Bread Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: bread
Bread Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Bread market, covering insights into market trends, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
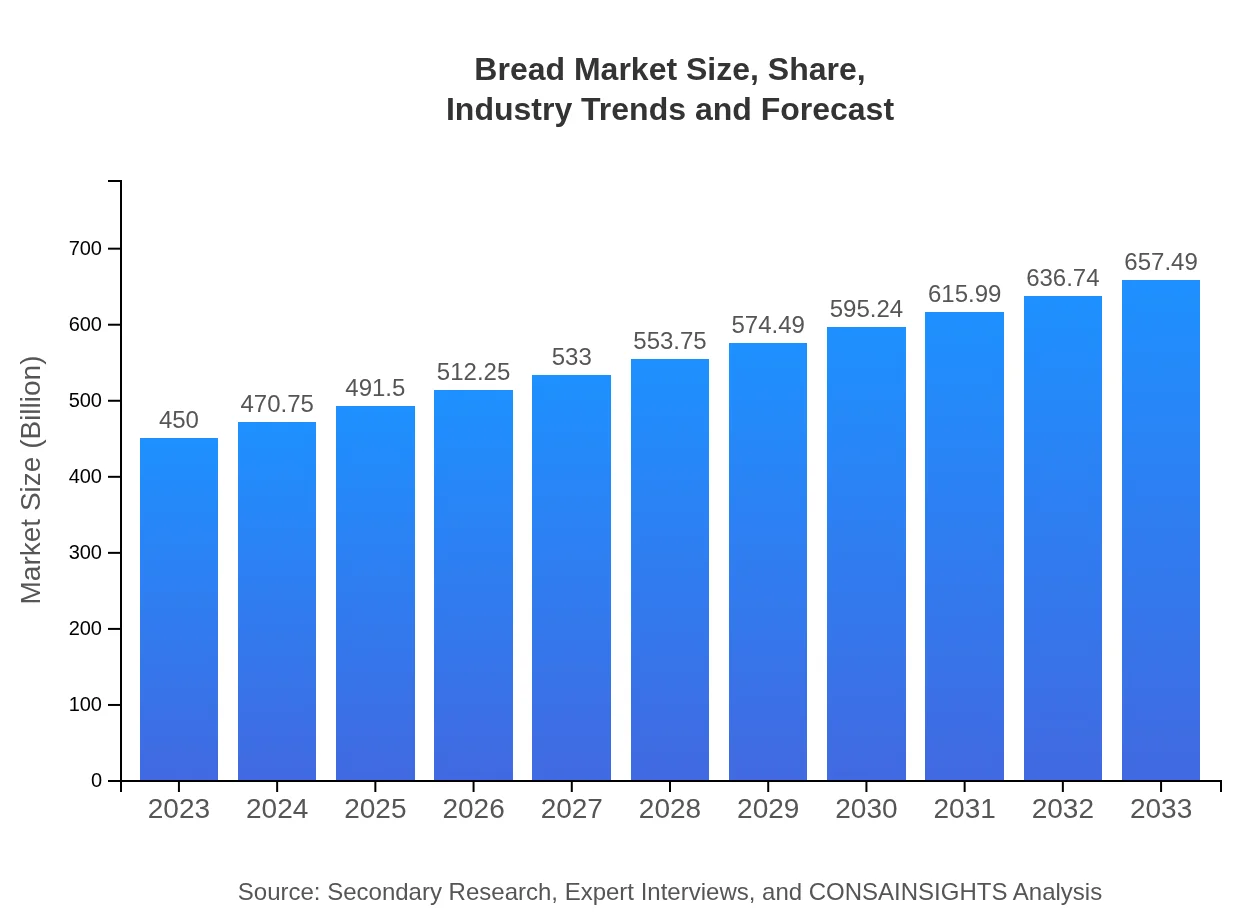
| 2023 Market Size | $450.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 3.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $657.49 Billion |
| Top Companies | Grupo Bimbo, Flowers Foods, United Biscuits, Kraft Heinz, Associated British Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Bread Market Overview
Customize Bread Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Bread market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Bread's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Bread
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Bread market in 2023?
Bread Industry Analysis
Bread Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Bread Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Bread Market Report:
In Europe, the Bread market valuation in 2023 stands at $155.25 billion, anticipated to rise to $226.83 billion by 2033. The region’s rich bread-making heritage, along with a growing inclination towards health-conscious products, contributes to its robust market growth.Asia Pacific Bread Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific Bread market is projected to be valued at $84.73 billion, expected to grow to $123.81 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, changing dietary habits, and a growing middle class interested in bakery products.North America Bread Market Report:
North America's Bread market size is estimated at $145.80 billion for 2023, with expectations to reach $213.03 billion by 2033. Factors such as high disposable income, health trends favoring whole grain options, and strong distribution networks play critical roles in this regional market's performance.South America Bread Market Report:
The Bread market in South America is estimated at $29.79 billion in 2023, with projections to reach $43.53 billion by 2033. Growing populations and an expanding retail sector, along with an increasing preference for bakery goods in consumer diets, support this growth.Middle East & Africa Bread Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are seeing a Bread market size of approximately $34.42 billion in 2023, with growth projections to $50.30 billion by 2033. The urbanizing population coupled with a youthful demographic largely supports the demand for convenient bread products.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Bread Market Analysis By Type
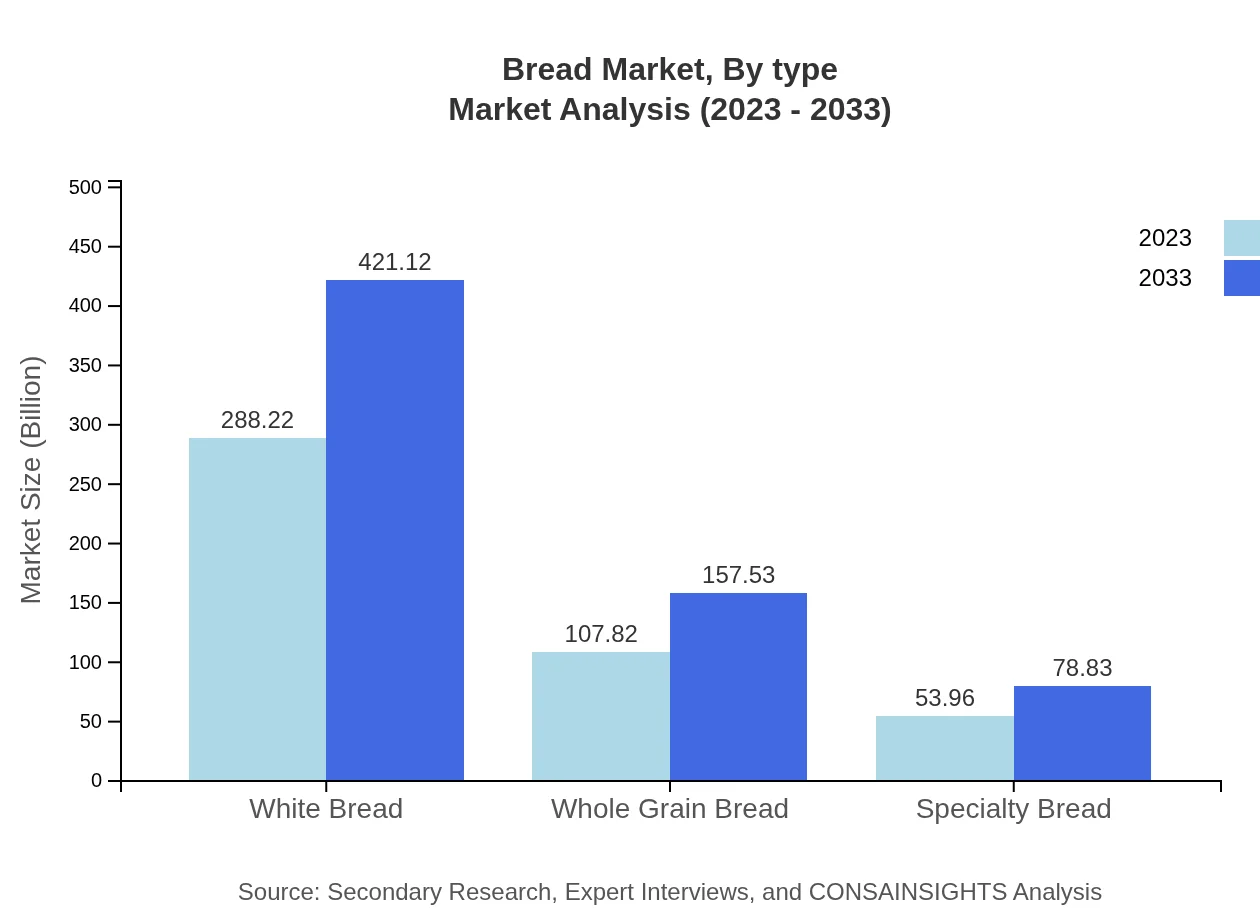
The analysis of the Bread market by type reveals significant insights. White Bread dominates with a market size of $288.22 billion in 2023 with a consistent market share of 64.05%. Whole Grain Bread follows, valued at $107.82 billion, holding a share of 23.96%. Specialty breads, such as artisan and gluten-free varieties, stand at $53.96 billion, claiming an 11.99% market share.
Bread Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
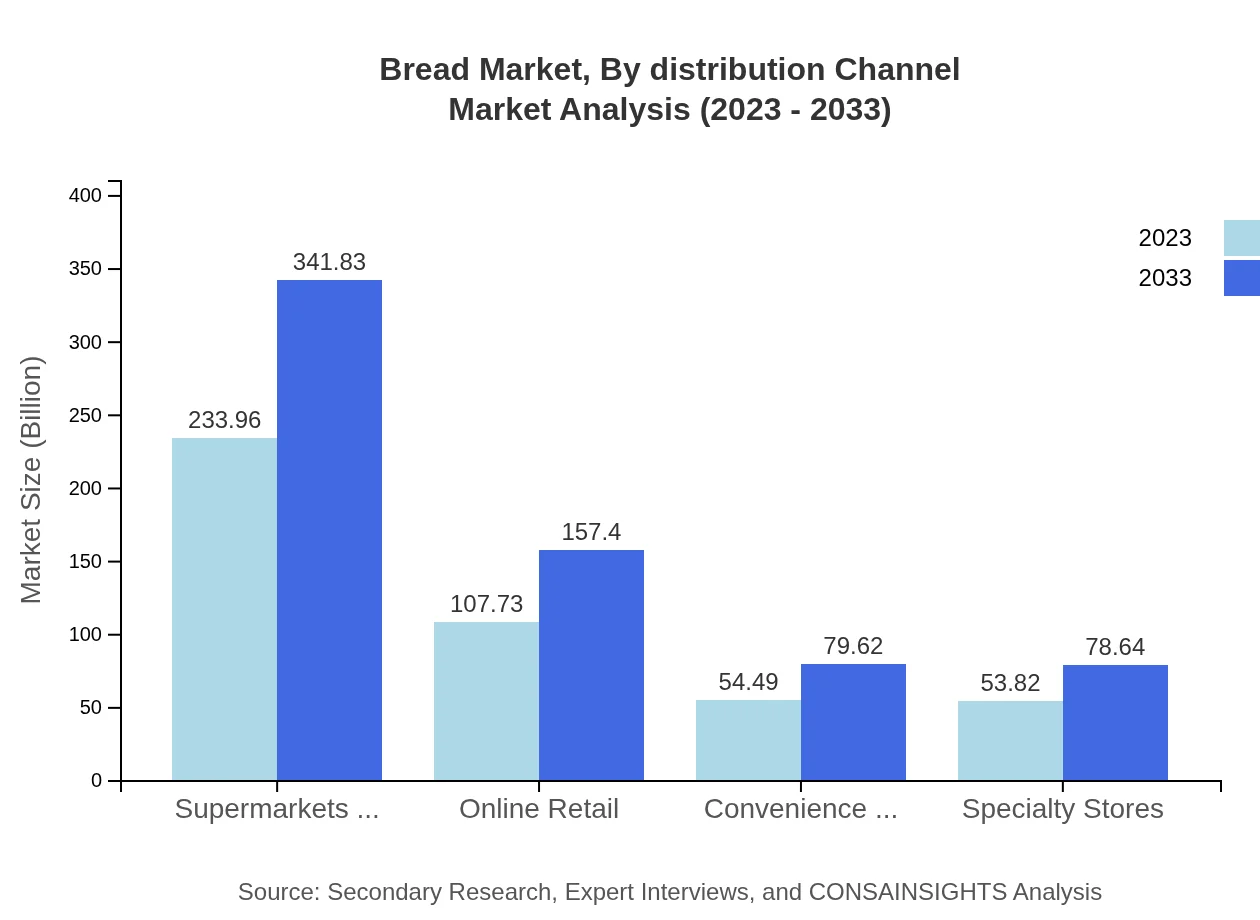
In terms of distribution, supermarkets and hypermarkets capture the largest share, providing a market size of $233.96 billion in 2023 at 51.99%. Online retail is gaining momentum, currently at $107.73 billion with a share of 23.94%. Convenience stores and specialty stores are also significant, providing targeted market options for specific segments.
Bread Market Analysis By Consumer Type
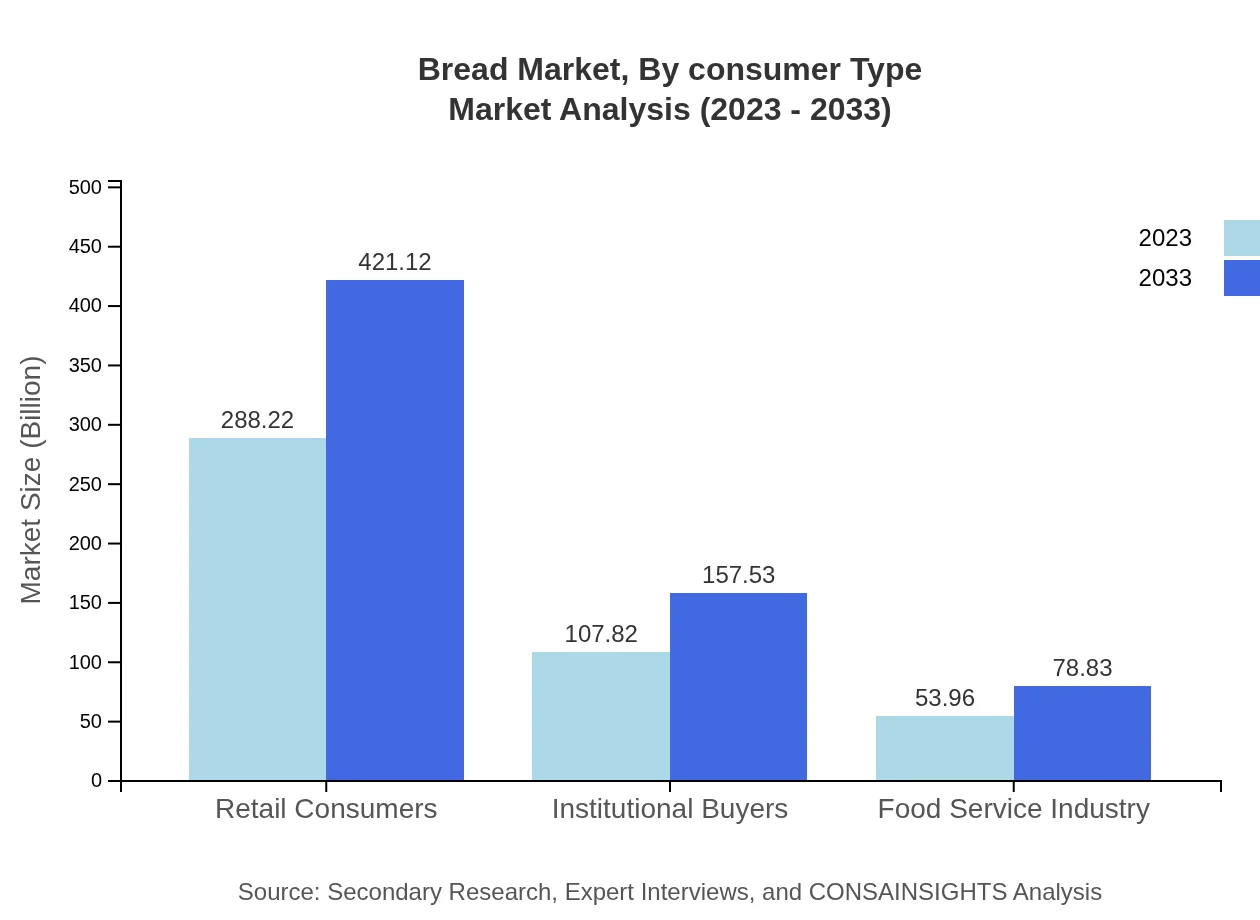
Consumer segmentation in the Bread market includes Retail Consumers, Institutional Buyers, and Food Service Industry. Retail Consumers dominate the market at $288.22 billion and a share of 64.05%. Institutional Buyers follow with a market size of $107.82 billion (23.96%), while the Food Service sector accounts for $53.96 billion (11.99%).
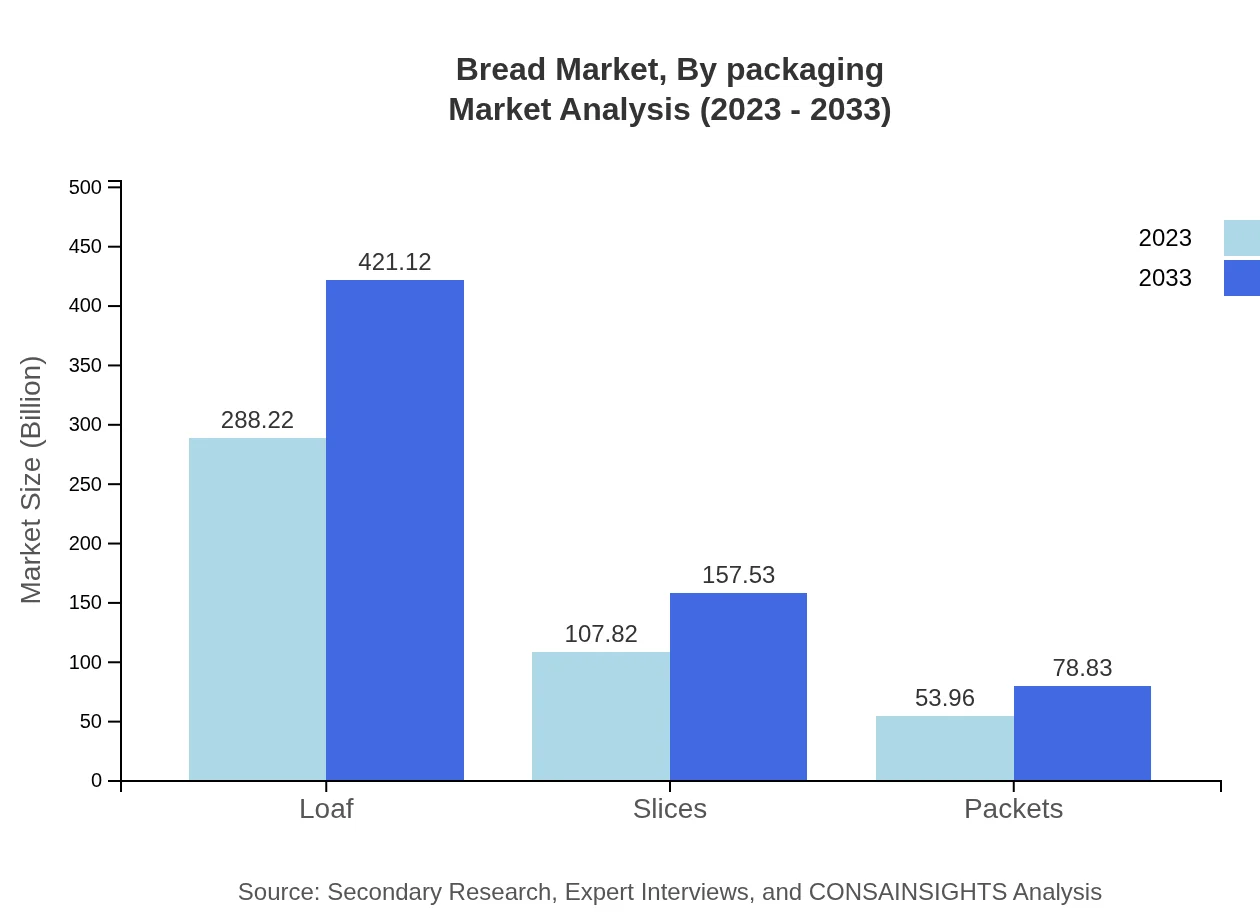
Bread Market Analysis By Packaging
Packaging types for the Bread market include Loaf, Slices, and Packets. The Loaf segment leads the market with a size of $288.22 billion and a share of 64.05%. Slices follow with a market size of $107.82 billion and 23.96%, while Packets are notably smaller, capturing a market size of $53.96 billion and a share of 11.99%.
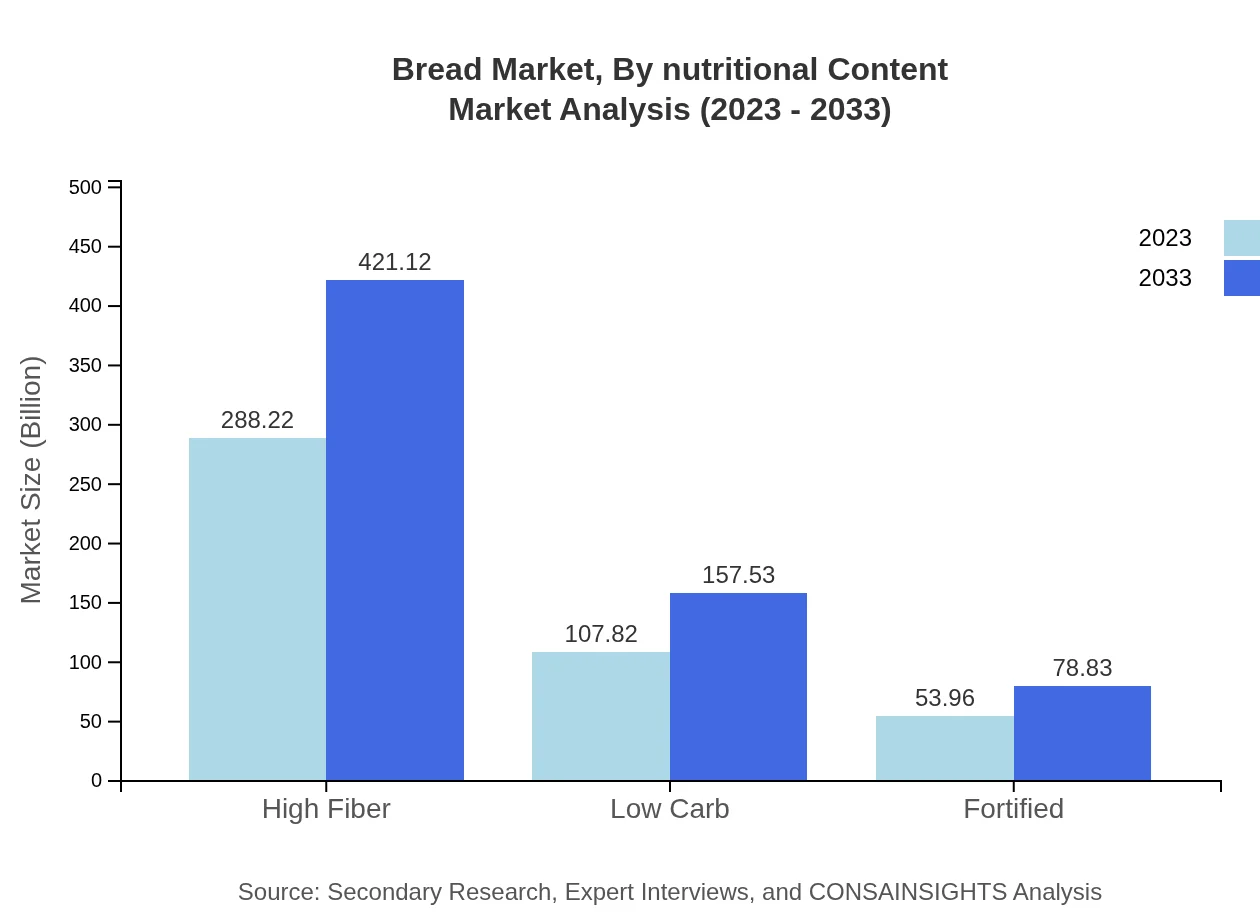
Bread Market Analysis By Nutritional Content
The nutritional content segment shows insights into High Fiber, Low Carb, and Fortified bread types. High Fiber variants stand out with a market size of $288.22 billion and 64.05%. Low Carb products follow at $107.82 billion (23.96%), while Fortified options capture a size of $53.96 billion (11.99%).
Bread Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Bread Industry
Grupo Bimbo:
Grupo Bimbo is a leading global baking company, producing high-quality bread and baked goods. It operates in over 33 countries, focusing on innovation and sustainability.Flowers Foods:
Flowers Foods, Inc. is one of the largest producers of packaged bakery foods in the United States, known for popular brands like Nature's Own and Dave's Killer Bread.United Biscuits:
United Biscuits is a British snack food company that also produces a variety of bread products, focusing on quality and heritage.Kraft Heinz:
The Kraft Heinz Company is an influential player in the bread market, emphasized by its vast portfolio of food products including breads and spreads.Associated British Foods:
Associated British Foods is well-known for its retail and grocery businesses while also having a significant market share in bakery products, including bread.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of bread?
The global market size of the bread industry is estimated at $450 billion with a projected CAGR of 3.8% from 2023 to 2033. This reflects steady growth driven by increasing demand for various bread types.
What are the key market players or companies in the bread industry?
Key players in the bread market include major brands and local bakeries, all contributing to a diverse landscape that accommodates a wide range of consumer preferences.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the bread industry?
The growth in the bread industry is primarily driven by increasing health consciousness, rising disposable incomes, and growing demand for convenience foods. These factors encourage consumption across diverse demographics.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the bread market?
The fastest-growing region in the bread market is Europe, projected to grow from $155.25 billion in 2023 to $226.83 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong demand for specialty and artisan bread.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the bread industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market research reports tailored to specific needs, providing in-depth insights into the bread industry including trends and forecasts.
What deliverables can I expect from this bread market research project?
From this bread market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports, detailed market analysis, consumer behavior insights, competitive landscape evaluations, and forecasts.
What are the market trends of bread?
Key market trends include a shift towards healthier bread options, increased demand for gluten-free products, and the rise of online retail sales alongside traditional in-store purchases.