Beer Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: beer
Beer Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Beer market, including current trends, market size, forecast data for 2023-2033, and regional insights, offering valuable information for stakeholders seeking to understand future dynamics in the brewery industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
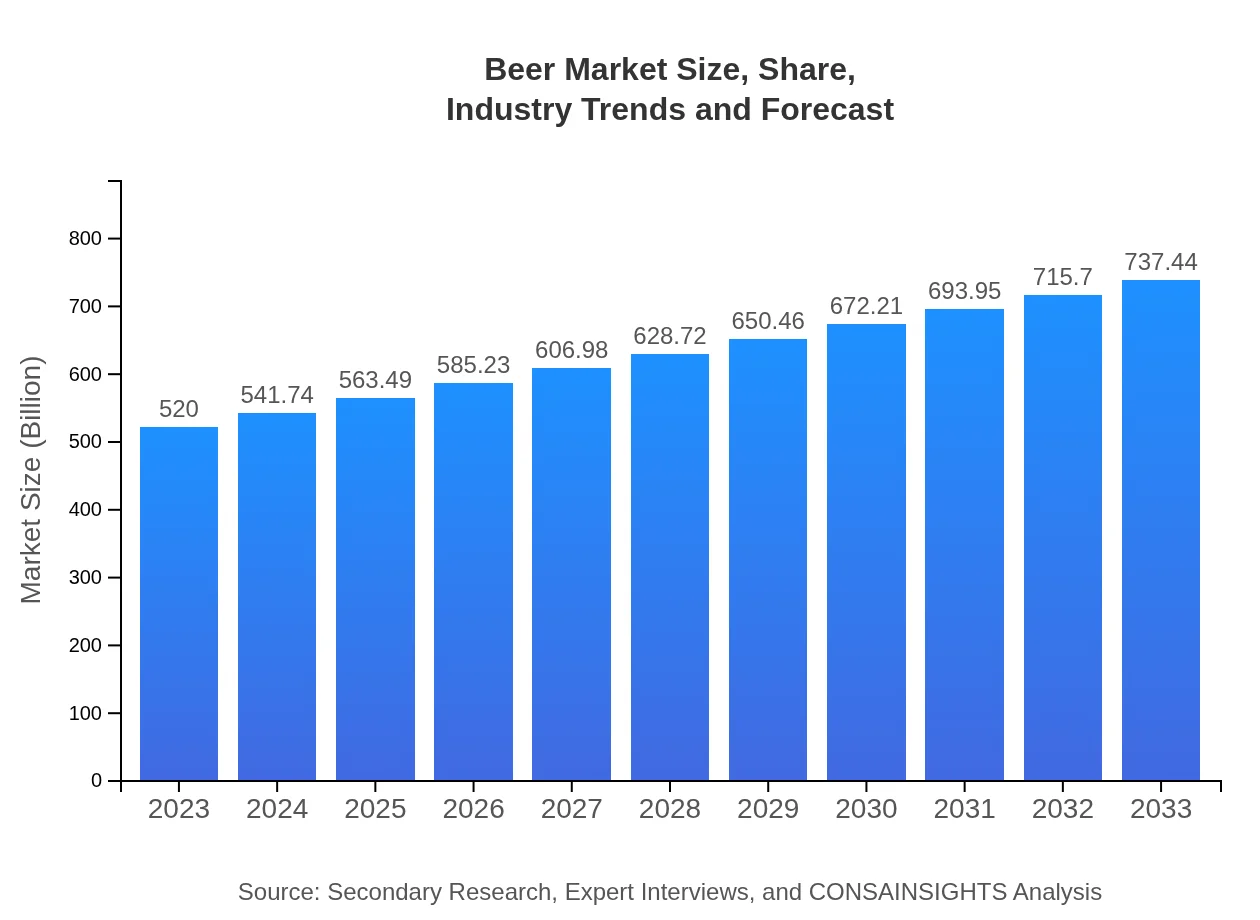
| 2023 Market Size | $520.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 3.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $737.44 Billion |
| Top Companies | Anheuser-Busch InBev, Heineken N.V., Diageo, Molson Coors Beverage Company, Boston Beer Company |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Beer Market Overview
Customize Beer Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Beer market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Beer's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Beer
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Beer market in 2023?
Beer Industry Analysis
Beer Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Beer Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Beer Market Report:
Europe's beer market is valued at USD 144.04 billion in 2023, with estimates suggesting it will grow to USD 204.27 billion by 2033. Countries like Germany and the UK are notable for their diverse beer offerings, with lager dominating. Increasing trends of microbreweries and regional craft beers highlight Europe’s rich brewing heritage.Asia Pacific Beer Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific beer market is valued at USD 104.83 billion and is expected to grow to USD 148.67 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by an evolving young consumer base, urbanization, and a rising middle class with higher spending power. The craft beer segment is particularly gaining traction in countries like China and India, reflecting a shift in taste towards more premium options.North America Beer Market Report:
North America is anticipated to lead the beer market with a size of USD 185.38 billion in 2023, forecasted to reach USD 262.90 billion by 2033. Craft breweries play a critical role here, consistently pushing consumer preferences. The focus on sustainability and health-conscious options significantly influences market dynamics, indicating a cultural shift in drinking habits.South America Beer Market Report:
For South America, the beer market in 2023 is valued at USD 29.28 billion, with projections estimating growth to USD 41.52 billion by 2033. The region has seen increased popularity of both local and international beers, aided by greater acceptance of diverse beer styles. Political and economic stability will be crucial for sustainable growth in this sector.Middle East & Africa Beer Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa beer market is expected to grow from USD 56.47 billion in 2023 to USD 80.09 billion by 2033. Market dynamics are affected by socio-cultural factors; however, there is potential growth in non-alcoholic options that align with cultural and religious norms. Countries like South Africa have shown growth due to changing regulations.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
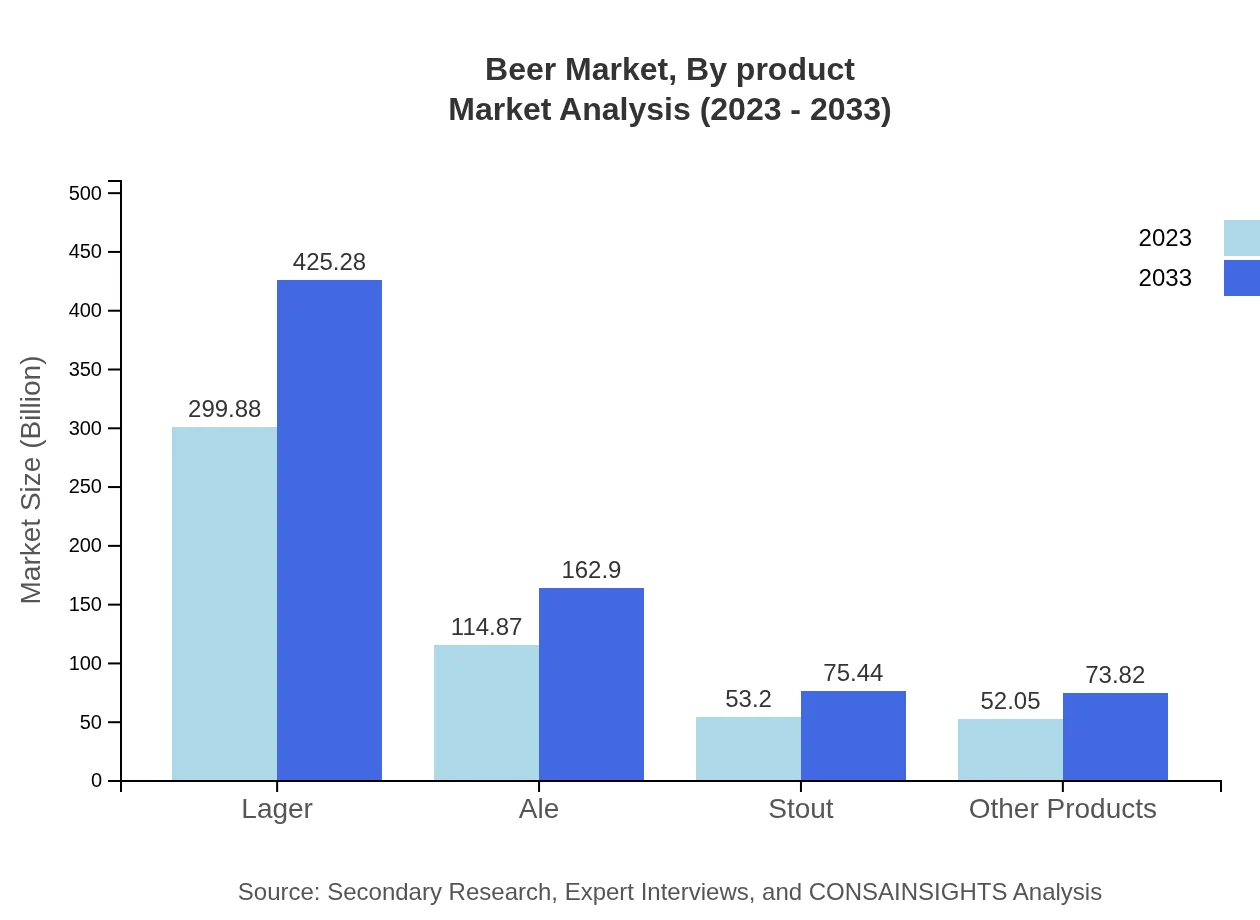
Beer Market Analysis By Product
In terms of product types, Lager dominates the market, projected to grow from USD 299.88 billion in 2023 to USD 425.28 billion by 2033. Ale follows as a significant contributor with a size of USD 114.87 billion expected to reach USD 162.90 billion. Stout and other specialty beers are also gaining market share, highlighting diverse consumer preferences.
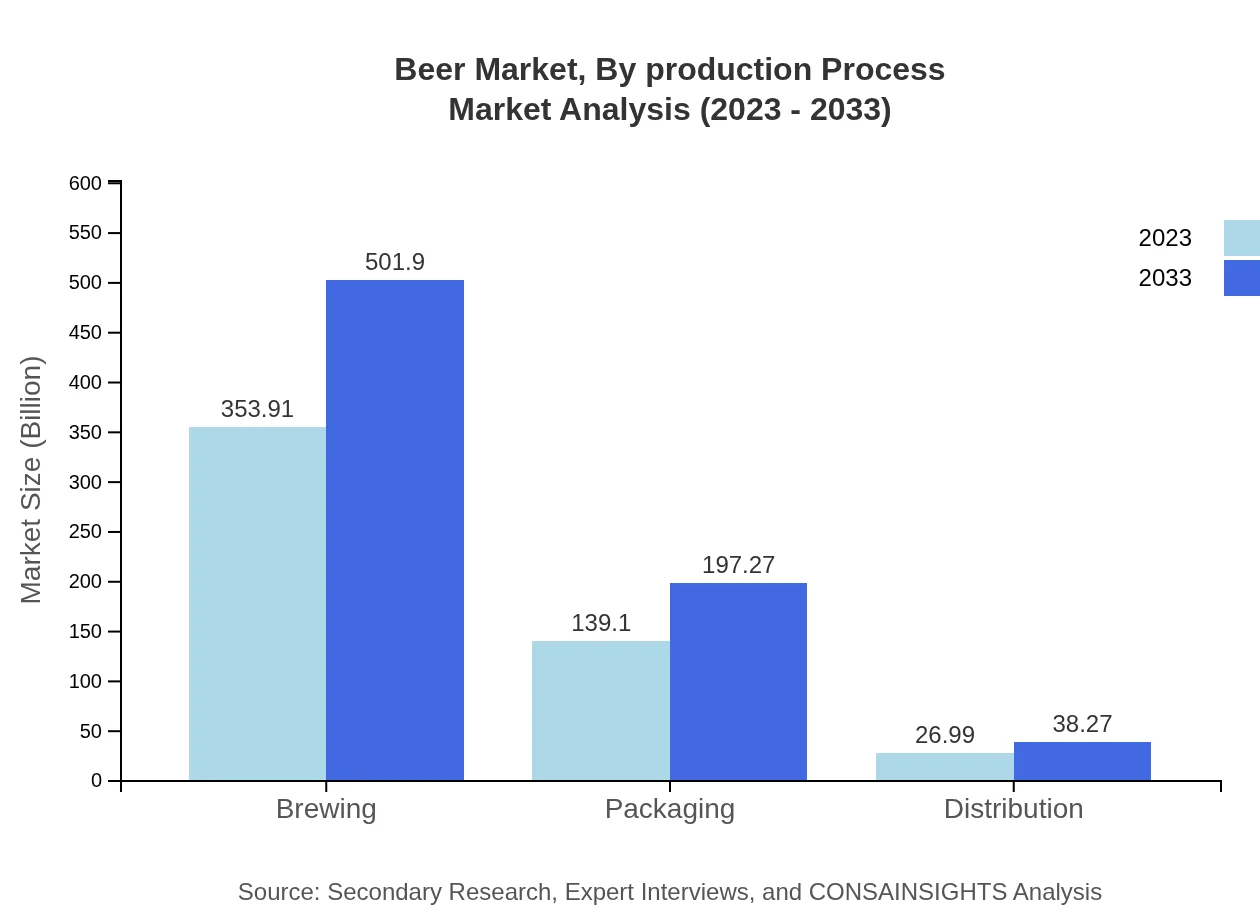
Beer Market Analysis By Production Process
The production processes in the beer market are primarily characterized by traditional and modern brewing methods. Craft beer production emphasizes artisanal methods, while large companies focus on automation to maintain consistency and scale. Innovations in brewing technology are leading to higher efficiencies and more sustainable practices.
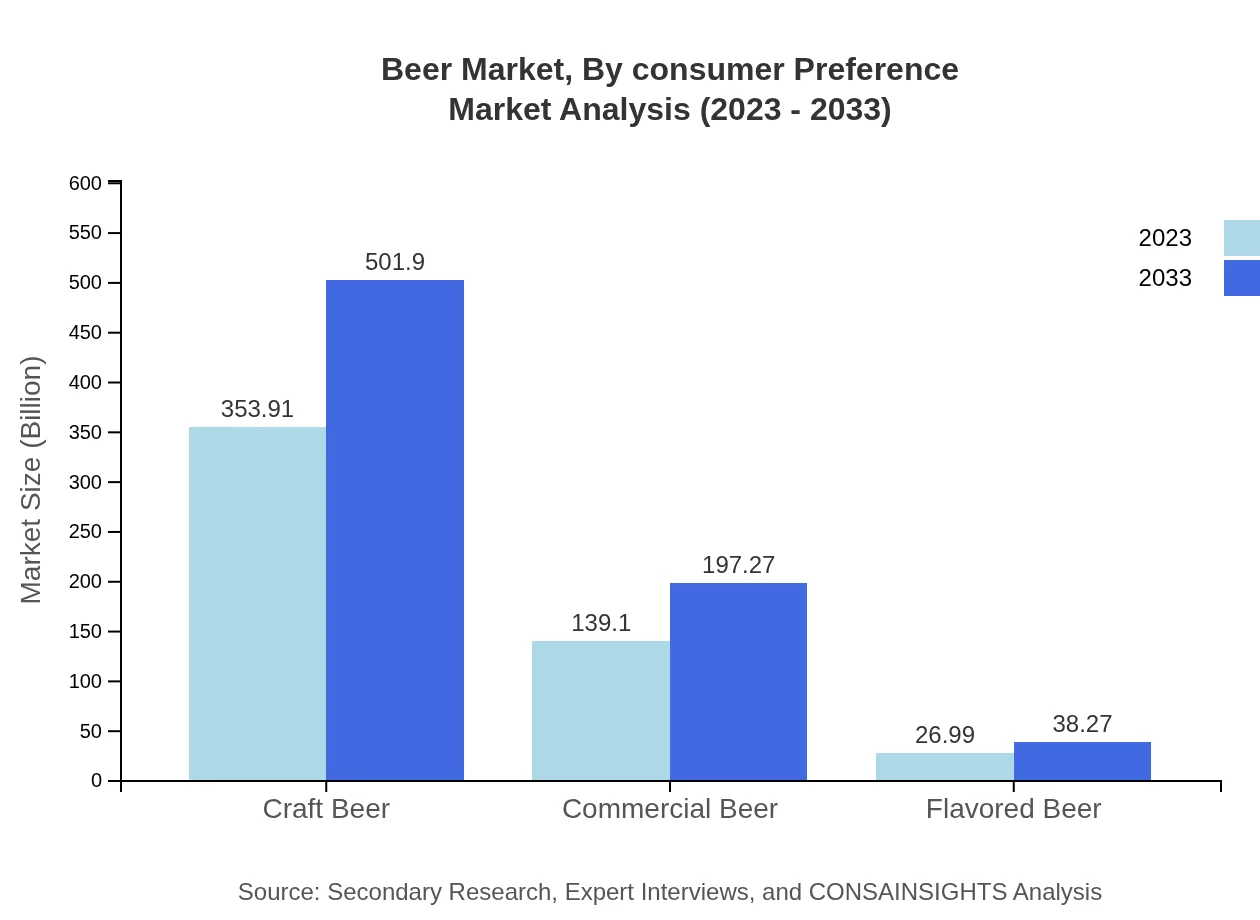
Beer Market Analysis By Consumer Preference
Consumer preferences are shifting towards health-conscious options, with low-alcohol and gluten-free beers gaining traction. There is an increasing demand for craft beers that prioritize quality over quantity, reflecting a growing interest in unique flavors and local breweries. This segment indicates a significant trend towards moderation and variety in consumer choices.
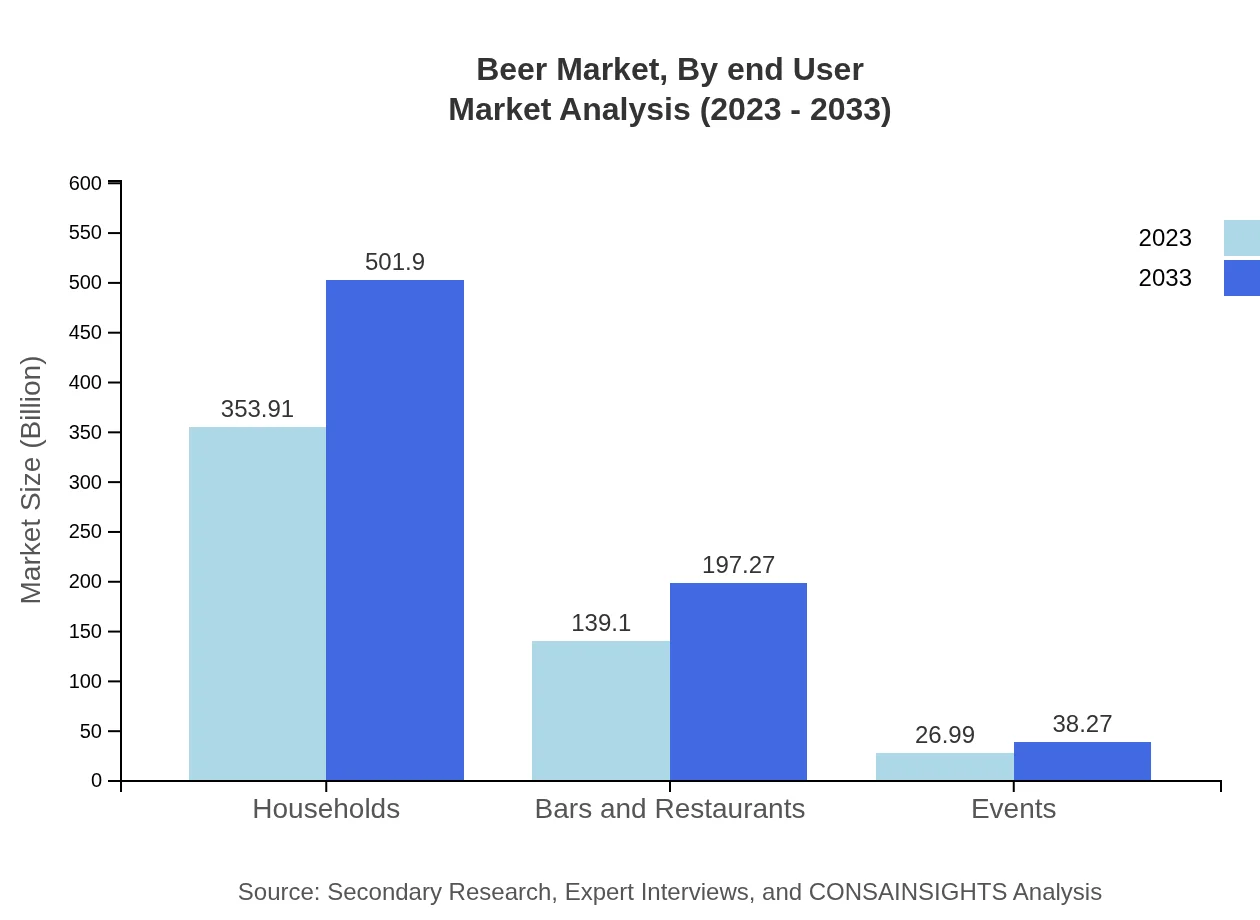
Beer Market Analysis By End User
Households represent the largest end-user segment, contributing significantly due to home consumption trends. The consumption in bars and restaurants is also vital, but the pandemic has accelerated the shift towards home consumption. The event sector is gradually recovering and shows promise as restrictions ease.
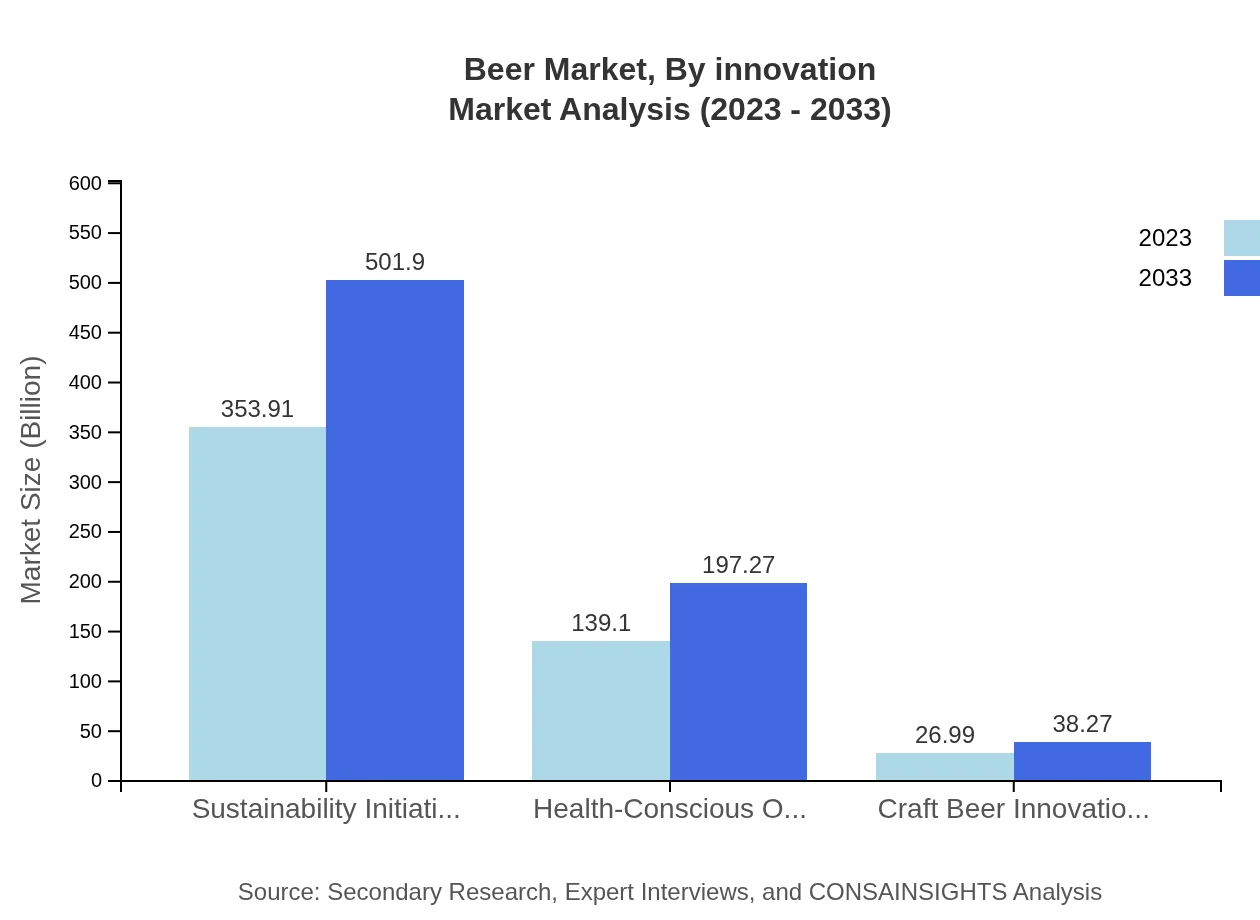
Beer Market Analysis By Innovation
Major trends include sustainable brewing practices, such as waste reduction and renewable energy usage. There’s also a focus on digital transformation and direct-to-consumer models, including e-commerce expansion, enabling breweries to reach consumers efficiently. Innovations in flavor, such as fruit infusions and new brewing techniques, underscore a competitive landscape.
Beer Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Beer Industry
Anheuser-Busch InBev:
As one of the largest brewing companies, Anheuser-Busch InBev operates a vast portfolio of brands, leading innovations in beer formulation and marketing strategies globally.Heineken N.V.:
Heineken is a key player in the global beer industry, renowned for its high-quality lagers and commitment to sustainable brewing practices across its operations.Diageo:
Recognized for its strong presence in both spirits and beer, Diageo focuses heavily on premium beers while also investing in sustainable and responsible drinking initiatives.Molson Coors Beverage Company:
This company produces iconic brands and is focusing on innovative brewing methods, especially in crafting low-calorie and low-alcohol beers to meet changing consumer preferences.Boston Beer Company:
Although smaller, Boston Beer Company is a leader in the craft beer market and has significantly influenced trends with its Samuel Adams range, focusing on quality and variety.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of beer?
The global beer market is valued at approximately $520 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 3.5% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the beer industry?
Key players in the beer industry include Anheuser-Busch InBev, Heineken N.V., Molson Coors Beverage Company, Carlsberg Group, and Diageo, which dominate various segments and markets globally.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the beer industry?
Key growth drivers include increasing consumer preference for craft and premium beers, innovative flavors, health-conscious options including low-alcohol beers, and sustainability initiatives by major breweries.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the beer market?
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for beer, expected to grow from $104.83 billion in 2023 to $148.67 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the beer industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the beer industry, tailored to specific business needs and insights required for targeted strategies.
What deliverables can I expect from this beer market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, segment performance details, competitor landscape insights, regional trends, and growth forecasts spanning a decade.
What are the market trends of beer?
Current trends in the beer market include the popularization of craft beers, a rise in health-conscious and sustainable products, innovative packaging solutions, and the integration of technology in brewing processes.