Biomass Power Generation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: biomass-power-generation
Biomass Power Generation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the Biomass Power Generation market, providing insights on market trends, forecasts from 2023 to 2033, and extensive analysis of various segments and regions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
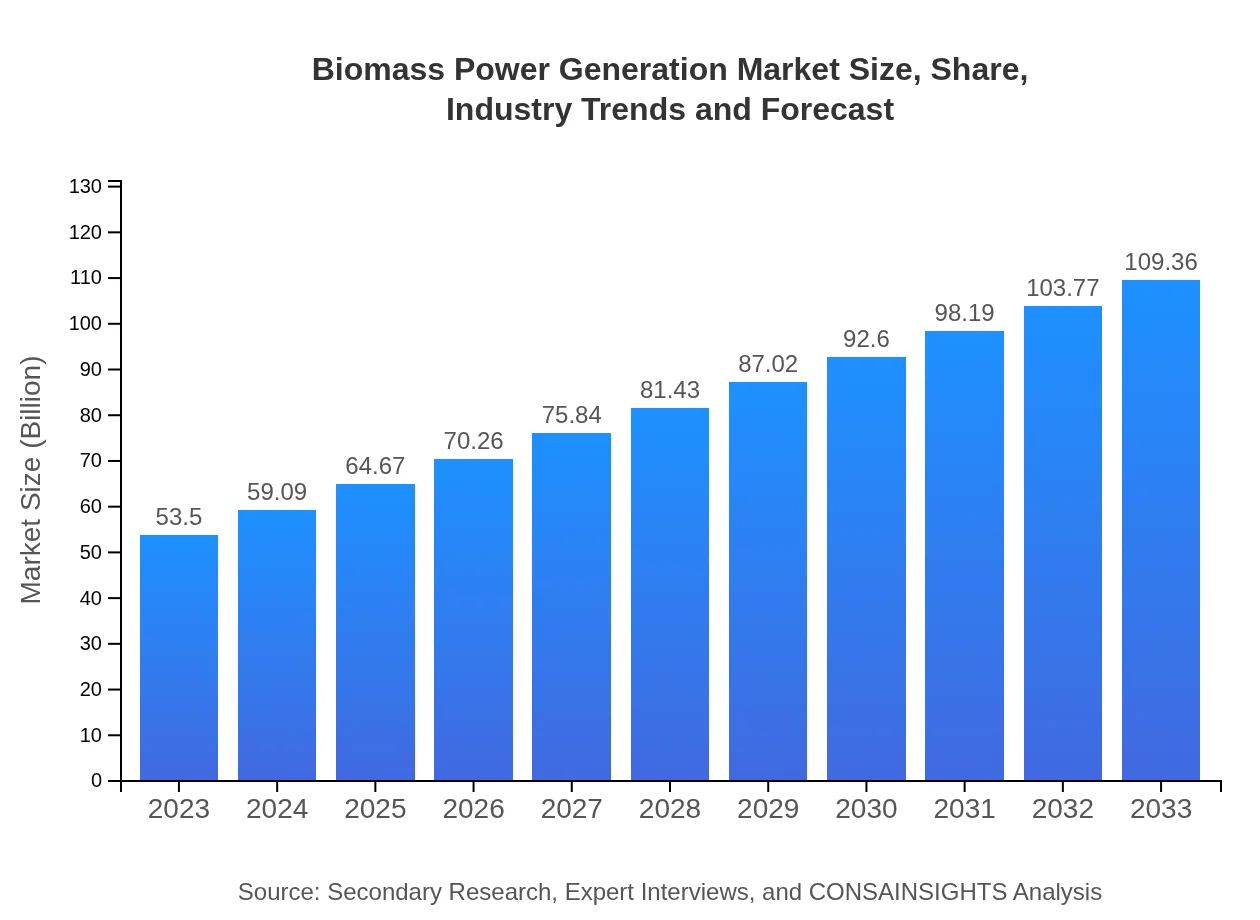
| 2023 Market Size | $53.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $109.36 Billion |
| Top Companies | Drax Group plc, Enviva Partners, LP, Nexterra Systems Corp., Fortum Oyj, PLT Energia |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Biomass Power Generation Market Overview
Customize Biomass Power Generation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Biomass Power Generation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Biomass Power Generation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Biomass Power Generation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Biomass Power Generation market in 2023?
Biomass Power Generation Industry Analysis
Biomass Power Generation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Biomass Power Generation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Biomass Power Generation Market Report:
The European market will see growth from USD 16.98 billion in 2023 to USD 34.70 billion by 2033. European countries are heavily investing in renewable energies, with biomass energy playing a significant role in meeting EU climate targets and sustainability goals.Asia Pacific Biomass Power Generation Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Biomass Power Generation market is expected to grow from USD 8.93 billion in 2023 to USD 18.25 billion by 2033. This growth can be attributed to the region's diverse agricultural sector, which supplies a steady stream of biomass feedstock, as well as increasing energy demand and government incentives for renewable energy.North America Biomass Power Generation Market Report:
North America is expected to witness a substantial increase in the Biomass Power Generation market size, from USD 20.08 billion in 2023 to USD 41.04 billion by 2033. Demand for renewable energy sources and the capacity to convert forestry waste into biomass fuel are key drivers of this growth.South America Biomass Power Generation Market Report:
The South American market for Biomass Power Generation is projected to grow from USD 4.17 billion in 2023 to USD 8.53 billion in 2033. The rich availability of biomass resources and supportive government policies will likely propel market growth, making the region an important player in the biomass industry.Middle East & Africa Biomass Power Generation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Biomass Power Generation market is projected to rise from USD 3.34 billion in 2023 to USD 6.84 billion in 2033. Given the growing energy needs and initiatives to diversify energy sources, biomass energy is garnering attention as a reliable option for both power generation and waste management.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
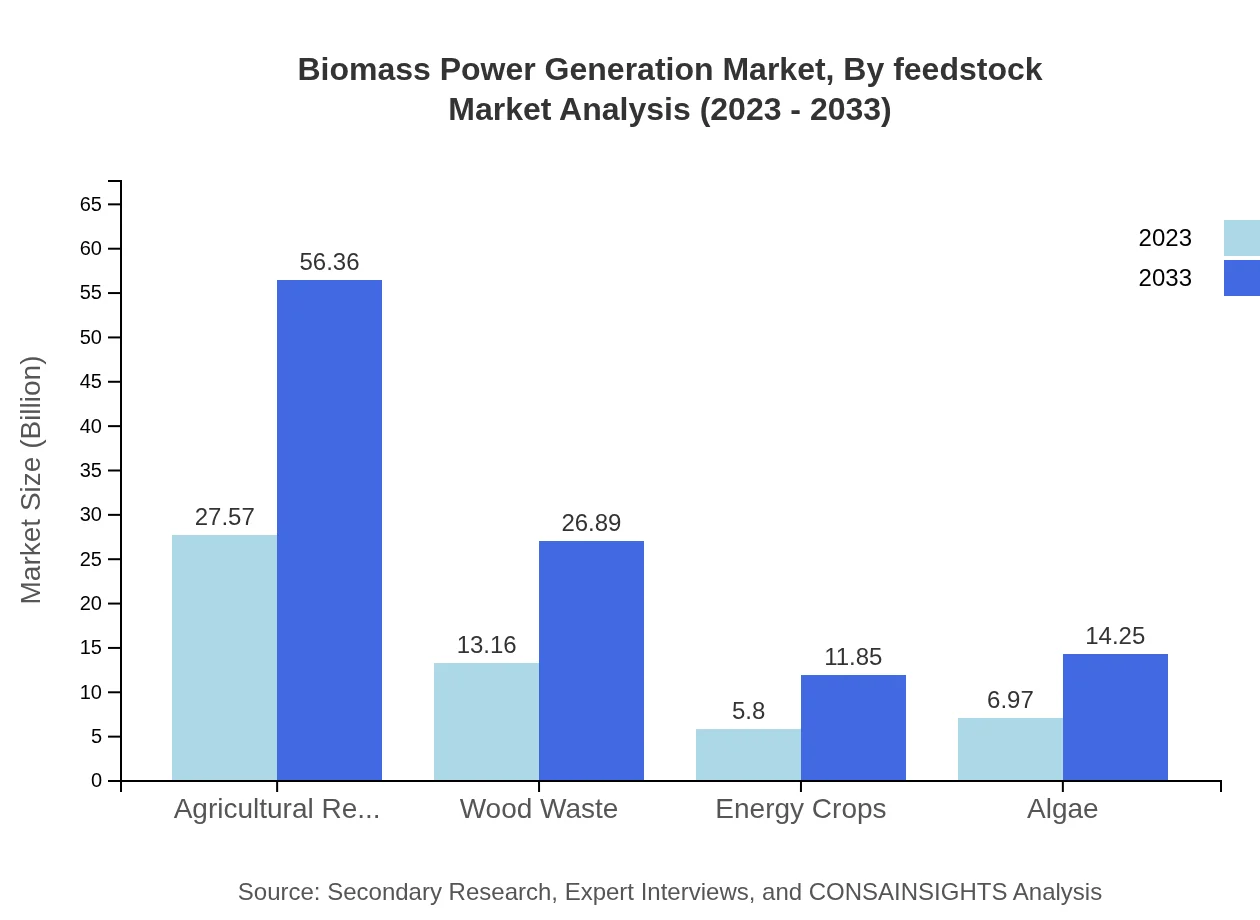
Biomass Power Generation Market Analysis By Feedstock
The market's primary feedstock segment, particularly Agricultural Residues, shows a strong performance with a size of USD 27.57 billion in 2023 and expected to reach USD 56.36 billion by 2033. Wood Waste and Energy Crops follow, with respective forecasts of USD 13.16 billion and USD 5.80 billion in 2023, expanding to USD 26.89 billion and USD 11.85 billion by 2033.
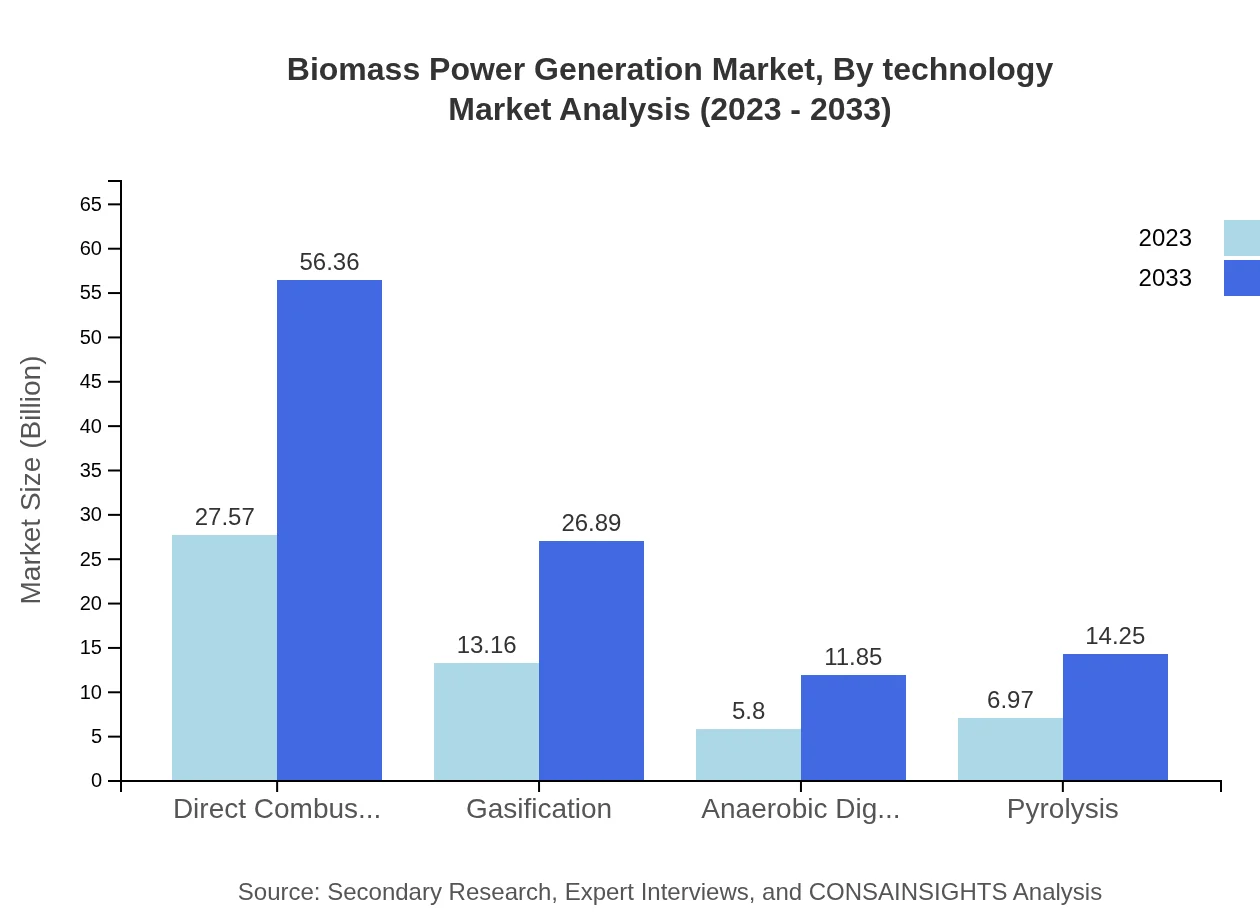
Biomass Power Generation Market Analysis By Technology
Significant technological advancements are observed in Direct Combustion, Gasification, Anaerobic Digestion, and Pyrolysis. The Direct Combustion segment, representing a 51.54% market share in 2023, is expected to maintain dominance with a strong growth trajectory projected along the forecast period.
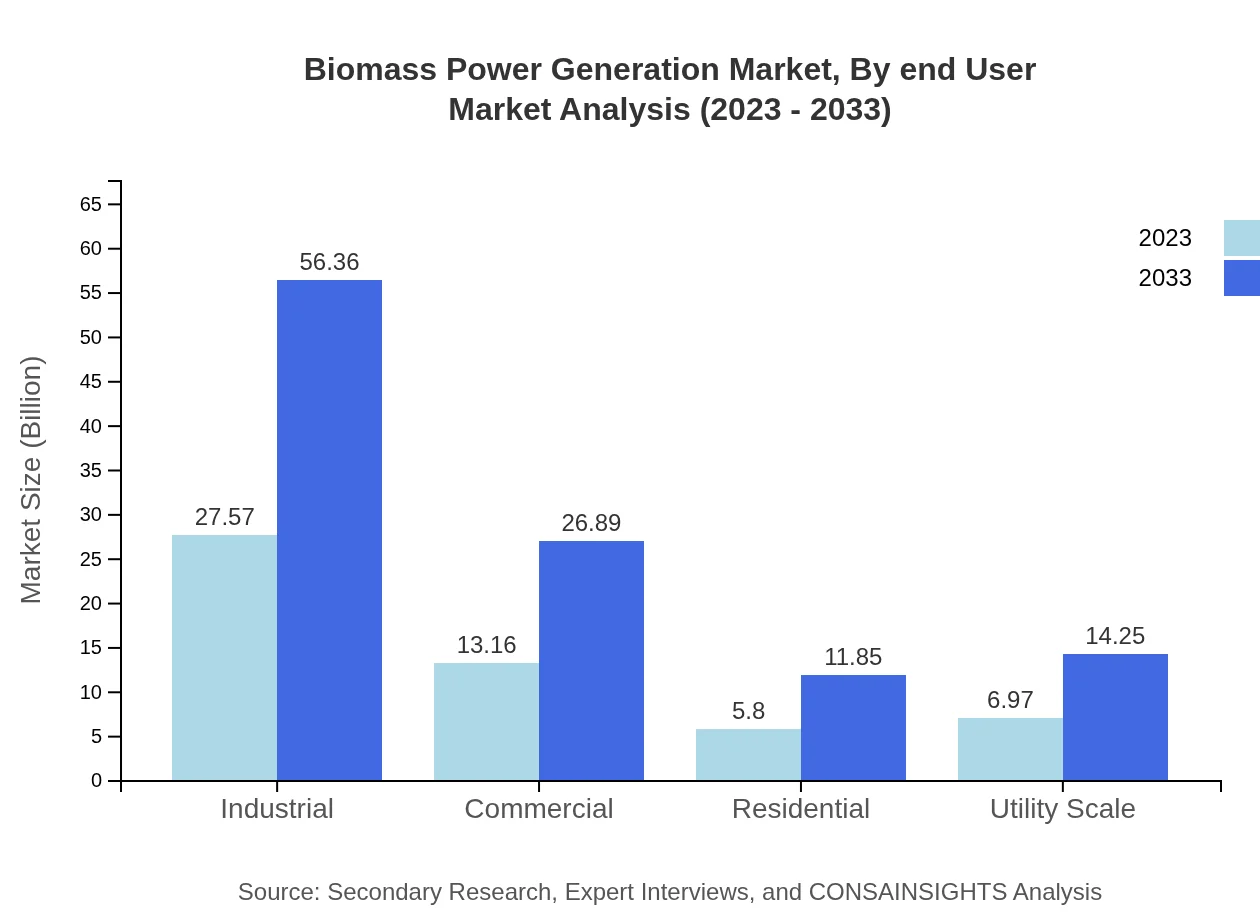
Biomass Power Generation Market Analysis By End User
The Biomass Power Generation market is categorized into Industrial, Commercial, Residential, and Utility Scale segments. The Industrial segment displays robust performance, anticipated to grow from USD 27.57 billion in 2023 to USD 56.36 billion by 2033.
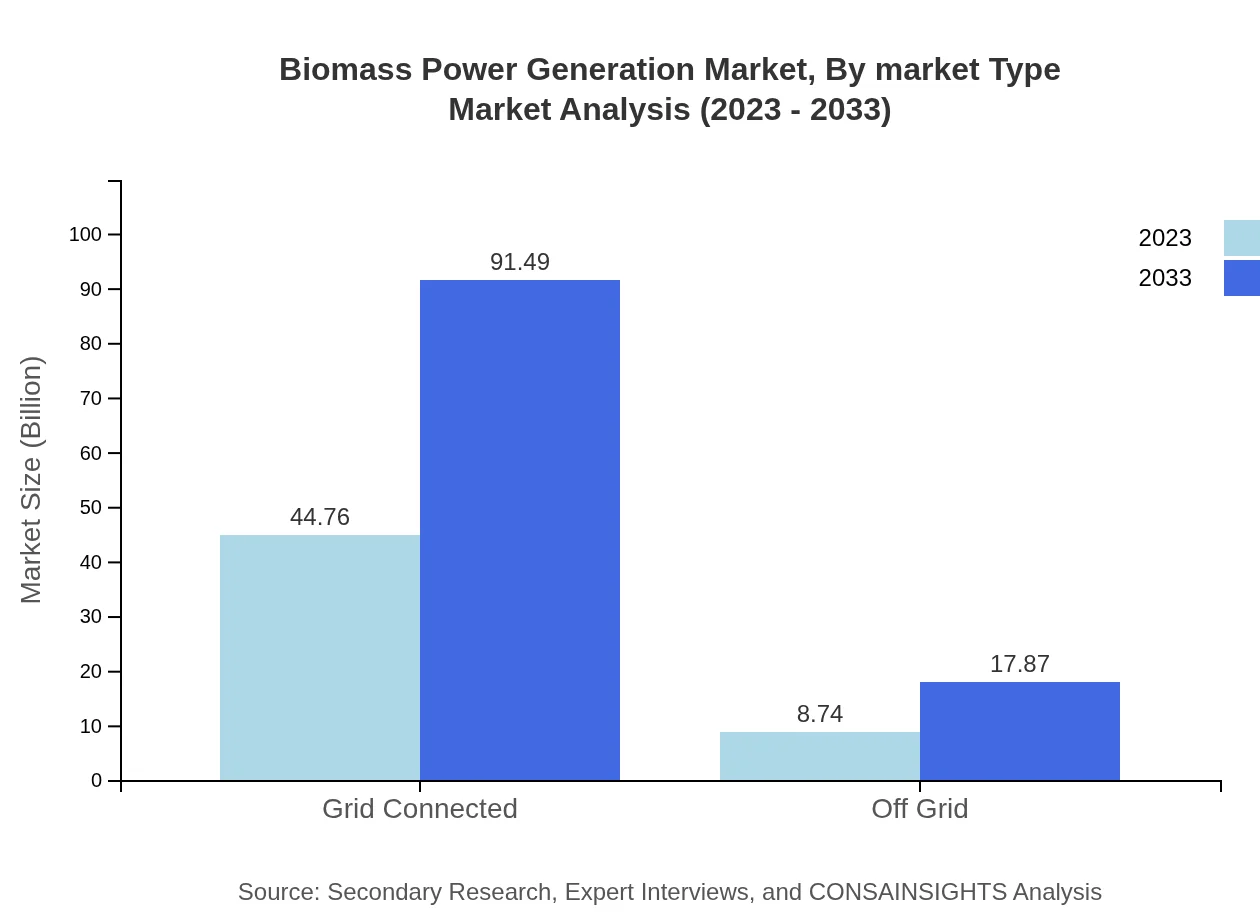
Biomass Power Generation Market Analysis By Market Type
The market is analyzed through Grid Connected and Off Grid types. The Grid Connected segment is the larger segment, with a market size of USD 44.76 billion in 2023, projected to increase to USD 91.49 billion by 2033.
Biomass Power Generation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Biomass Power Generation Industry
Drax Group plc:
Drax Group is a leading renewable energy company based in the UK, primarily known for its biomass power stations and innovation in renewable technologies.Enviva Partners, LP:
Enviva is the world's largest producer of wood pellets, a key feedstock for biomass power generation, emphasizing sustainability and responsible sourcing.Nexterra Systems Corp.:
Nexterra is a leading provider of pioneering biomass gasification solutions that convert biomass into clean energy.Fortum Oyj:
Fortum is a Finnish energy company that promotes renewable energy solutions and operates several biomass power plants across Europe.PLT Energia:
PLT Energia is part of PLT Group and operates in the Italian biomass sector, focusing on sustainable energy production and efficiency.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of biomass power generation?
The global biomass power generation market is valued at approximately $53.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 7.2%. By 2033, the market is expected to grow significantly, driven by increasing green energy initiatives.
What are the key market players or companies in this biomass power generation industry?
Key players in the biomass power generation sector include major companies such as Veolia, Drax Group, and Enel Green Power. These companies are essential in driving technological advancements and expanding market reach.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the biomass power generation industry?
The growth of the biomass power generation industry is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, government support for sustainable practices, technological advancements, and rising environmental concerns associated with fossil fuels.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the biomass power generation?
The fastest-growing region in biomass power generation from 2023 to 2033 is North America, projected to grow from $20.08 billion to $41.04 billion. Europe closely follows, expected to grow from $16.98 billion to $34.70 billion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the biomass power generation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs in the biomass power generation industry. This includes detailed market analysis and insights tailored to stakeholder requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this biomass power generation market research project?
From this biomass power generation market research project, you can expect comprehensive deliverables including market size data, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, and insights into market trends and regional developments.
What are the market trends of biomass power generation?
Current trends in the biomass power generation market highlight a shift towards innovation in technology, increased investment in sustainable energy projects, and growing partnerships for research and development in biomass energy solutions.