Cargo Shipping Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: cargo-shipping
Cargo Shipping Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global Cargo Shipping market, covering key insights, market trends, and comprehensive regional breakdowns for the forecast period of 2023 to 2033. Key data includes market size, growth rates, and forecasts for various market segments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
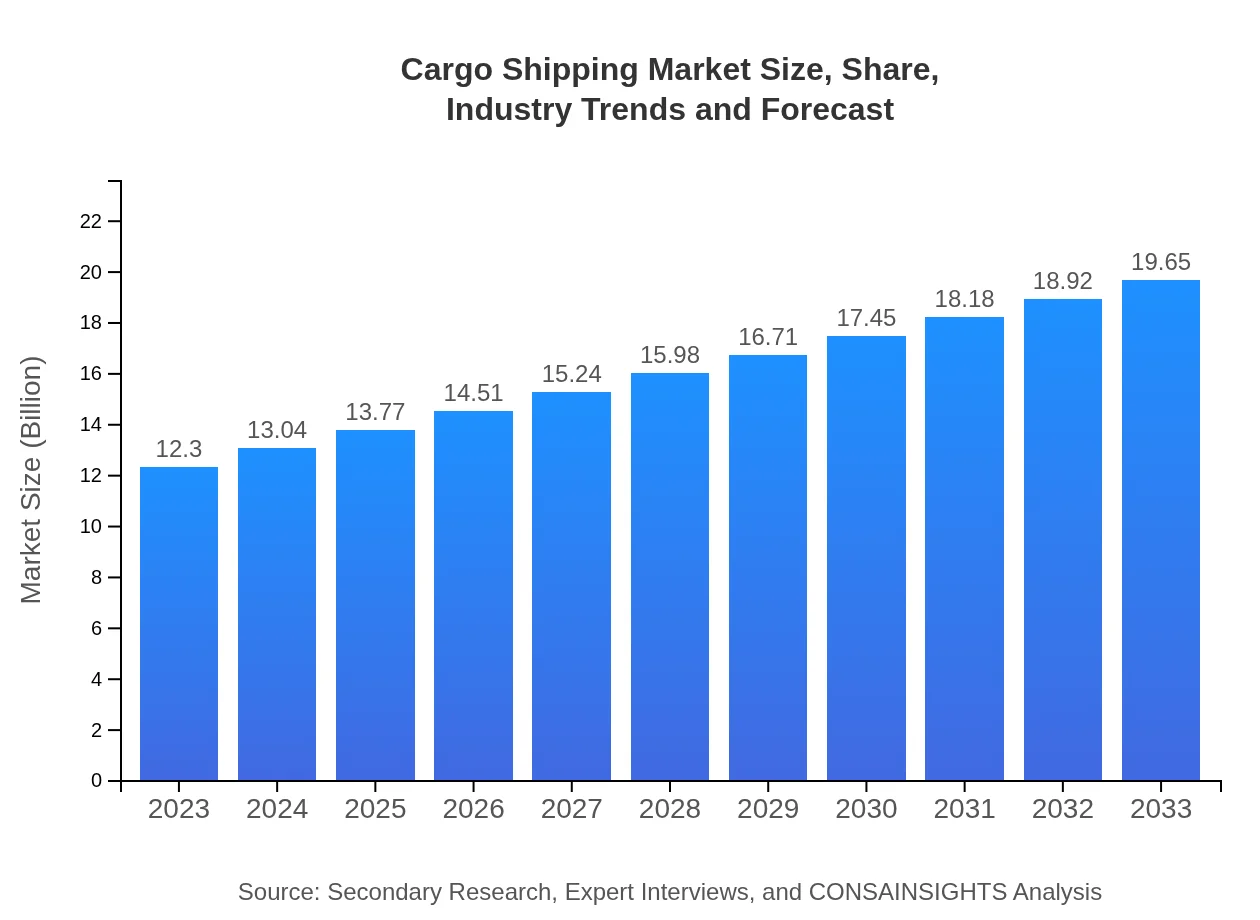
| 2023 Market Size | $12.30 Trillion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $19.65 Trillion |
| Top Companies | Maersk Line, Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), CMA CGM, Hapag-Lloyd |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Cargo Shipping Market Overview
Customize Cargo Shipping Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cargo Shipping market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cargo Shipping's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cargo Shipping
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cargo Shipping market in 2023 and 2033?
Cargo Shipping Industry Analysis
Cargo Shipping Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cargo Shipping Market Report:
Europe’s Cargo Shipping market is expected to expand from $3.07 billion in 2023 to $4.90 billion by 2033. The European Union plays a pivotal role in regulating shipping standards and sustainability norms. The region's diversified economies rely heavily on cargo shipping, leading to sustained growth opportunities.Asia Pacific Cargo Shipping Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region, with a market size of $2.40 billion in 2023 projected to grow to $3.84 billion by 2033, is a powerhouse in global trade. The robust manufacturing sector and increasing consumer demand for shipping have simultaneously driven demand in this region. Major routes connecting countries such as China, Japan, and India facilitate significant cargo movement, making it a crucial market for investment.North America Cargo Shipping Market Report:
North America, holding a market size of $4.09 billion in 2023, is estimated to rise to $6.54 billion by 2033. The area benefits from advanced port facilities and logistics networks. Trade agreements such as USMCA have bolstered cargo movements across borders, showcasing the importance of collaborative trade policies.South America Cargo Shipping Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to grow from $1.06 billion in 2023 to $1.70 billion in 2033. Key drivers include mineral exports and increasing efforts in infrastructure enhancement, although challenges like regulatory discrepancies remain. Countries like Brazil and Chile have established trade agreements that foster cargo shipping growth.Middle East & Africa Cargo Shipping Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region have a market size projected to increase from $1.68 billion in 2023 to $2.68 billion by 2033. The strategic location of countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia as transshipment hubs drives significant trade, while investments in shipping technology and infrastructure enhance capacity.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis By Cargo Type
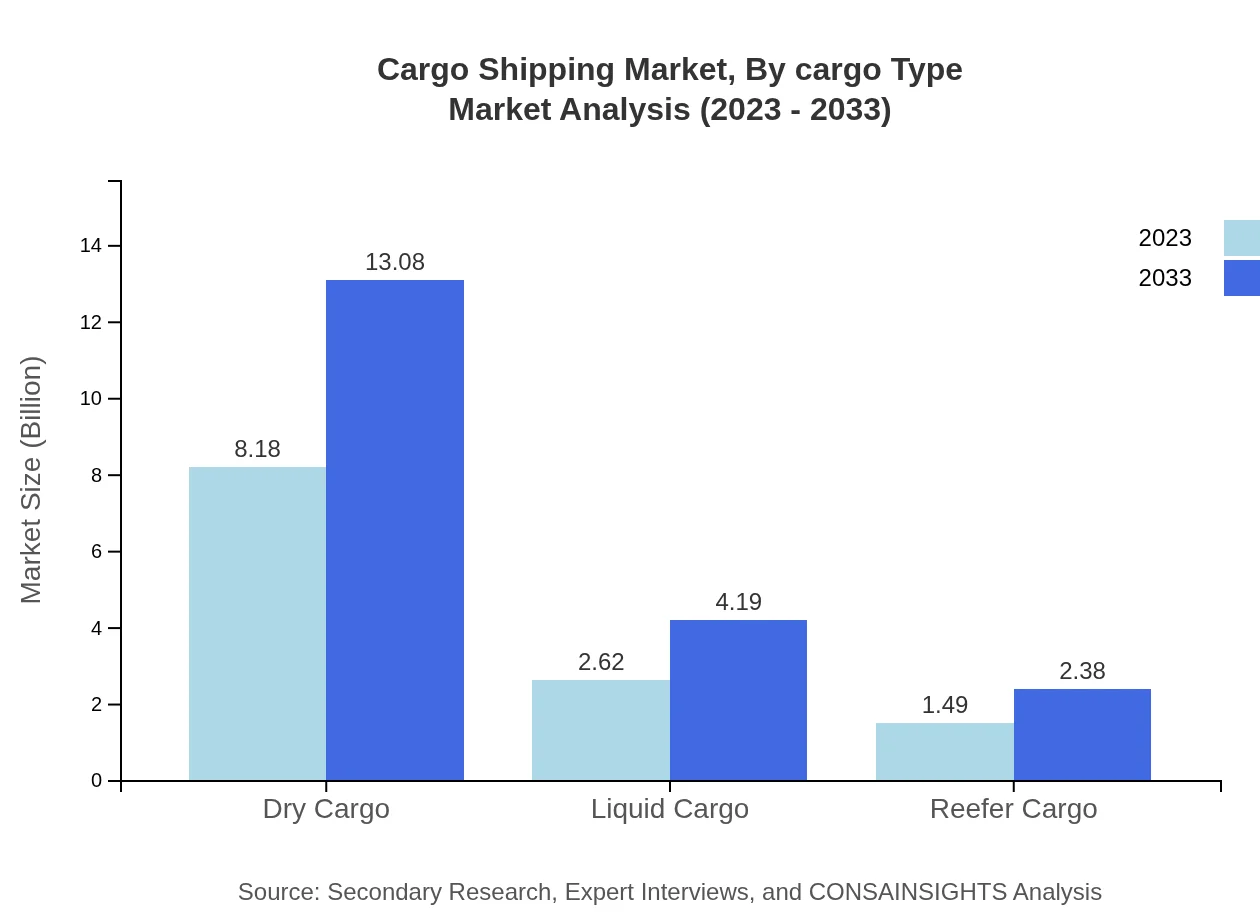
The cargo shipping market is primarily segmented by cargo type. The dry cargo segment dominates, forecasted to grow from $8.18 billion in 2023 to $13.08 billion by 2033, maintaining a share of 66.54%. Liquid cargo follows, with a growth projection from $2.62 billion to $4.19 billion, taking up 21.33% of the market. Reefer cargo, while smaller, contributes significantly, with expectations of rising from $1.49 billion to $2.38 billion, indicating its critical role in shipping perishable goods.
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis By Shipping Method
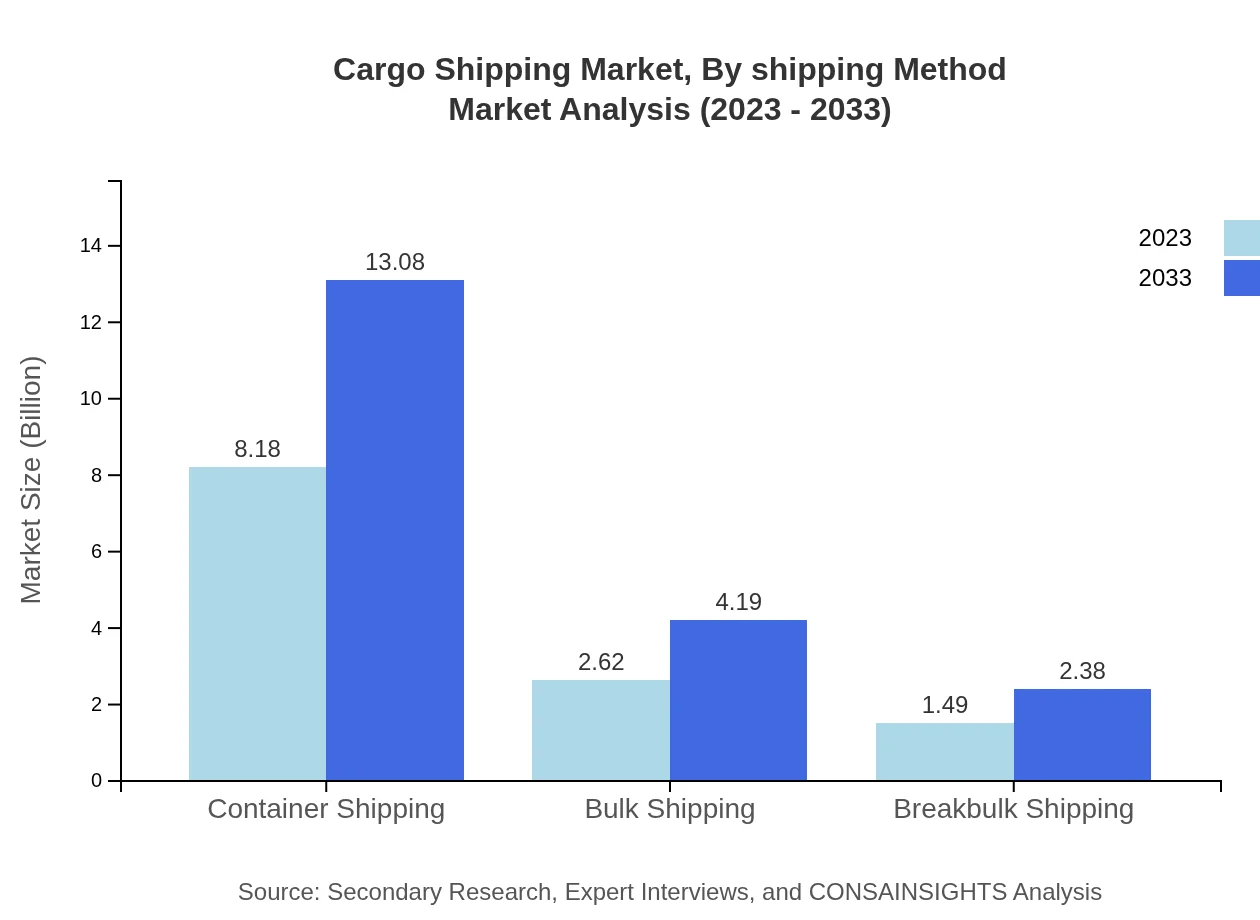
This segment highlights the dichotomy between traditional and modern shipping practices. Traditional methods will maintain a steady market size from $8.18 billion in 2023 to $13.08 billion in 2033. Meanwhile, digital technologies are set to enhance operational capabilities, also projected to grow from $2.62 billion to $4.19 billion. Green technology, albeit at a smaller scale, anticipates growth from $1.49 billion to $2.38 billion, reflecting a broader shift toward sustainability.
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis By End User Industry
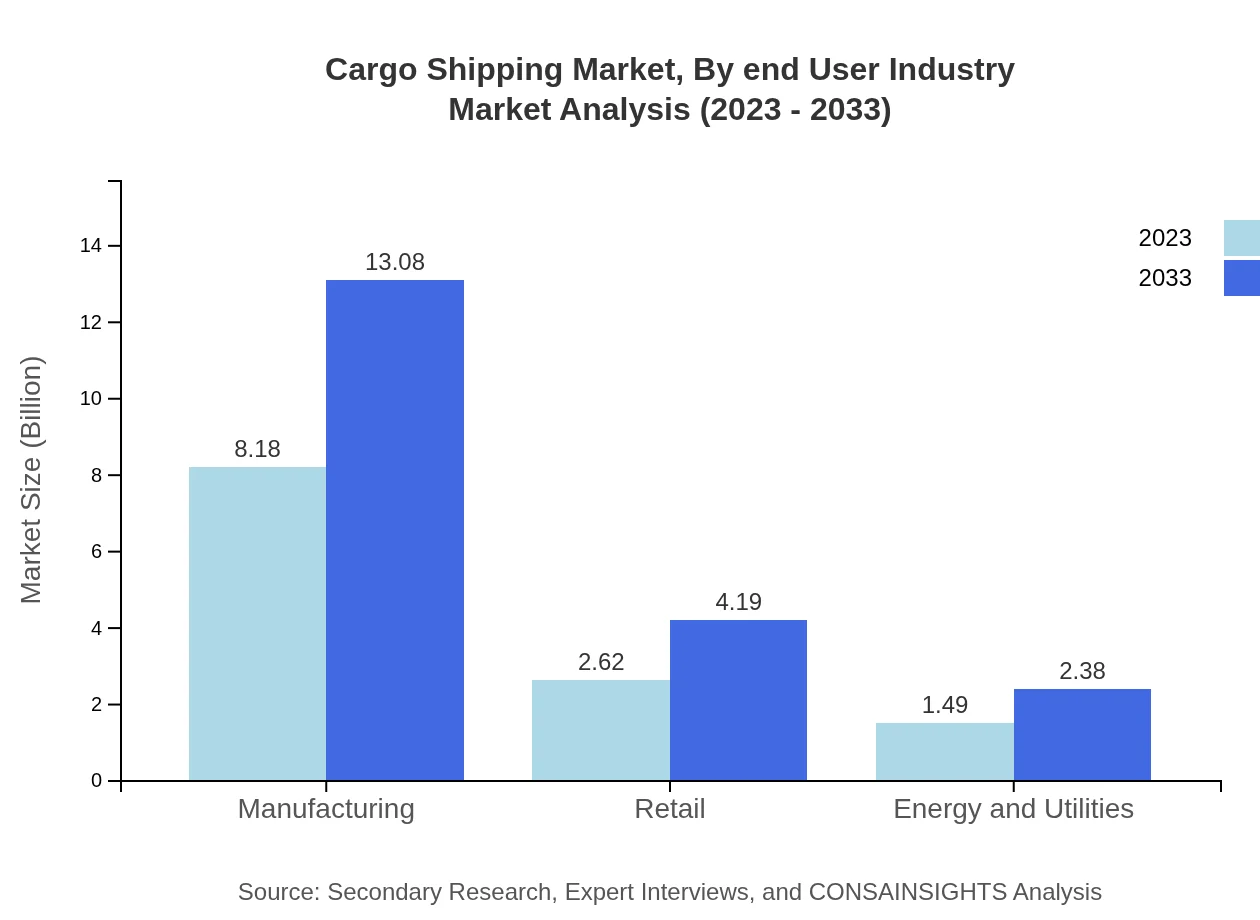
The end-user industry segmentation illustrates that manufacturing continues to be the leading consumer of cargo shipping services, maintaining a share of 66.54% from $8.18 billion in 2023 to $13.08 billion in 2033. The retail sector also significantly contributes, expanding from $2.62 billion to $4.19 billion, representing 21.33%. Energy and utilities will grow from $1.49 billion to $2.38 billion, underscoring its increasing reliance on efficient cargo shipping systems.
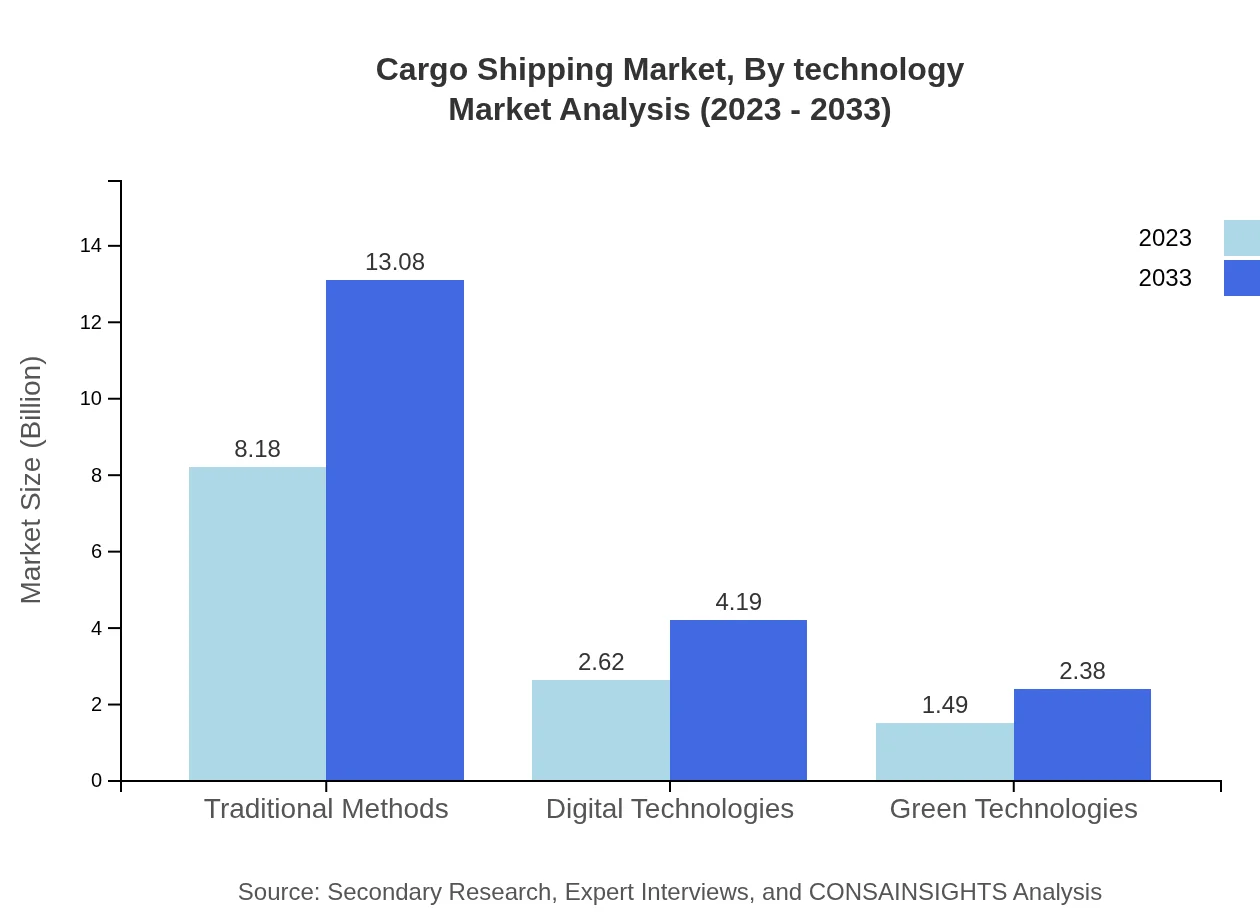
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are reshaping the cargo shipping landscape, with a marked emphasis on digital and green technologies. Digital solutions, crucial for improving supply chain transparency and operational efficiency, will grow from $2.62 billion to $4.19 billion. Meanwhile, investments in green technologies will equally see growth from $1.49 billion to $2.38 billion, addressing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures.
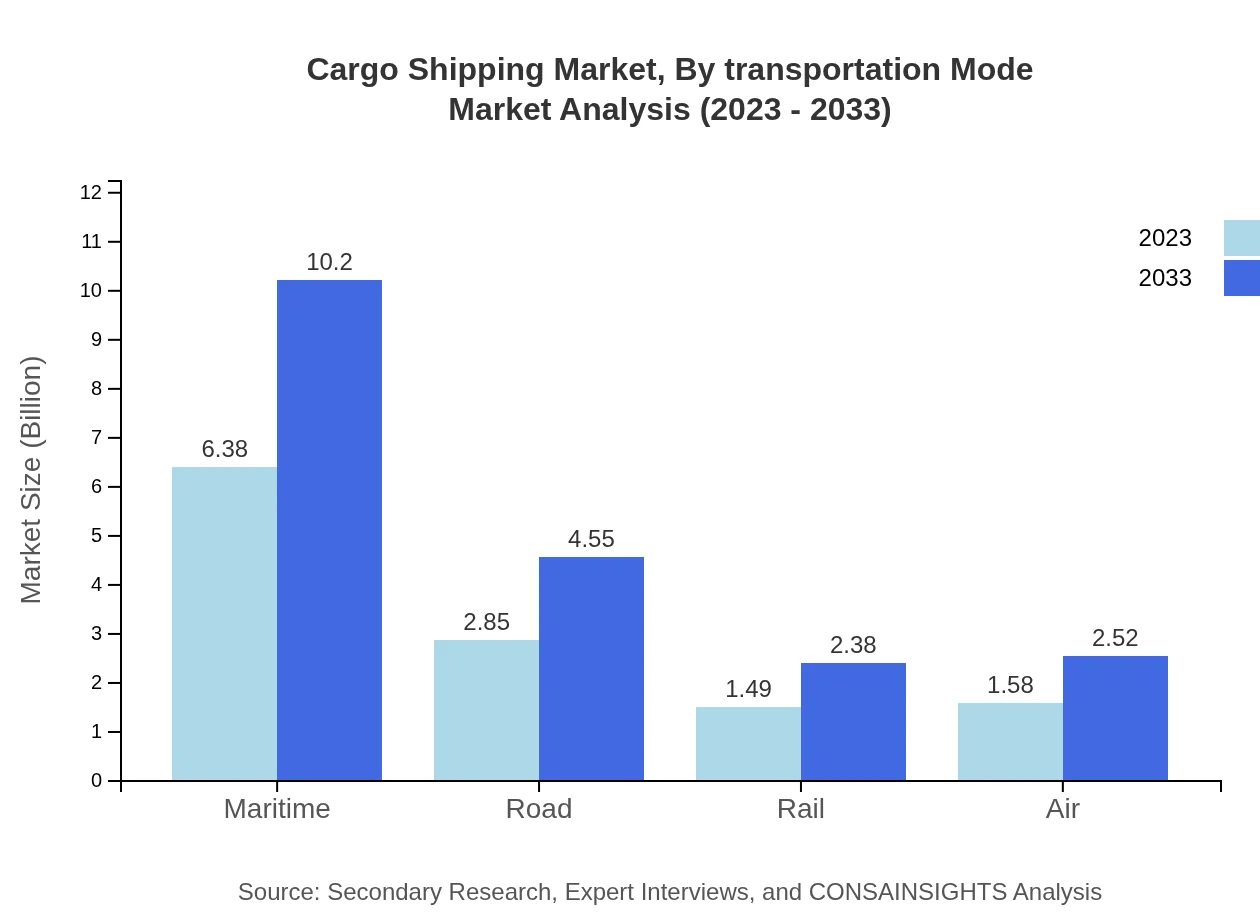
Cargo Shipping Market Analysis By Transportation Mode
The transportation mode analysis illustrates the dominance of maritime shipping with an approximate market share of 51.9%, growing from $6.38 billion in 2023 to $10.20 billion by 2033. Road transportation, crucial in logistics, will expand significantly as well, growing from $2.85 billion to $4.55 billion. Air and rail modes are projected to grow modestly, reflecting the necessity of integrated multimodal transport solutions.
Cargo Shipping Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cargo Shipping Industry
Maersk Line:
As the world's largest container shipping company, Maersk Line operates an extensive fleet and offers a range of integrated logistics solutions, driving innovation in the shipping industry.Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC):
MSC is one of the leading shipping lines globally, known for its commitment to sustainability and growth in container transport services across key maritime routes.CMA CGM:
CMA CGM is globally recognized for its maritime transport services, offering innovative logistics solutions, emphasizing intermodal transport to optimize cargo movements.Hapag-Lloyd:
Hapag-Lloyd provides reliable shipping services and is known for its commitment to environmental sustainability and enhancing customer connectivity through digital solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cargo shipping?
The cargo shipping market is projected to reach a size of $12.3 trillion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.7%. This expansion reflects increasing global trade and the rising demand for logistics solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the cargo shipping industry?
Key players in the cargo shipping industry include Maersk Line, Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), CMA CGM, Hapag-Lloyd, and Evergreen Marine Corp. These companies dominate the market by providing extensive shipping services worldwide.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cargo shipping industry?
Growth in the cargo shipping industry is driven by globalization, increasing consumer demands, e-commerce expansion, and technological advancements in logistics and shipping. These factors enhance efficiency and facilitate global trade.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cargo shipping industry?
The North America region is expected to be the fastest-growing in the cargo shipping industry, with market size projected to grow from $4.09 trillion in 2023 to $6.54 trillion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cargo shipping industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs, allowing businesses to gain personalized insights on the cargo shipping industry, including market trends and forecasts.
What deliverables can I expect from this cargo shipping market research project?
From a cargo shipping market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, segment performance, competitive analysis, and regional breakdowns, offering in-depth insights.
What are the market trends of cargo shipping?
Current trends in the cargo shipping industry include a shift towards digital technologies, increased use of green technologies, growing demand for container shipping, and enhanced focus on sustainability practices across the sector.