Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: cocoa-beans-trade
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cocoa Beans Trade market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market dynamics, trends, sizes, and forecasts across various regions and segments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
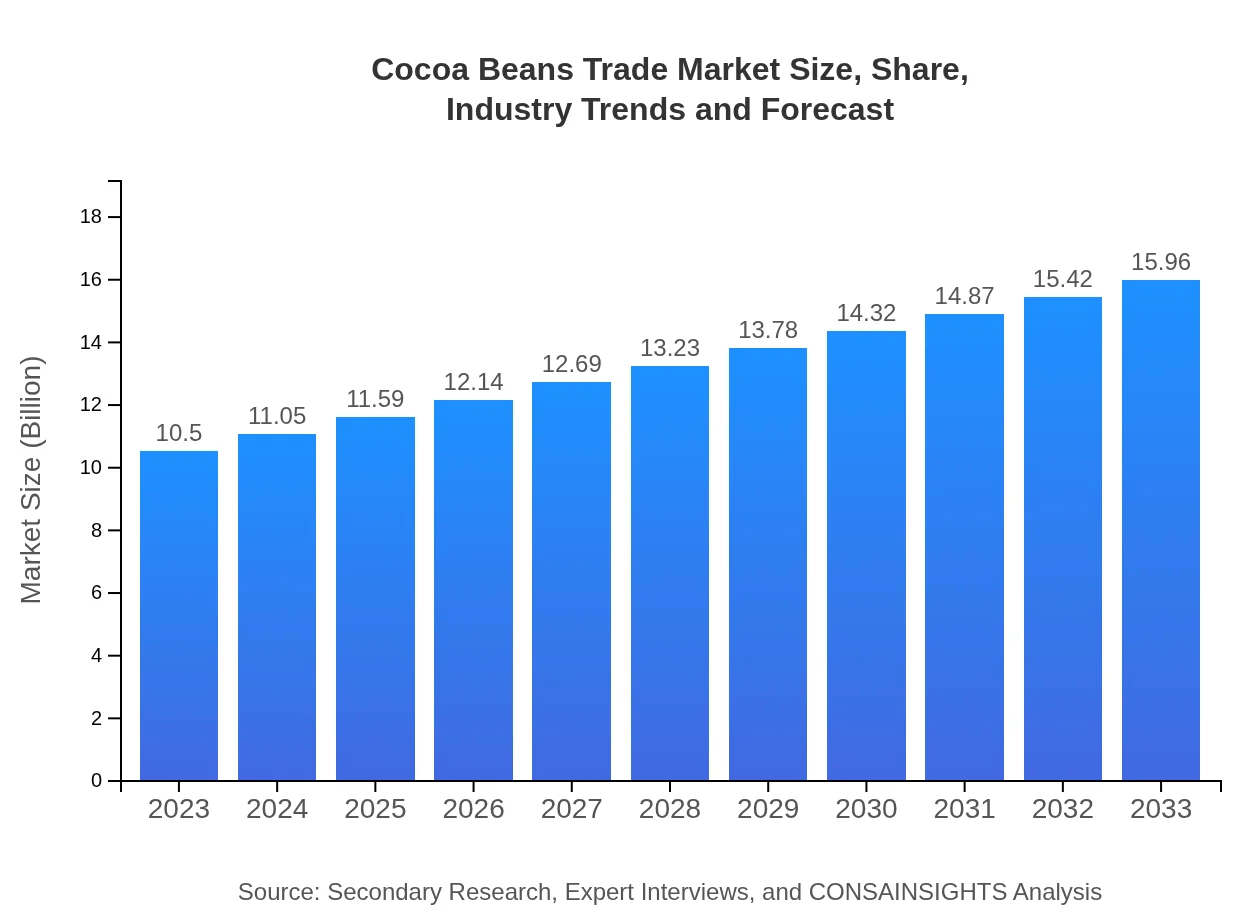
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $15.96 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill Inc., Olam International, Barry Callebaut, Mars Incorporated, Cocoa Processing Company Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Overview
Customize Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cocoa Beans Trade market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cocoa Beans Trade's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cocoa Beans Trade
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cocoa Beans Trade market in 2023?
Cocoa Beans Trade Industry Analysis
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report:
The European market for cocoa beans is valued at $2.53 billion in 2023, expected to reach $3.84 billion by 2033. Europe remains the largest consumer of cocoa products, driven by the chocolate industry, with a strong push towards organic and fair trade products in response to consumer preferences.Asia Pacific Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report:
In 2023, the Cocoa Beans Trade market in the Asia Pacific is valued at $2.13 billion, projected to reach $3.24 billion by 2033. The region's growing chocolate consumption, coupled with increasing investment in cocoa farming innovations, drives growth. Additionally, emerging economies are witnessing rising disposable incomes, leading to enhanced demand for chocolate products.North America Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report:
North America stands as a significant player in the Cocoa Beans Trade market, with a valuation of $3.82 billion in 2023 and estimated growth to $5.81 billion by 2033. The region's demand for high-quality cocoa products in the food and beverage sector is propelling market expansion, along with the rise in health-conscious product offerings.South America Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report:
The South American cocoa market is valued at $0.60 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $0.91 billion by 2033. Countries like Ecuador and Brazil are gaining prominence in organic cocoa production, capitalizing on the increasing global demand for sustainable and ethically sourced cocoa.Middle East & Africa Cocoa Beans Trade Market Report:
In 2023, the Cocoa Beans Trade market in the Middle East and Africa is valued at $1.43 billion, projected to grow to $2.17 billion by 2033. The growing bakery and confectionery sectors in the region, along with increasing import demands, contribute to market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
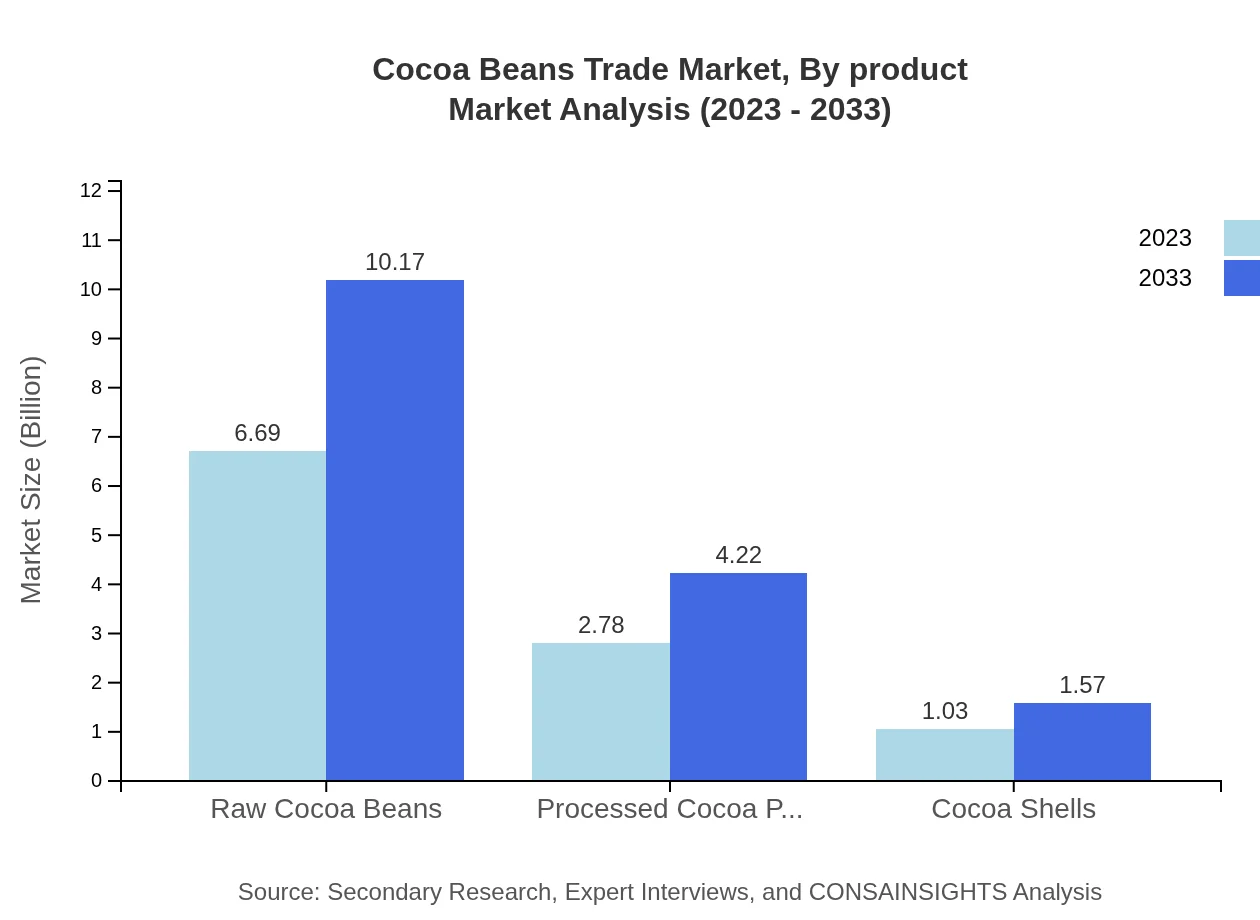
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Analysis By Product
The market is significantly influenced by both raw cocoa beans and processed cocoa products. In 2023, raw cocoa beans account for $6.69 billion and are expected to grow to $10.17 billion by 2033, representing 63.74% of the total market share. Processed cocoa products, including cocoa powder and butter, hold a market size of $2.78 billion, anticipated to rise to $4.22 billion by 2033, with a share of 26.45%. Cocoa shells, though a smaller segment at $1.03 billion in 2023, are projected to experience growth driven by their diverse applications in agriculture and animal feed, reaching $1.57 billion by 2033.
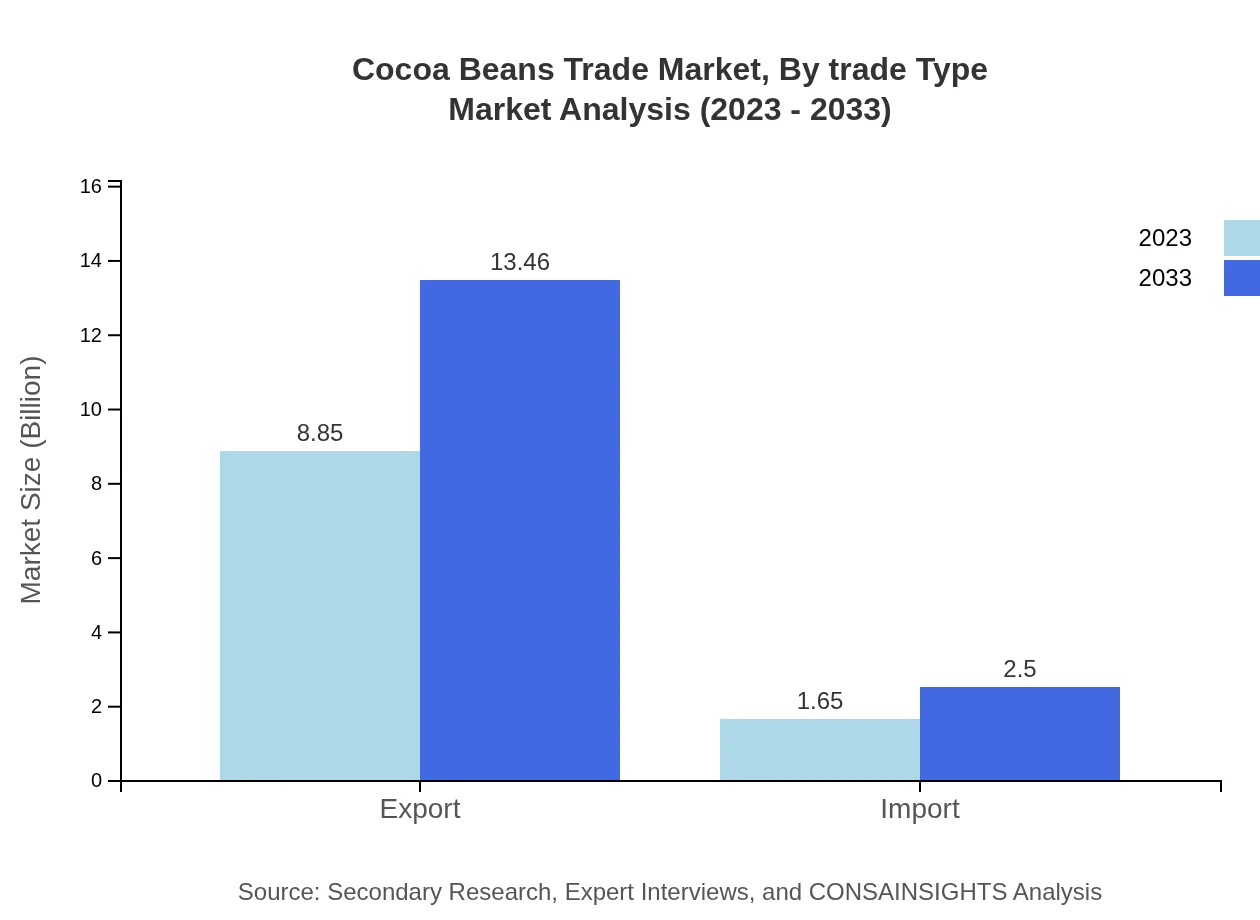
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Analysis By Trade Type
The Cocoa Beans Trade includes both exports and imports, with exports valued at $8.85 billion in 2023, expected to reach $13.46 billion by 2033, contributing 84.31% to the market. Meanwhile, imports are valued at $1.65 billion, projected to increase to $2.50 billion, comprising 15.69% of the market share. This indicates a robust demand for cocoa in importing nations, underlining the trade dynamics and opportunities across borders.
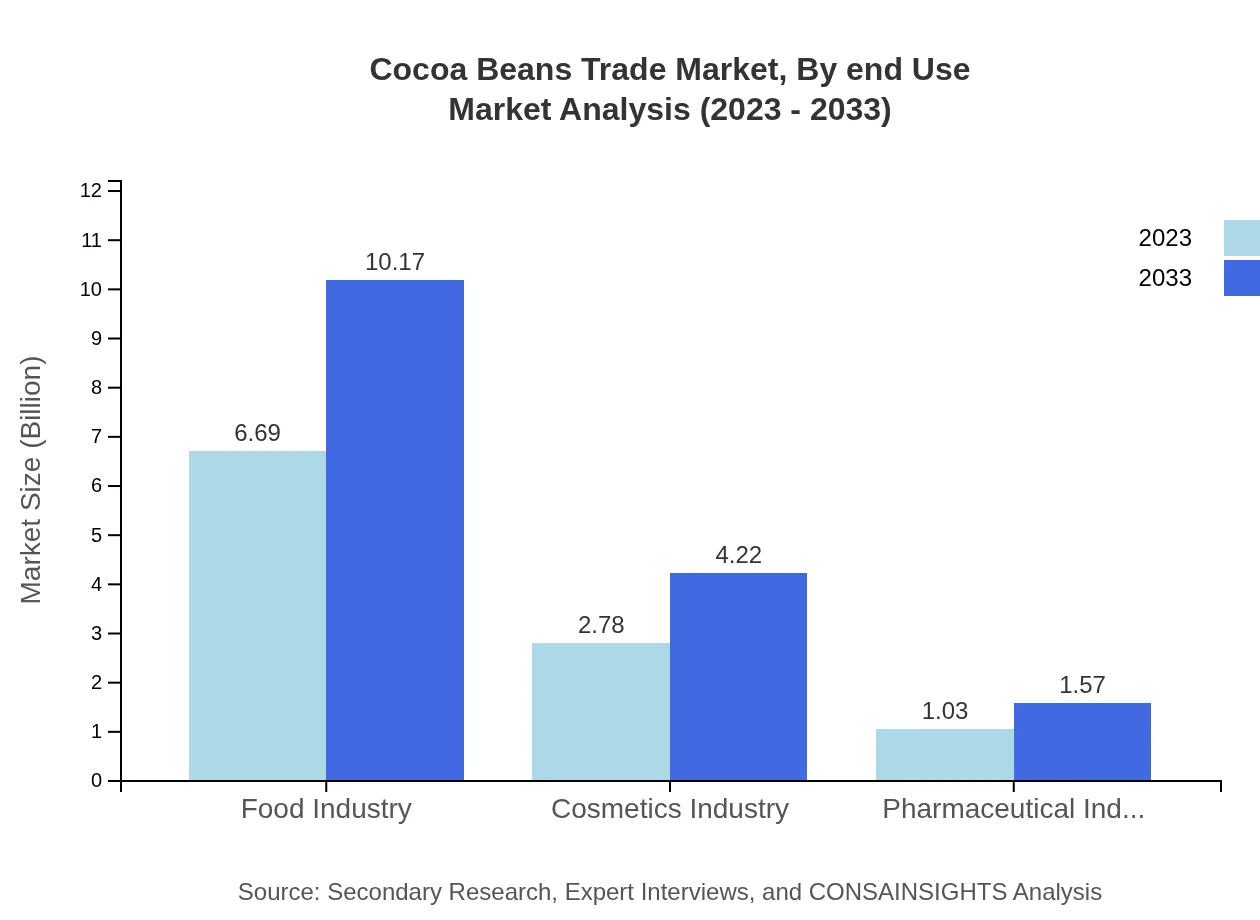
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Analysis By End Use
The end-use segments reveal significant insights into market performance. The food industry, with a market size of $6.69 billion in 2023, is expected to grow to $10.17 billion by 2033, representing a 63.74% market share. The cosmetics industry follows, valued at $2.78 billion and anticipated to reach $4.22 billion, maintaining a 26.45% share. The pharmaceutical sector, while smaller, is also notable, with a size of $1.03 billion projected to grow to $1.57 billion, indicating a steady demand for cocoa-based compounds.
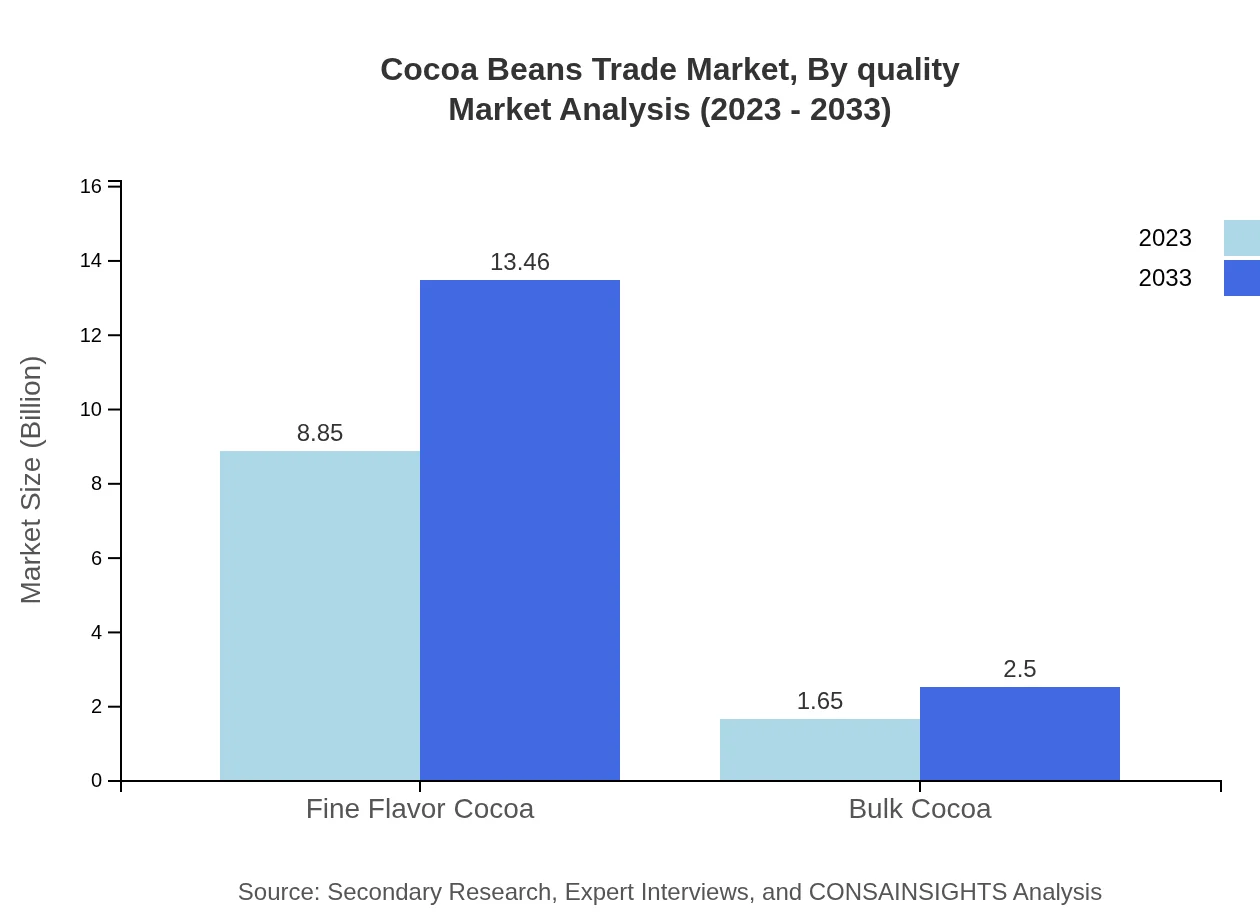
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Analysis By Quality
Quality segmentation is critical in the cocoa beans market, with Fine Flavor Cocoa leading the segment. Valued at $8.85 billion in 2023, it is expected to grow to $13.46 billion by 2033, commanding an 84.31% market share. Bulk cocoa, representing lower-quality beans, is valued at $1.65 billion and is projected to reach $2.50 billion, holding a 15.69% share. This distinction in quality influences buyer preferences and pricing strategies significantly.
Cocoa Beans Trade Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cocoa Beans Trade Industry
Cargill Inc.:
Cargill is one of the largest global providers of food, agriculture, financial, and industrial products and services. In the cocoa sector, Cargill is recognized for its sustainable cocoa sourcing strategies.Olam International:
Olam is a leading supply chain manager and processor of cocoa beans, with operations in multiple countries. Their focus on sustainability and innovation has positioned them as key players in the cocoa market.Barry Callebaut:
Barry Callebaut is the world's largest manufacturer of chocolate and cocoa products, serving the entire value chain from chocolate makers to retailers. They are known for their commitment to sustainable cocoa sourcing.Mars Incorporated:
Mars is not only one of the largest chocolate producers in the world but also plays a significant role in cocoa sourcing and sustainability initiatives globally.Cocoa Processing Company Ltd.:
Based in Ghana, Cocoa Processing Company Ltd. specializes in cocoa products manufacturing, contributing significantly to the local economy and the global cocoa supply chain.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cocoa Beans Trade?
The cocoa beans trade market is valued at approximately $10.5 billion as of 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.2% through 2033. This growth is driven by increasing global demand in various sectors, particularly food production.
What are the key market players or companies in this cocoa Beans Trade industry?
Key players in the cocoa beans trade industry include major international companies like Barry Callebaut, Cargill, and Olam International, which dominate supply chains by providing raw cocoa beans and processed products to various industries.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cocoa Beans Trade industry?
The growth in the cocoa beans trade industry is primarily fueled by rising consumer demand for chocolate and confectionery products, health benefits associated with cocoa, and expanding applications in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, contributing to market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cocoa Beans Trade?
The fastest-growing region in the cocoa beans trade from 2023 to 2033 is North America, with market growth expected from $3.82 billion to $5.81 billion, driven by an increase in chocolate consumption and investment in supply chain enhancements.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cocoa Beans Trade industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific requirements in the cocoa beans trade industry, allowing clients to gain insights relevant to their market segment and strategic needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this cocoa Beans Trade market research project?
Deliverables from the cocoa beans trade market research project typically include comprehensive reports on market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, regional insights, and segmentation data, ensuring clients have actionable intelligence.
What are the market trends of cocoa Beans Trade?
Current trends in the cocoa beans trade industry include an increasing shift towards sustainable sourcing, growth in organic cocoa products, and the rising popularity of dark chocolate, reflecting changing consumer preferences and market dynamics.