Biobanks Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: biobanks
Biobanks Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Biobanks market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth potential, regional insights, and trends that are shaping the industry. It aims to equip stakeholders with valuable data for strategic planning.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
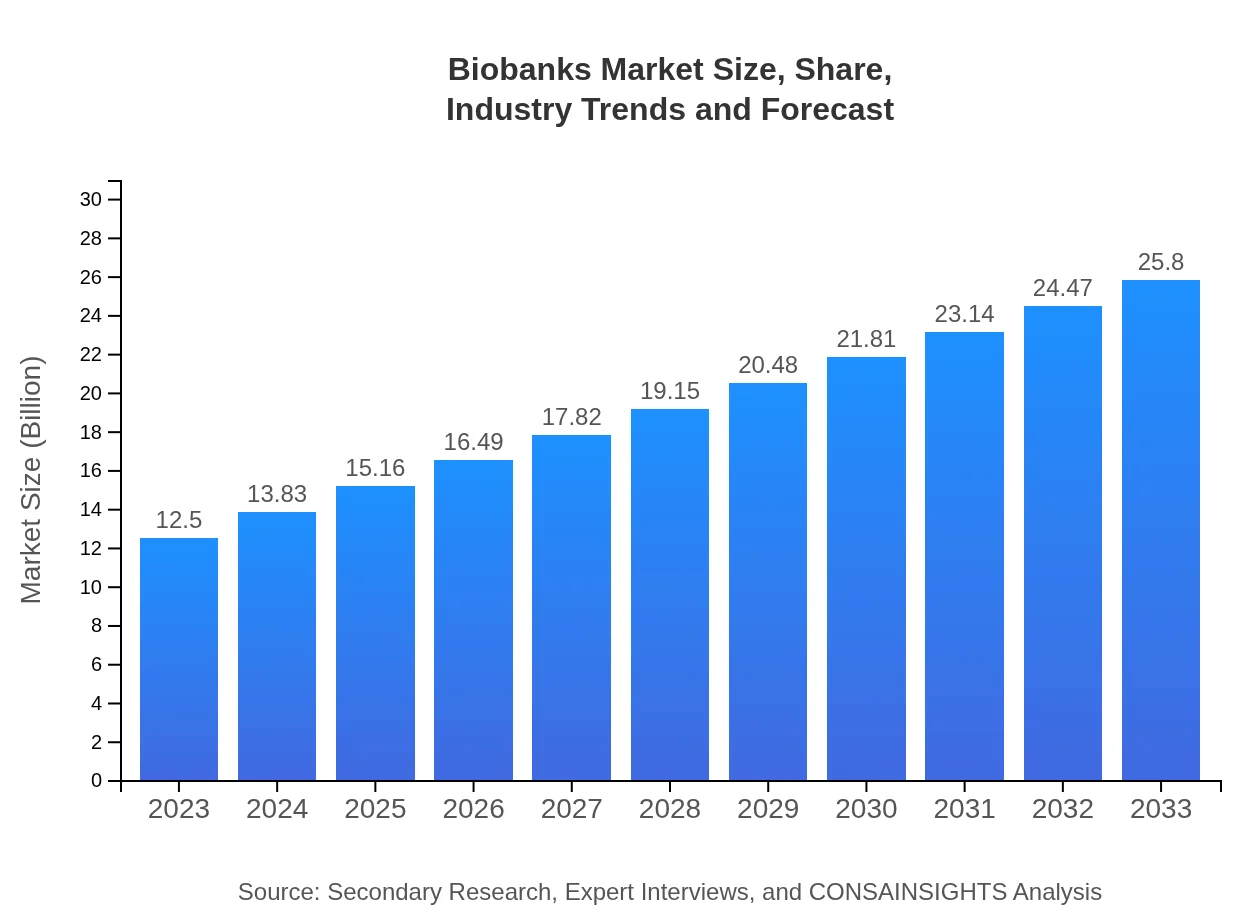
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $25.80 Billion |
| Top Companies | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen , Bristol Myers Squibb, Luminex Corporation, Medpace |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Biobanks Market Overview
Customize Biobanks Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Biobanks market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Biobanks's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Biobanks
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Biobanks market in 2023?
Biobanks Industry Analysis
Biobanks Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
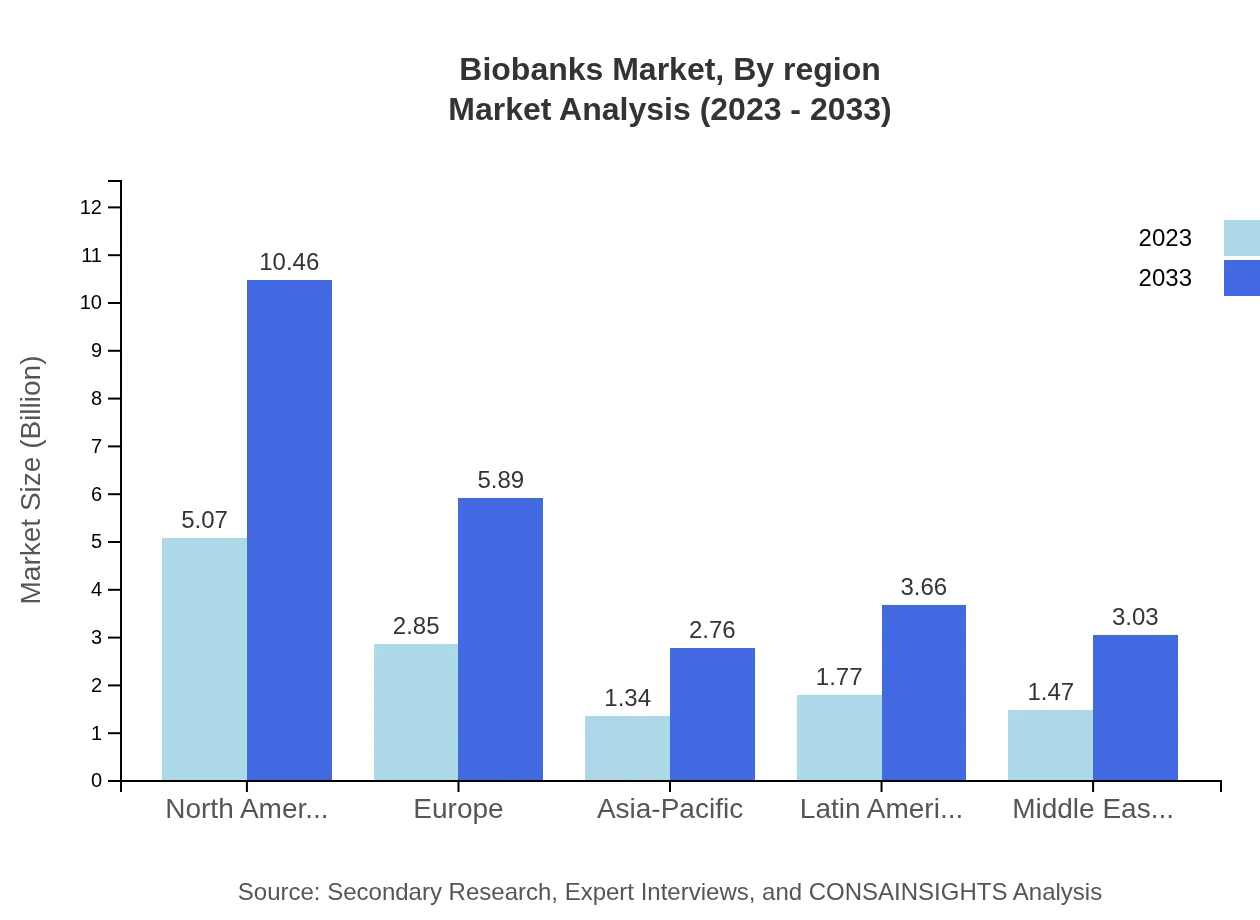
Biobanks Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Biobanks Market Report:
The European biobanks market is anticipated to grow from $3.39 billion in 2023 to $7.01 billion by 2033, fueled by supportive regulatory frameworks and increased funding for research programs. Countries such as the UK, Germany, and France are key contributors to the region's growth.Asia Pacific Biobanks Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the biobanks market is projected to grow from $2.45 billion in 2023 to $5.06 billion in 2033. This growth is driven by increasing investments in biotechnology research, rising awareness of personalized medicine, and the establishment of national biobanking initiatives. Countries like China and India are emerging as key players in this sector.North America Biobanks Market Report:
North America dominates the global biobanks market with a projected growth from $4.28 billion in 2023 to $8.84 billion in 2033. The strong presence of major pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, alongside robust research initiatives, significantly drives the market.South America Biobanks Market Report:
The South American biobanks market is expected to witness growth from $1.15 billion in 2023 to $2.38 billion by 2033. This region is characterized by the growing emphasis on health research and collaborations with global organizations to improve healthcare outcomes through biobanking.Middle East & Africa Biobanks Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's biobanks market is projected to expand from $1.22 billion in 2023 to $2.51 billion by 2033. This growth can be attributed to increasing healthcare investments and partnerships to establish sustainable biobanking infrastructures.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Biobanks Market Analysis By Type
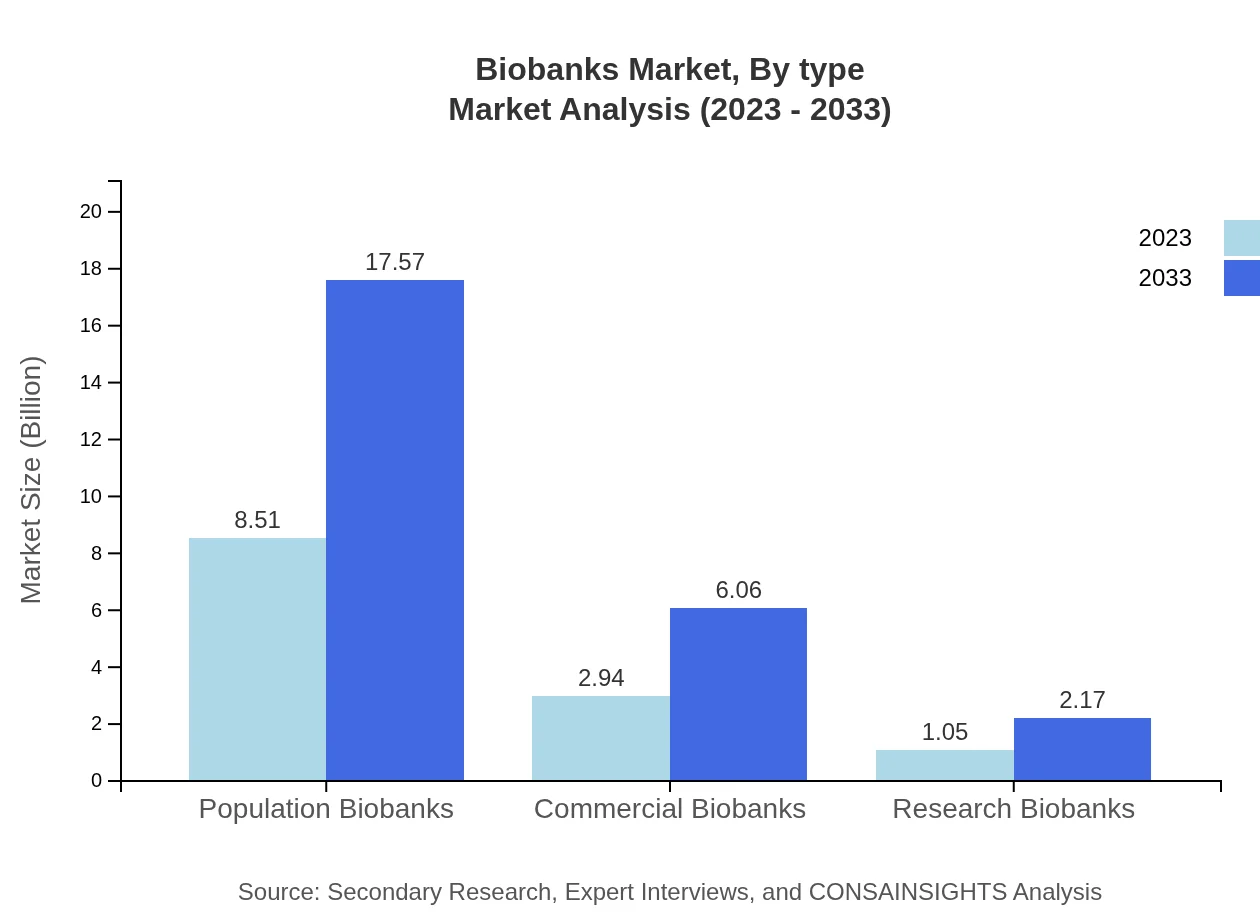
The Biobanks market is primarily segmented into three major types: Population Biobanks, Commercial Biobanks, and Research Biobanks. Population Biobanks account for a significant market share, driven by their crucial role in epidemiological studies and public health research. In 2023, Population Biobanks are valued at $8.51 billion and are expected to grow to $17.57 billion by 2033. Commercial Biobanks represent around $2.94 billion in 2023, likely reaching $6.06 billion by 2033, facilitating drug discovery and development. Research Biobanks, while smaller in size at $1.05 billion in 2023, are projected to grow to $2.17 billion by 2033, supporting academic and research organization needs.
Biobanks Market Analysis By Sample Type
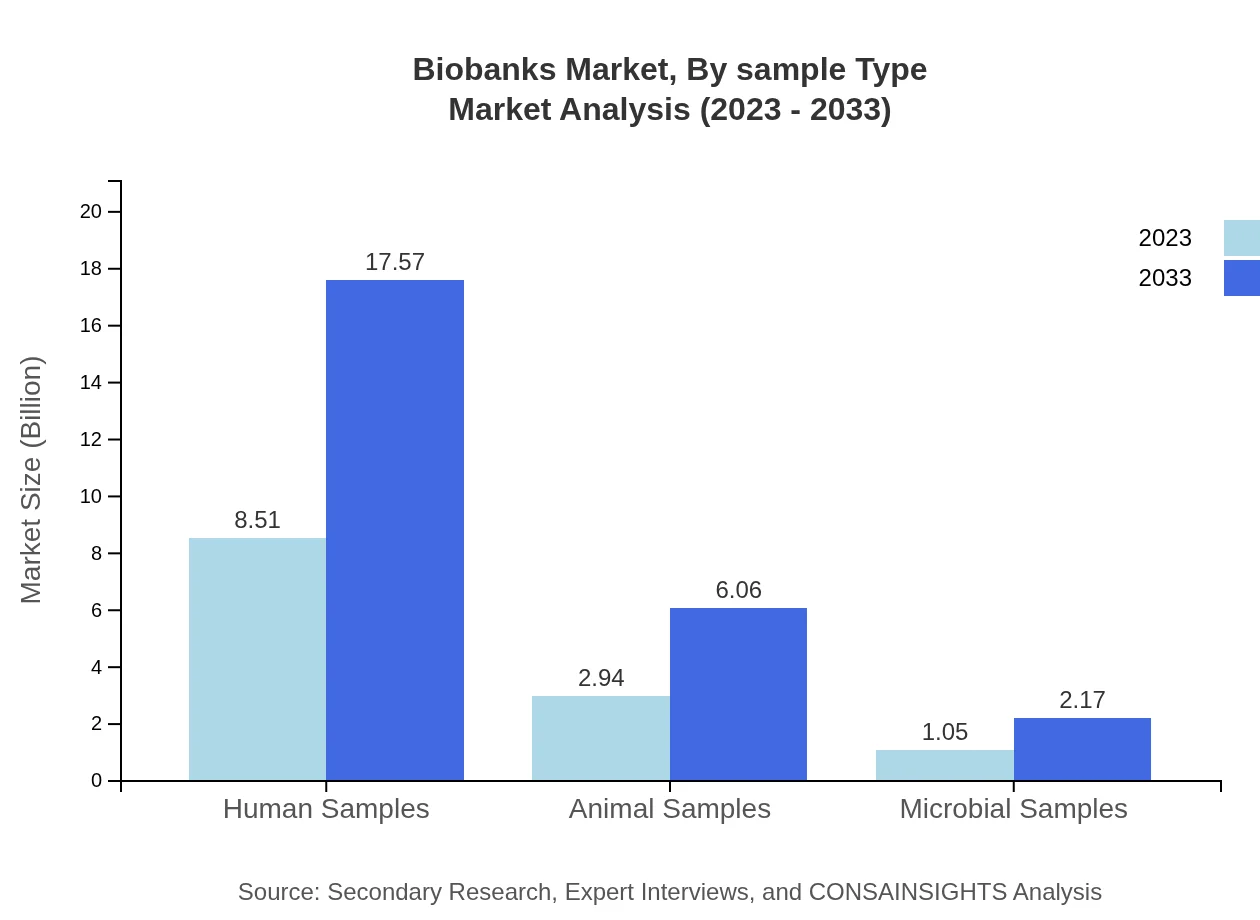
Segments include Human Samples, Animal Samples, and Microbial Samples. Human Samples dominate the market, valued at $8.51 billion in 2023, expected to reach $17.57 billion by 2033. Animal Samples are projected to grow from $2.94 billion to $6.06 billion, while Microbial Samples, valued at $1.05 billion, aim to hit $2.17 billion, indicating a diverse landscape for biobanks catering to varied research needs.
Biobanks Market Analysis By End User
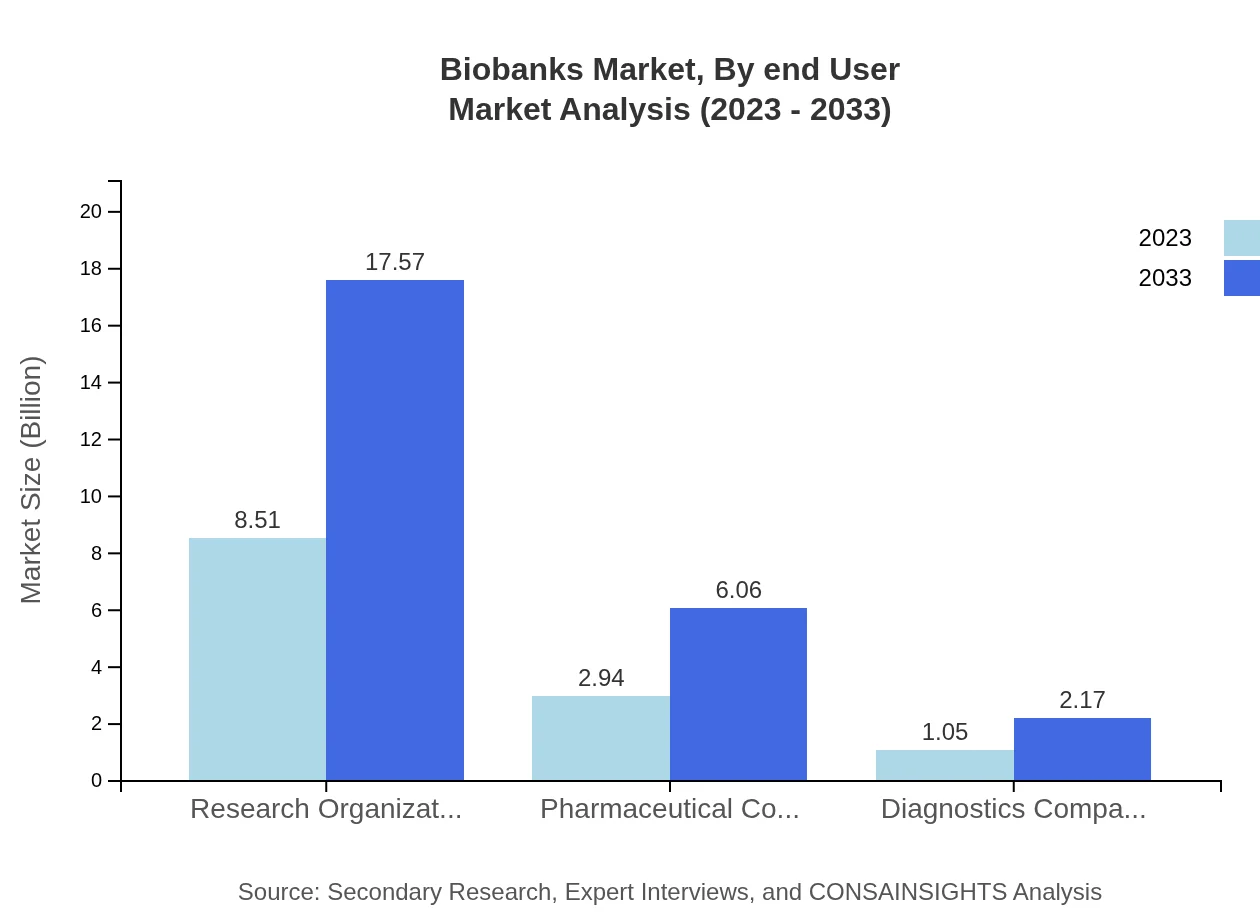
The Biobanks market also segments based on end-users, including Research Organizations, Pharmaceutical Companies, and Diagnostics Companies. Research Organizations are the largest segment, valued at $8.51 billion in 2023, projected to surge to $17.57 billion by 2033. Pharmaceutical Companies are expected to increase from $2.94 billion to $6.06 billion, while Diagnostics Companies grow from $1.05 billion to $2.17 billion, reflecting increasing reliance on biobanks for innovation and product development.
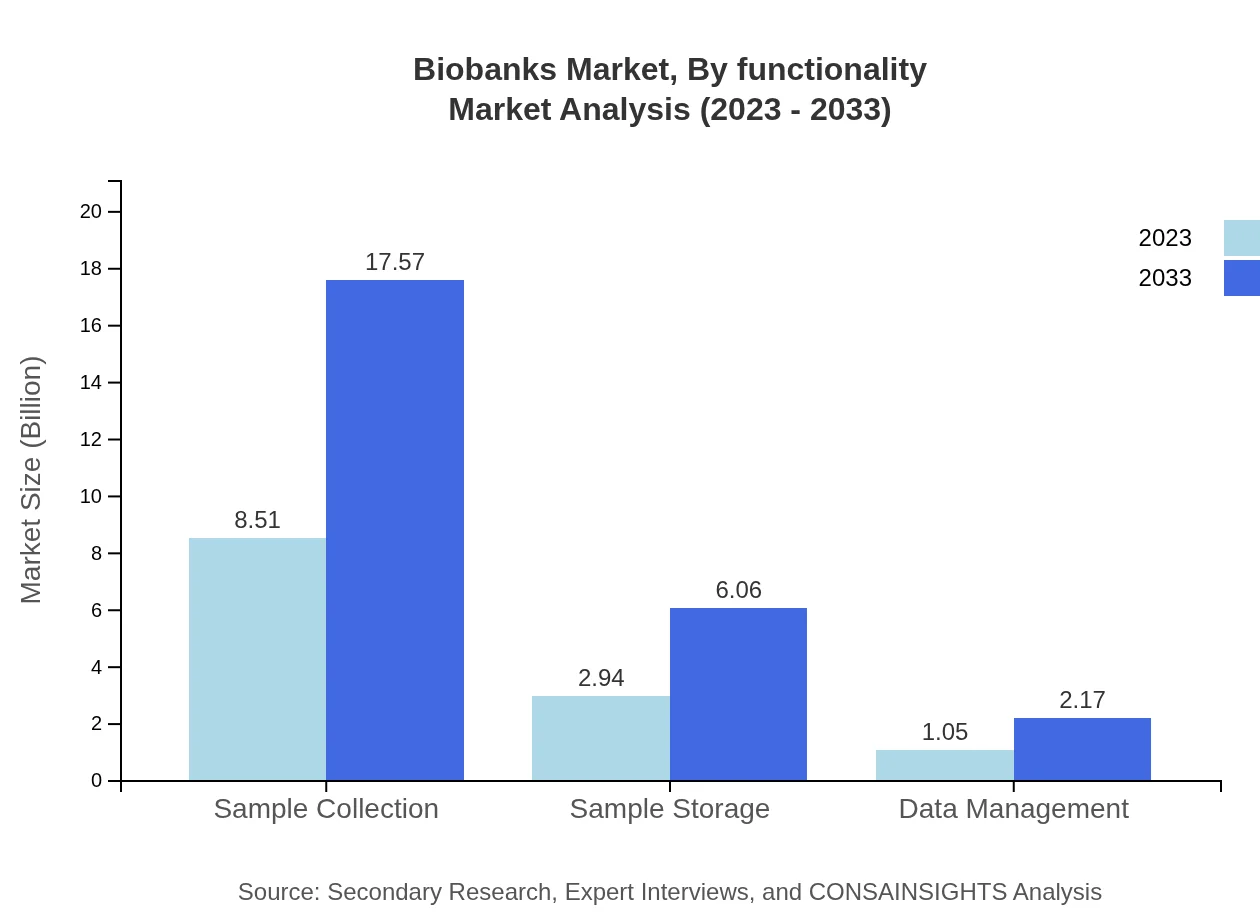
Biobanks Market Analysis By Functionality
Functional segments in the Biobanks market encompass Sample Collection, Sample Storage, and Data Management. Sample Collection accounts for a significant share at $8.51 billion in 2023, anticipated to rise to $17.57 billion by 2033, central for biobank operations. Sample Storage, with market values of $2.94 billion and projections to $6.06 billion, plays a critical role in ensuring sample integrity. Data Management is also essential, projected to grow from $1.05 billion to $2.17 billion, highlighting the importance of effective data handling in biobanking.
Biobanks Market Analysis By Region
Regional analysis reveals differing dynamics across markets. North America leads with significant investments and a strong framework for biobanks, while Europe follows closely, emphasizing research collaboration. Asia-Pacific is witnessing rapid growth driven by increasing healthcare demands. South America and Middle East & Africa are emerging markets, showing promising growth due to global partnerships fostering biobank establishment.
Biobanks Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Biobanks Industry
Thermo Fisher Scientific:
A leading company providing a wide range of products and services that support biobanking, including sample storage, data management solutions, and innovative equipment.Qiagen :
A prominent player in the biotech sector, Qiagen specializes in sample preparation and diagnostics, which are critical for biobanking applications.Bristol Myers Squibb:
A global biopharmaceutical company that extensively utilizes biobanks in its R&D processes to enhance drug development and personalized medicine.Luminex Corporation:
Known for its multiplexing technology that enables efficient biobanking practices, Luminex provides solutions that streamline sample analysis.Medpace:
A clinical contract research organization that partners with biobanks to facilitate drug development and clinical trials with a focus on regulatory compliance.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of biobanks?
The biobanks market is projected to reach approximately $12.5 billion by the year 2033, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from its current valuation in 2023.
What are the key market players or companies in the biobanks industry?
Key players in the biobanks market include research organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and diagnostics companies, with significant contributions from entities that manage human, animal, and microbial samples.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the biobanks industry?
Driving factors include the increasing demand for biological samples, advancements in genomic studies, and the rising need for personalized medicine, propelling the expansion of biobanks.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the biobanks?
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth, with the market expected to rise from $2.45 billion in 2023 to $5.06 billion by 2033, indicating significant investment and development in biobank infrastructure.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the biobanks industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the biobanks industry, ensuring comprehensive insights and detailed analytics.
What deliverables can I expect from this biobanks market research project?
Deliverables include detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, regional breakdowns, and segmentation data, providing a thorough understanding of the biobanks market.
What are the market trends of biobanks?
Current trends include a shift towards population-based biobanks, increasing collaboration among biotech firms, advancements in data management technologies, and a heightened focus on sustainable practices within sample collection and storage.