Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cell-banking-outsourcing
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Cell Banking Outsourcing market, including market size forecasts and insights from 2023 to 2033, along with trends, regional breakdowns, and company profiles for key industry players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
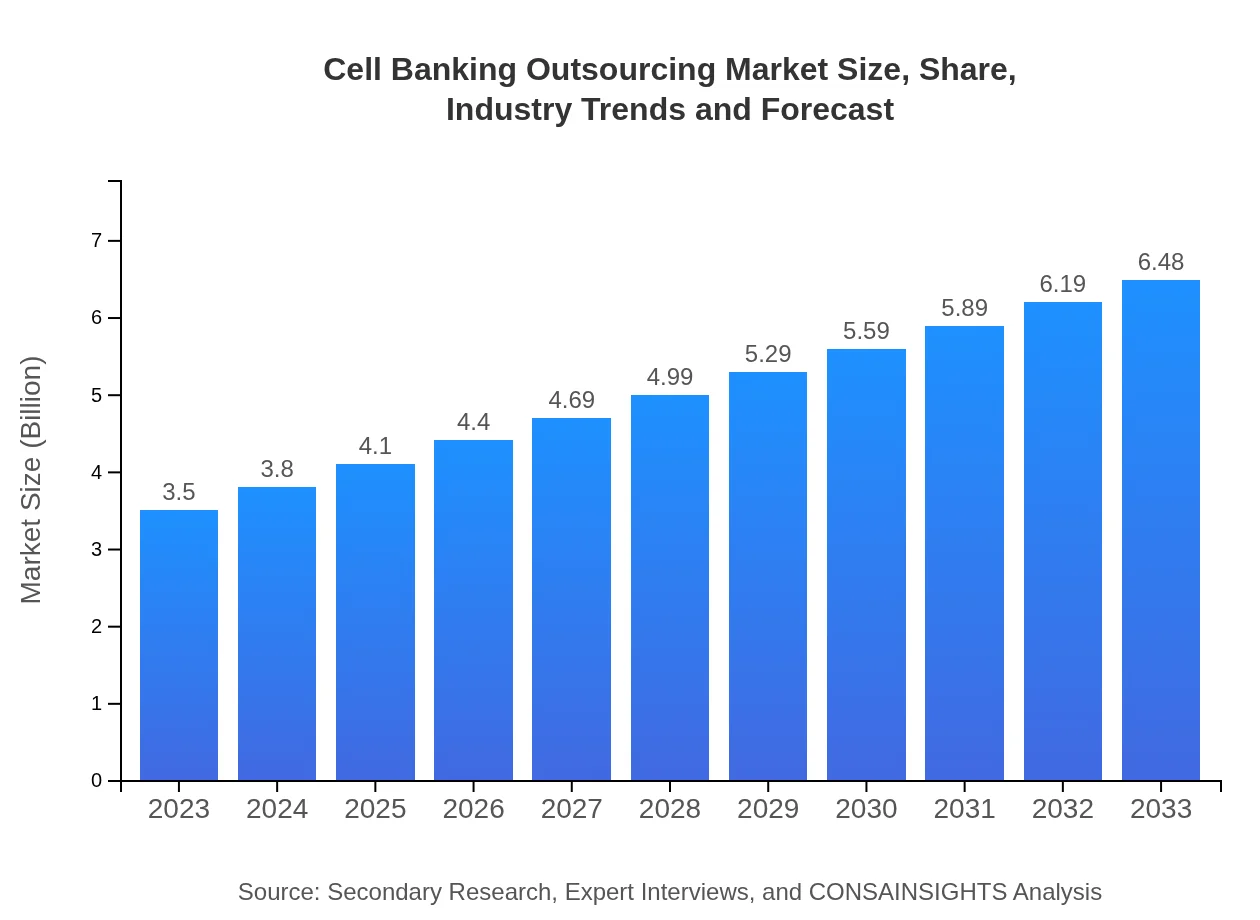
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $6.48 Billion |
| Top Companies | Lonza Group, CryoBanking International, Source BioScience, STEMCELL Technologies |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Overview
Customize Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cell Banking Outsourcing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cell Banking Outsourcing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cell Banking Outsourcing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cell Banking Outsourcing market in 2023?
Cell Banking Outsourcing Industry Analysis
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report:
The European market for cell banking outsourcing is currently valued at $0.90 billion and is expected to reach approximately $1.66 billion by 2033. The growth is bolstered by stringent regulations governing cell storage and handling, coupled with rising investments from biotechnology firms seeking innovative solutions.Asia Pacific Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region, valued at $0.73 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to $1.35 billion by 2033. The rise in biotechnology initiatives and increased funding in stem cell research in countries like Japan and China are key growth drivers. Additionally, the growing number of research institutions and the adoption of advanced storage technologies in the region are propelling market expansion.North America Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report:
North America holds the largest market share, with a projected increase from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $2.22 billion by 2033. The region is characterized by a strong presence of key players, a robust regulatory environment, and significant investment in R&D, particularly in cellular therapies and biobanking technologies.South America Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report:
In South America, the cell banking outsourcing market is forecasted to increase from $0.29 billion in 2023 to $0.55 billion by 2033. Growth in this region is attributed to increased healthcare spending and improved access to advanced biobanking services, particularly in Brazil and Argentina, where partnerships with global players are emerging.Middle East & Africa Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is set to rise from $0.38 billion in 2023 to $0.70 billion by 2033. The expansion is supported by increases in awareness of stem cell research and therapy in GCC countries, alongside investment in healthcare infrastructure and biobanking facilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis By Service Type
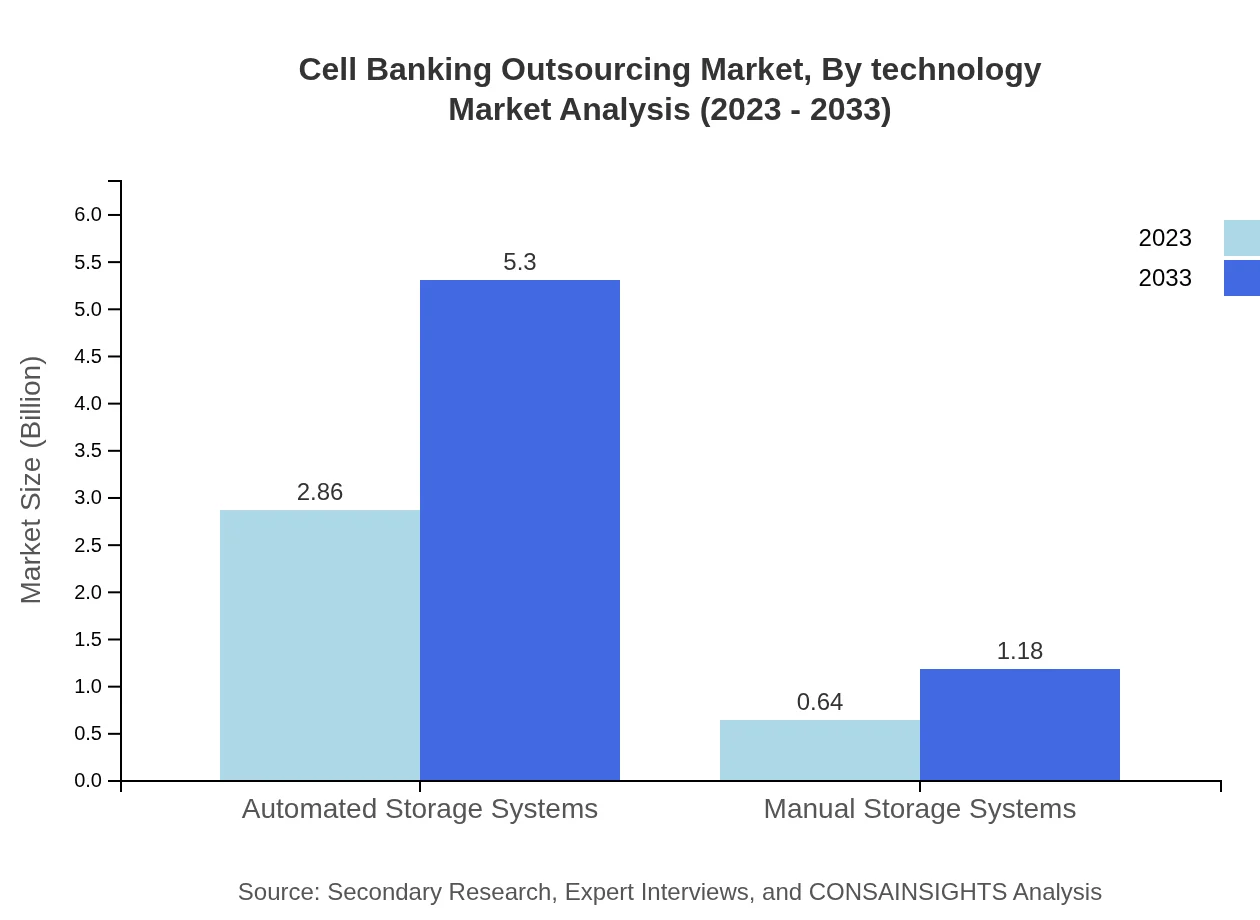
The major service types in the cell banking outsourcing market include automated storage systems and manual storage systems. Automated storage systems accounted for a significant market share in 2023 due to their efficiency and reliability. The market for automated storage systems is projected to grow from $2.86 billion in 2023 to $5.30 billion by 2033, demonstrating strong adoption in biobanking operations. In contrast, manual storage systems represented a smaller segment, with expected growth from $0.64 billion to $1.18 billion, highlighting the gradual shift toward automation.
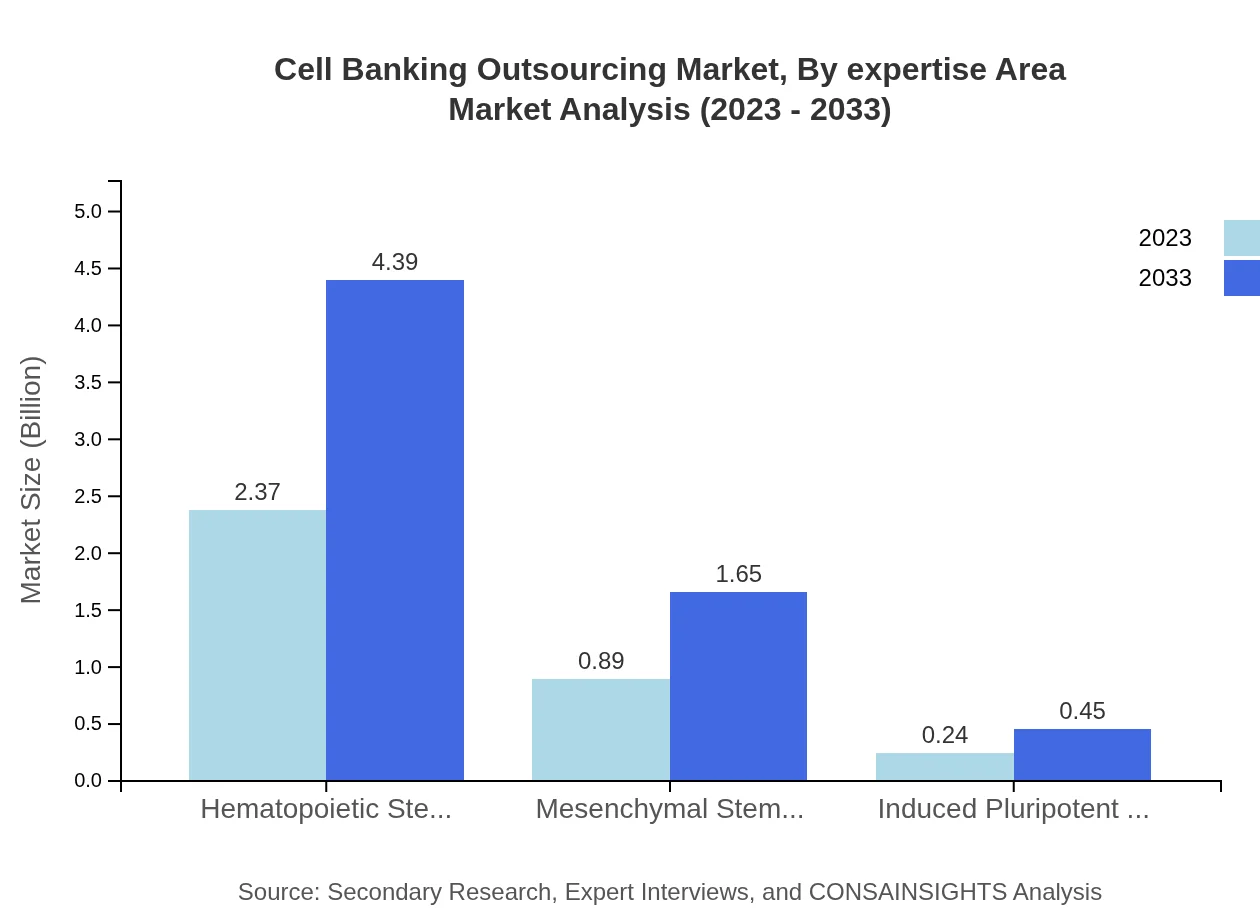
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis By Expertise Area
Segmented by expertise area, the market features Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Hematopoietic stem cells dominate the market, projected to rise from $2.37 billion in 2023 to $4.39 billion by 2033. This segment's growth is driven by increasing research and clinical applications in regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells are similarly significant, extending from $0.89 billion to $1.65 billion, while Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells, though smaller in market size, are gaining traction due to innovations in regenerative therapies.
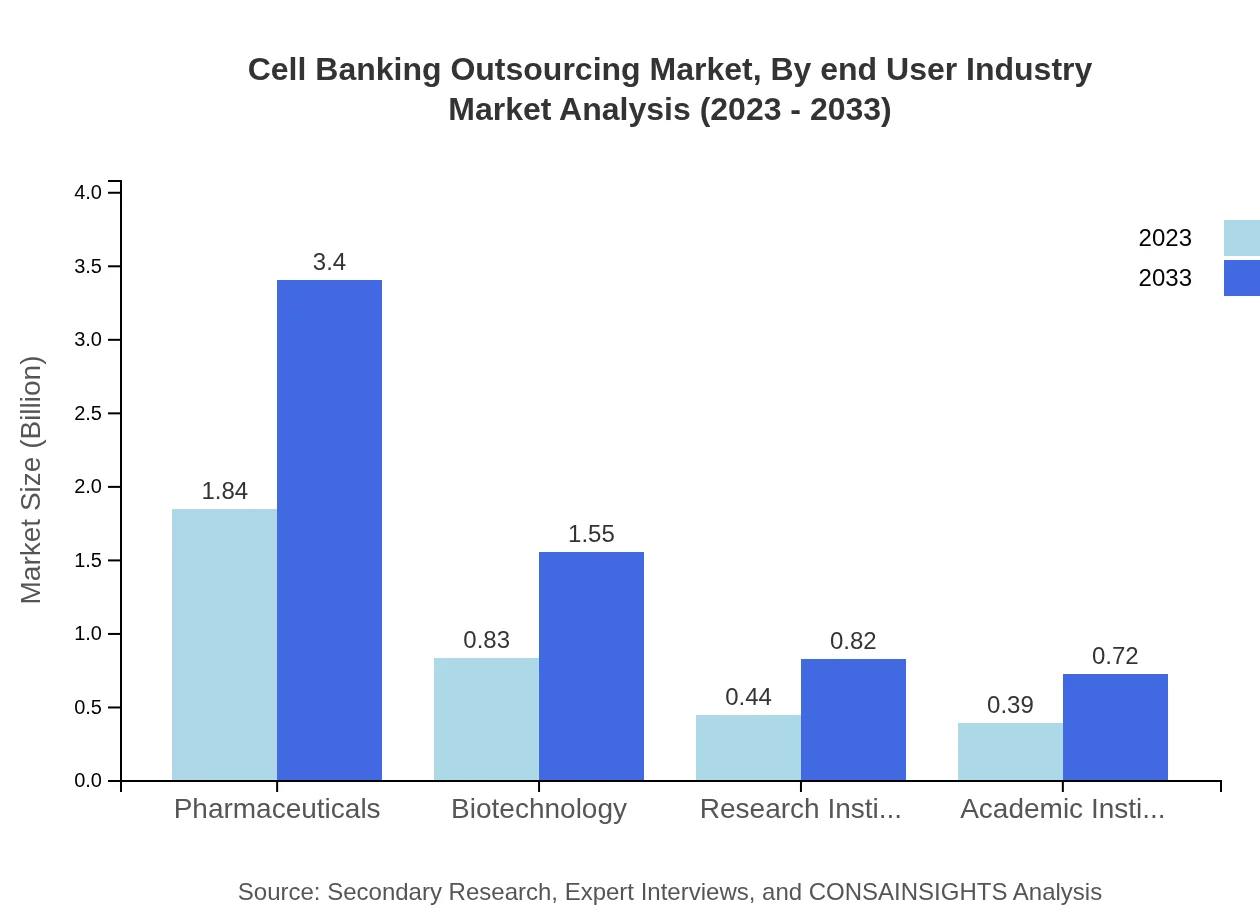
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis By End User Industry
The end-user industries for cell banking outsourcing include pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, research institutes, and academic institutions. Pharmaceuticals lead with a size of $1.84 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $3.40 billion by 2033. This reflects the heavy reliance on cell banking for drug development processes. Biotechnology firms follow with growth from $0.83 billion to $1.55 billion, indicating an expanding intersection between biotechnology advancements and cellular therapies.
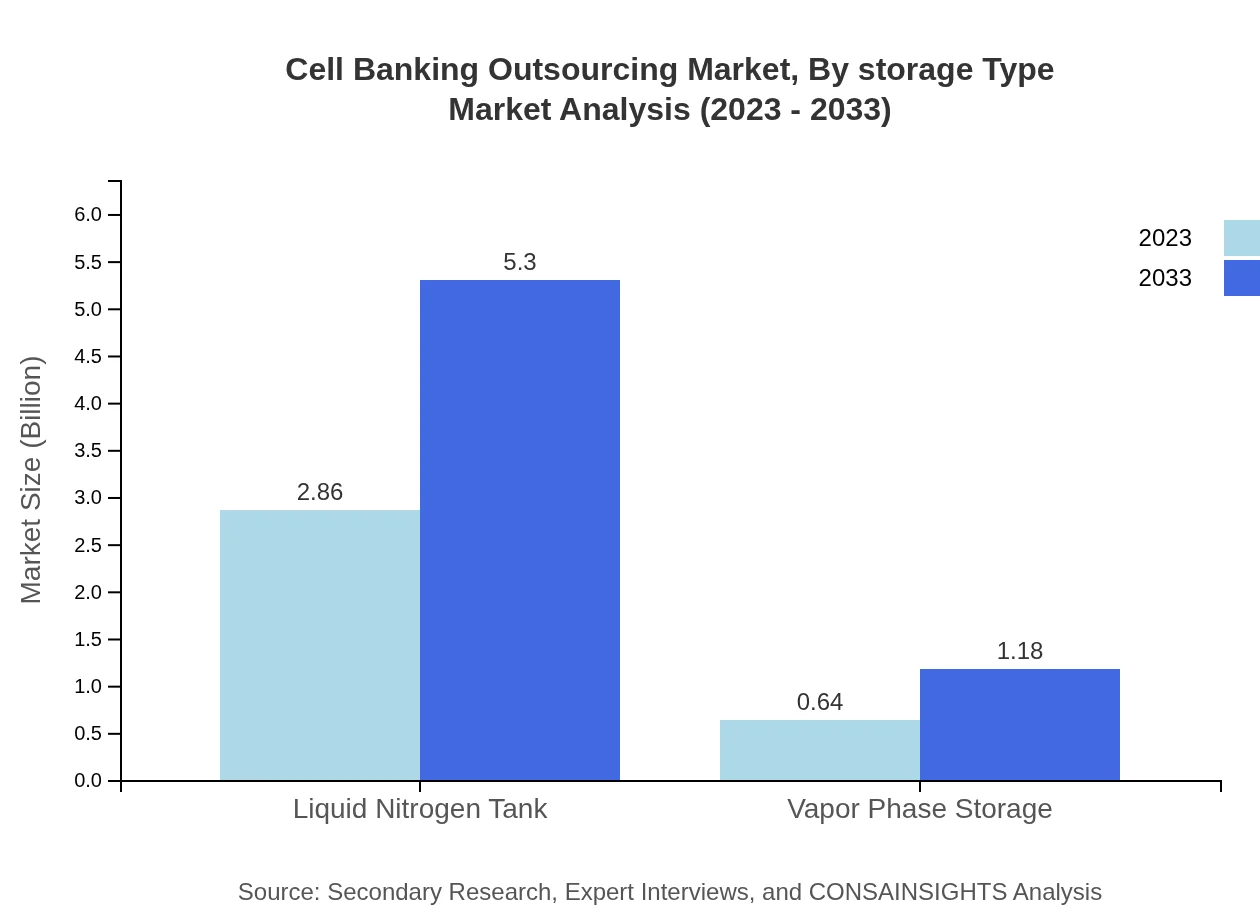
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis By Storage Type
Storage types include Liquid Nitrogen Tanks and Vapor Phase Storage. Liquid Nitrogen Tanks dominate with a share of 81.79%, projected to grow from $2.86 billion to $5.30 billion by 2033, while Vapor Phase Storage, with an 18.21% share, is expected to rise from $0.64 billion to $1.18 billion. The efficiency of liquid nitrogen storage in preserving biological materials under ultra-low temperatures fuels its continued preference among operators.
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Analysis By Technology
In terms of technology, the market reflects ongoing advancements in cellular preservation techniques, including cryopreservation technology and automated storage solutions. Companies are increasingly adopting innovative technological solutions to meet the regulatory requirements of biobanking, as well as enhance operational standards. This sector is projected to witness continuous evolution, ensuring optimized preservation and retrieval of biological samples.
Cell Banking Outsourcing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cell Banking Outsourcing Industry
Lonza Group:
Lonza is a global leader in bioproducts and contract manufacturing, providing comprehensive services for cell banking and regenerative medicine.CryoBanking International:
A prominent player in the cell banking market, CryoBanking specializes in umbilical cord blood banking, providing critical services for stem cell storage.Source BioScience:
Source BioScience offers a range of bioservices, including cell line banking and biobanking solutions for research and clinical use.STEMCELL Technologies:
STEMCELL Technologies focuses on developing comprehensive tools for cell culture, differentiation, and storage, serving the research and clinical communities.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Cell Banking Outsourcing?
The cell banking outsourcing market is valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6.2% over the next decade, suggesting steady growth driven by increasing demand for cell-based therapies and biobank services.
What are the key market players or companies in this Cell Banking Outsourcing industry?
Key players in the cell banking outsourcing industry include prominent biotech firms, pharmaceutical companies, and specialized biobanking service providers, enhancing their presence through strategic partnerships and innovations to support research and clinical trials.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Cell Banking Outsourcing industry?
The growth in cell banking outsourcing is driven by rising investments in biotechnology, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in stem cell research, and the growing demand for personalized medicine and regenerative therapies.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Cell Banking Outsourcing?
North America leads the cell banking outsourcing market, projected to grow from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $2.22 billion by 2033, followed closely by Europe and Asia Pacific, indicating dynamic investments in healthcare and biotechnology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Cell Banking Outsourcing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs, providing insights into market dynamics, key players, and growth strategies, ensuring businesses make informed decisions based on the latest trends and forecasts.
What deliverables can I expect from this Cell Banking Outsourcing market research project?
Expect comprehensive research deliverables, including detailed market analysis, competitive landscape reports, growth forecasts, and insights into segmentation, ensuring you have a clear understanding of the cell banking outsourcing landscape.
What are the market trends of Cell Banking Outsourcing?
Key trends include increasing adoption of automated storage systems, advancements in cell preservation technologies, and a growing focus on renewable and sustainable methods, reflecting the industry's evolution toward innovative biobanking solutions.