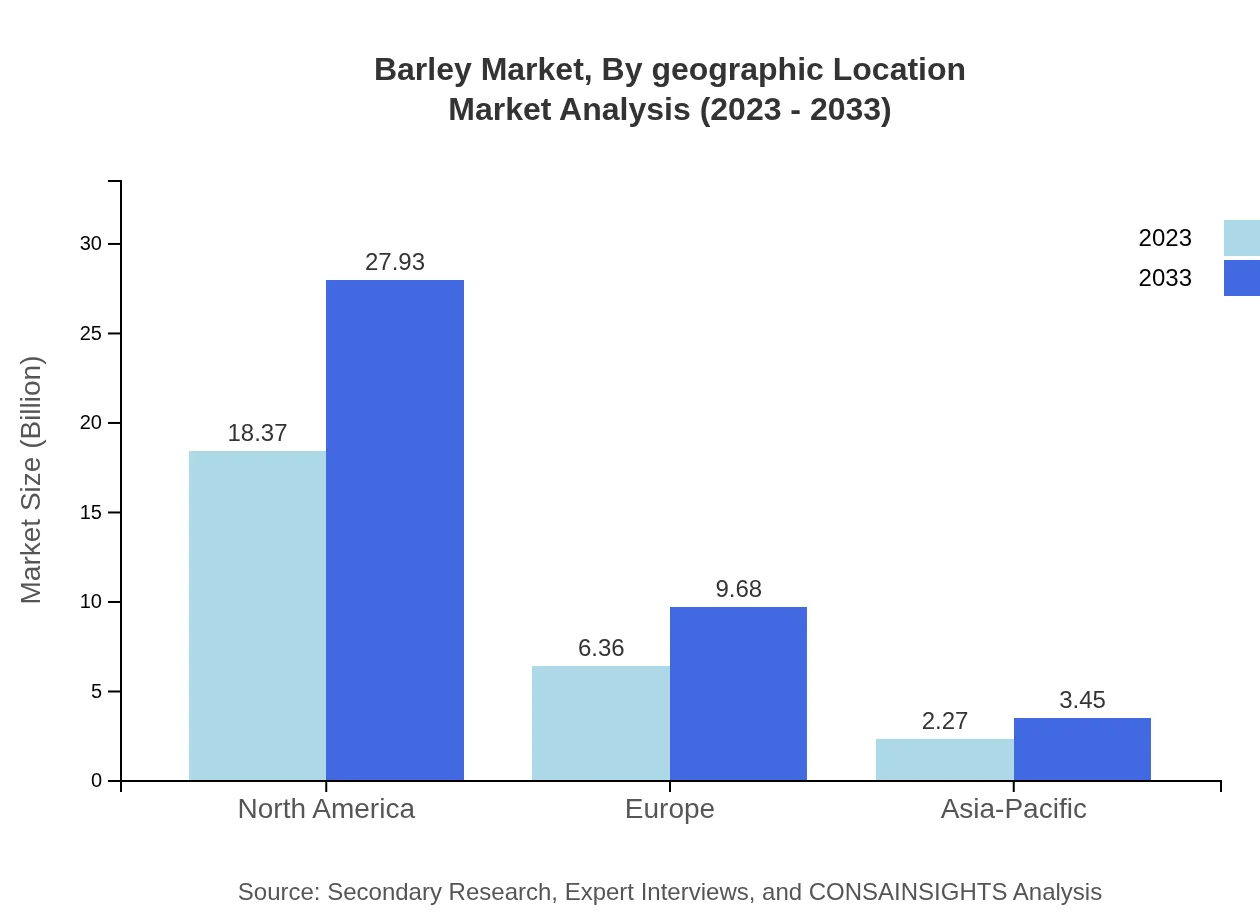
Barley Market Analysis By Geographic Location
Geographically, North America leads in barley production with a market size of $18.37 billion in 2023, projected to increase to $27.93 billion. Europe follows with an expected increase from $6.36 billion to $9.68 billion, while Asia-Pacific is projected to grow from $2.27 billion to $3.45 billion, reflecting ongoing enhancements in cultivation and processing.
Barley Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Barley Industry
AB InBev:
A leading global brewer that utilizes barley for brewing a large portfolio of beers, promoting quality production standards.Cargill :
Global agribusiness company involved in the barley trade, focusing on innovative farming practices and supply chain efficiency.Malteurop:
One of the world's major malt producers, specializing in high-quality malting barley to meet global brewing demand.Barley Farmers Federation:
An organization representing barley farmers aiming to promote sustainable farming and market access improvement.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of barley?
The global barley market is valued at approximately $27 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% through 2033, reflecting steady growth driven by increasing demand.
What are the key market players or companies in this barley industry?
Key players in the barley market include major agricultural firms and food manufacturers who focus on malting, animal feed, and food production, ensuring a competitive landscape that drives innovation and market efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the barley industry?
Growth in the barley industry is propelled by increasing consumption in brewing and animal feed sectors, advancements in farming technology, and expanding international trade facilitating wider market access for barley producers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the barley?
The fastest-growing region in the barley market is North America, with market size expected to expand from $9.25 billion in 2023 to $14.06 billion by 2033, demonstrating a strong growth trajectory.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the barley industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the barley industry, enabling clients to make informed decisions based on detailed insights and trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this barley market research project?
Deliverables from the barley market research project include comprehensive reports on market size, growth forecasts, segmentation analyses, competitive landscape insights, and detailed regional market overviews.
What are the market trends of barley?
Current trends in the barley market include a shift towards sustainable farming practices, increasing demand for gluten-free products, and a rise in innovative uses of barley in health foods and beverages.