Biobanking Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: biobanking
Biobanking Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global biobanking market, encompassing trends, forecasts, and insights tailored for the period from 2023 to 2033. It highlights critical data points, regional dynamics, and industry analysis essential for stakeholders in the biobanking sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
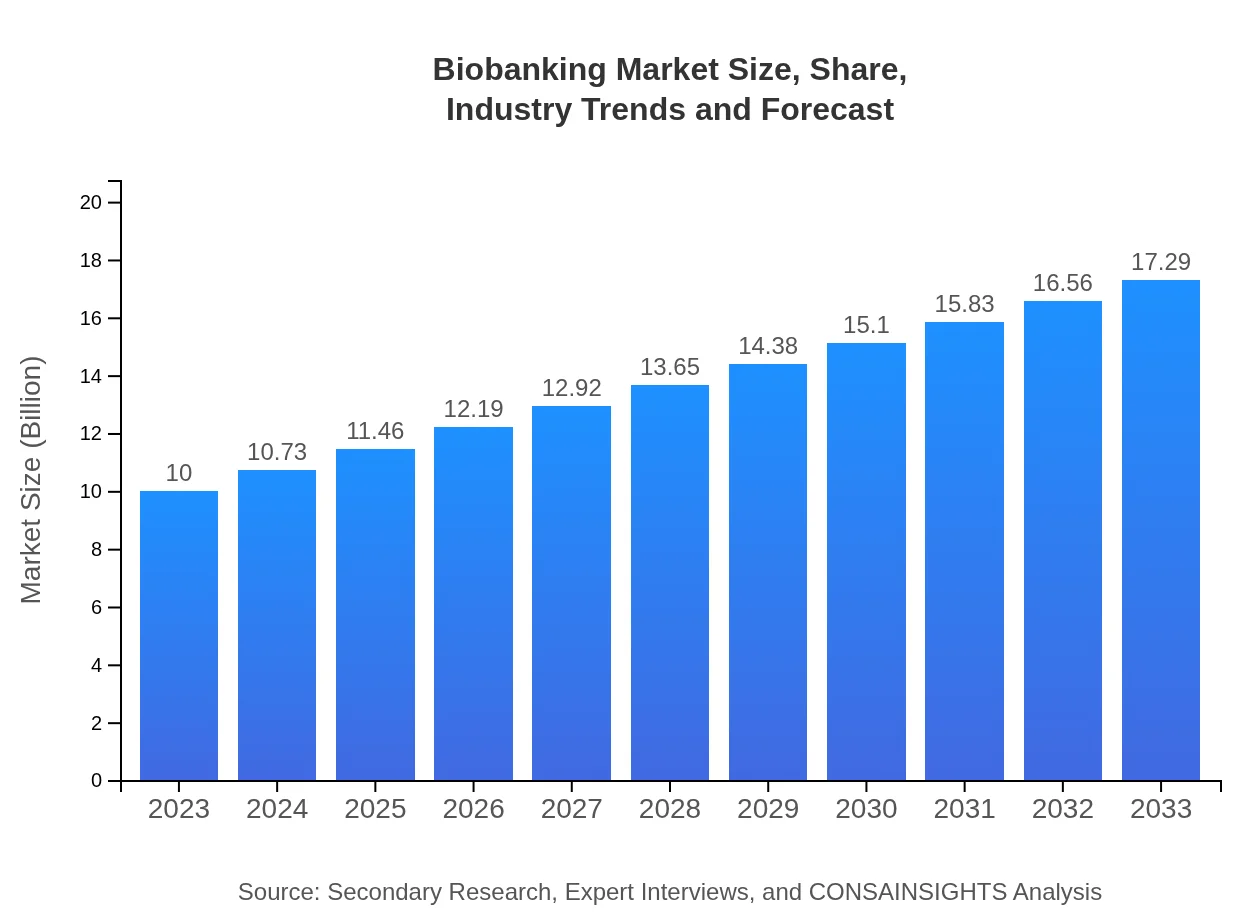
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $17.29 Billion |
| Top Companies | BD Biosciences, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen , Eppendorf AG, VWR International LLC |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Biobanking Market Overview
Customize Biobanking Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Biobanking market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Biobanking's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Biobanking
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Biobanking market in 2023?
Biobanking Industry Analysis
Biobanking Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Biobanking Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Biobanking Market Report:
The European biobanking market is currently valued at approximately $3.25 billion, projected to grow to $5.62 billion by 2033. The market is driven by extensive academic research, progressive legislation regarding biobanking practices, and collaborations among research institutions and biotechnology firms in countries like Germany, France, and the UK.Asia Pacific Biobanking Market Report:
The Asia Pacific biobanking market, valued at $1.85 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $3.20 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust growth trajectory. Significant investments in research initiatives and increasing collaboration between healthcare and academic sectors are driving this growth. Countries like Japan, China, and India are becoming influential players in biobanking.North America Biobanking Market Report:
North America represents a significant portion of the global biobanking market, with an estimated size of $3.63 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach $6.28 billion by 2033. The region's leadership in biotechnological advancements and strong funding for research projects, particularly in the U.S. and Canada, have led to substantial investments in biobanking operations.South America Biobanking Market Report:
In South America, the biobanking market is expected to grow from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $1.03 billion by 2033. Factors such as rising healthcare expenditure, growing biopharmaceutical industries, and governmental emphasis on healthcare innovations are contributing to expanding biobanking initiatives across the region.Middle East & Africa Biobanking Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are gradually emerging as key regions for biobanking, with the market estimated at $0.67 billion in 2023, likely reaching $1.16 billion by 2033. Government initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure, coupled with rising awareness about the importance of biobanking in clinical research, are pivotal in driving market growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
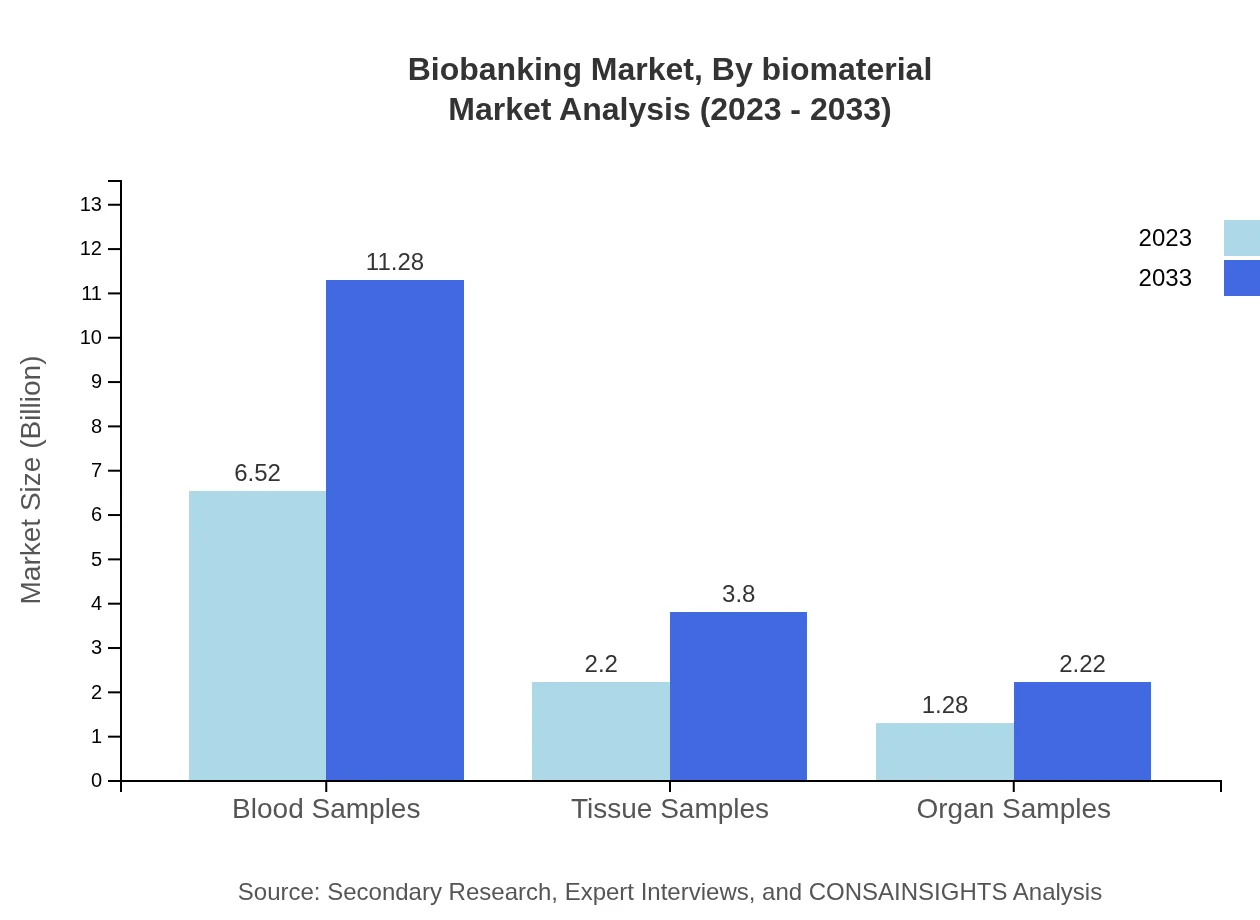
Biobanking Market Analysis By Biomaterial
In terms of biomaterials, the biobanking market is significantly driven by blood samples, which accounted for $6.52 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow to $11.28 billion by 2033. Tissue samples and organ samples also play pivotal roles, with tissue samples generating $2.20 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $3.80 billion by 2033, while organ samples projected to grow from $1.28 billion to $2.22 billion in the same timeframe.
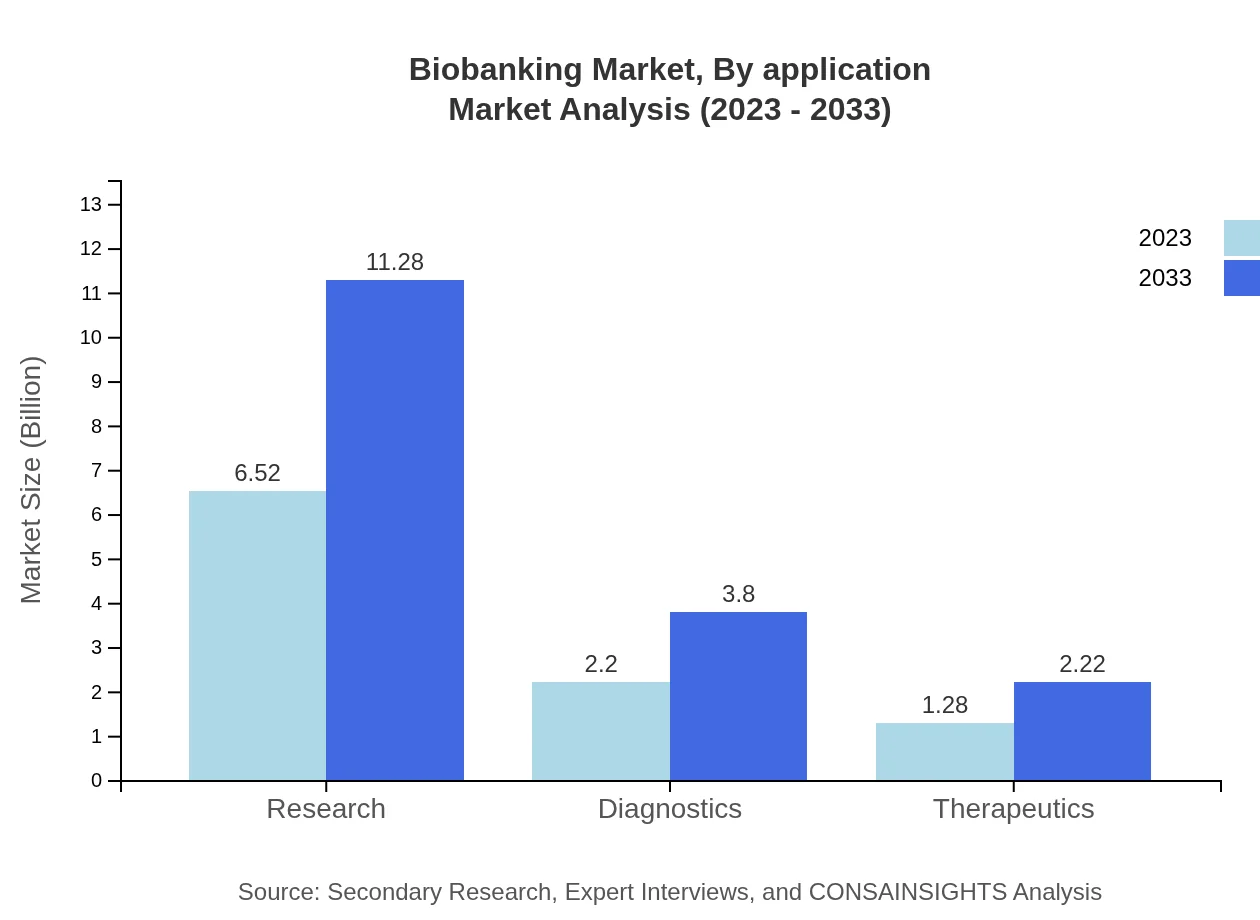
Biobanking Market Analysis By Application
The research application in the biobanking market is prominent, valued at approximately $6.52 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $11.28 billion by 2033. Diagnostics and therapeutics follow suit, with diagnostics starting at $2.20 billion and expected to rise to $3.80 billion, while therapeutics will grow from $1.28 billion to $2.22 billion during the same period.
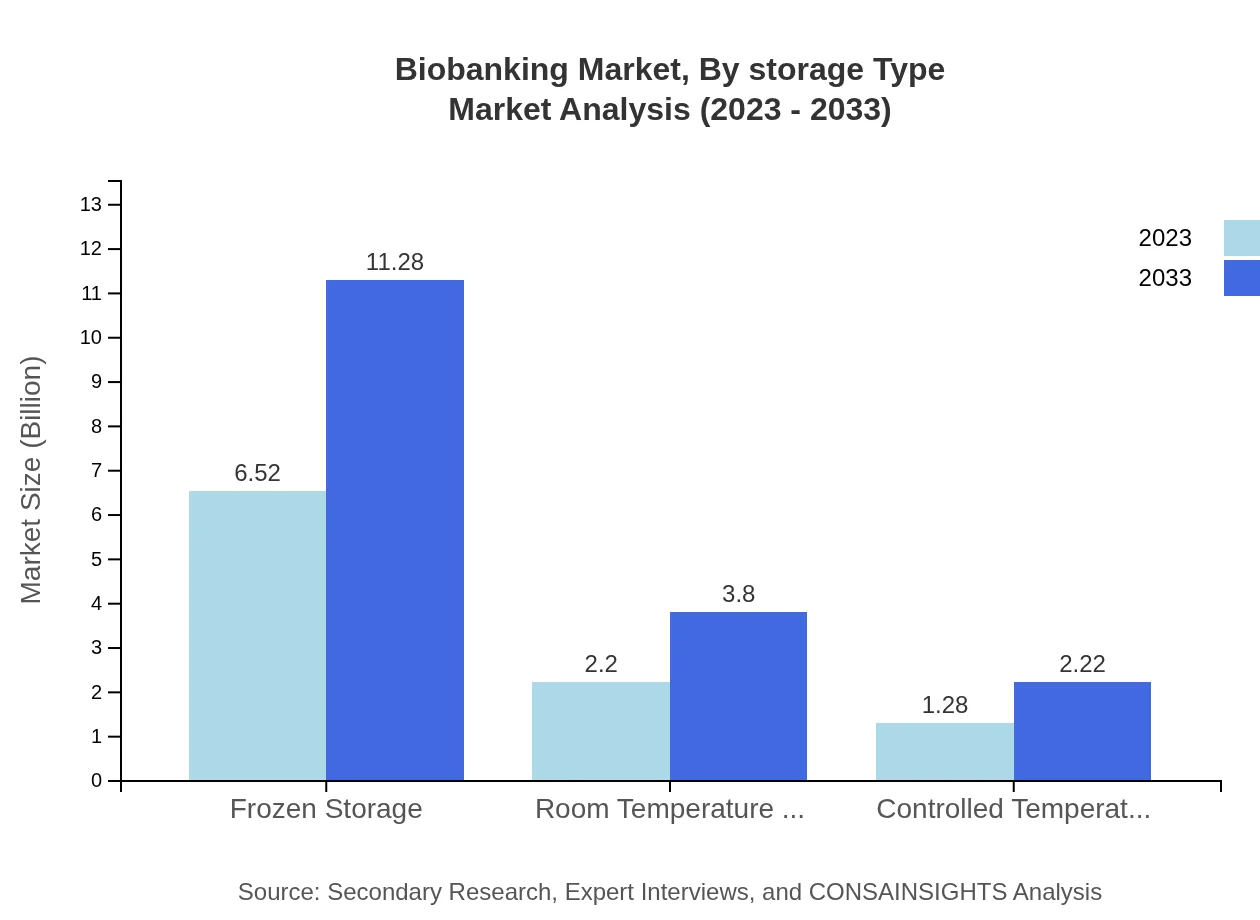
Biobanking Market Analysis By Storage Type
Preferring frozen storage technology, the market is estimated at $6.52 billion in 2023, projected to increase to $11.28 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, room temperature storage holds a market size of $2.20 billion and is expected to grow to $3.80 billion, emphasizing the varied methodologies of sample preservation available in biobanking.
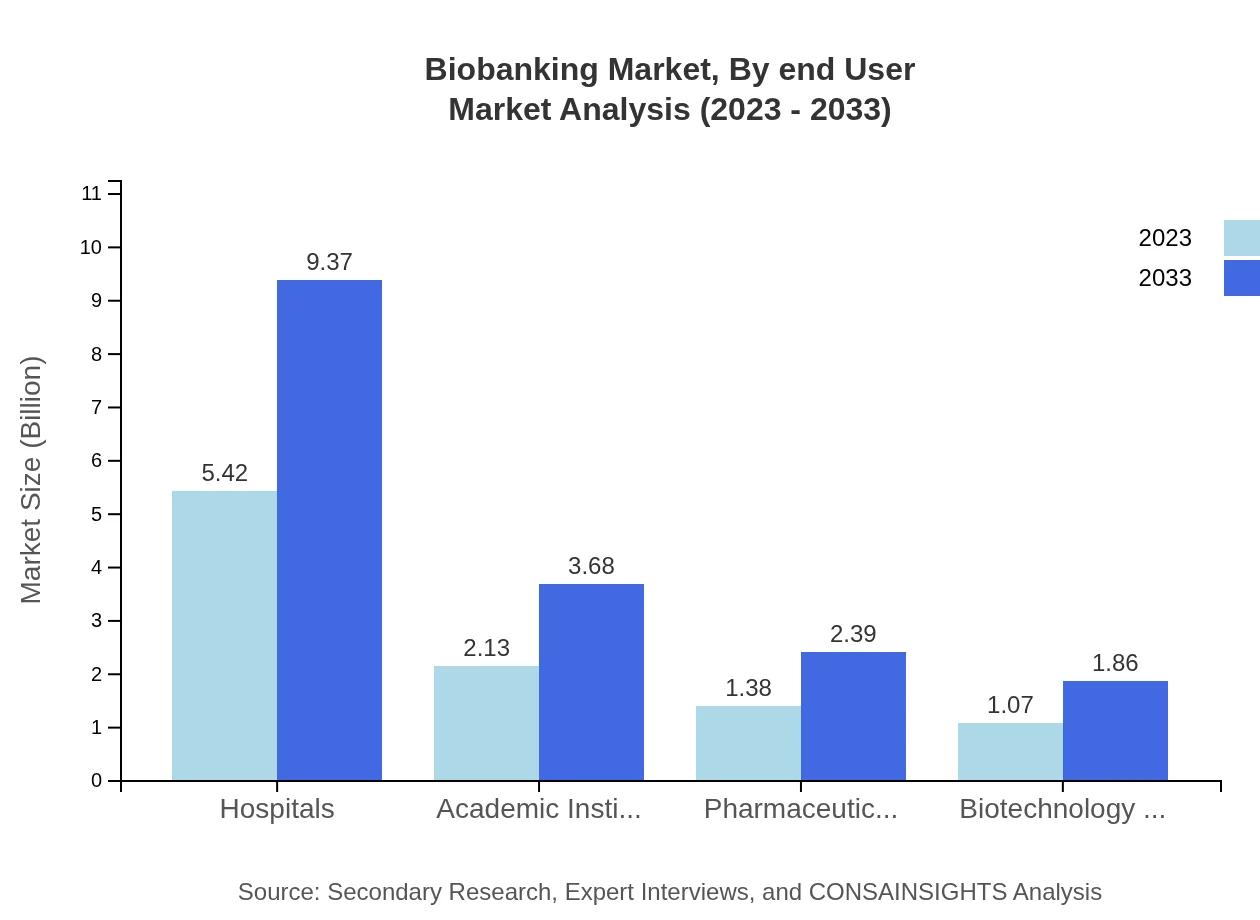
Biobanking Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals dominate the biobanking market, representing a value of $5.42 billion in 2023 with a forecasted rise to $9.37 billion by 2033. Academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies hold significant shares too, contributing $2.13 billion and $1.38 billion in 2023, respectively. Their importance is underscored by their roles in research and therapeutic developments.
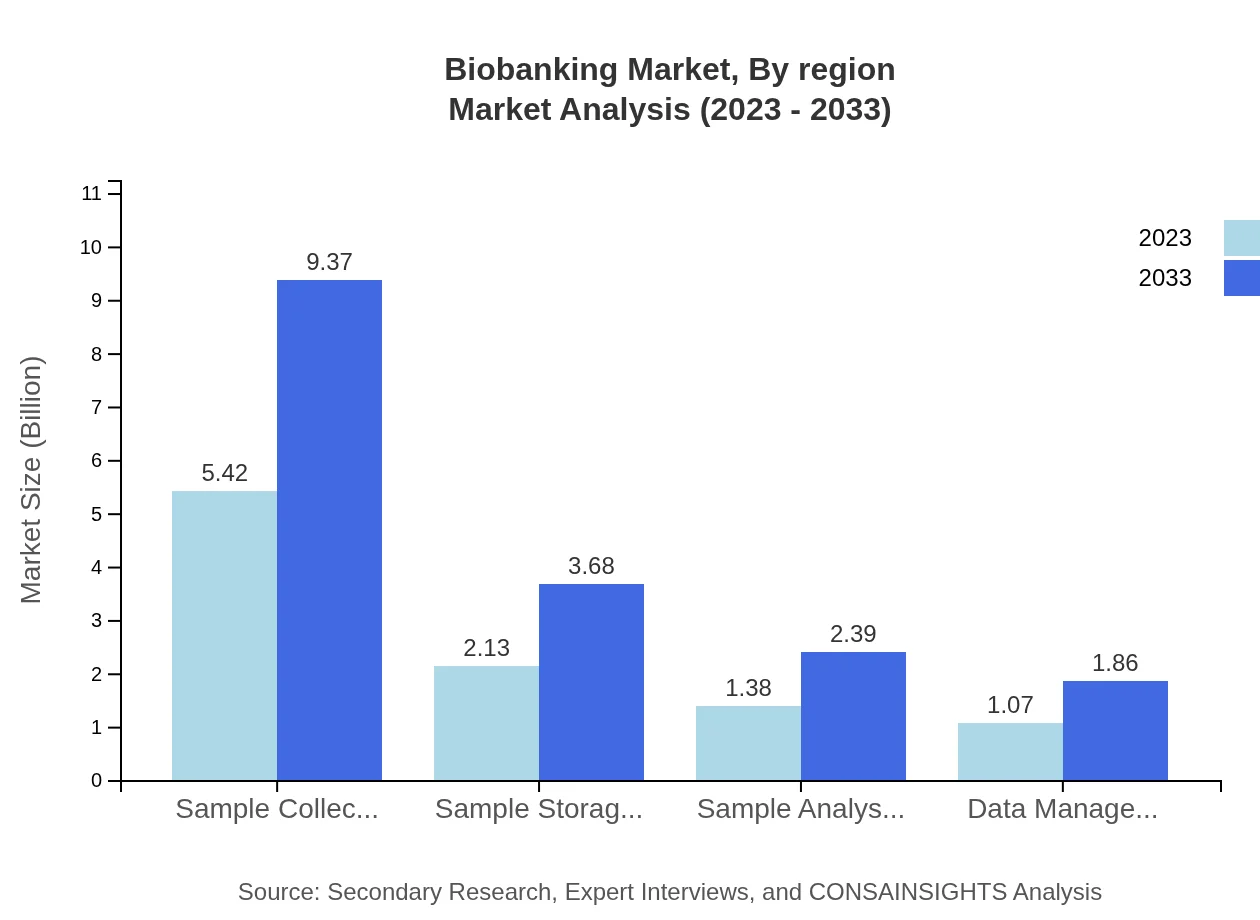
Biobanking Market Analysis By Region
Technology-driven analysis indicates that sample collection technologies command a substantial share of the market, valued at $5.42 billion in 2023, projected to reach $9.37 billion by 2033. Data management solutions are also pivotal, growing from $1.07 billion to $1.86 billion, reflecting the technological advancements in biobanking.
Biobanking Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Biobanking Industry
BD Biosciences:
A leader in the development of innovative technologies for the collection and preparation of biological samples, BD Biosciences provides solutions that enhance the efficiency of biobanks globally.Thermo Fisher Scientific:
Known for its extensive portfolio of biobank reagents and equipment, Thermo Fisher Scientific is at the forefront of biobanking technology, enabling researchers to accelerate their studies.Qiagen :
Qiagen specializes in sample and assay technologies, providing integrated solutions that are essential for biobanking, including sample preparation and management tools.Eppendorf AG:
Eppendorf is renowned for its laboratory equipment and accessories, including solutions that support the cooling and preservation of biological samples in biobanks.VWR International LLC:
A global leader in laboratory supplies and equipment, VWR offers a broad range of products and services tailored for the needs of biobanks and their operations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of biobanking?
The biobanking market is valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with an expected CAGR of 5.5%. By 2033, the market is projected to reach higher levels, driven by advancements in healthcare and bioresearch.
What are the key market players or companies in this biobanking industry?
Key players in the biobanking industry include renowned institutes, pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology firms globally, contributing significantly to sample collection, storage, and bioinformatics solutions, thus shaping the landscape of biobanking.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the biobanking industry?
The biobanking industry is growing due to a rise in personalized medicine, need for disease research, government initiatives, technological advancements in sample preservation, and increasing collaborations between healthcare organizations.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the biobanking?
North America leads the biobanking market growth due to advanced healthcare infrastructure. Europe and Asia-Pacific are also growing significantly, with Asia-Pacific projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2033, highlighting expanding research initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the biobanking industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs in the biobanking sector, helping organizations gain insights that precisely reflect their interests and market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this biobanking market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, growth projections, competitive landscape assessments, regional insights, and segmented data, tailored to support strategic decision-making in the biobanking industry.
What are the market trends of biobanking?
Current market trends include increased focus on data management solutions, innovative sample storage technologies, and the use of biobanks in developing personalized therapeutics, illustrating the evolving needs of medical research.