Cider Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cider
Cider Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cider market, covering insights on market trends, size, segmentation, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It examines key players, regional dynamics, and technological advancements shaping the industry's future.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
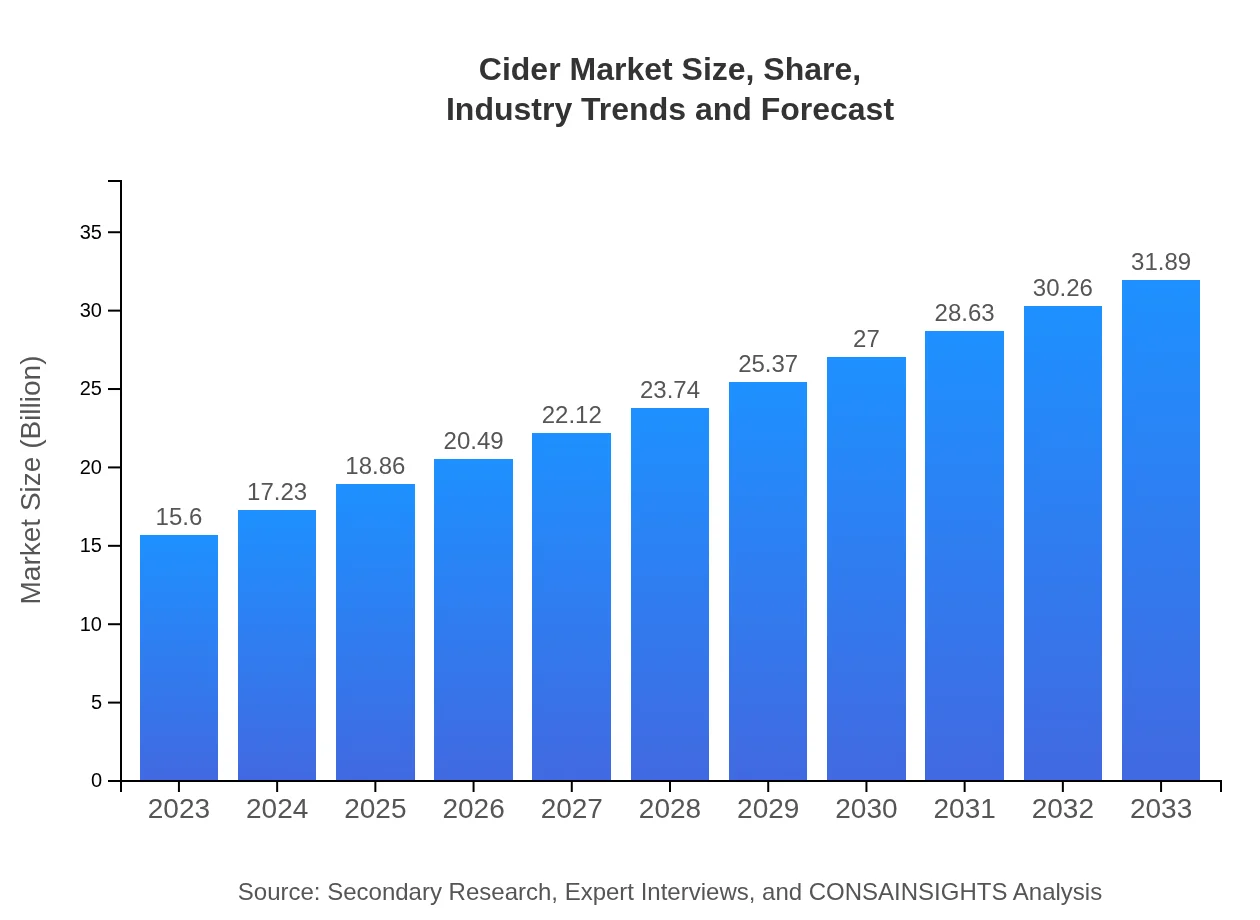
| 2023 Market Size | $15.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $31.89 Billion |
| Top Companies | Anheuser-Busch InBev, Heineken, Cider Brothers |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cider Market Overview
Customize Cider Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cider market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cider's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cider
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cider market in 2023?
Cider Industry Analysis
Cider Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cider Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cider Market Report:
Europe remains one of the largest markets for cider, forecasted to grow from $5.78 billion in 2023 to $11.82 billion by 2033. The UK leads in cider consumption due to its long-standing tradition and consumer familiarity with diverse cider brands.Asia Pacific Cider Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the cider market is estimated to reach $5.59 billion by 2033, up from $2.73 billion in 2023. The rise is driven by increasing Western influence and craft beverage trends. The growth of the middle class and urbanization are expected to further elevate demand, particularly in countries like China and Japan.North America Cider Market Report:
North America represents a significant portion of the cider market, with revenues expected to nearly double from $5.08 billion in 2023 to $10.38 billion by 2033. The strong demand for craft ciders and expansive distribution networks through retailers and e-commerce platforms contribute to this growth.South America Cider Market Report:
The cider market in South America is projected to grow modestly from $0.09 billion in 2023 to $0.19 billion by 2033. This growth is primarily driven by increasing interest among consumers in alternative alcoholic beverages and the rise in local production of ciders.Middle East & Africa Cider Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa cider market is anticipated to grow from $1.91 billion in 2023 to $3.91 billion by 2033, driven by rising tourism and a growing expatriate population, fostering new tastes and preferences for cider.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cider Market Analysis By Type
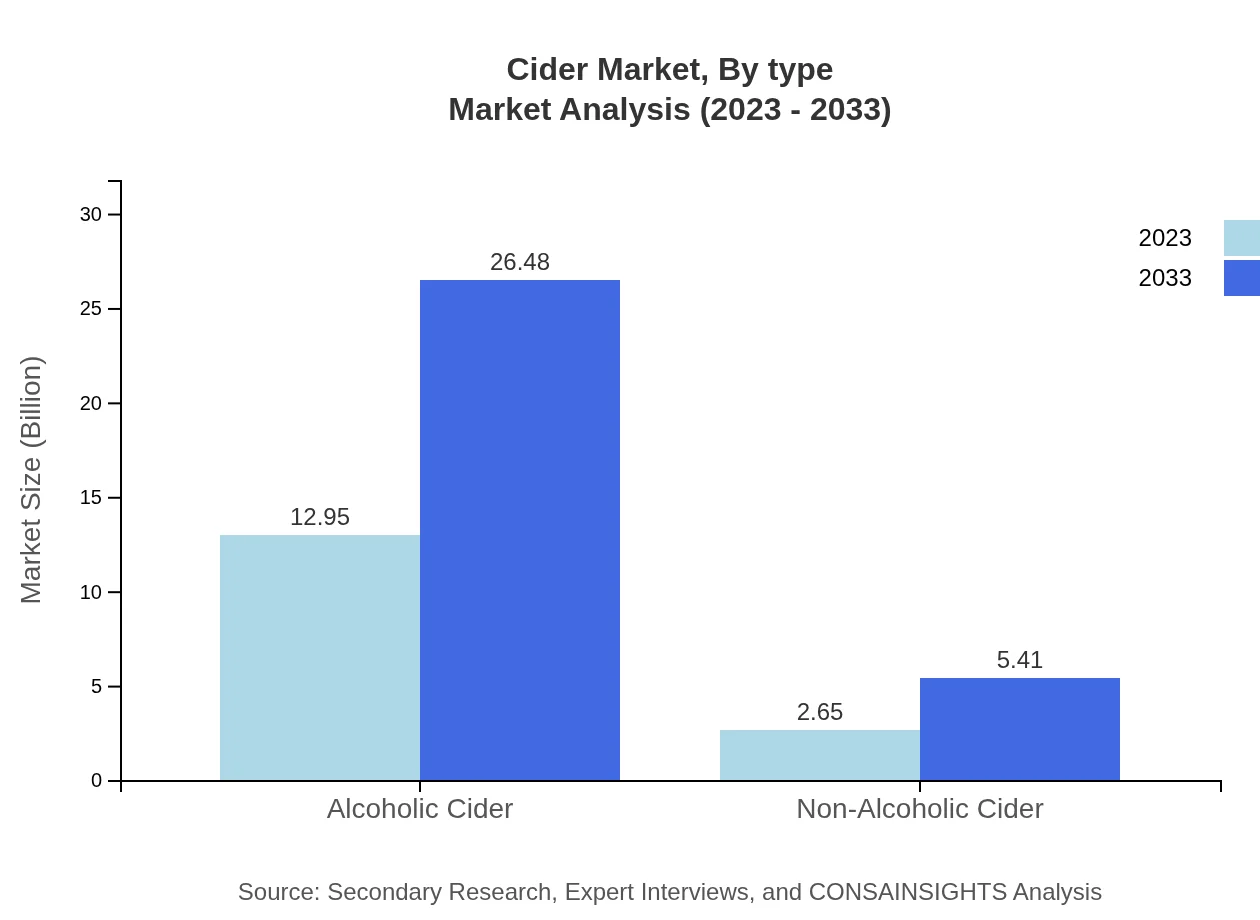
The cider market is mainly divided into alcoholic and non-alcoholic segments. Alcoholic cider accounted for a market size of $12.95 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $26.48 billion by 2033. Non-alcoholic cider holds a smaller share, valued at $2.65 billion in 2023, projected to reach $5.41 billion by 2033.
Cider Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
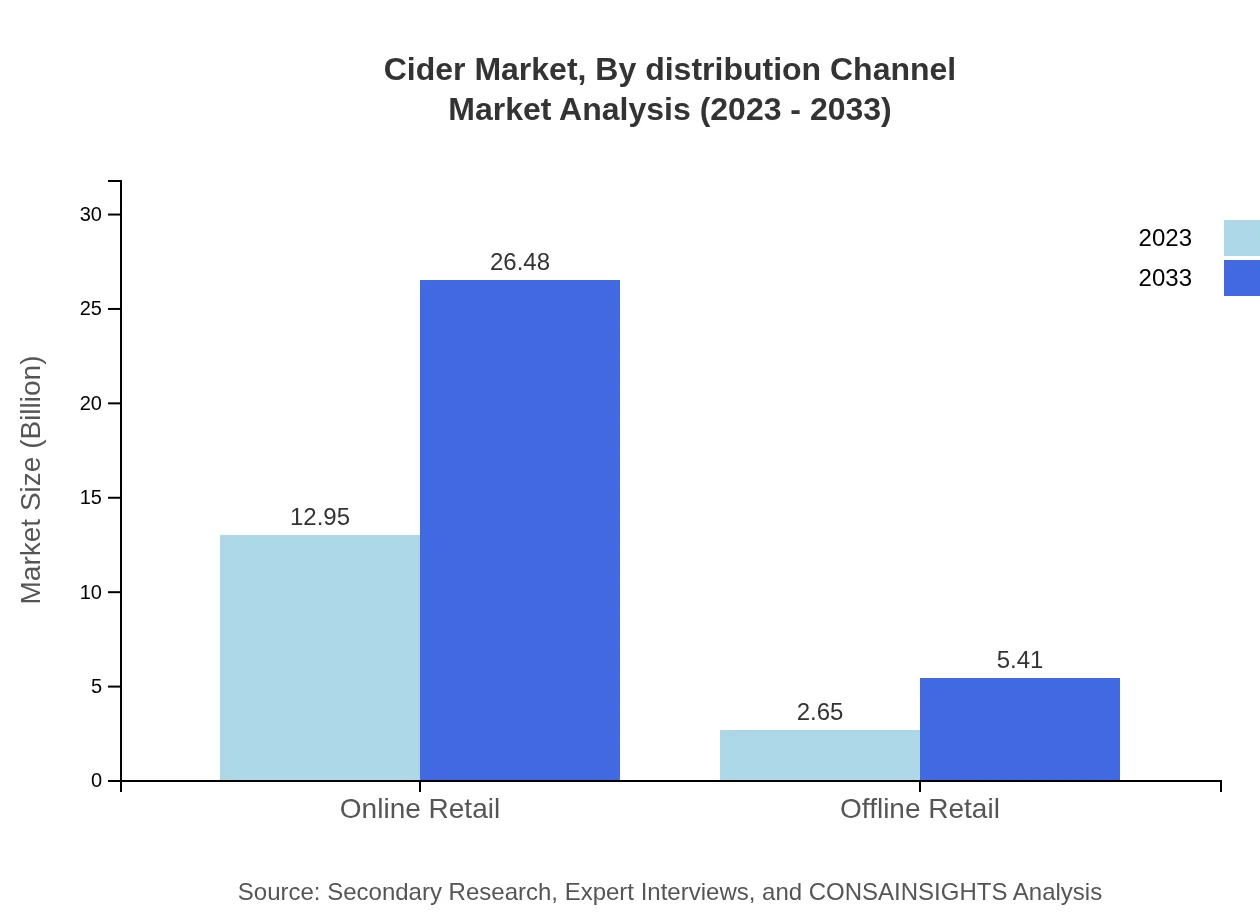
Distribution is segmented between online and offline channels. The online retail segment showcases robust growth, increasing from $12.95 billion in 2023 to an anticipated $26.48 billion by 2033, while offline retail is expected to grow from $2.65 billion to $5.41 billion.
Cider Market Analysis By Consumer Group
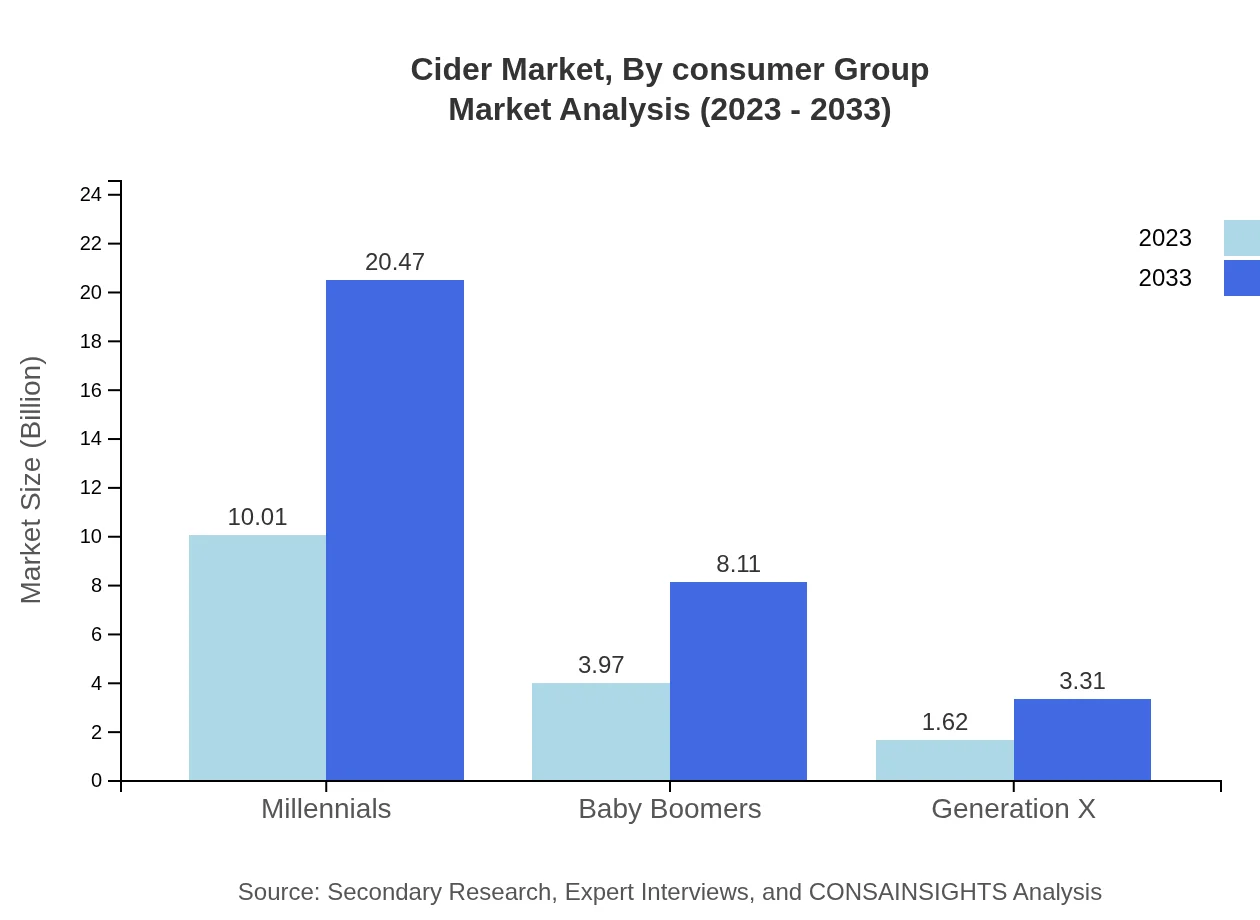
Market segmentation by consumer group indicates that millennials will dominate, growing from $10.01 billion in 2023 to $20.47 billion by 2033. Other groups, including baby boomers, are also significant, with a size increasing from $3.97 billion to $8.11 billion.
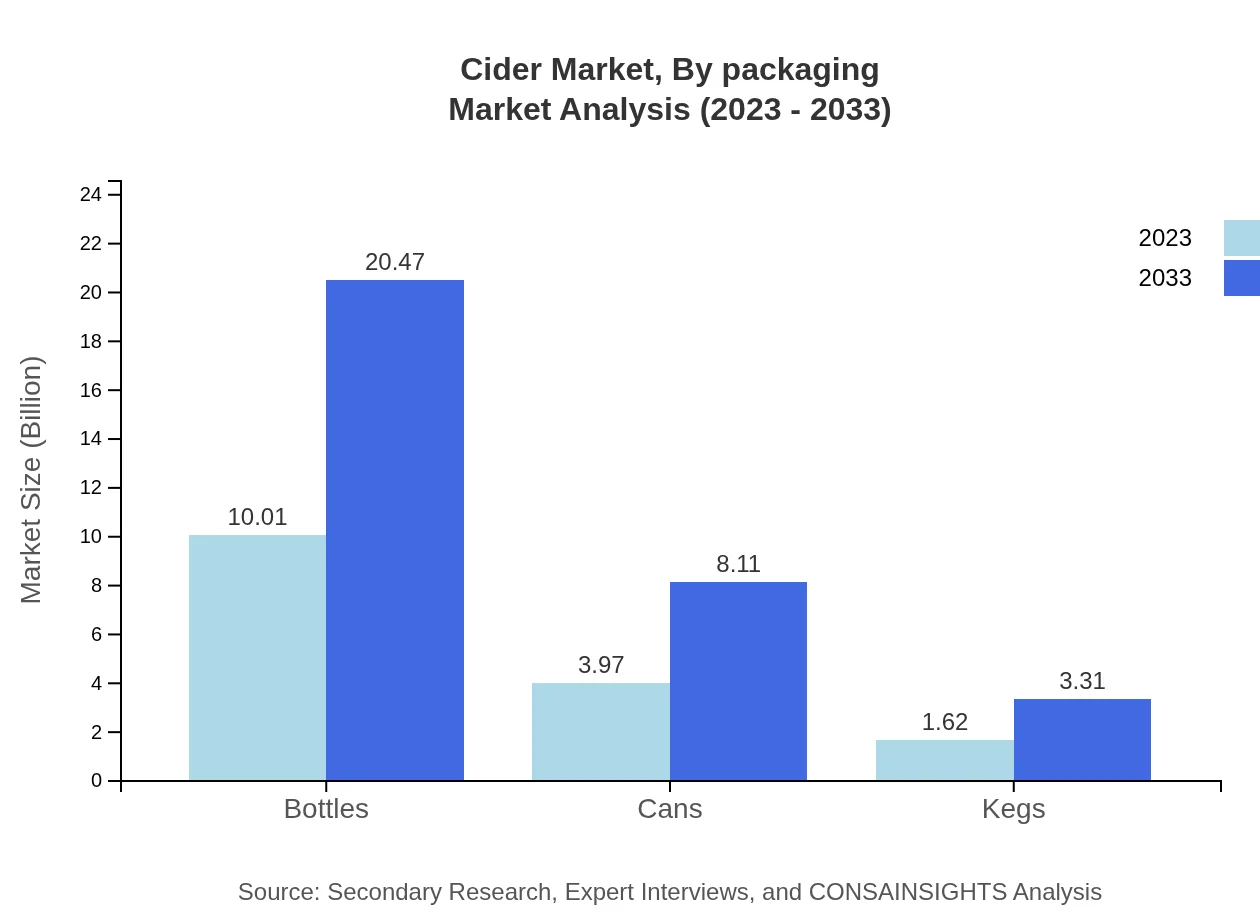
Cider Market Analysis By Packaging
Packaging analysis reveals bottles leading the market with size growing from $10.01 billion in 2023 to $20.47 billion by 2033. Cans are also gaining traction, expected to rise from $3.97 billion to $8.11 billion, while kegs maintain a smaller share.
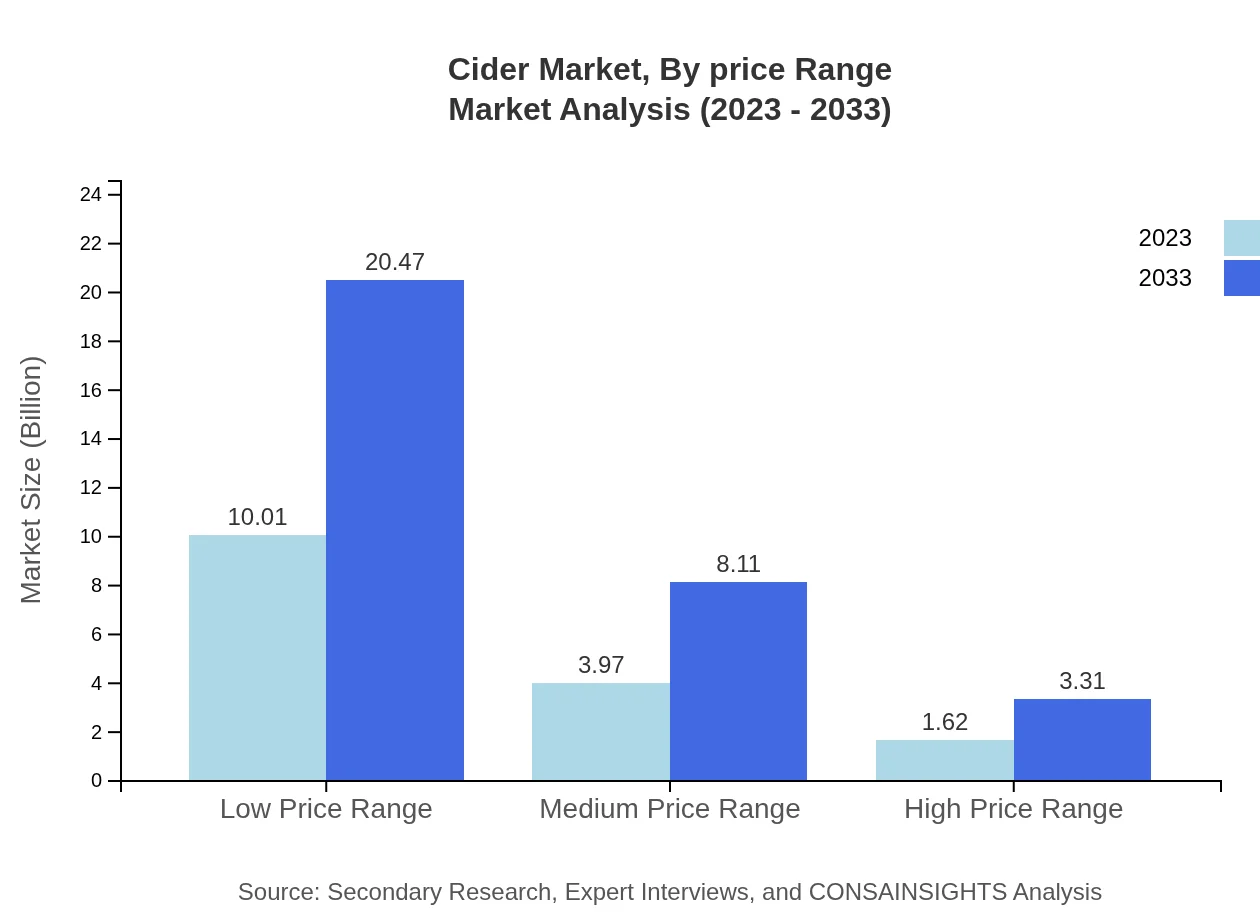
Cider Market Analysis By Price Range
Price range segmentation reveals that the low price range segment remains dominant, growing from $10.01 billion in 2023 to $20.47 billion by 2033, capturing significant market share, while medium and high price ranges also show gradual growth.
Cider Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cider Industry
Anheuser-Busch InBev:
A leading global brewer known for its extensive portfolio of beer brands, Anheuser-Busch has incorporated cider into its offerings through brands like Strongbow.Heineken:
Heineken has increased its presence in the cider market by acquiring popular cider brands such as Bulmers, expanding its reach in various global markets.Cider Brothers:
An upcoming cider brand known for its craft and premium quality, focusing on organic ingredients and environmental sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cider?
The global cider market is expected to reach a size of approximately $15.6 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.2%. This growth reflects increasing consumer demand and a diversification of product offerings within the industry.
What are the key market players or companies in this cider industry?
Key players in the cider industry include well-established brands such as Strongbow, Angry Orchard, and Magners. These companies dominate the market, leveraging strong distribution channels and innovative marketing to attract consumers.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cider industry?
Growth in the cider industry is driven by the rising popularity of craft beverages, health-conscious consumer trends favoring lower-alcohol options, and increasing innovation in flavors and product types that cater to diverse preferences.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cider market?
The fastest-growing region in the cider market is expected to be Europe, projected to evolve from $5.78 billion in 2023 to $11.82 billion by 2033, driven by growing consumer interest in premium and craft cider varieties.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cider industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports specifically tailored to the cider industry, allowing businesses to receive unique insights and data relevant to their specific needs and competitive landscape.
What deliverables can I expect from this cider market research project?
From the cider market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, and a breakdown of consumer preferences across regions and segments.
What are the market trends of cider?
Current market trends in the cider industry include a shift towards non-alcoholic variants, increased online retail sales, and a focus on sustainable production practices, reflecting changing consumer expectations and environmental concerns.