Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: cocoa-bean-value-chain-analysis
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a detailed analysis of the Cocoa Bean Value Chain, covering market trends, regional insights, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It includes critical data on industry size, growth rates, and technology impacts, assisting stakeholders in making informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
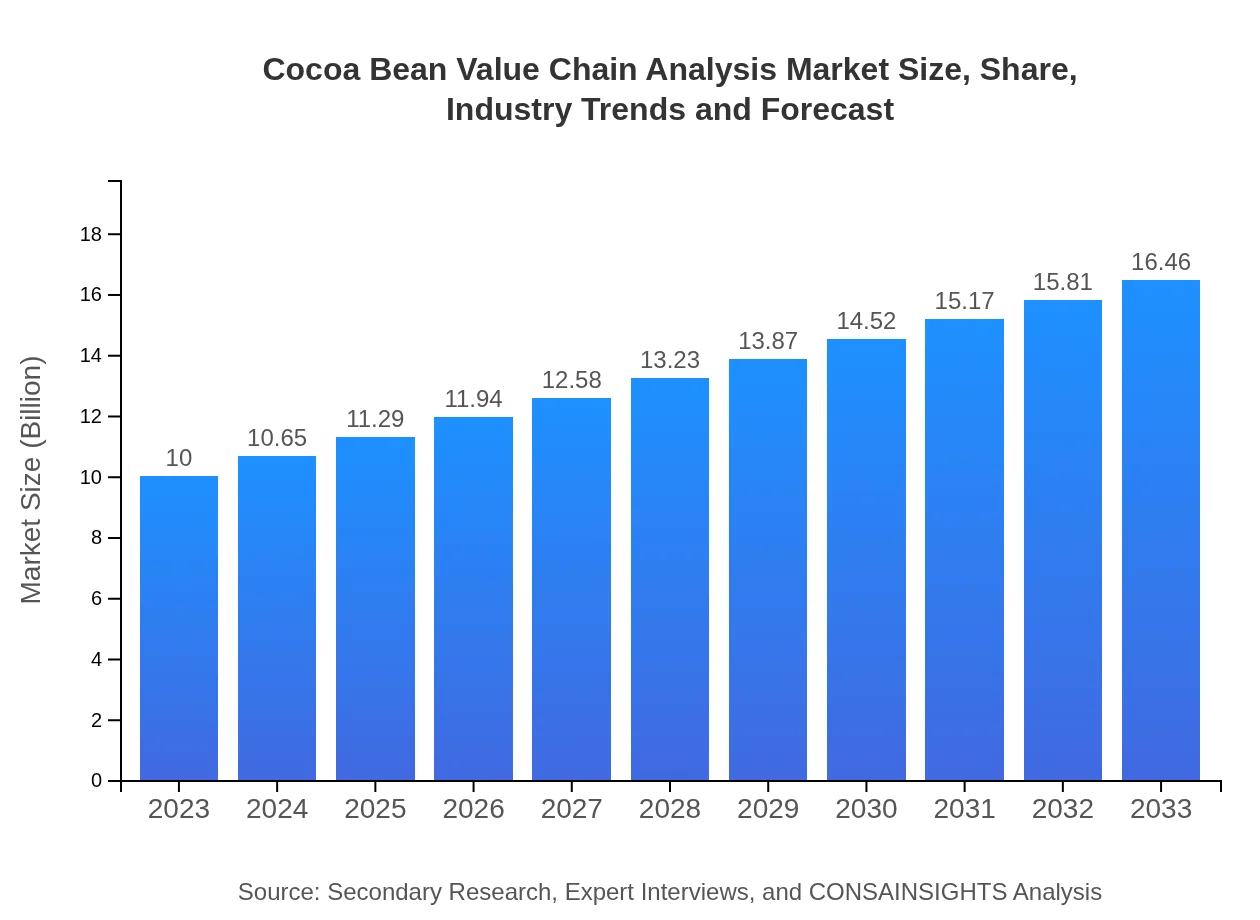
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $16.46 Billion |
| Top Companies | Barry Callebaut, Cargill , Olam International, Mondelēz International |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Overview
Customize Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis market in 2033?
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Industry Analysis
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report:
Europe currently dominates the cocoa bean value chain market with a valuation of $3.61 billion in 2023, growing to approximately $5.94 billion by 2033. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Switzerland are leading in cocoa processing and consumption, bolstered by a strong chocolate industry and increasing demand for premium products.Asia Pacific Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific market is valued at $1.82 billion and is forecasted to grow to $3.00 billion by 2033. Countries like Indonesia and Vietnam are significant players, with increasing cocoa production driven by changing consumer preferences for chocolate and confectionery products. The region's growth is also attributed to improved agricultural practices and processing efficiencies.North America Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report:
North America's market is projected to expand from $3.26 billion in 2023 to $5.36 billion by 2033. The rising demand for artisan chocolates and health-focused cocoa products significantly drives this growth. Additionally, consumer trends favoring organic and fair-trade options are shaping the market dynamics in this region.South America Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report:
The South American market stood at $0.58 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach $0.96 billion by 2033. Key countries like Brazil and Ecuador are expected to play major roles thanks to their rich biodiversity and cocoa farming traditions. However, the region faces challenges related to sustainable farming practices and climatic changes that could affect production.Middle East & Africa Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market value is set to grow from $0.73 billion in 2023 to $1.21 billion by 2033. The increase is driven by rising chocolate consumption and improved supply chain management in cocoa producing countries. However, challenges related to infrastructural limitations and market access still persist.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis By Product
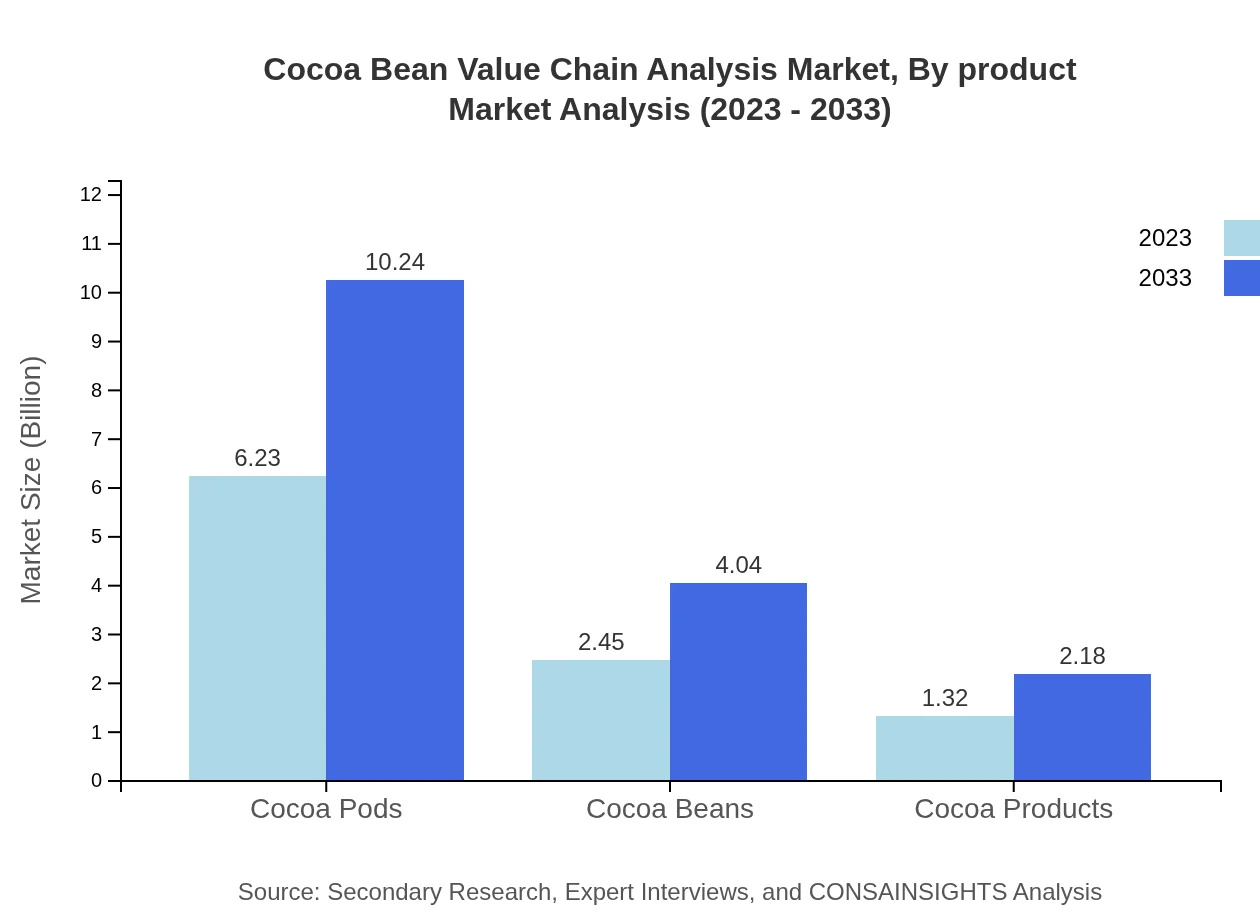
In 2023, cocoa pods dominate the market with a value of $6.23 billion, accounting for 62.25% of the market share, expected to grow to $10.24 billion by 2033. This is followed by cocoa beans and cocoa products, valued at $2.45 billion and $1.32 billion respectively in 2023, with projections indicating substantial growth in these areas as consumer demand for cocoa-based products increases.
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis By Region
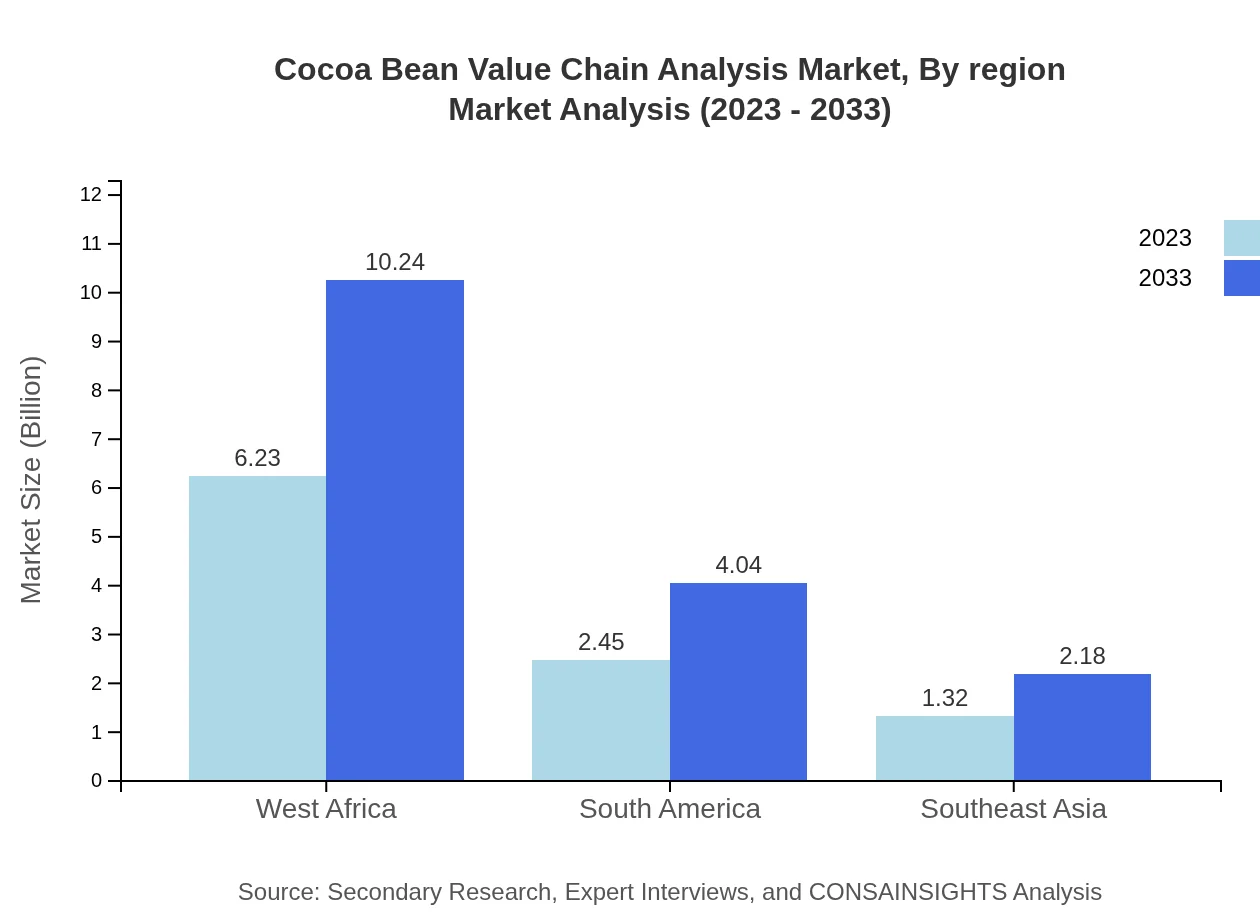
Geographically, West Africa remains a critical region for cocoa bean production, holding a market size of $6.23 billion with a stable share of 62.25%. South America and Southeast Asia are emerging markets with significant growth potential, especially in sustainable and specialty cocoa products.
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis By Application
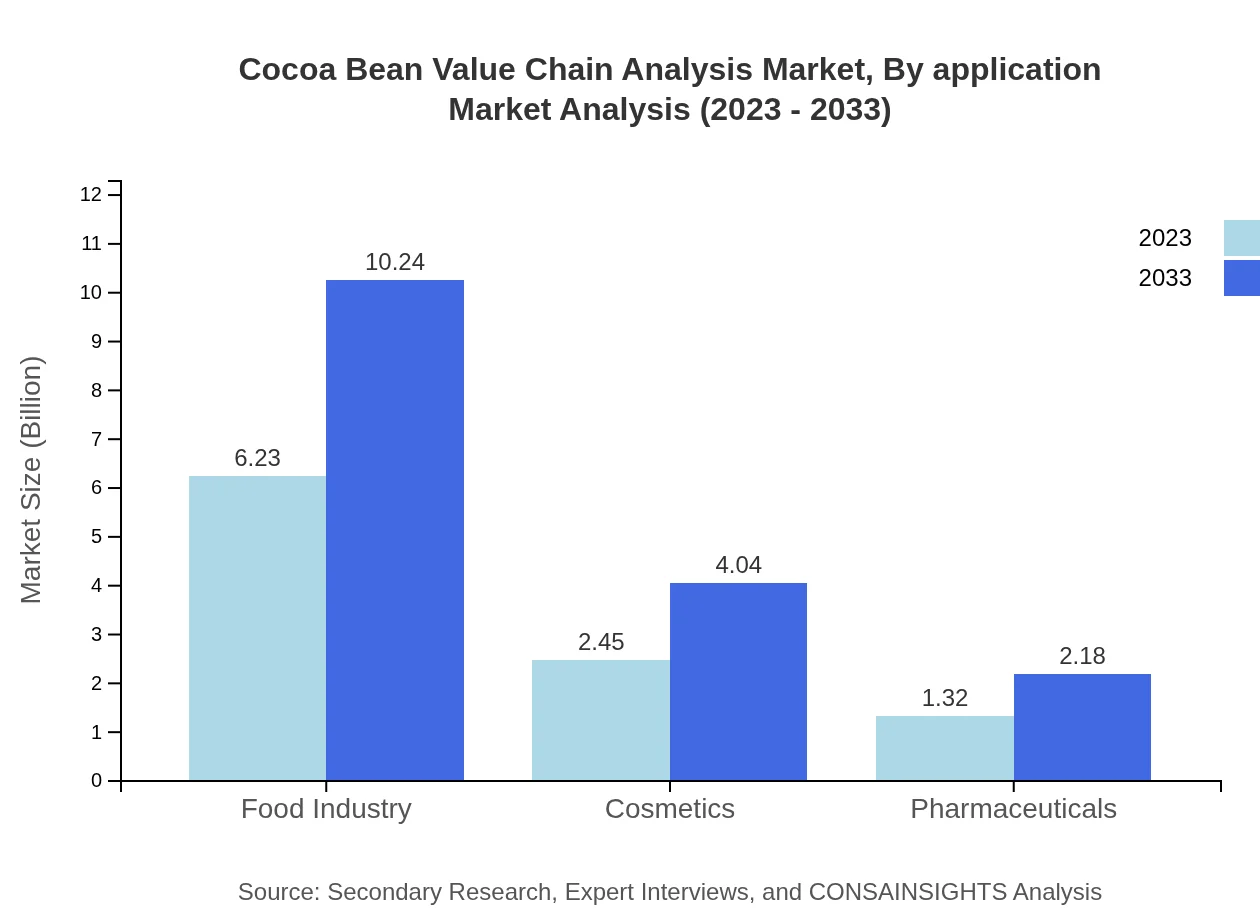
The food industry is the largest application segment, valued at $6.23 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $10.24 billion by 2033. The cosmetics and pharmaceuticals sectors also contribute significantly, with values of $2.45 billion and $1.32 billion. Each application segment indicates the versatility of cocoa products and their growing importance in diverse industries.
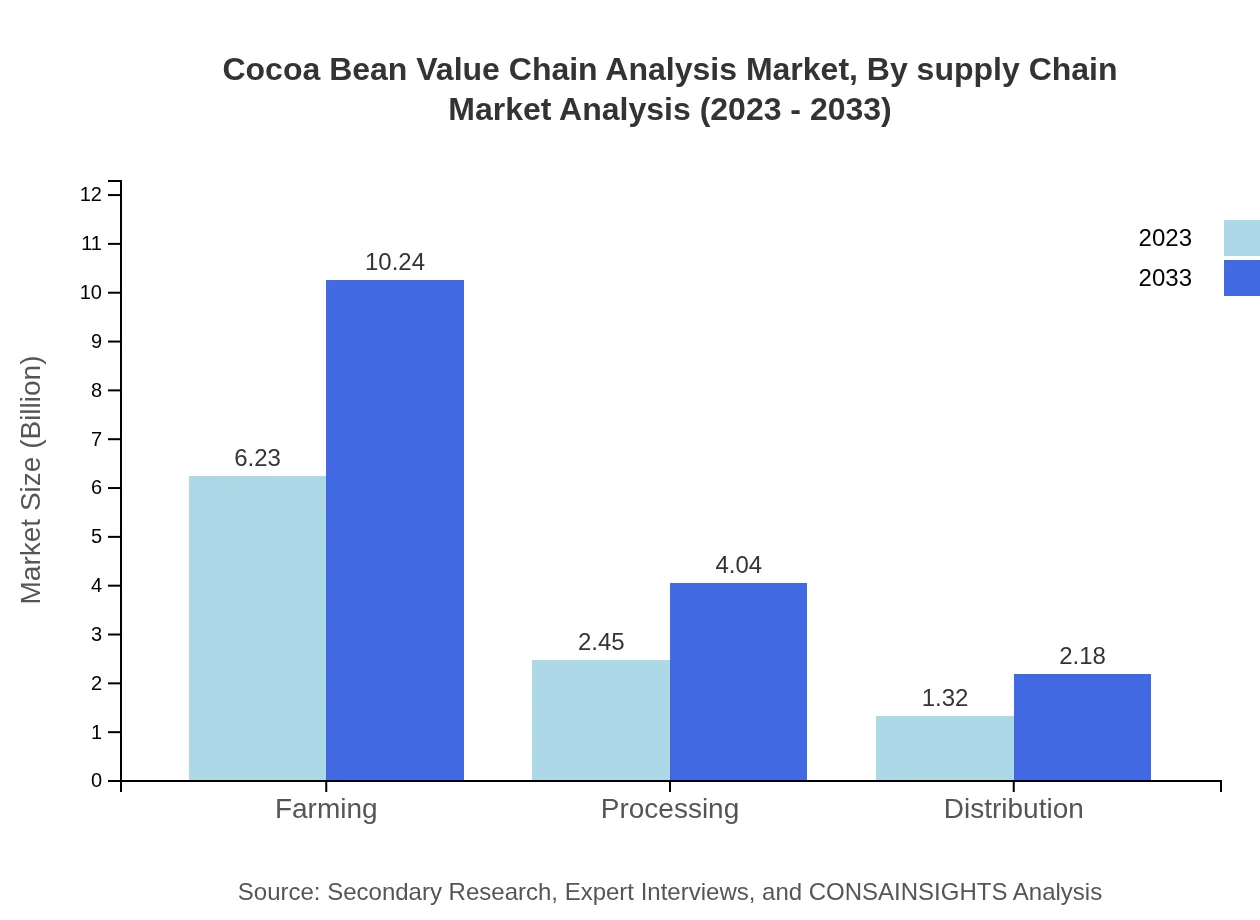
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis By Supply Chain
The supply chain stage analysis reveals that farming accounts for 62.25% of the market share, followed by processing and distribution. This segmentation highlights the need for greater efficiency and sustainability practices throughout the entire supply chain to meet future demand.
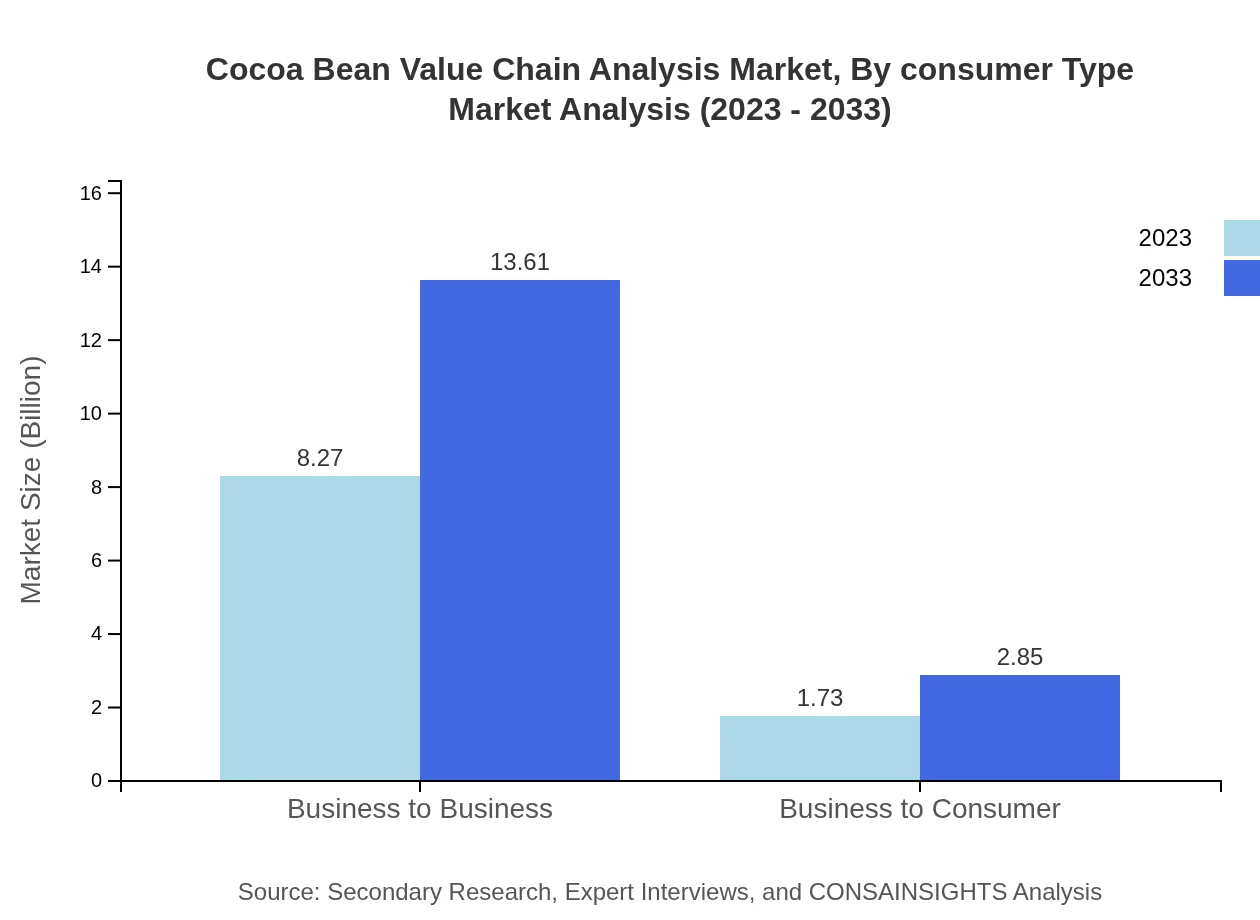
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Analysis By Consumer Type
The business-to-business segment comprises 82.7% of the market share, indicating the dominance of wholesale transactions in the cocoa industry. However, the business-to-consumer sector is gradually growing, projected to expand from $1.73 billion in 2023 to $2.85 billion by 2033.
Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis Industry
Barry Callebaut:
A leading global supplier of high-quality chocolate and cocoa products, Barry Callebaut operates in various countries and emphasizes sustainability and innovation in their sourcing practices.Cargill :
Cargill is a food industry giant involved in cocoa sourcing, processing, and product development, known for its commitment to sustainable agriculture practices and technology advancements.Olam International:
Focused on sourcing and supply chain management, Olam plays a crucial role in the cocoa bean value chain by promoting responsible sourcing practices and investing in sustainable farming initiatives.Mondelēz International:
Mondelēz is one of the largest snack companies in the world, utilizing significant volumes of cocoa products in its production lines while committing to sustainability in sourcing and operations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis?
The Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis market is valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5%. By 2033, the market is expected to expand significantly as demand increases.
What are the key market players or companies in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis industry?
Key players in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis include major cocoa producers, distributors, and manufacturers involved in processing. Companies like Cargill and Barry Callebaut significantly influence market dynamics through their vast operations and market reach.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis industry?
Growth in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain is driven by increasing consumer preferences for chocolate products, the rise in health consciousness, and expanding applications of cocoa in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, innovations in farming and processing methods fuel market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain?
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis, with expected growth from $1.82 billion in 2023 to $3.00 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to rising demand for cocoa in various sectors.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs in the Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis industry, helping stakeholders make informed decisions based on detailed insights and market trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market reports, segmentation analysis, competitive landscape overviews, and regional growth projections for the Cocoa Bean Value Chain, providing actionable insights for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of Cocoa Bean Value Chain Analysis?
Current trends include a shift towards sustainable sourcing, increased consumption of dark chocolate, and technology adoption in processing. These trends indicate an evolving market landscape focused on quality and ethical practices in cocoa production.