Cloud Computing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cloud-computing
Cloud Computing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report explores the Cloud Computing market from 2023 to 2033, analyzing market size, growth trends, regional insights, key technologies, and industry leaders. Providing data-driven insights, this report aims to guide businesses and investors in navigating the evolving landscape of cloud services.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
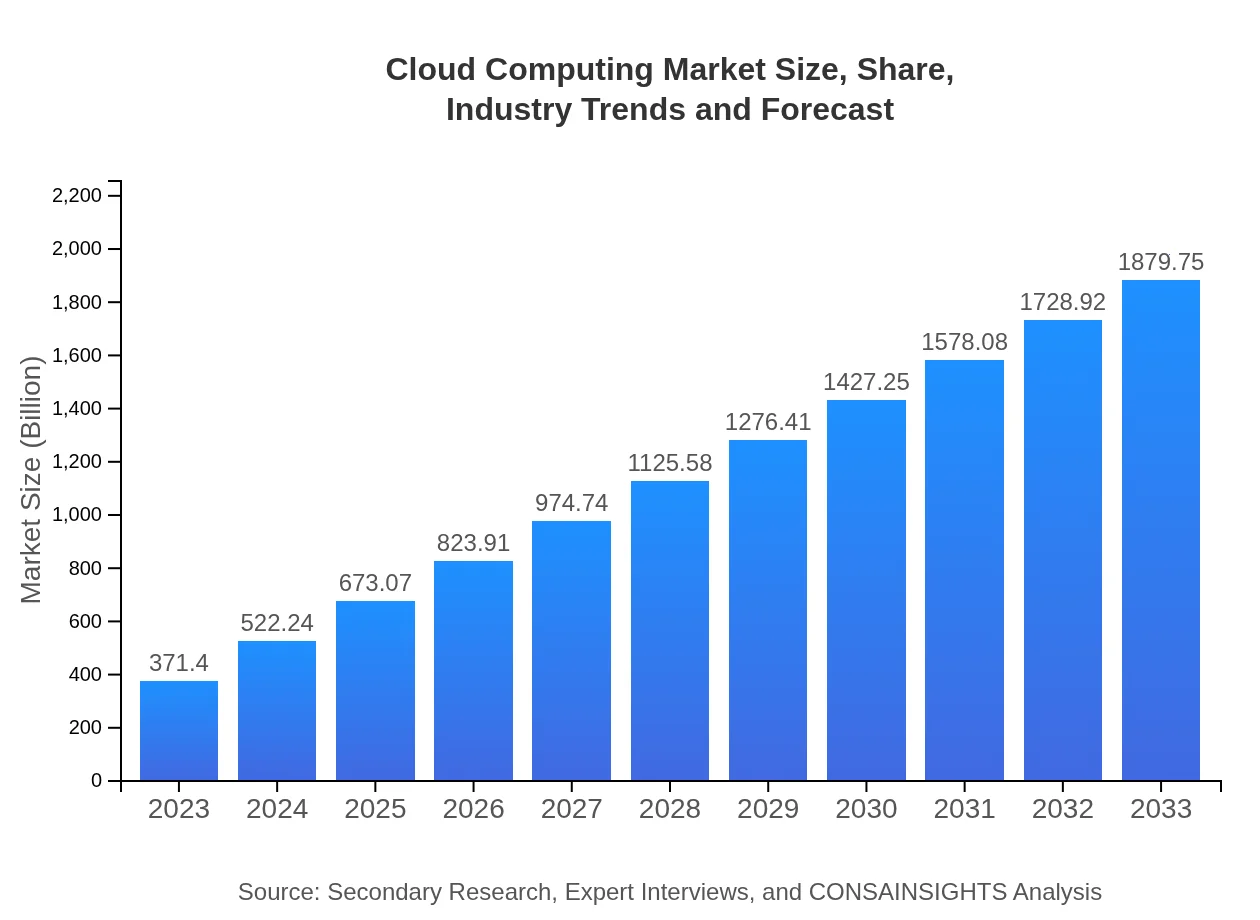
| 2023 Market Size | $371.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 16.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $1879.75 Billion |
| Top Companies | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, Salesforce |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cloud Computing Market Overview
Customize Cloud Computing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cloud Computing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cloud Computing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cloud Computing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cloud Computing market in 2023?
Cloud Computing Industry Analysis
Cloud Computing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cloud Computing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cloud Computing Market Report:
In Europe, the cloud computing market is projected to grow from $121.26 billion in 2023 to $613.74 billion by 2033. The increase in compliance regulations for data security coupled with the growing trend of remote work drives demand for cloud solutions.Asia Pacific Cloud Computing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing significant growth in the cloud computing market, with a projected market size of $353.39 billion by 2033, up from $69.82 billion in 2023. Factors driving this growth include increased digitalization across industries, favorable government initiatives, and the rise of start-ups leveraging cloud technologies.North America Cloud Computing Market Report:
North America remains the largest market for cloud computing, projected to grow from $125.50 billion in 2023 to $635.17 billion by 2033. The presence of major cloud service providers and high IT spending among enterprises significantly contribute to this growth.South America Cloud Computing Market Report:
In South America, the cloud computing market is poised to reach $46.62 billion by 2033, growing from $9.21 billion in 2023. The burgeoning e-commerce sector and increased adoption of cloud services amongst small to medium enterprises are primary drivers of this expansion.Middle East & Africa Cloud Computing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are expected to see a rise in their cloud market from $45.61 billion in 2023 to $230.83 billion by 2033. Growing interests in digital transformation and improved internet connectivity are enhancing the appeal of cloud services in the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
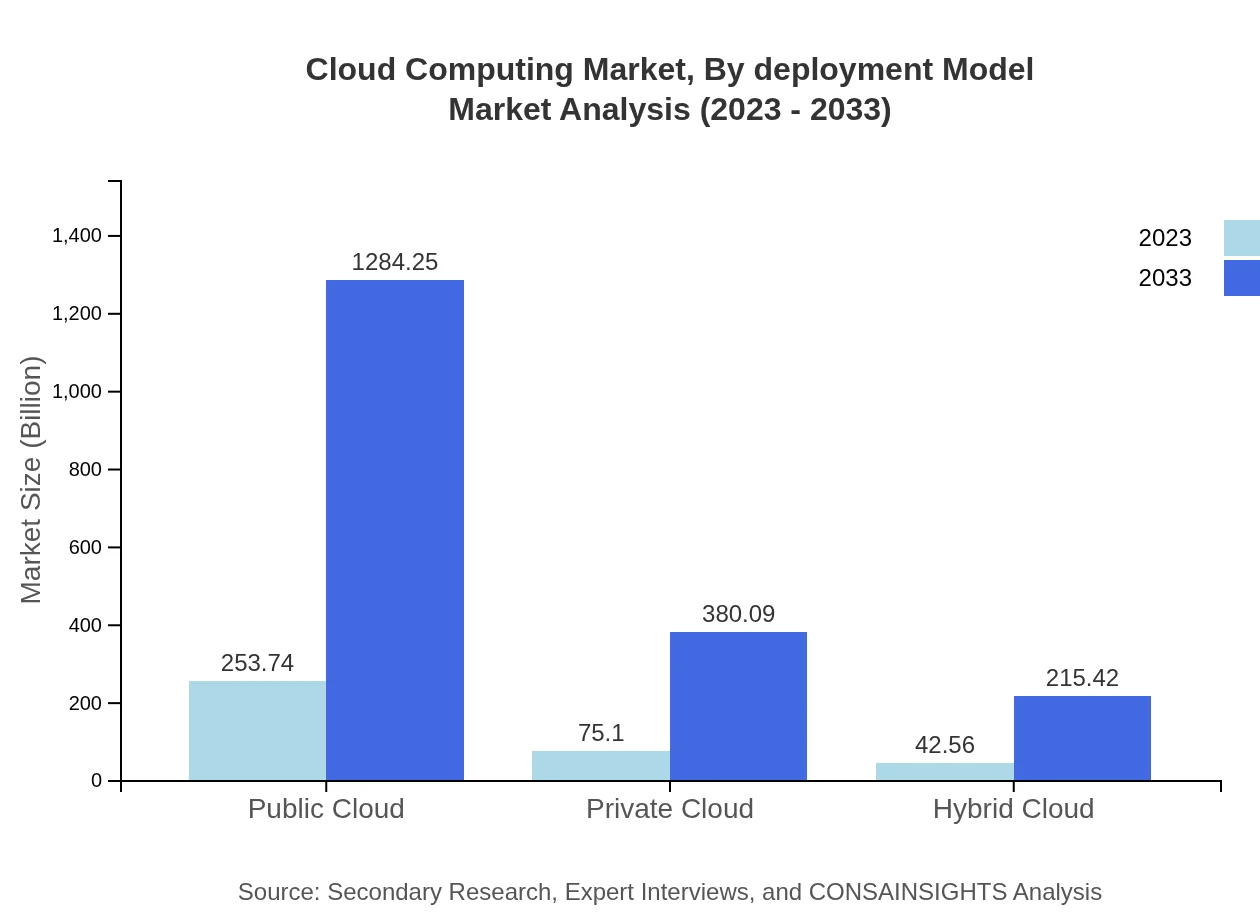
Cloud Computing Market Analysis By Deployment Model
The deployment model segment highlights significant variability in performance, comprising public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid clouds. In 2023, public clouds lead the market, driven by affordability and scalability. The private cloud segment, valued for security, will gain traction among finance and healthcare sectors, while hybrid solutions become increasingly popular due to their flexibility.
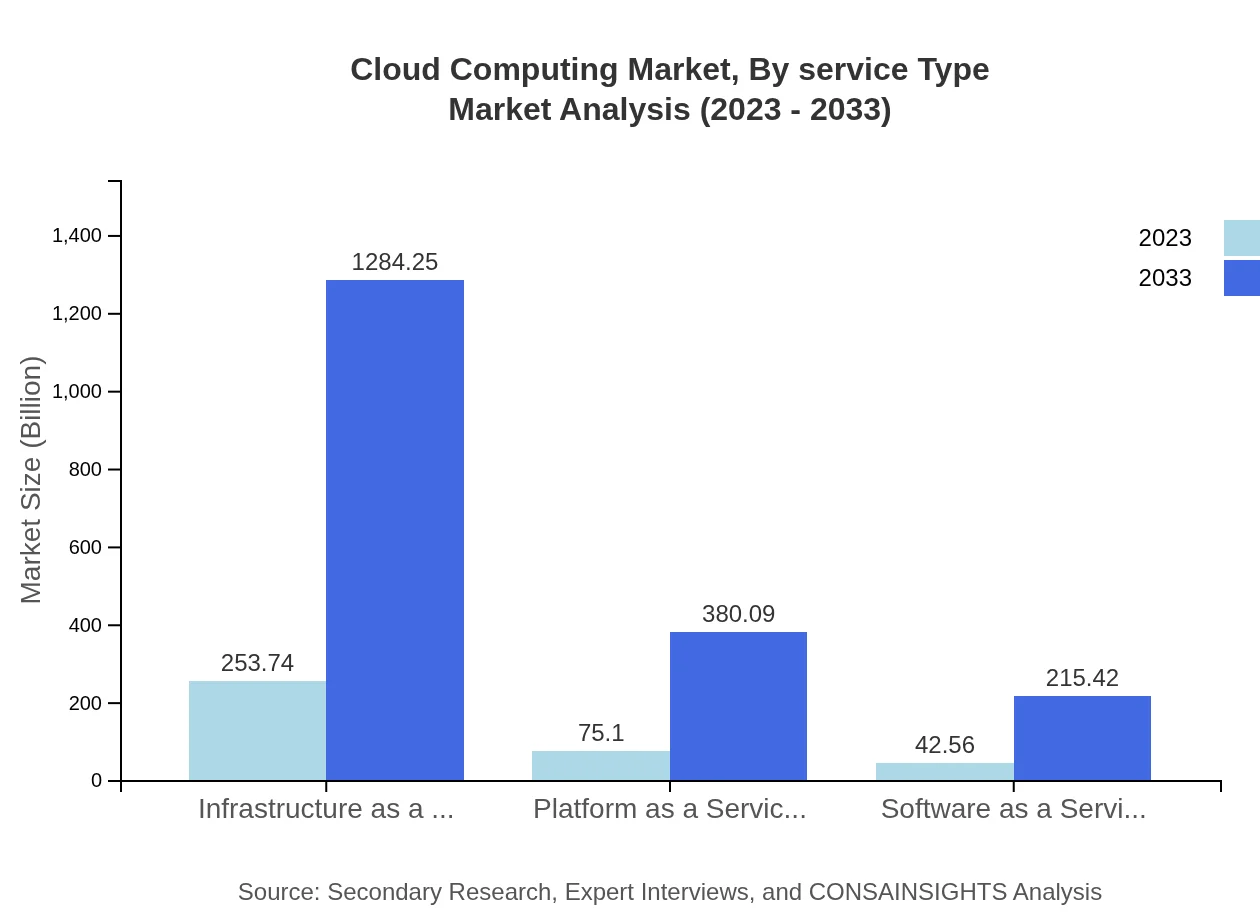
Cloud Computing Market Analysis By Service Type
Cloud services are split primarily into IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, with IaaS being the largest segment. IaaS, valued at $253.74 billion in 2023, dominates due to its infrastructure flexibility, while SaaS ($42.56 billion) is favored by businesses for operational software availability.
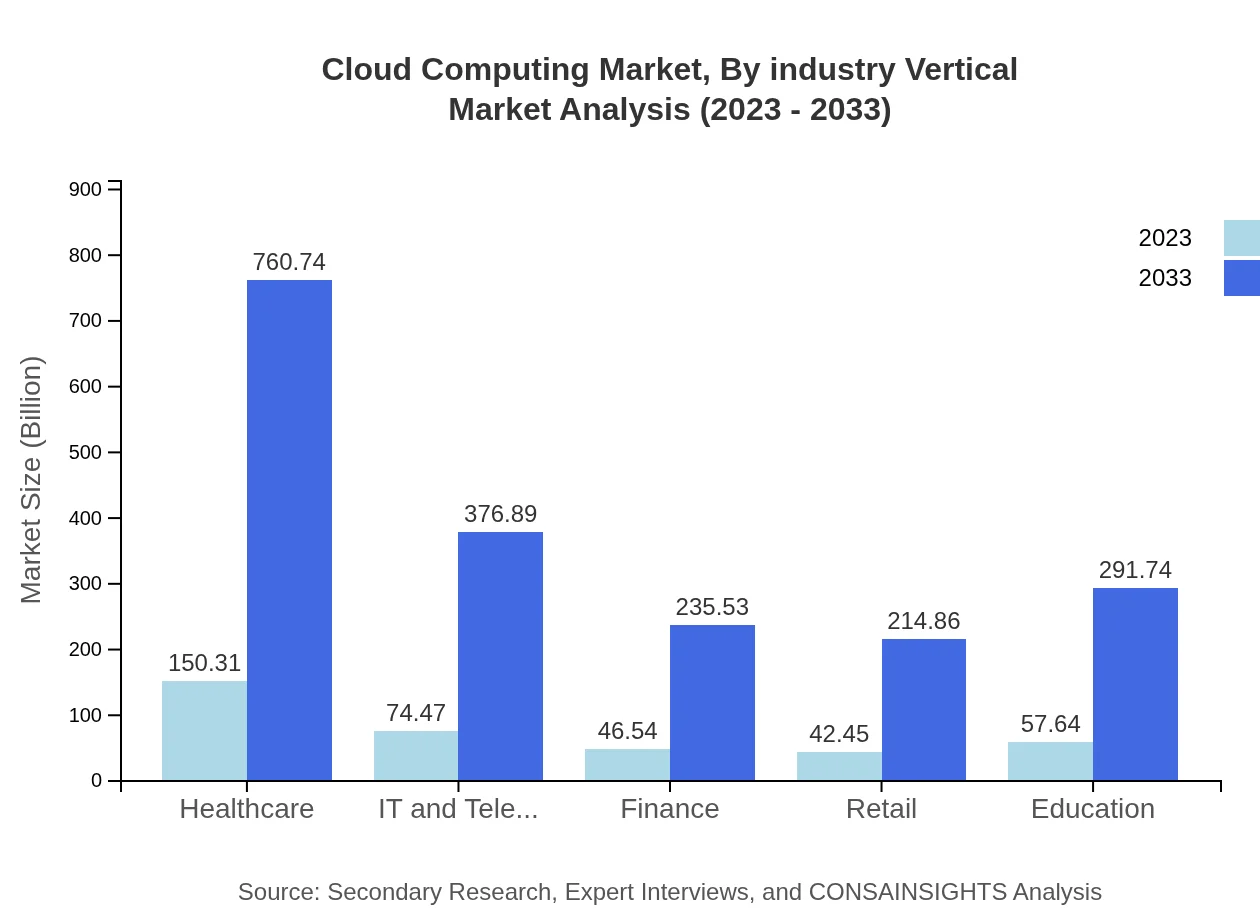
Cloud Computing Market Analysis By Industry Vertical
Industries capitalize on cloud capabilities to streamline operations. In 2023, healthcare leads with $150.31 billion, boosted by telemedicine and data management needs, followed by IT & Telecom ($74.47 billion) and finance ($46.54 billion), which require high-security cloud offerings for data integrity.
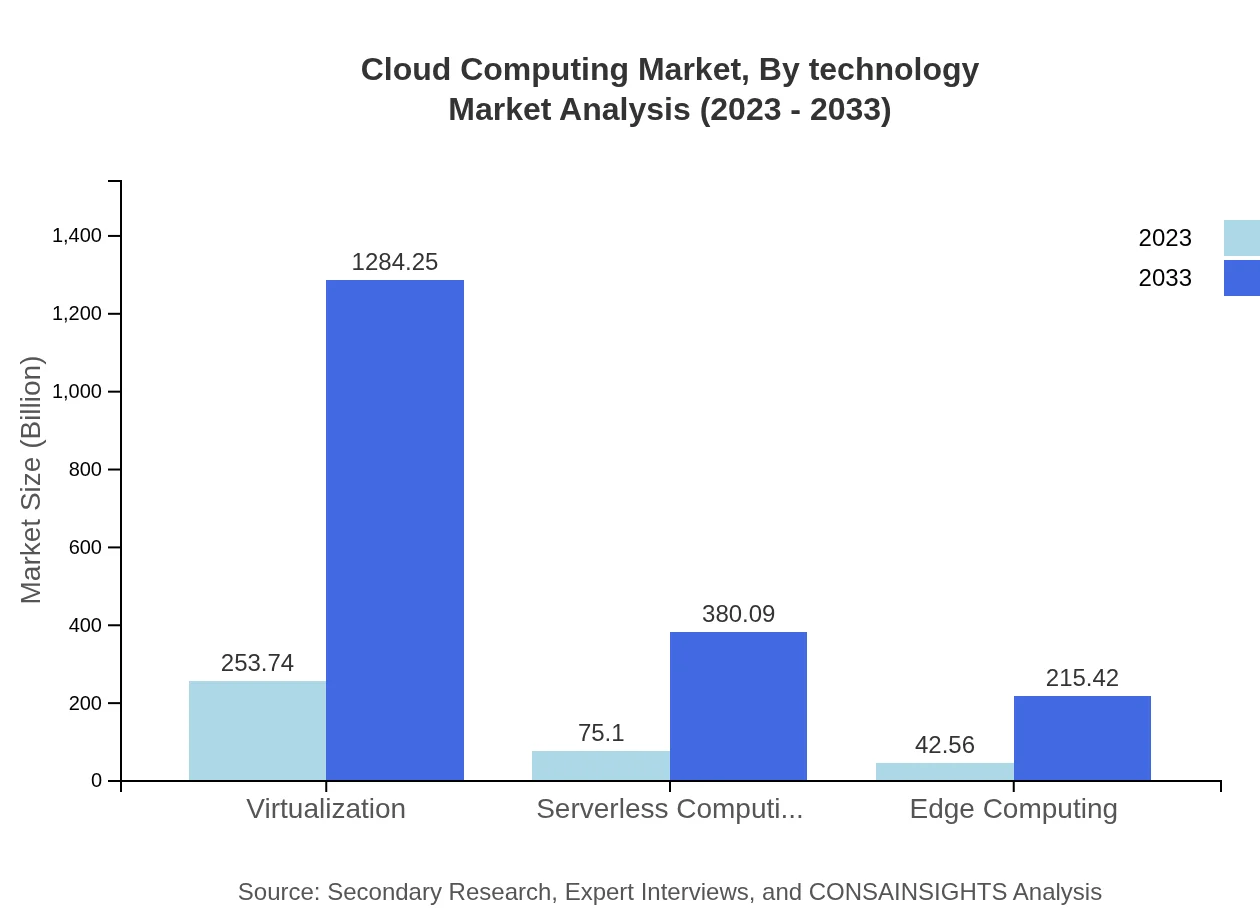
Cloud Computing Market Analysis By Technology
Emerging technologies such as AI and edge computing significantly impact the cloud landscape. The push towards serverless and edge computing models is providing organizations with new possibilities for scaling applications and enhancing user experiences worldwide.
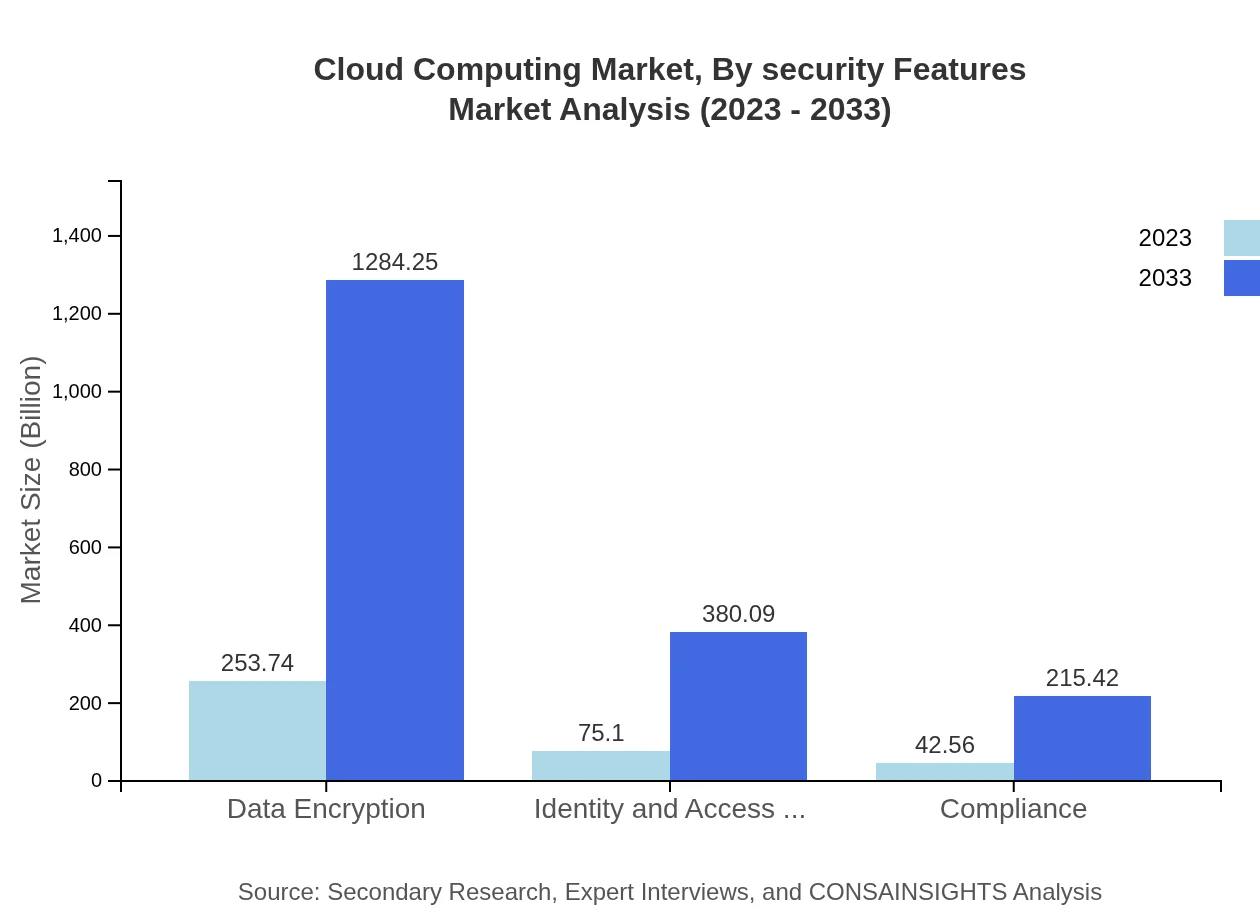
Cloud Computing Market Analysis By Security Features
Cloud security remains paramount, directly influencing purchasing decisions. Features including identity and access management ($75.10 billion) and data encryption ($253.74 billion) are critical market components as businesses prioritize robust security solutions to combat rising cyber threats.
Cloud Computing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cloud Computing Industry
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS, a division of Amazon.com, is a dominant player in cloud computing, providing a wide range of services including computing power, storage, and machine learning solutions.Microsoft Azure:
Microsoft Azure offers cloud services for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers, leading in enterprise solutions.Google Cloud Platform:
Google Cloud provides a suite of cloud computing services, including data analytics, machine learning, and storage solutions, focused on scalability and security.IBM Cloud:
IBM Cloud incorporates both Infrastructure as a Service and Platform as a Service, along with cognitive services enhanced by AI technologies.Salesforce:
Salesforce is a key player in providing CRM applications delivered through the cloud, renowned for its service and customer relationship management solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cloud Computing?
The global cloud computing market is valued at approximately $371.4 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.7% through 2033. This rapid growth highlights the increasing adoption of cloud solutions across various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the cloud Computing industry?
Key players in the cloud computing industry include major technology firms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud. Their competitive landscape shapes the market through innovation and investment.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cloud Computing industry?
The growth in the cloud computing industry is driven by factors such as increased digital transformation initiatives, rising demand for scalable infrastructure, advancements in cloud technologies, and the need for cost-effective IT solutions among businesses.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cloud Computing market?
The fastest-growing region in the cloud computing market is the Asia Pacific, projected to grow from $69.82 billion in 2023 to $353.39 billion by 2033. North America also shows strong growth potential, from $125.50 billion to $635.17 billion in the same period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cloud Computing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the cloud computing industry. This flexibility allows businesses to gain insights relevant to their strategic requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this cloud Computing market research project?
Deliverables from a cloud computing market research project include comprehensive reports on market size, growth projections, regional analysis, competitive landscape, and insights into current trends and consumer behavior metrics.
What are the market trends of cloud Computing?
Key market trends in cloud computing include the rise of hybrid and multi-cloud solutions, increasing focus on cybersecurity measures, adoption of serverless computing models, and enhanced integration of artificial intelligence within cloud services.