Big Data In Power Sector Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: big-data-in-power-sector
Big Data In Power Sector Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Big Data in the Power Sector market, providing insights about market trends, size, segmentation, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
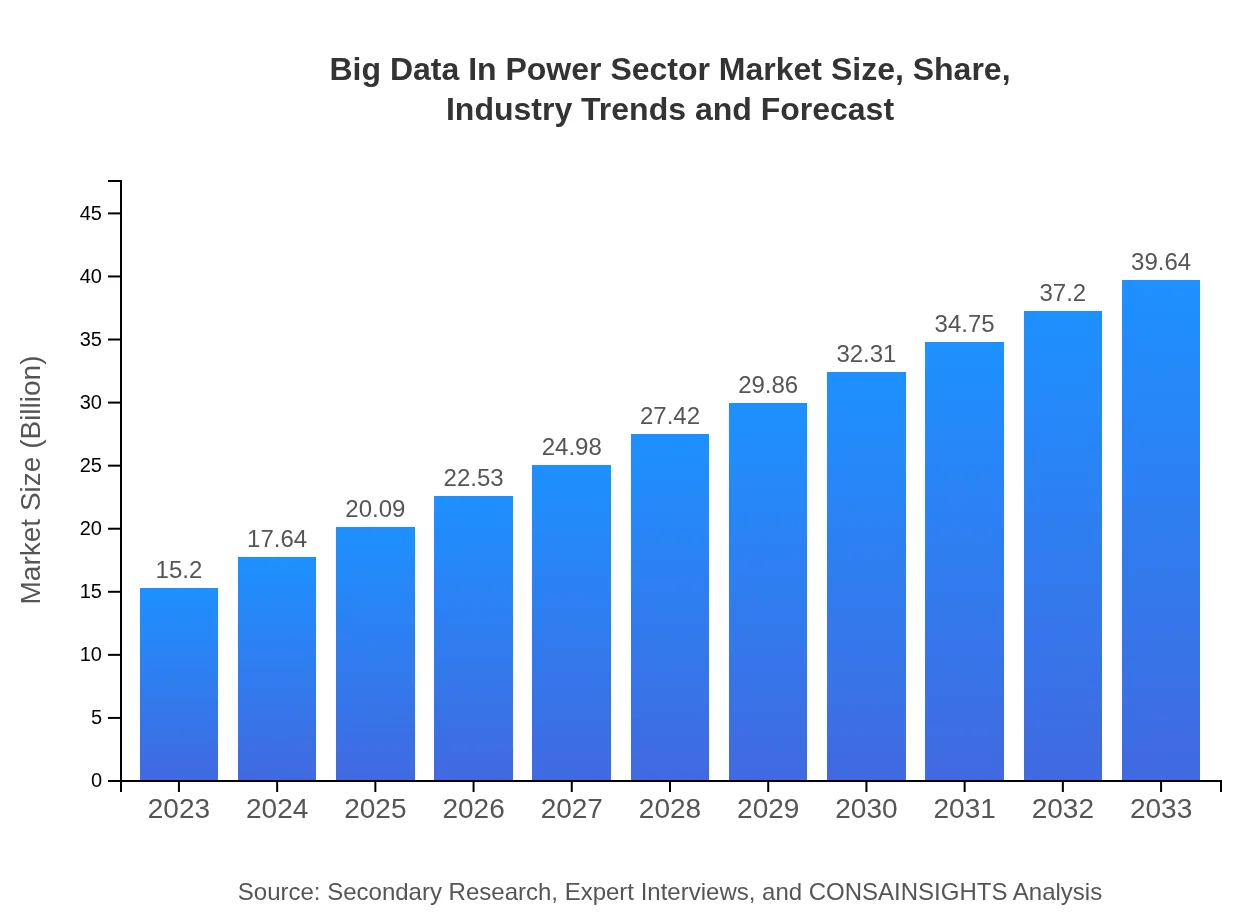
| 2023 Market Size | $15.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $39.64 Billion |
| Top Companies | IBM, Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric (GE), Oracle Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Big Data In Power Sector Market Overview
Customize Big Data In Power Sector Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Big Data In Power Sector market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Big Data In Power Sector's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Big Data In Power Sector
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Big Data In Power Sector market in 2023?
Big Data In Power Sector Industry Analysis
Big Data In Power Sector Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Big Data In Power Sector Market Report:
Europe's market size is projected to grow from USD 5.69 billion in 2023 to USD 14.85 billion by 2033. The EU’s stringent regulations on emissions and the increasing reliance on renewable energy sources drive the need for effective data management solutions to comply with environmental standards.Asia Pacific Big Data In Power Sector Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Big Data in Power Sector market is set to grow from USD 2.45 billion in 2023 to USD 6.38 billion by 2033, driven by industrialization and urbanization. Countries like China and India are rapidly adopting big data solutions to streamline energy management processes amid rising energy demands.North America Big Data In Power Sector Market Report:
In North America, the market will expand from USD 4.94 billion in 2023 to USD 12.88 billion in 2033. The region is at the forefront of adopting big data solutions, influenced by technological advancements and a strong focus on sustainability, which necessitates efficient energy management practices.South America Big Data In Power Sector Market Report:
South America, though emerging in this sector, is expected to grow from USD 0.64 billion in 2023 to USD 1.67 billion by 2033. The region's focus on expanding renewable energy initiatives will significantly boost the deployment of big data analytics in optimizing energy consumption and integration.Middle East & Africa Big Data In Power Sector Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are anticipated to grow from USD 1.48 billion in 2023 to USD 3.86 billion by 2033, with increasing investments in energy diversification and smart technologies, enhancing the region's capability to adopt big data initiatives in the power sector.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis By Technology
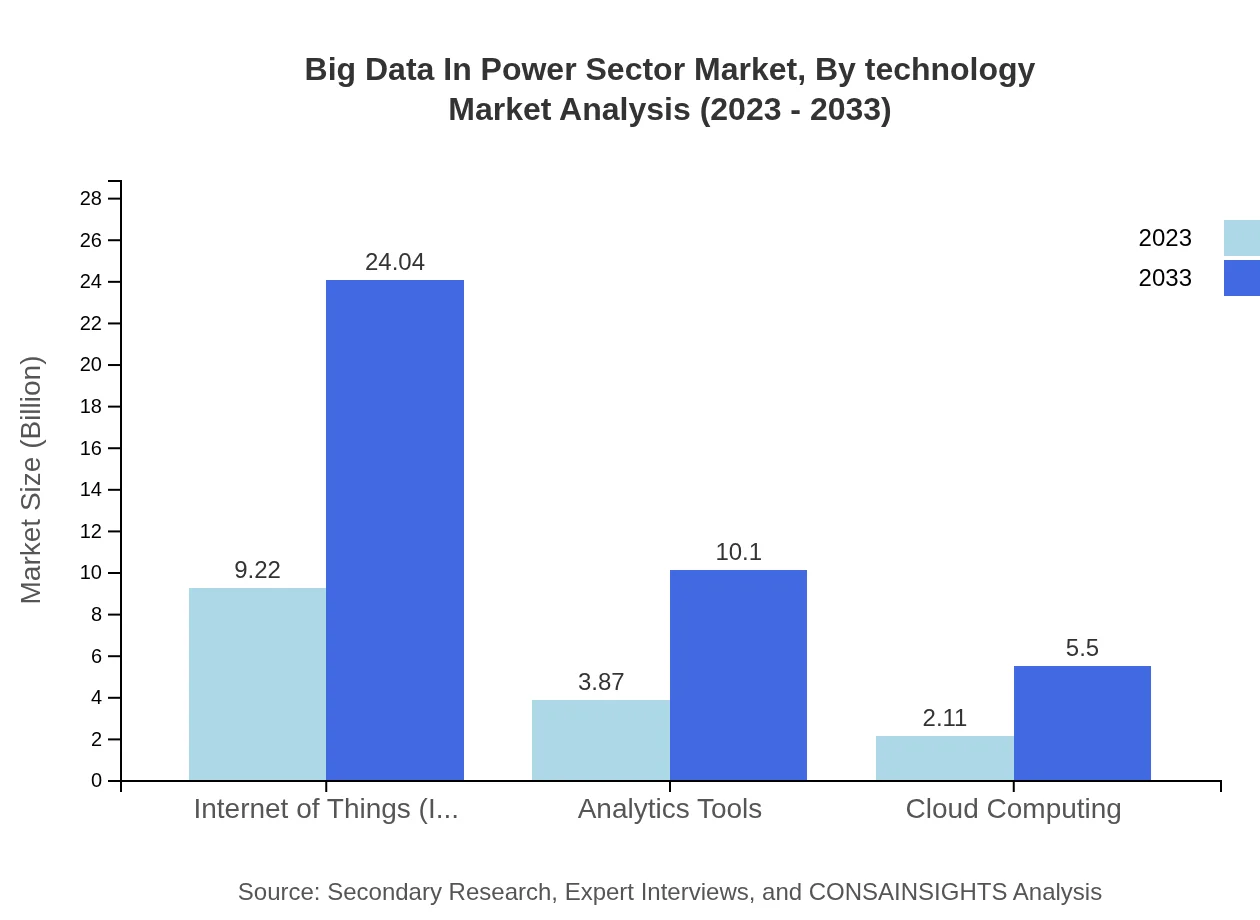
The analysis of the Big Data in Power Sector market reveals significant growth within various technology segments. In particular, the Internet of Things (IoT) segment will grow from USD 9.22 billion in 2023 to USD 24.04 billion by 2033, holding a share of 60.65% by 2033. Analytics tools, cloud computing, and energy management also contribute significantly, with respective growth projections of USD 3.87 billion to USD 10.10 billion and USD 2.11 billion to USD 5.50 billion in the same period.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis By Applications
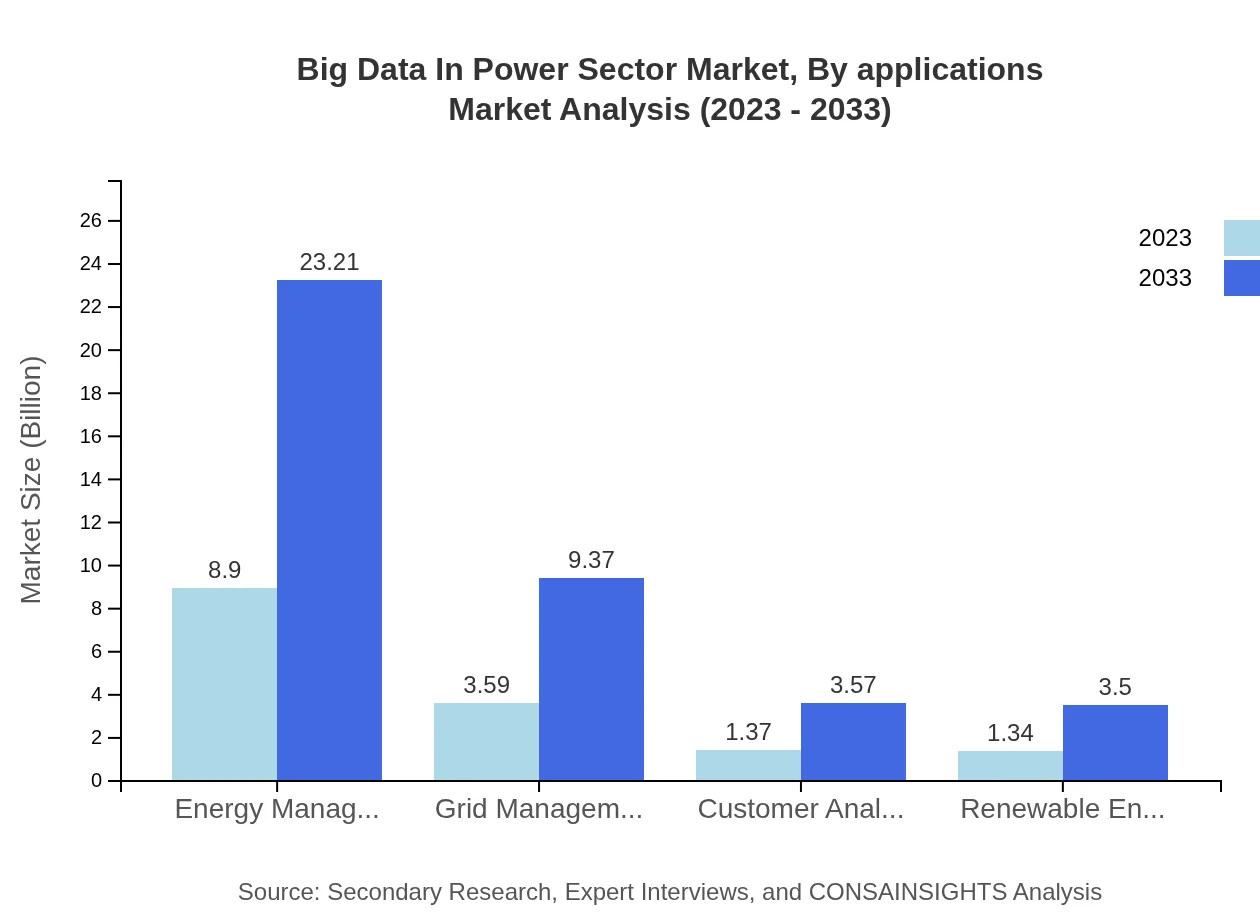
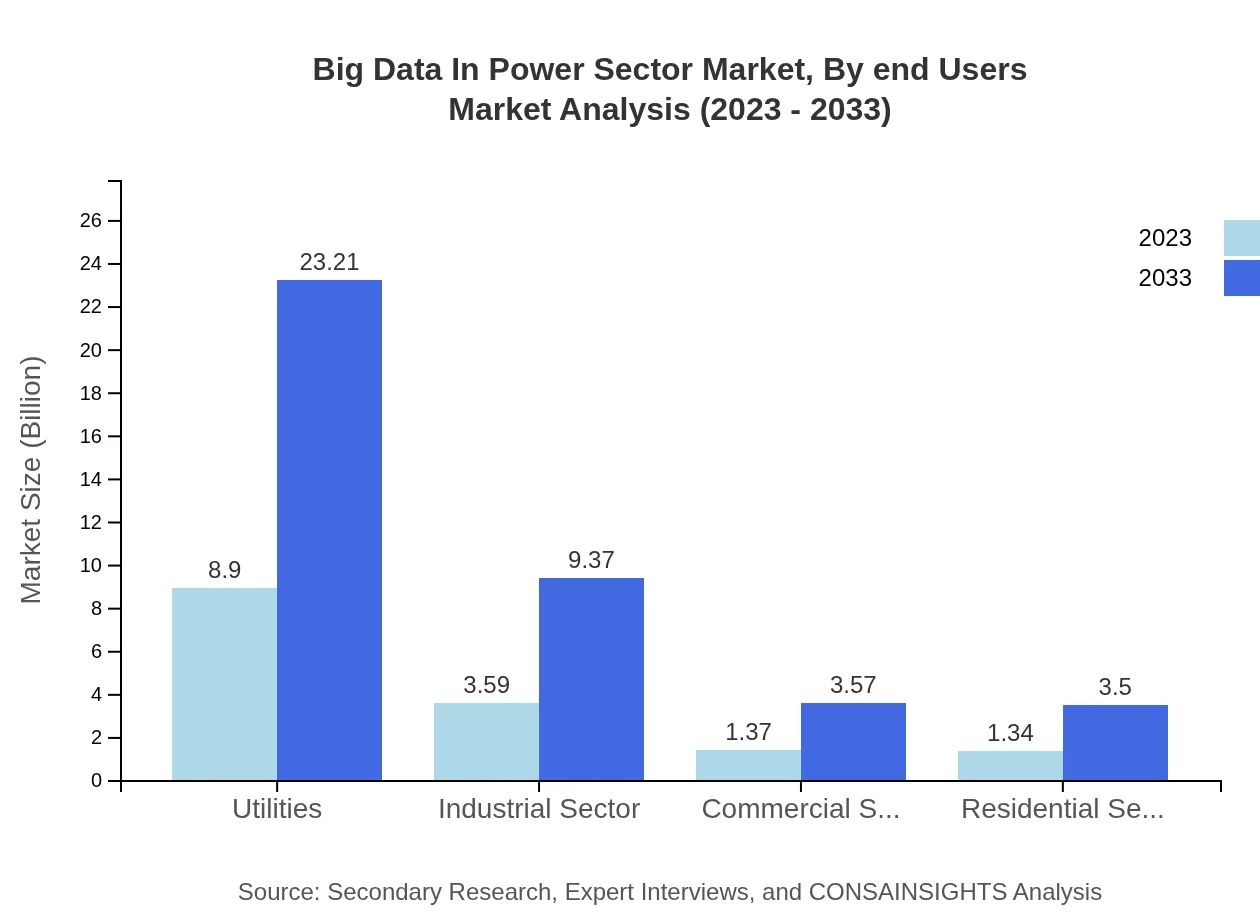
In terms of applications, utilities remain the core area with a market size from USD 8.90 billion in 2023 to USD 23.21 billion by 2033, maintaining an impressive market share of 58.55%. The industrial sector increases from USD 3.59 billion to USD 9.37 billion with a 23.63% share, while the commercial and residential sectors also depict steady growth, indicating the widespread applicability of big data solutions across energy management spheres.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
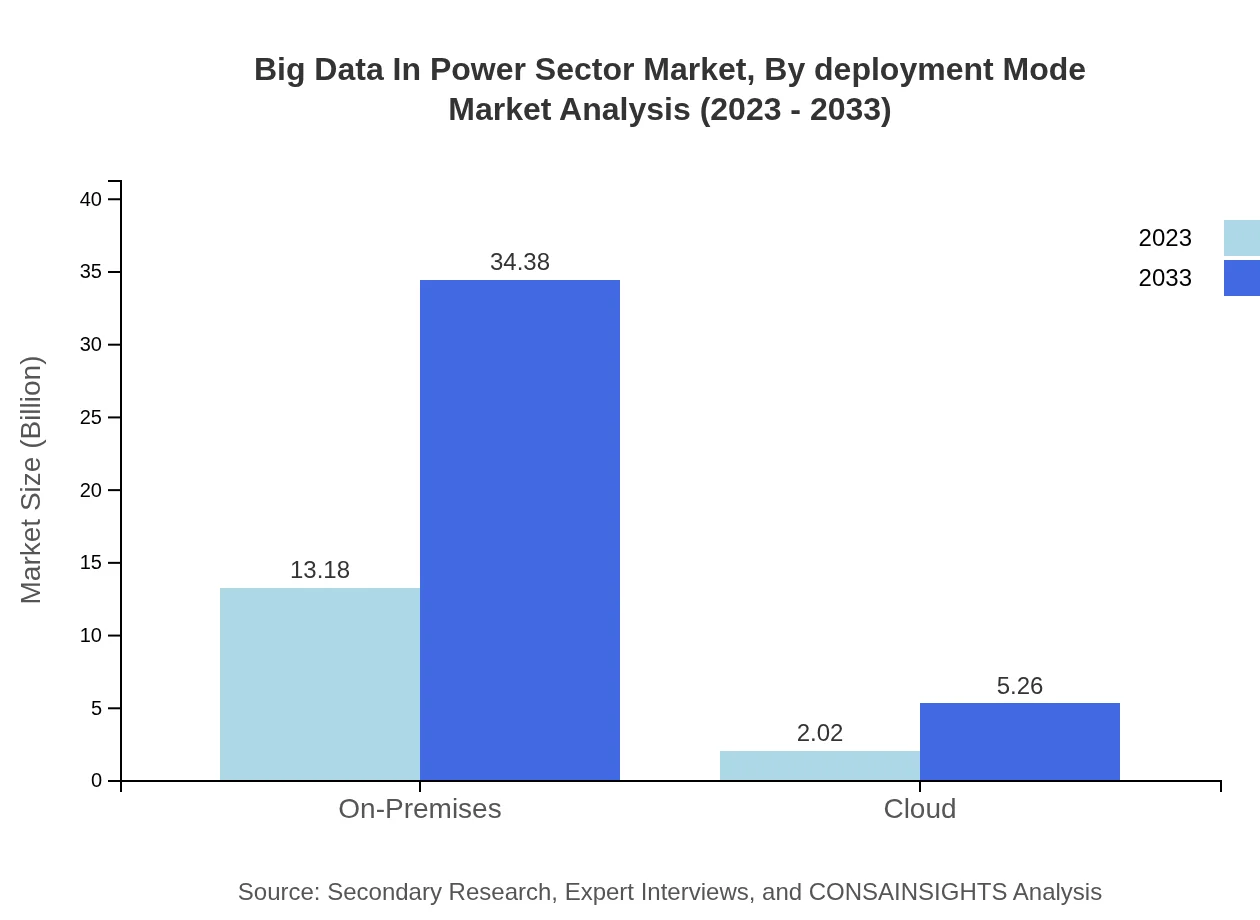
The market for Big Data in the Power Sector is segmented into On-Premises and Cloud deployment modes. The On-Premises solution dominates the market with a size of USD 13.18 billion in 2023 and projected growth to USD 34.38 billion by 2033, while Cloud solutions span from USD 2.02 billion to USD 5.26 billion, reflecting the shift towards flexible, scalable solutions.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis By End Users
The end-user segmentation clearly indicates that utility companies drive the demand for big data solutions. This sector is projected to cover 58.55% by 2033. Other users, including industrial and commercial sectors, will also contribute substantially, with increasing investments in data-driven operational enhancements.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Analysis By Issues And Challenges
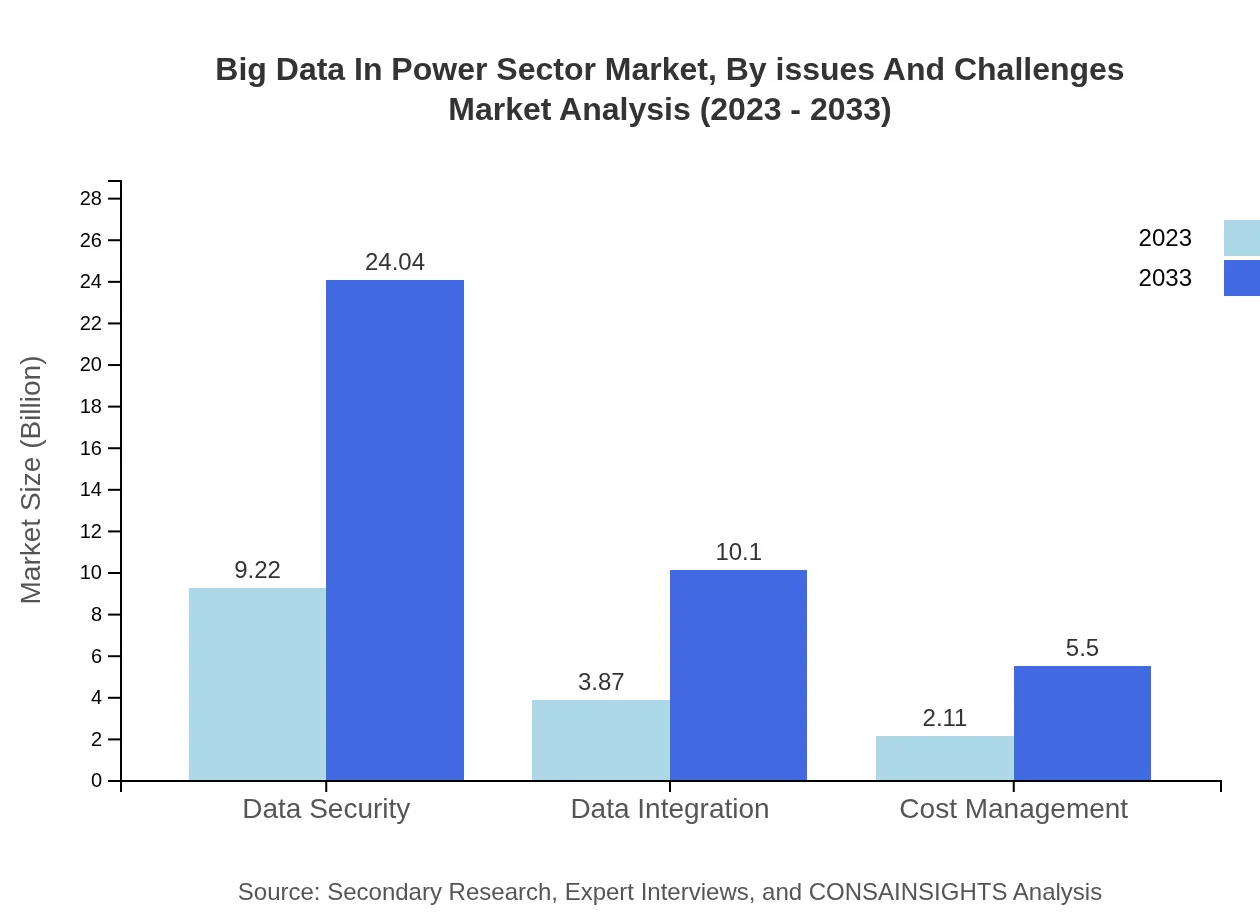
Challenges in the Big Data in Power Sector include data security, privacy, and integration. As organizations handle vast volumes of sensitive consumer and infrastructure data, regulatory compliance becomes paramount. Furthermore, integrating new data solutions with legacy systems poses significant obstacles for many power sector players.
Big Data In Power Sector Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Big Data In Power Sector Industry
IBM:
IBM provides innovative big data solutions that enhance operational efficiency for energy companies through analytics and cloud technology.Siemens AG:
Siemens offers comprehensive digital solutions encompassing big data analytics, aiding power sector organizations to optimize their grid management.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric specializes in energy management and automation solutions, utilizing big data to enhance operational sustainability.General Electric (GE):
GE integrates big data with industrial internet applications, optimizing energy production and consumption models across the power sector.Oracle Corporation:
Oracle delivers advanced analytics and cloud solutions that facilitate sophisticated data management for power sector clients.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Big Data in Power Sector?
The Big Data in Power Sector market is currently valued at approximately $15.2 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 9.7%, indicating robust growth as the industry adapts to data-driven technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in this Big Data in Power Sector industry?
Key players in the Big Data in Power Sector include leading tech giants and specialized firms focusing on analytics, IoT solutions, and cloud computing technologies tailored to enhance energy efficiency and grid management.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Big Data in Power Sector industry?
Growth in this sector is primarily fueled by increasing energy demand, regulatory incentives for renewable energy, advancements in IoT and AI technologies, and the urgent need for efficient energy management solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Big Data in Power Sector?
Europe is the fastest-growing region with a market growth from $5.69 billion in 2023 to $14.85 billion by 2033, closely followed by Asia Pacific, expanding from $2.45 billion to $6.38 billion in the same timeframe.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Big Data in Power Sector industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific business needs, providing in-depth insights and analyses applicable to the Big Data in Power Sector.
What deliverables can I expect from this Big Data in Power Sector market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market reports, detailed market segmentation analyses, competitive landscape evaluations, and tailored insights to support strategic business decisions in the Big Data in Power Sector.
What are the market trends of Big Data in Power Sector?
Current market trends include increased adoption of IoT solutions, significant investments in data security and analytics tools, and a shift towards cloud computing, which is shaping the future of the Power Sector.