Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: biofuel-from-sugar-crops
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the biofuel from sugar crops market from 2023 to 2033, examining market trends, regional insights, technology advancements, and competitive landscape to offer valuable insights for stakeholders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
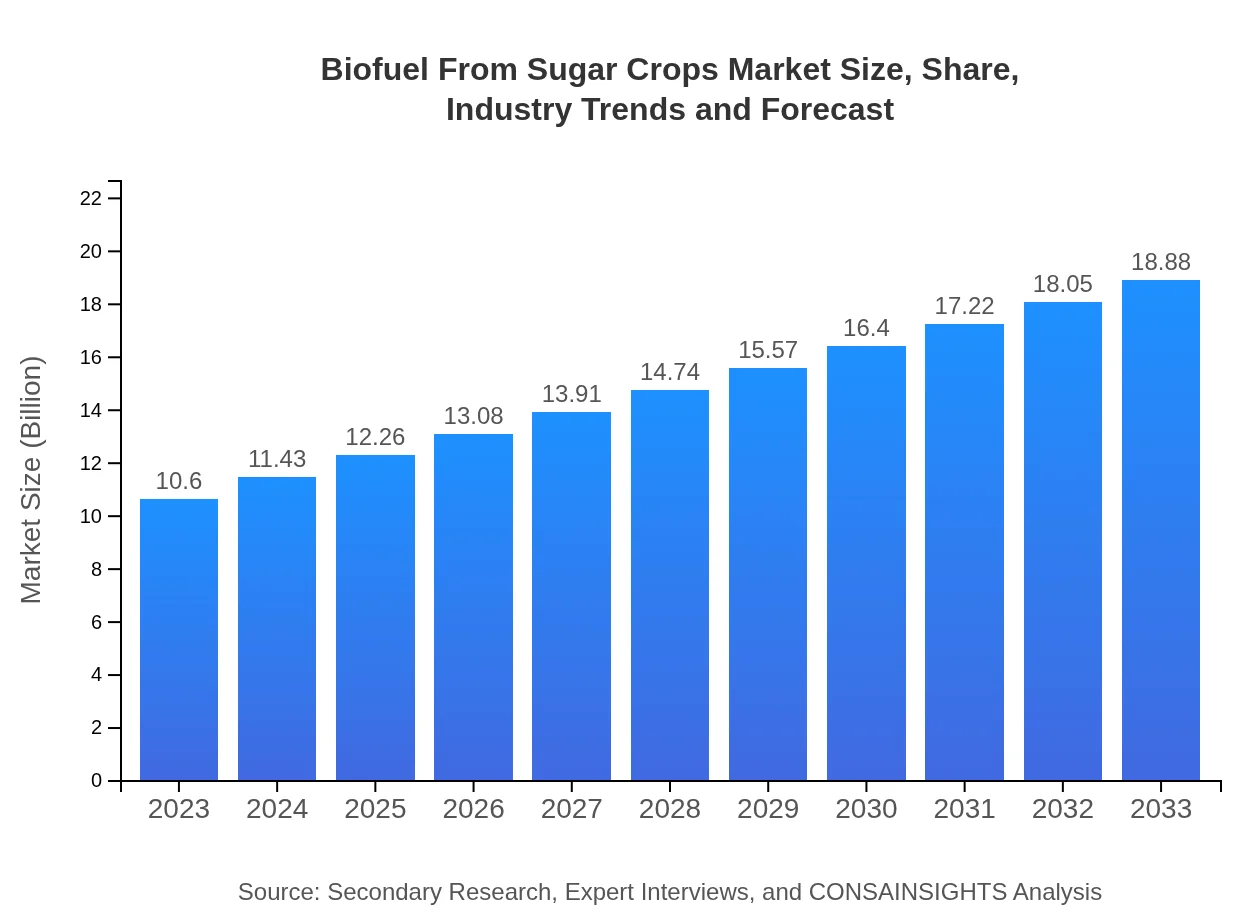
| 2023 Market Size | $10.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.88 Billion |
| Top Companies | Green Plains Inc., Raízen, Dupont, Cargill, Inc., Neste |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Overview
Customize Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Biofuel From Sugar Crops market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Biofuel From Sugar Crops's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Biofuel From Sugar Crops
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Biofuel From Sugar Crops market in 2023?
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Industry Analysis
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report:
The European market is expected to grow from $2.94 billion in 2023 to $5.24 billion by 2033. Stringent environmental regulations and a shift towards greener energy sources have spurred investments in biofuel technologies, making Europe a key player in this industry.Asia Pacific Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's biofuel from sugar crops market is valued at $2.11 billion, projected to grow to $3.76 billion by 2033. With rapid industrialization, increasing energy demands, and investment in biofuel projects, this region is becoming a pivotal market for biofuel production.North America Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report:
North America's biofuel from sugar crops market is significant, growing from $3.51 billion in 2023 to $6.25 billion by 2033. The presence of a strong regulatory framework fostering biofuel development, alongside technological advancements, continues to drive market growth in the region.South America Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report:
South America, with a market size of $0.90 billion in 2023 and an expected growth to $1.60 billion by 2033, benefits from its agricultural resources and the support of policies favoring biofuel adoption. Brazil, as a leading producer, emphasizes bioethanol production from sugarcane.Middle East & Africa Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region, starting with a market size of $1.14 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $2.02 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increasing investments in renewable energy projects, aimed at diversifying energy sources amid economic challenges.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
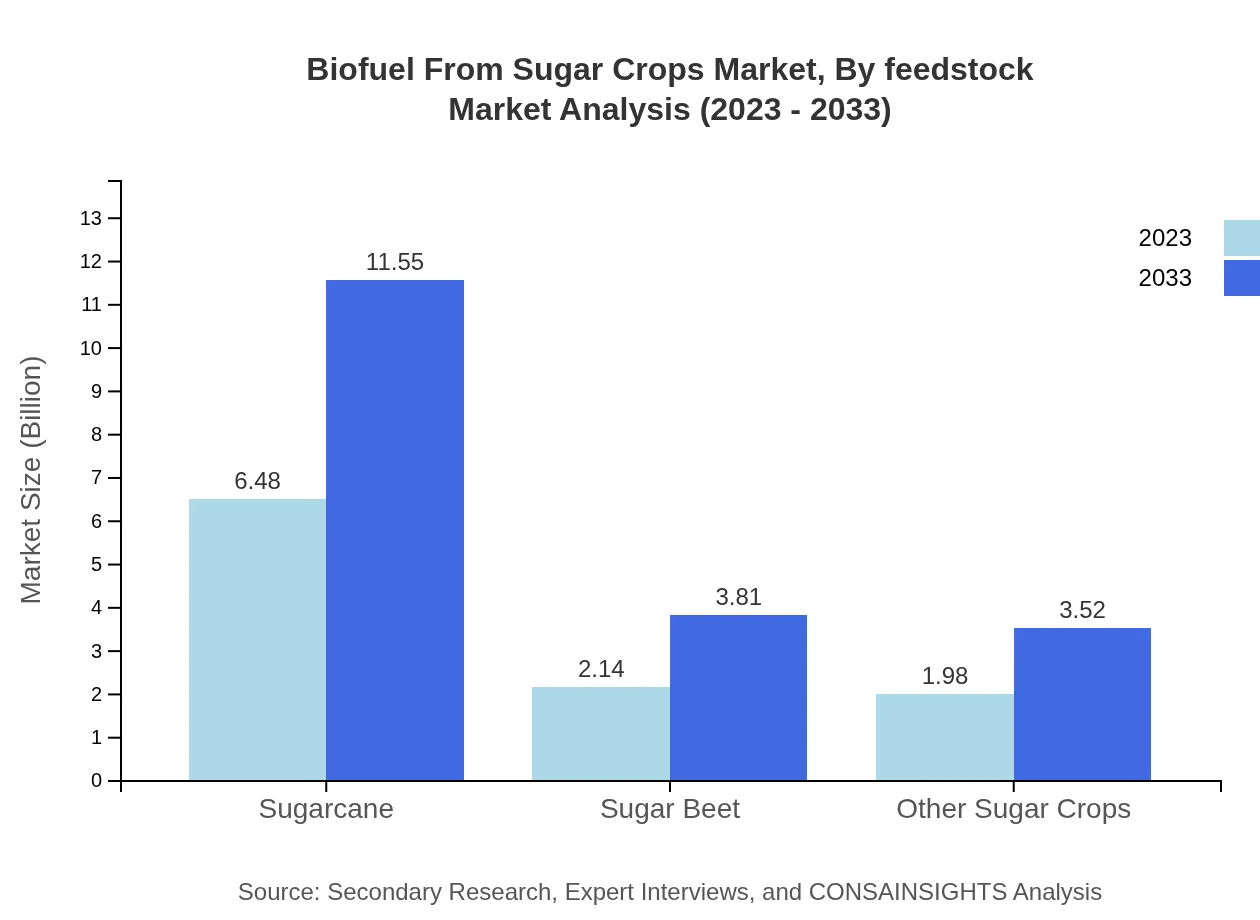
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis By Feedstock
In terms of feedstock, sugarcane dominates with a market share of 61.17%, reflecting a size of $6.48 billion in 2023, projected to rise to $11.55 billion by 2033. Sugar beet follows with 20.18% market share, projected to expand from $2.14 billion to $3.81 billion during the same period.
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis By Production Process
The primary production processes include fermentation and chemical processing, where fermentation leads with a substantial share of the market. With technological innovations, these processes are expected to become more efficient, further boosting market growth.
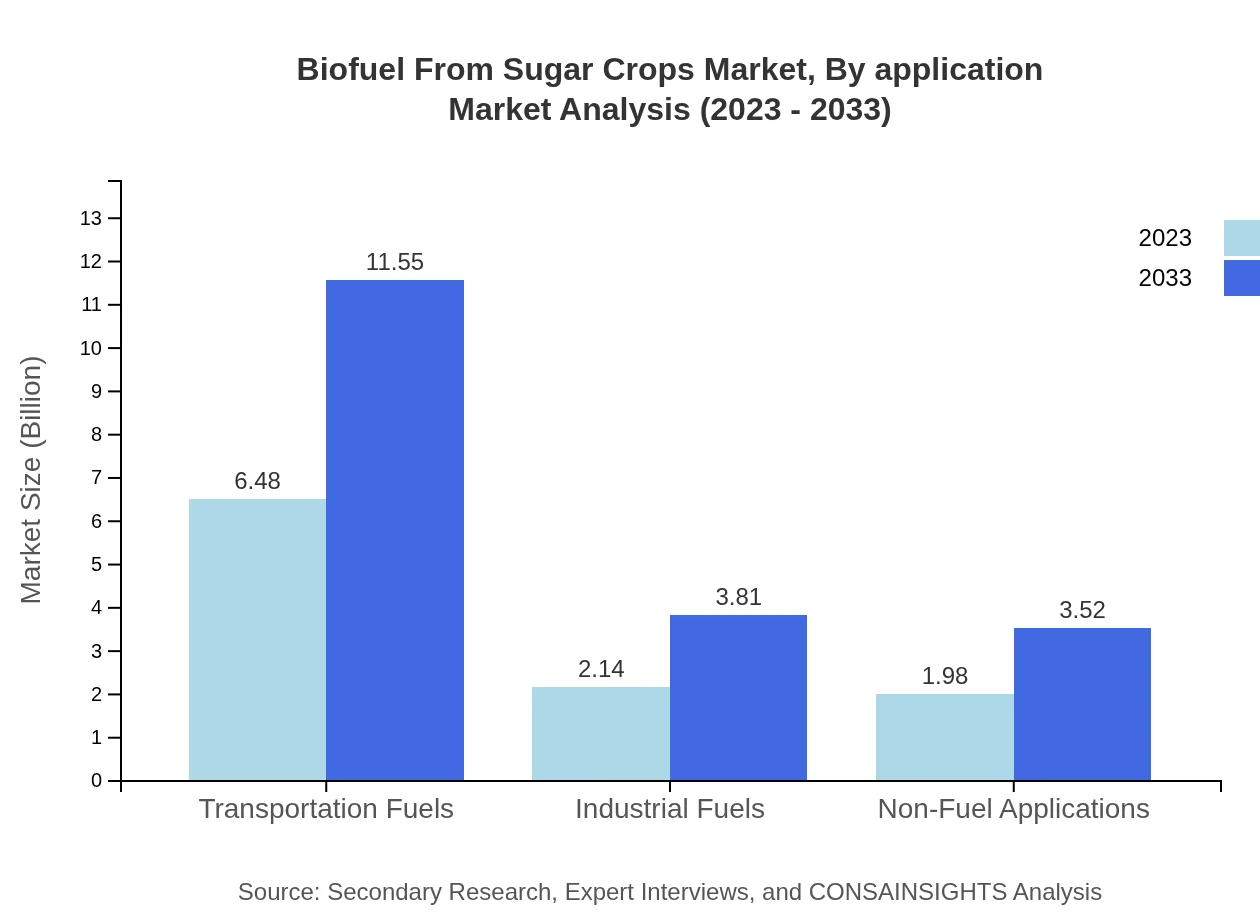
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis By Application
The application segment for transportation fuels holds a significant proportion with a market size of $6.48 billion in 2023, which is projected to grow to $11.55 billion by 2033. Non-fuel applications are also important, showing steady growth in demand.
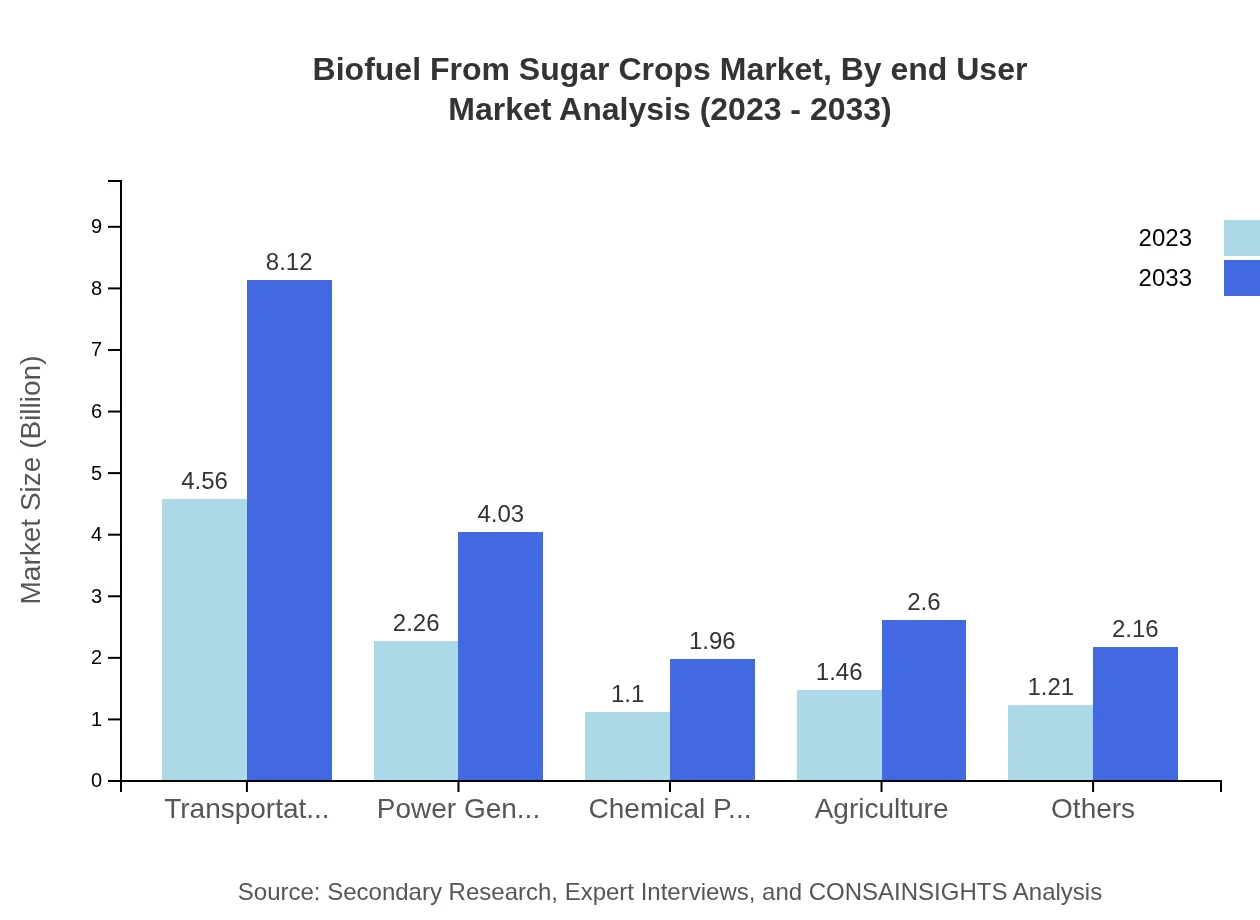
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis By End User
Key end-user industries include automotive, industrial, and agricultural sectors, where biofuels are essential for reducing carbon footprints and complying with regulations focused on sustainability.
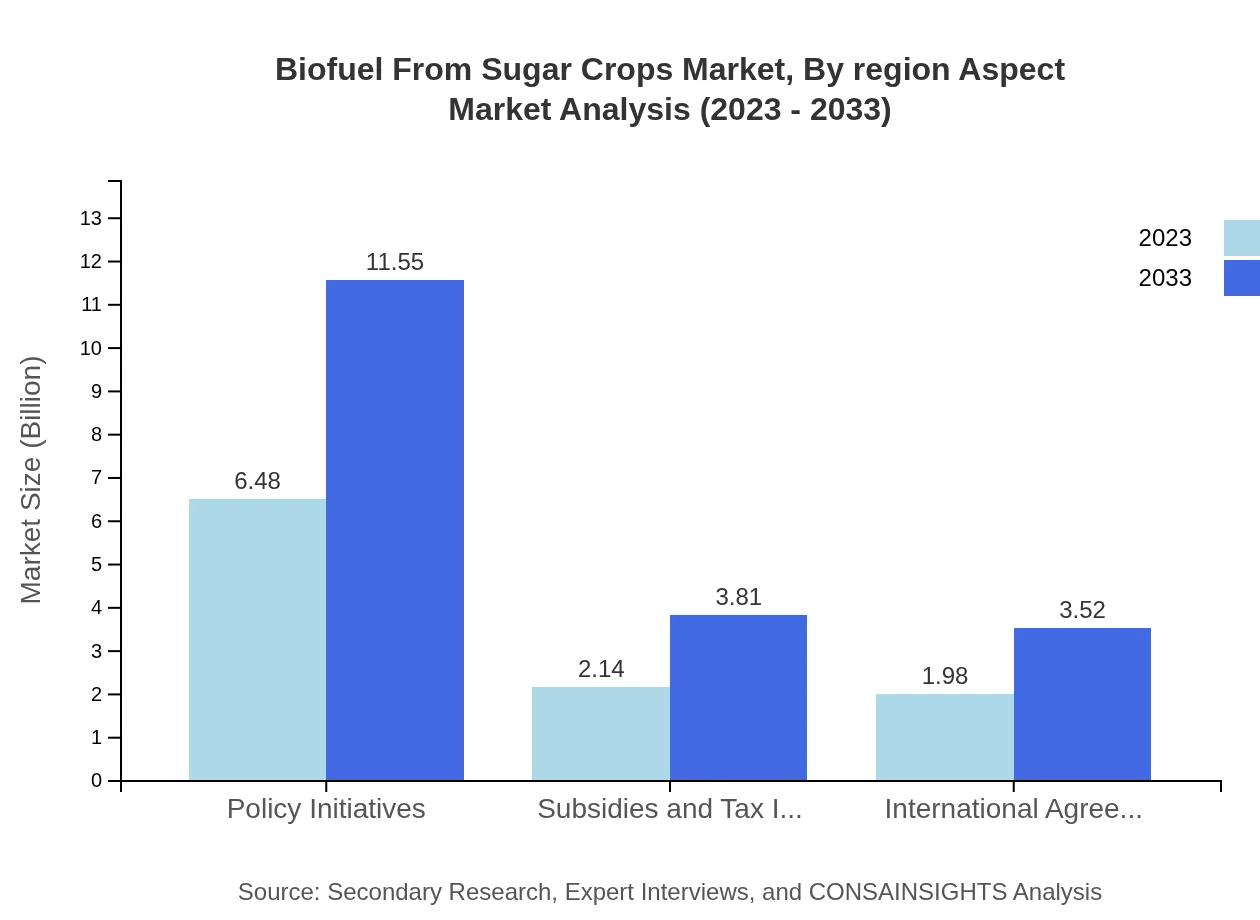
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Analysis By Region Aspect
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in biofuel adoption across regions, with incentives such as subsidies and tax breaks promoting investments and research into biofuel technologies, ensuring the market’s potential is fully realized.
Biofuel From Sugar Crops Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Biofuel From Sugar Crops Industry
Green Plains Inc.:
A leading biofuel producer based in the United States, heavily invested in ethanol production from corn and sugarcane.Raízen:
One of the largest producers of sugarcane bioethanol in Brazil, combining extensive agricultural experience with cutting-edge biorefining technologies.Dupont:
Known for its innovative biofuel solutions derived from sugar crops, focusing on sustainable manufacturing practices.Cargill, Inc.:
Global food corporation actively engaged in biofuels, leveraging its agricultural resources to produce high-quality biofuel products.Neste:
A Finnish company specializing in renewable diesel production, Neste is increasingly investing in sugar crop biofuels to diversify its energy portfolio.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of biofuel From Sugar Crops?
The biofuel from sugar crops market is projected to grow significantly, currently valued at approximately 10.6 billion USD in 2023. It is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8%, showcasing strong demand in the coming years.
What are the key market players or companies in this biofuel From Sugar Crops industry?
Key players in the biofuel from sugar crops industry include major corporations that specialize in renewable energy and agricultural products. These companies are involved in the production, distribution, and technological advancements of biofuels derived from sugar crops.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the biofuel From Sugar Crops industry?
Growth in the biofuel from sugar crops industry is driven by rising energy demands, increasing environmental regulations, and the shift towards renewable energy sources. Additionally, government incentives and technological advancements support industry expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the biofuel From Sugar Crops market?
The biofuel from sugar crops market in North America is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region, projected to reach 6.25 billion USD by 2033, up from 3.51 billion USD in 2023. Europe and Asia Pacific also show significant growth.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the biofuel From Sugar Crops industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the biofuel from sugar crops industry. Clients can request insights focused on particular market segments or geographical areas to aid in strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this biofuel From Sugar Crops market research project?
Deliverables from the biofuel from sugar crops market research project include comprehensive reports with market size data, segment analysis, regional insights, competitive landscape overview, trend forecasts, and strategic recommendations for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of biofuel From Sugar Crops?
Current trends in the biofuel from sugar crops market include a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, technological advancements in biofuel production processes, and an increasing focus on regulatory compliance, promoting renewable energy utilization globally.