Biomass Gasification Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: biomass-gasification
Biomass Gasification Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the Biomass Gasification market, highlighting growth trends, market opportunities, and projections from 2023 to 2033. Insights into technological advancements, market segmentation, and regional analysis are included to inform stakeholders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
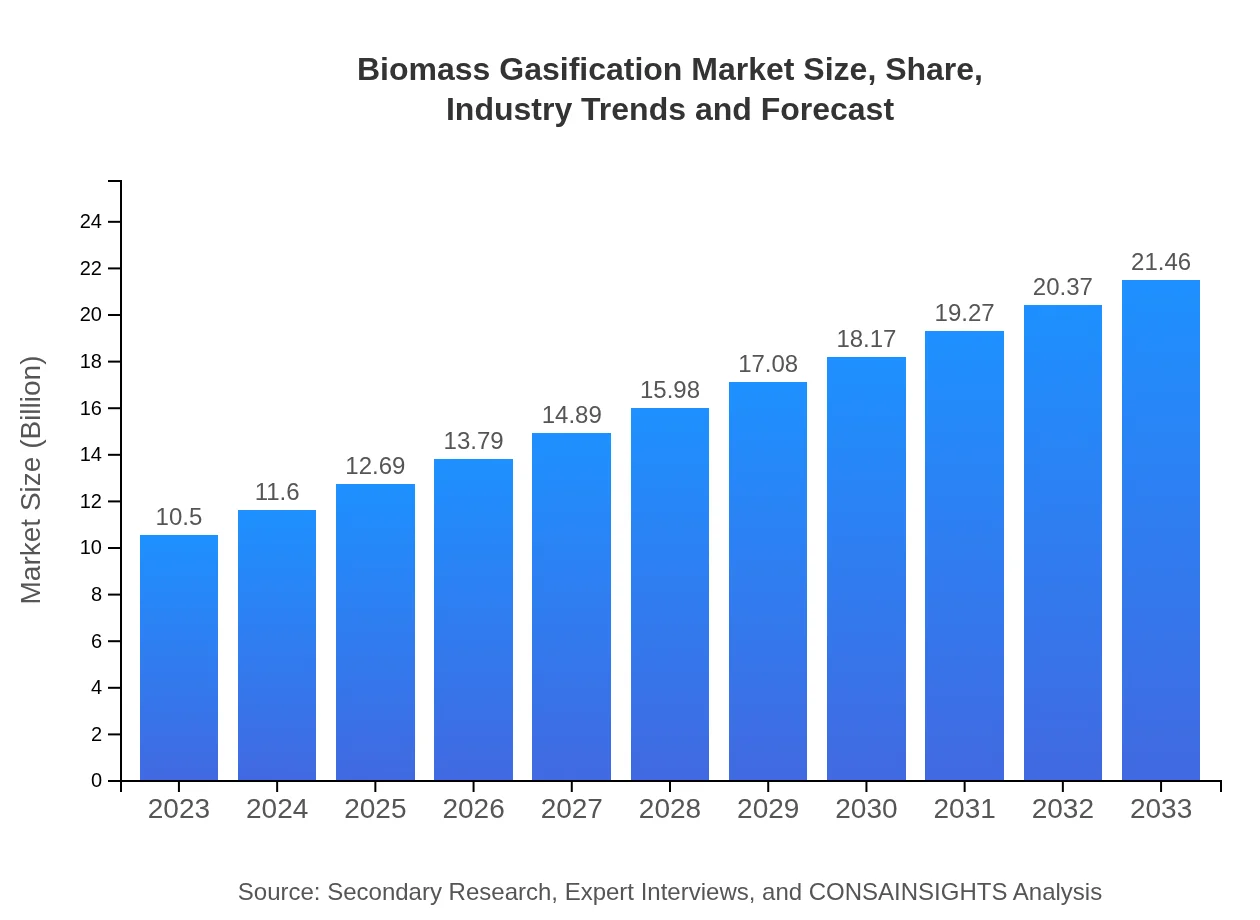
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.46 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens , GE Renewable Energy, Air Liquide, Royal Dutch Shell |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Biomass Gasification Market Overview
Customize Biomass Gasification Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Biomass Gasification market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Biomass Gasification's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Biomass Gasification
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Biomass Gasification market in 2023 and 2033?
Biomass Gasification Industry Analysis
Biomass Gasification Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Biomass Gasification Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Biomass Gasification Market Report:
In Europe, the market is set to expand from $2.85 billion in 2023 to $5.82 billion by 2033. The EU's focus on achieving climate targets makes this region a hub for biomass technology, with increasing investments in research and sustainable practices.Asia Pacific Biomass Gasification Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Biomass Gasification market is expected to grow from $2.02 billion in 2023 to $4.13 billion by 2033. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in biomass technologies as part of their energy transition strategies. The focus on renewable energy combined with government incentives is expected to further boost market growth.North America Biomass Gasification Market Report:
North America's market is projected to grow from $4.00 billion in 2023 to $8.18 billion by 2033. The U.S. and Canada are leading the way in biomass gasification technologies, supported by strong governmental policies and initiatives aimed at promoting clean energy, coupled with the region's abundant biomass resources.South America Biomass Gasification Market Report:
The South American Biomass Gasification market is anticipated to grow from $0.73 billion in 2023 to $1.49 billion by 2033. Increasing agricultural activities and a rich variety of biomass feedstock are driving the market, alongside the region's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions as part of international climate agreements.Middle East & Africa Biomass Gasification Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from $0.90 billion in 2023 to $1.84 billion by 2033. As countries in this region diversify their energy sources and invest in renewable technologies, biomass gasification is seen as a viable option for energy sustainability and resource management.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
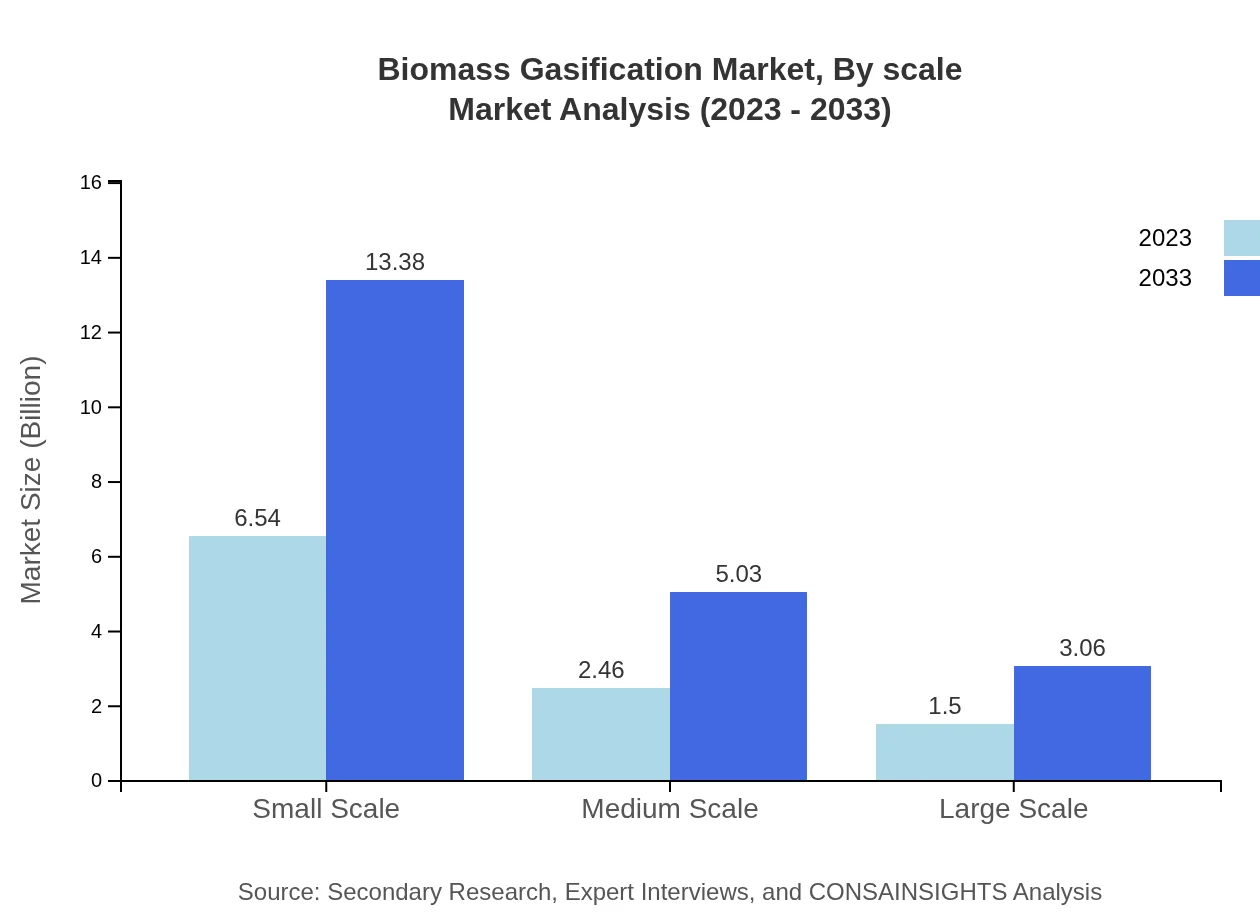
Biomass Gasification Market Analysis By Scale
The Biomass Gasification market is categorized into Small Scale, Medium Scale, and Large Scale operations. In 2023, the small scale segment captures 62.32% of the market share, with expectations to reach 13.38 billion by 2033. The medium scale segment holds a 23.42% share and is expected to grow significantly, while large scale operations, although smaller in share (14.26%), are crucial for industrial applications, set to expand from $1.50 billion in 2023 to $3.06 billion by 2033.
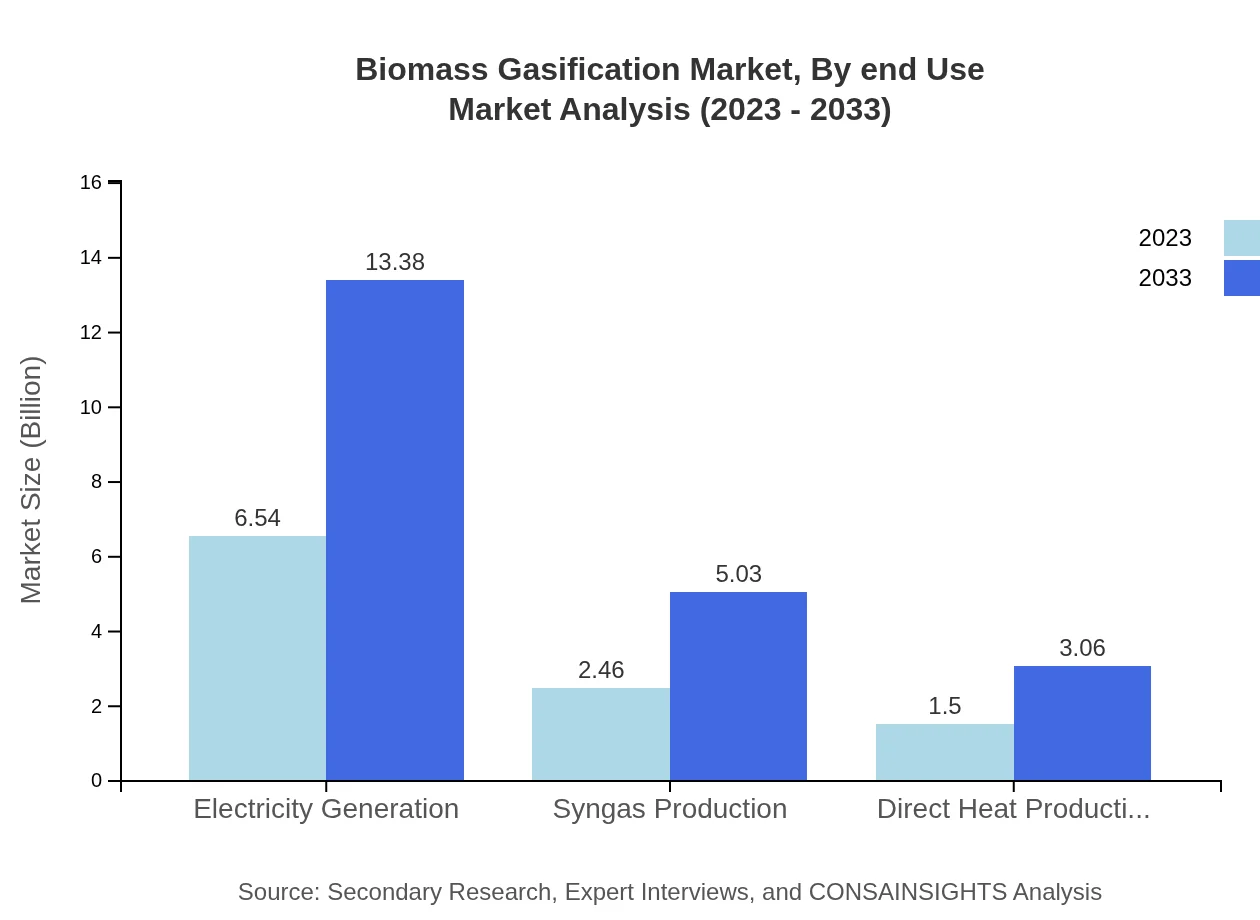
Biomass Gasification Market Analysis By End Use
In terms of end-use applications, electricity generation accounts for a substantial market share, holding 62.32% and projected to grow to $13.38 billion by 2033. Syngas production represents 23.42% of the market, poised to reach $5.03 billion. Direct heat production currently makes up 14.26% of the market, expected to see growth as energy efficiency becomes a priority.
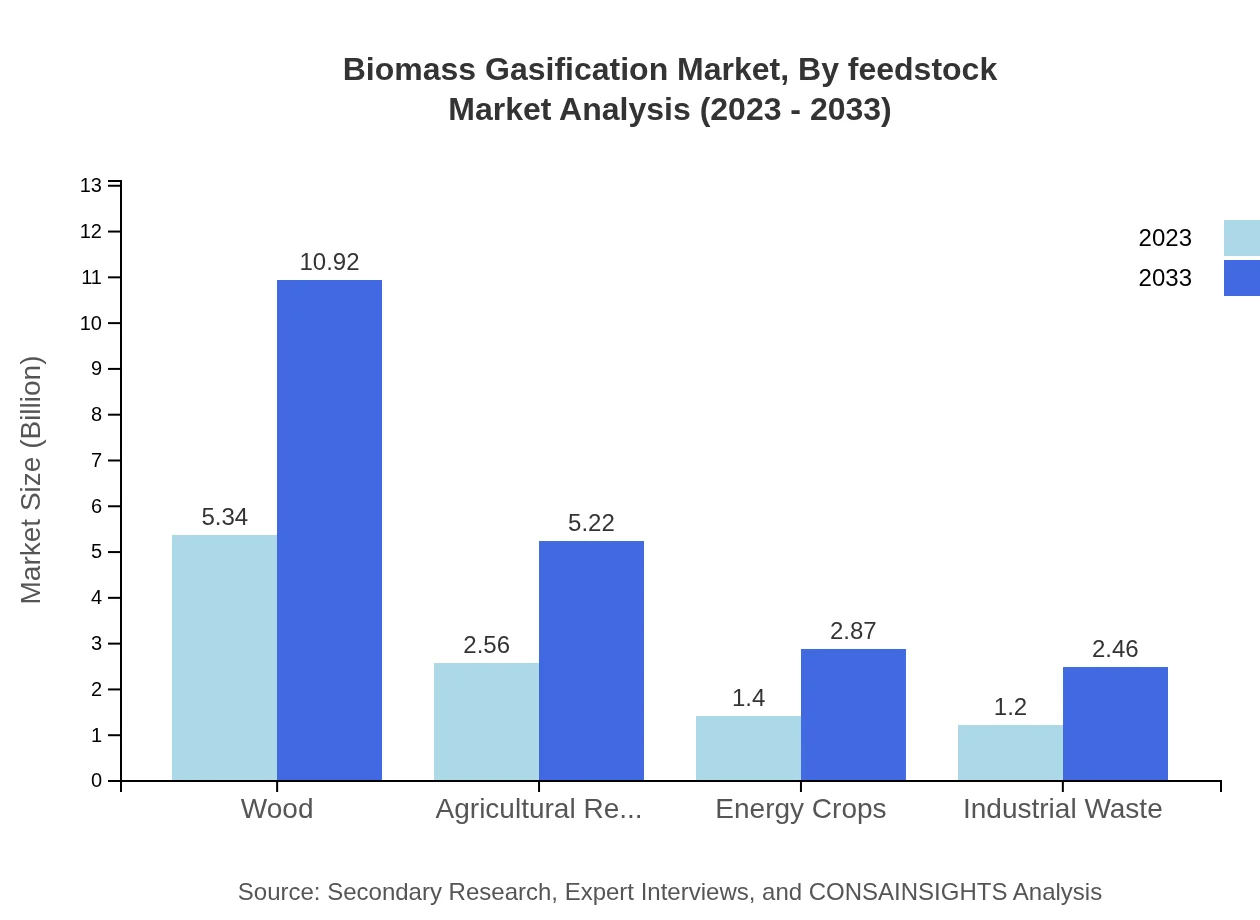
Biomass Gasification Market Analysis By Feedstock
Feedstock segmentation plays a crucial role in market dynamics. Wood remains the dominant feedstock, constituting 50.86% of the market in 2023 and growing to $10.92 billion by 2033. Agricultural residues are significant contributors with a 24.34% share and projected growth to $5.22 billion. Energy crops and industrial waste follow, making notable contributions to market diversity and sustainability.
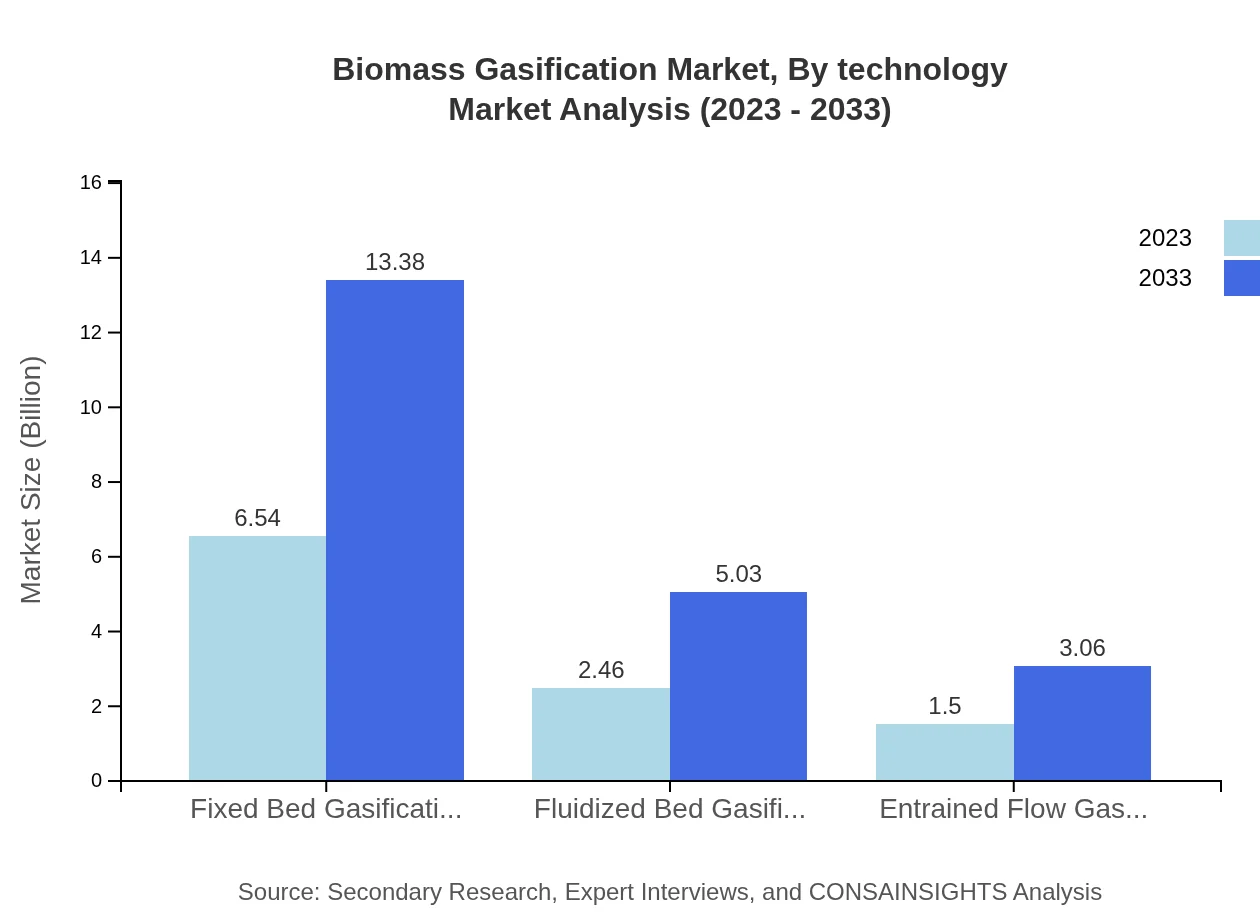
Biomass Gasification Market Analysis By Technology
Technology plays an essential role in the advancement of biomass gasification methods. Fixed bed gasification currently leads the sector with a market share of 62.32%, projected to grow exponentially, while fluidized bed gasification realizes 23.42% of the market. Entrained flow systems, being more suitable for larger operations, are expected to see increasing adoption in future projects.
Biomass Gasification Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Biomass Gasification Industry
Siemens :
Siemens is a leader in technology and innovation in biomass gasification and focuses on developing solutions for renewable energies, including high-efficiency gasification systems.GE Renewable Energy:
GE Renewable Energy offers a range of products related to gasification and works extensively on projects aimed at reducing emissions and enhancing sustainability.Air Liquide:
Air Liquide specializes in gas technologies and has been pivotal in advancing biomass gasification processes for commercial applications.Royal Dutch Shell:
Royal Dutch Shell has been active in integrating biomass gasification into their operations and pushing forward innovative energy solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Biomass Gasification?
The Biomass Gasification market is projected to grow from $10.5 billion in 2023 to an estimated $22 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 7.2%. This growth is driven by increasing energy demands and the need for sustainable energy solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the Biomass Gasification industry?
Key players in the Biomass Gasification industry include established companies such as Air Liquide, Valmet, and Siemens. These companies are focusing on technological advancements and global partnerships to enhance their market presence and offerings.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Biomass Gasification industry?
Major factors driving growth in Biomass Gasification include increased government initiatives for renewable energy, rising energy costs, and growing awareness of sustainable practices. Additionally, advancements in gasification technologies significantly contribute to market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Biomass Gasification market?
Among regions, North America is the fastest-growing market for Biomass Gasification, with a projected increase from $4.00 billion in 2023 to $8.18 billion by 2033, driven by investments in clean energy projects and energy security initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Biomass Gasification industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients in the Biomass Gasification industry. Clients can request insights based on their distinct requirements, ensuring relevant and actionable information.
What deliverables can I expect from this Biomass Gasification market research project?
Deliverables from the Biomass Gasification market research project include comprehensive market analysis reports, trend forecasts, detailed segmentation data, and competitive landscape assessments, aiding stakeholders in strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of Biomass Gasification?
Key market trends include a shift towards small-scale biomass gasification systems, technological innovations in gasification methods, and increasing utilization of diverse feedstocks such as agricultural residues and industrial waste, enhancing market sustainability.