Beet Sugar Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: beet-sugar
Beet Sugar Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Beet Sugar market from 2023 to 2033, covering insights on market size, trends, segmentation, regional dynamics, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
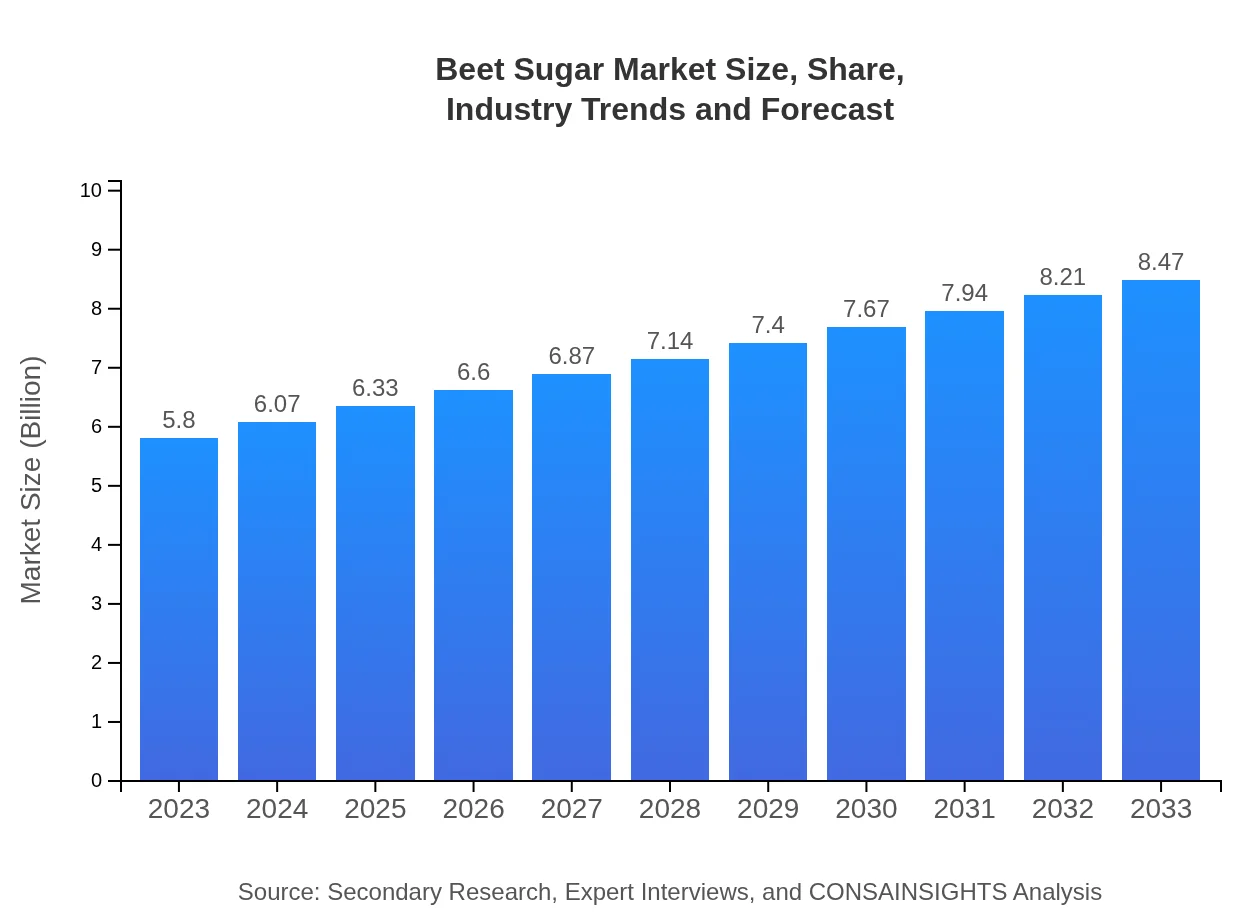
| 2023 Market Size | $5.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 3.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.47 Billion |
| Top Companies | American Crystal Sugar Company, Südzucker AG, Tereos SCA, Nordzucker AG |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Beet Sugar Market Overview
Customize Beet Sugar Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Beet Sugar market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Beet Sugar's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Beet Sugar
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Beet Sugar market in 2023?
Beet Sugar Industry Analysis
Beet Sugar Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Beet Sugar Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Beet Sugar Market Report:
The European market is set to expand from $1.62 billion in 2023 to $2.36 billion by 2033. Europe is a significant market for beet sugar, largely due to favorable agricultural conditions and strong demand from the confectionery and bakery sectors.Asia Pacific Beet Sugar Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market is projected to grow from $1.22 billion in 2023 to $1.78 billion in 2033. This growth is driven by dietary changes and the increasing adoption of organic products. Countries such as China and India are leading consumers, emphasizing local production capabilities and sustainable practices.North America Beet Sugar Market Report:
In North America, the market is projected to grow from $1.98 billion in 2023 to $2.89 billion by 2033. The rising demand for natural sweeteners and organic products, along with substantial investments in research and development, are key growth drivers.South America Beet Sugar Market Report:
The South America region is expected to see an increase from $0.38 billion in 2023 to $0.55 billion by 2033. The growing health awareness combined with enhanced agricultural practices and government support for sugar beet cultivation contributes to this growth.Middle East & Africa Beet Sugar Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is anticipated to rise from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $0.88 billion by 2033. The growth in this region is supported by increasing food retail channels and awareness of health benefits associated with beet sugar.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Beet Sugar Market Analysis By Product
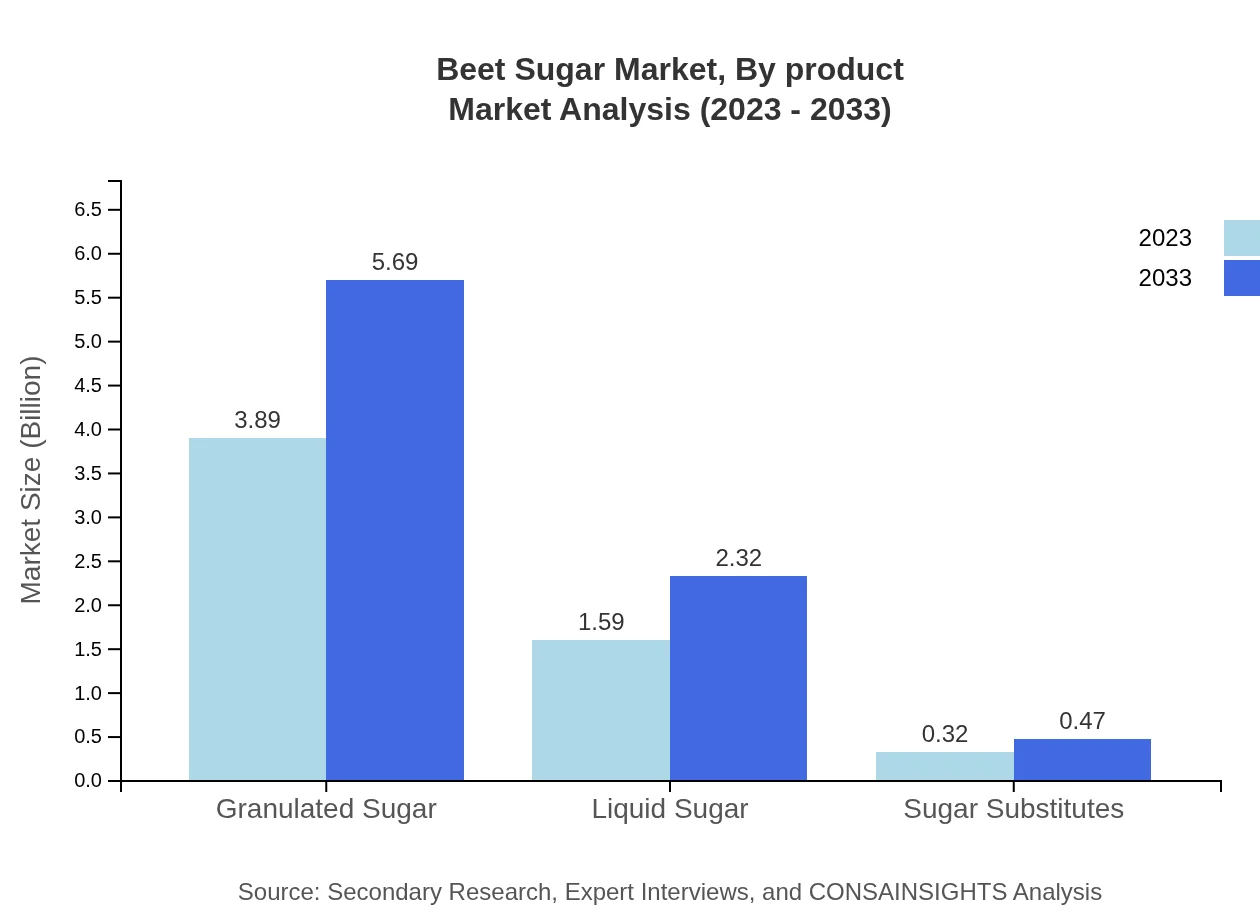
The beet sugar market is predominantly segmented into granulated sugar, liquid sugar, and sugar substitutes. Granulated sugar holds the largest market share, growing from $3.89 billion in 2023 to $5.69 billion in 2033, constituting 67.12% of the market. Liquid sugar is also gaining traction due to its versatility in food manufacturing and is expected to grow from $1.59 billion to $2.32 billion over the same period. Sugar substitutes are a smaller segment, growing steadily from $0.32 billion to $0.47 billion as health-conscious consumers seek alternatives.
Beet Sugar Market Analysis By Application
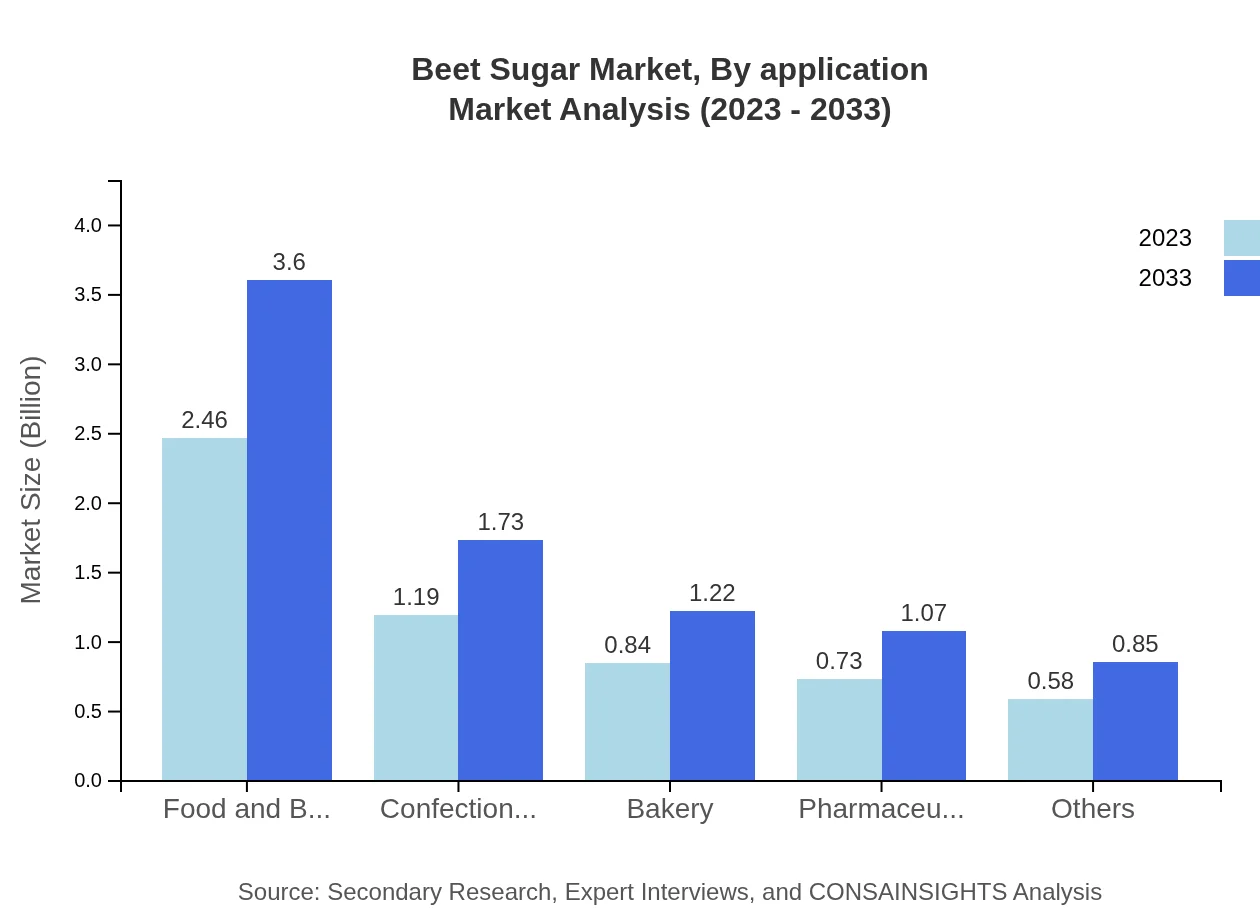
The application segment highlights the extensive use of beet sugar in the food and beverages, confectionery, and baking industries. The food and beverages sector is significant, projected to climb from $2.46 billion in 2023 to $3.60 billion in 2033, representing 42.49% of the market share. The confectionery sector is also notable, with expected growth from $1.19 billion to $1.73 billion, driven by the demand for quality products and innovative offerings.
Beet Sugar Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
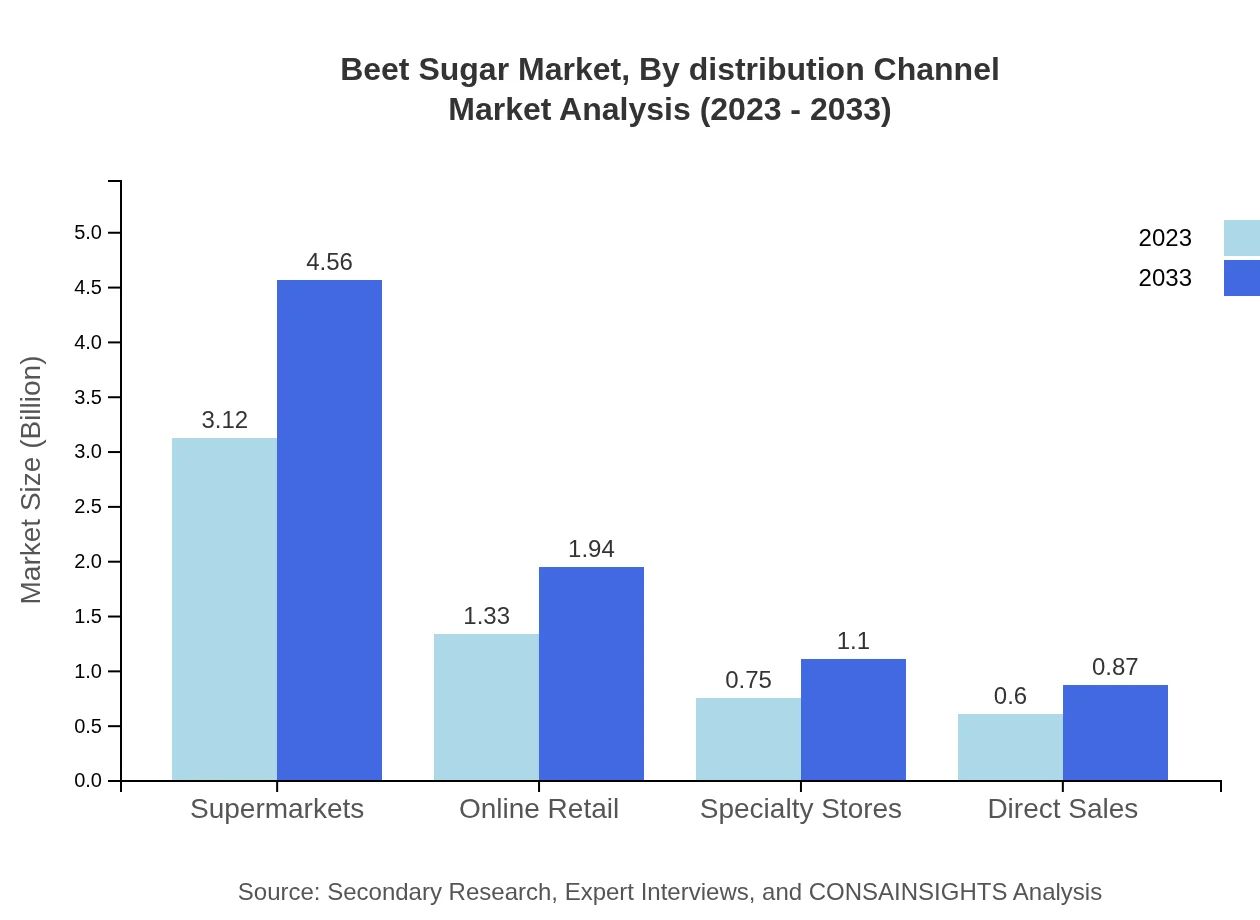
The distribution channels for beet sugar include supermarkets, online retail, and specialty stores. Supermarkets remain the dominant channel, with market size expected to increase from $3.12 billion in 2023 to $4.56 billion by 2033, reflecting 53.85% share. Online retail is on the rise as consumer preferences shift, projected to rise from $1.33 billion to $1.94 billion, indicating a growing trend towards convenient shopping experiences.
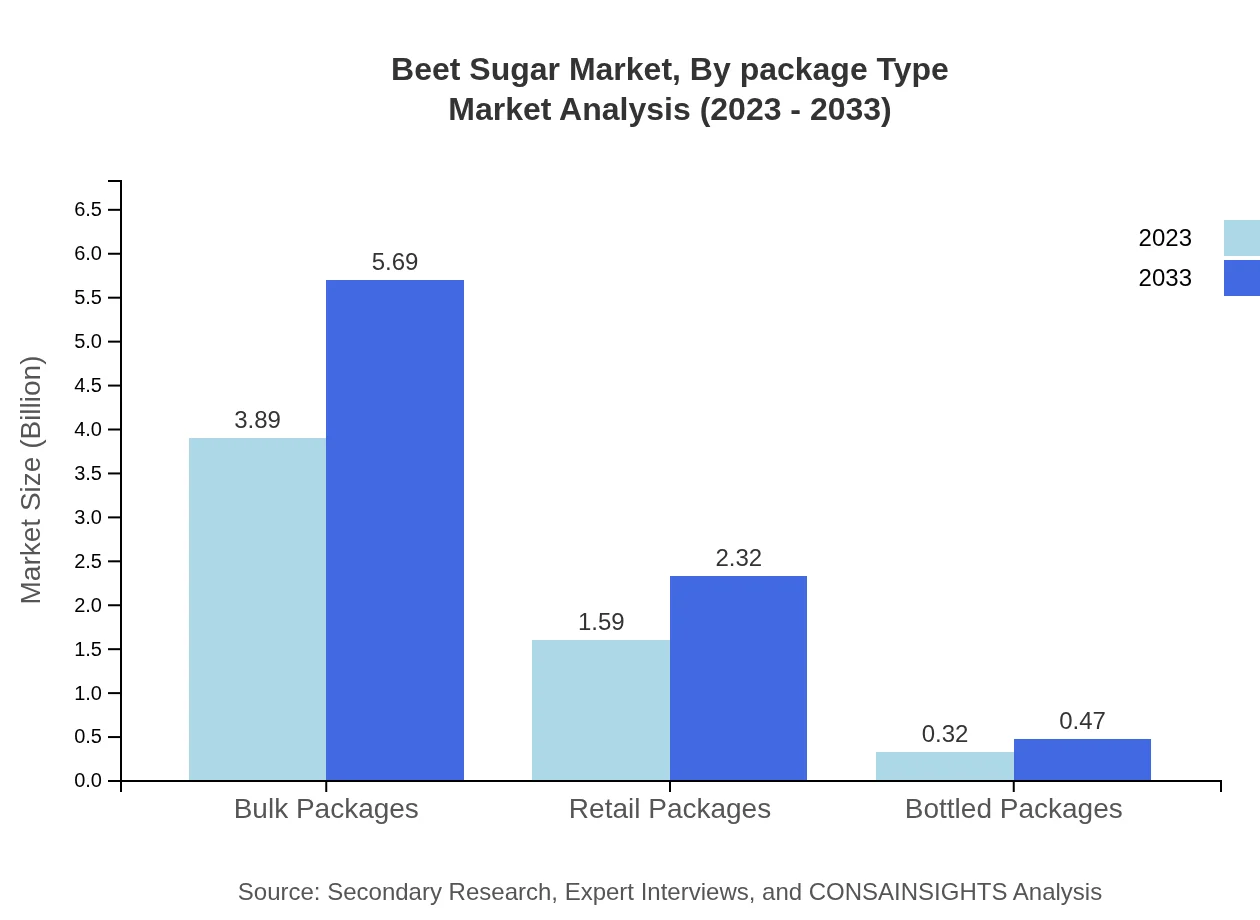
Beet Sugar Market Analysis By Package Type
Packaging plays a crucial role in the beet sugar market, with bulk packages and retail packages being the most significant. Bulk packages currently dominate the market and will increase from $3.89 billion to $5.69 billion by 2033, aligning with professional use in food services. Retail packages are also significant, increasing from $1.59 billion to $2.32 billion as consumer preference shifts towards convenient, pre-packaged units.
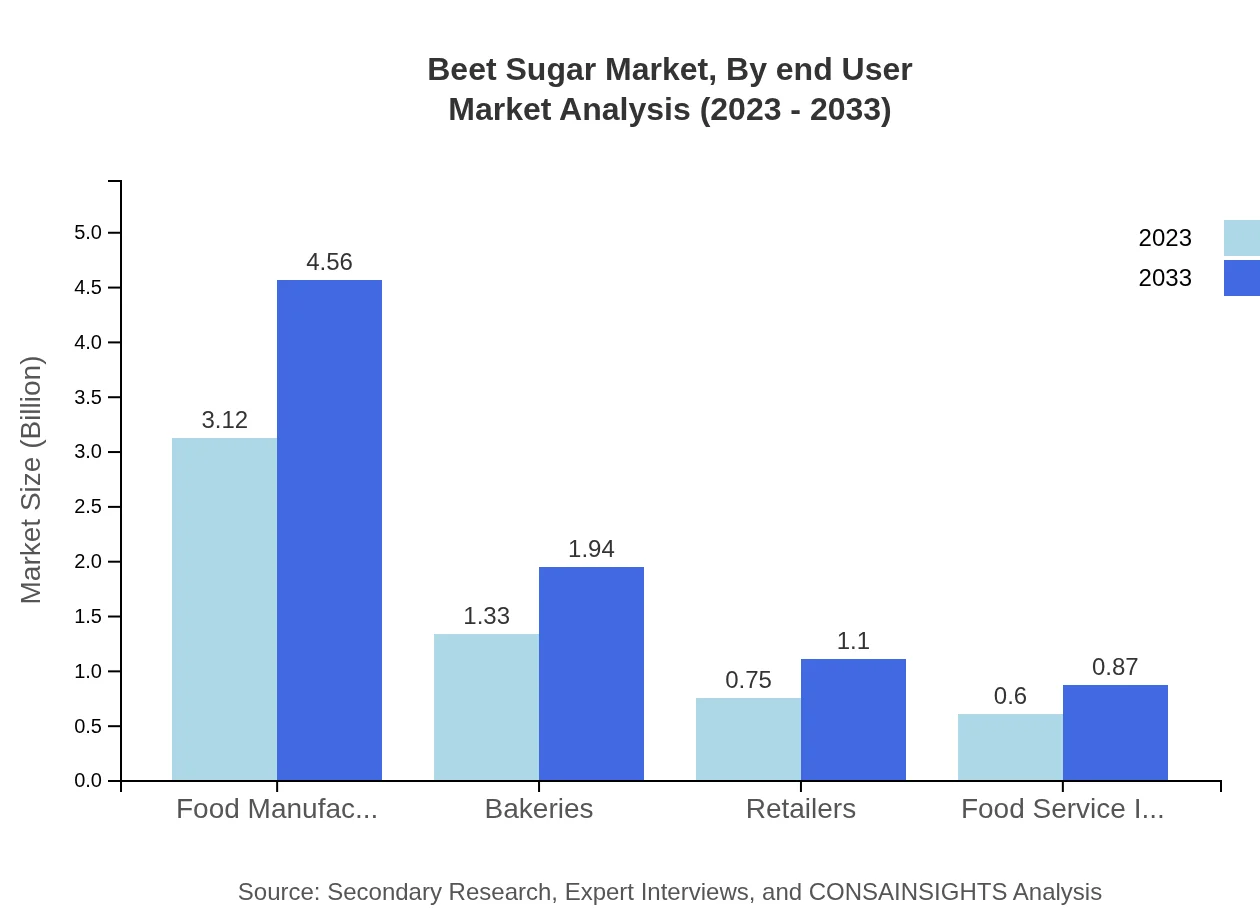
Beet Sugar Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment includes food manufacturers, bakeries, retailers, and the food service industry. Food manufacturers are the largest end-user, expected to grow from $3.12 billion to $4.56 billion, constituting 53.85% market share. Bakeries and the food service industry also represent substantial opportunities, transitioning as trends towards organic and naturally sweetened products continue to gain traction.
Beet Sugar Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Beet Sugar Industry
American Crystal Sugar Company:
A leading grower and processor of sugar beets, American Crystal Sugar holds significant market share in the United States and focuses on sustainable production practices.Südzucker AG:
Europe’s largest sugar producer, Südzucker AG is involved in sugar beet cultivation and processing, providing a range of sugar products to meet diverse market needs.Tereos SCA:
Headquartered in France, Tereos is a global player in the sugar market with a strong presence in beet sugar processing and commitment to sustainable agriculture.Nordzucker AG:
Nordzucker operates one of Europe's largest sugar beet processing systems, focusing on the production of high-quality beet sugar products.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of beet Sugar?
The global beet sugar market size is valued at approximately $5.8 billion in 2023, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8%, indicating strong growth potential in the coming years.
What are the key market players or companies in the beet Sugar industry?
Key market players in the beet sugar industry include major companies such as Südzucker AG, American Crystal Sugar Company, and Cargill, among others, which dominate the market and influence trends in production and distribution.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the beet Sugar industry?
Growth is primarily driven by increasing demand for sugar in food and beverages, rising health consciousness encouraging the use of sugar substitutes, and innovations in sugar production processes to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the beet Sugar market?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the beet sugar market, projected to expand from $1.98 billion in 2023 to $2.89 billion by 2033, due to increasing consumer preferences and a growing food service industry.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the beet Sugar industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the beet-sugar industry, helping clients understand market dynamics and make informed business decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this beet Sugar market research project?
Deliverables from the beet-sugar market research project typically include comprehensive market analysis reports, detailed forecasts, segment breakdowns, and insights into competitive landscape and consumer behavior.
What are the market trends of beet sugar?
Current trends in the beet sugar market include a shift towards organic and natural sugar alternatives, increased consumer awareness regarding health impacts, and growth in online retail channels for sugar products.