Cocoa Fiber Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cocoa-fiber
Cocoa Fiber Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cocoa Fiber market, covering current market conditions, industry insights, segmentation, regional performance, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
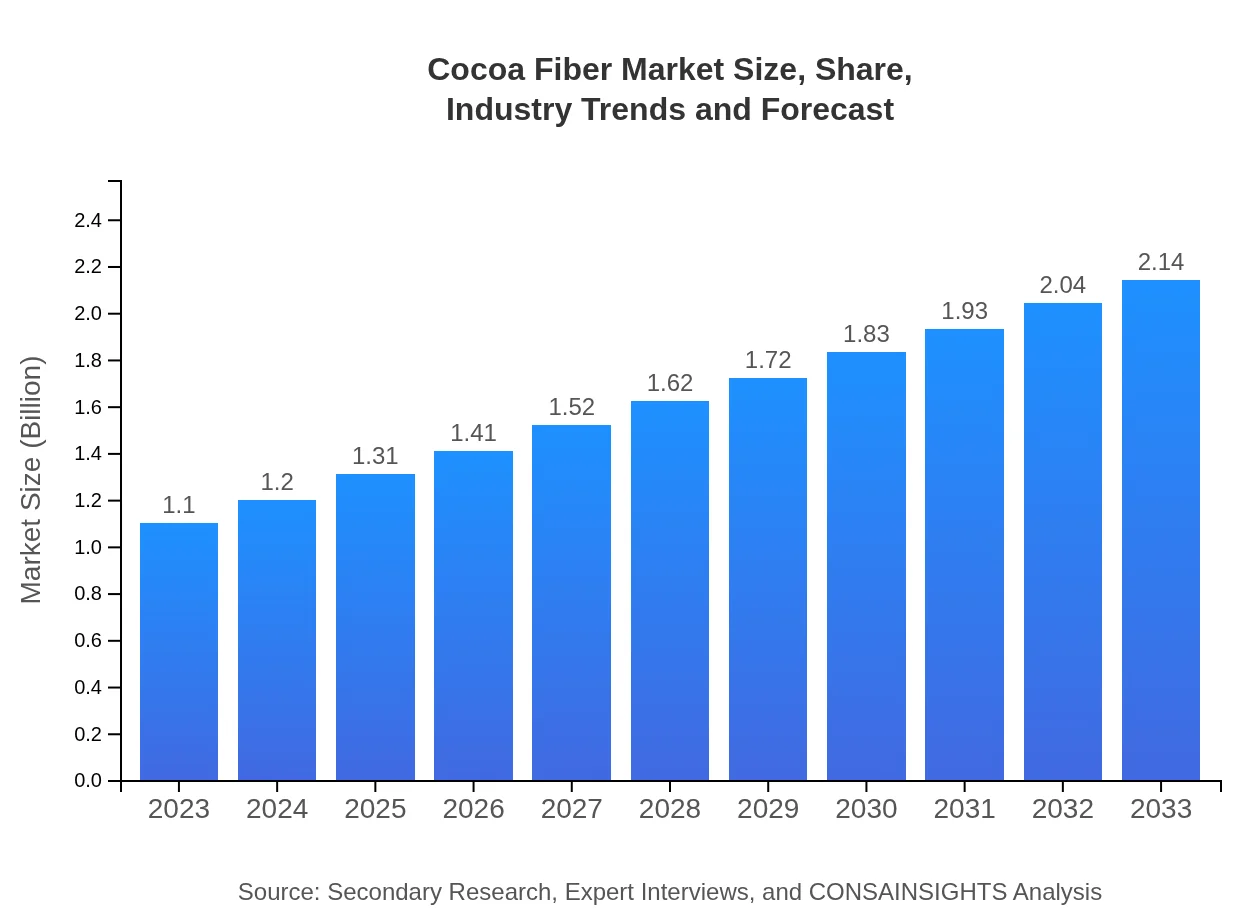
| 2023 Market Size | $1.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.14 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Incorporated, Barry Callebaut, The Hershey Company, Olam Group |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cocoa Fiber Market Overview
Customize Cocoa Fiber Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cocoa Fiber market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cocoa Fiber's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cocoa Fiber
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cocoa Fiber market in 2023?
Cocoa Fiber Industry Analysis
Cocoa Fiber Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cocoa Fiber Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cocoa Fiber Market Report:
Europe's cocoa fiber market size is expected to grow from $0.33 billion in 2023 to $0.64 billion by 2033. The region has a mature market with high demand for organic and fair-trade products, especially in the health food and cosmetic sectors.Asia Pacific Cocoa Fiber Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region's cocoa fiber market is poised for growth, expected to expand from $0.24 billion in 2023 to $0.46 billion by 2033. The rise in health consciousness among consumers and the increasing popularity of natural ingredients in the food industry drive demand significantly in countries like China and India.North America Cocoa Fiber Market Report:
North America shows a robust cocoa fiber market, growing from $0.36 billion in 2023 to $0.70 billion in 2033. The demand from health food manufacturers and the presence of leading cocoa processing companies contribute to this growth, along with the increasing trend of veganism.South America Cocoa Fiber Market Report:
In South America, the market is anticipated to increase from $0.10 billion in 2023 to $0.20 billion by 2033. Brazil and Ecuador are notable players due to their cocoa production volumes. The region benefits from a rich agricultural landscape that supports cocoa cultivation.Middle East & Africa Cocoa Fiber Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's cocoa fiber market is projected to increase from $0.07 billion in 2023 to $0.13 billion by 2033. The growth is fueled by an increase in awareness regarding health benefits and a preference for natural products.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
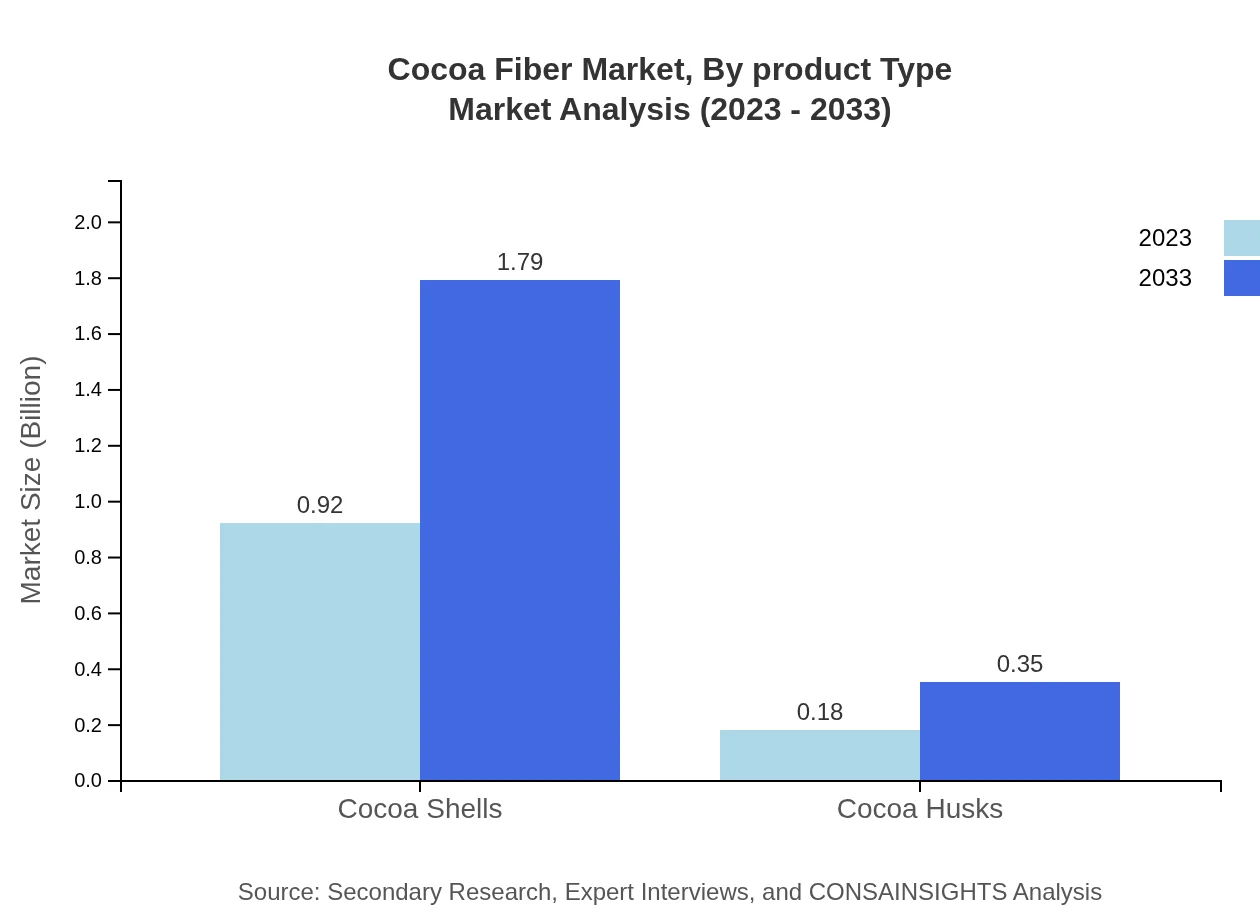
Cocoa Fiber Market Analysis By Product Type
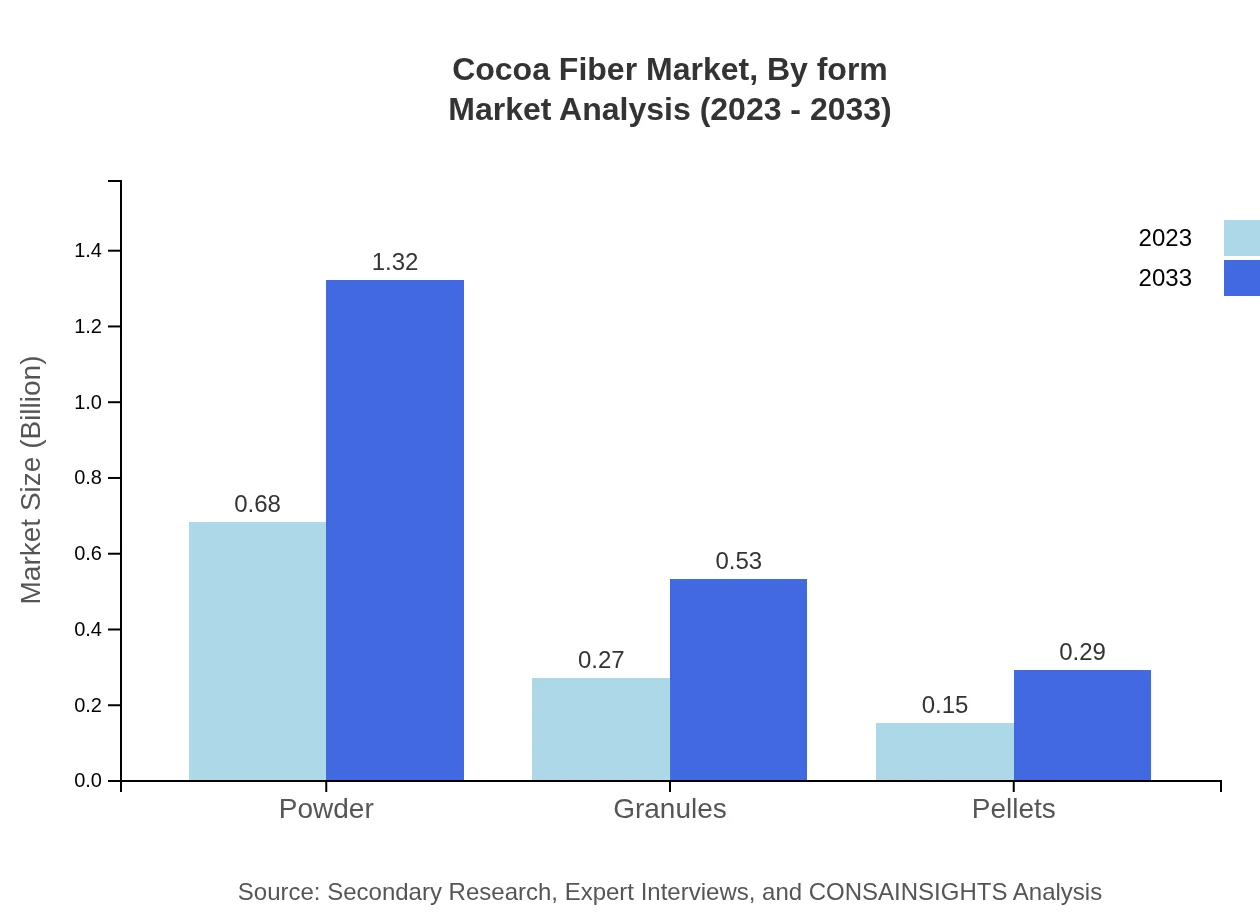
The cocoa fiber market by product type includes powder, granules, and pellets. In 2023, the cocoa powder segment dominates with a market size of $0.68 billion and is projected to reach $1.32 billion by 2033, holding a 61.58% share throughout the decade. Granules and pellets segment are also growing, with granules moving from $0.27 billion to $0.53 billion, maintaining a 24.7% share.
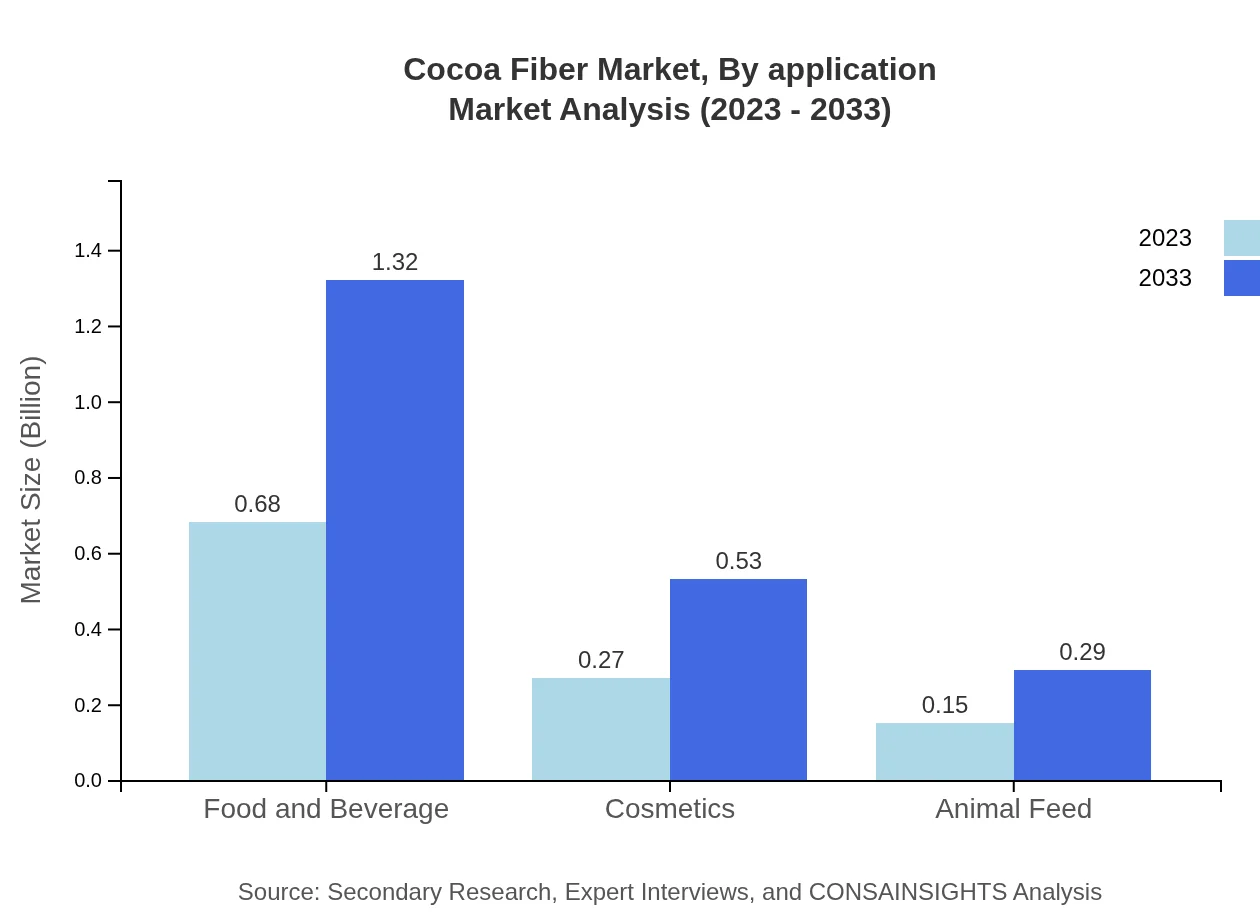
Cocoa Fiber Market Analysis By Application
The applications of cocoa fiber span across food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and personal care. The food industry leads with a size of $0.64 billion in 2023, expected to achieve $1.24 billion by 2033, representing 57.74% of the market share. Pharmaceuticals and personal care utilize cocoa fiber for its health benefits, growing from $0.25 billion to $0.48 billion and $0.11 billion to $0.21 billion, respectively.
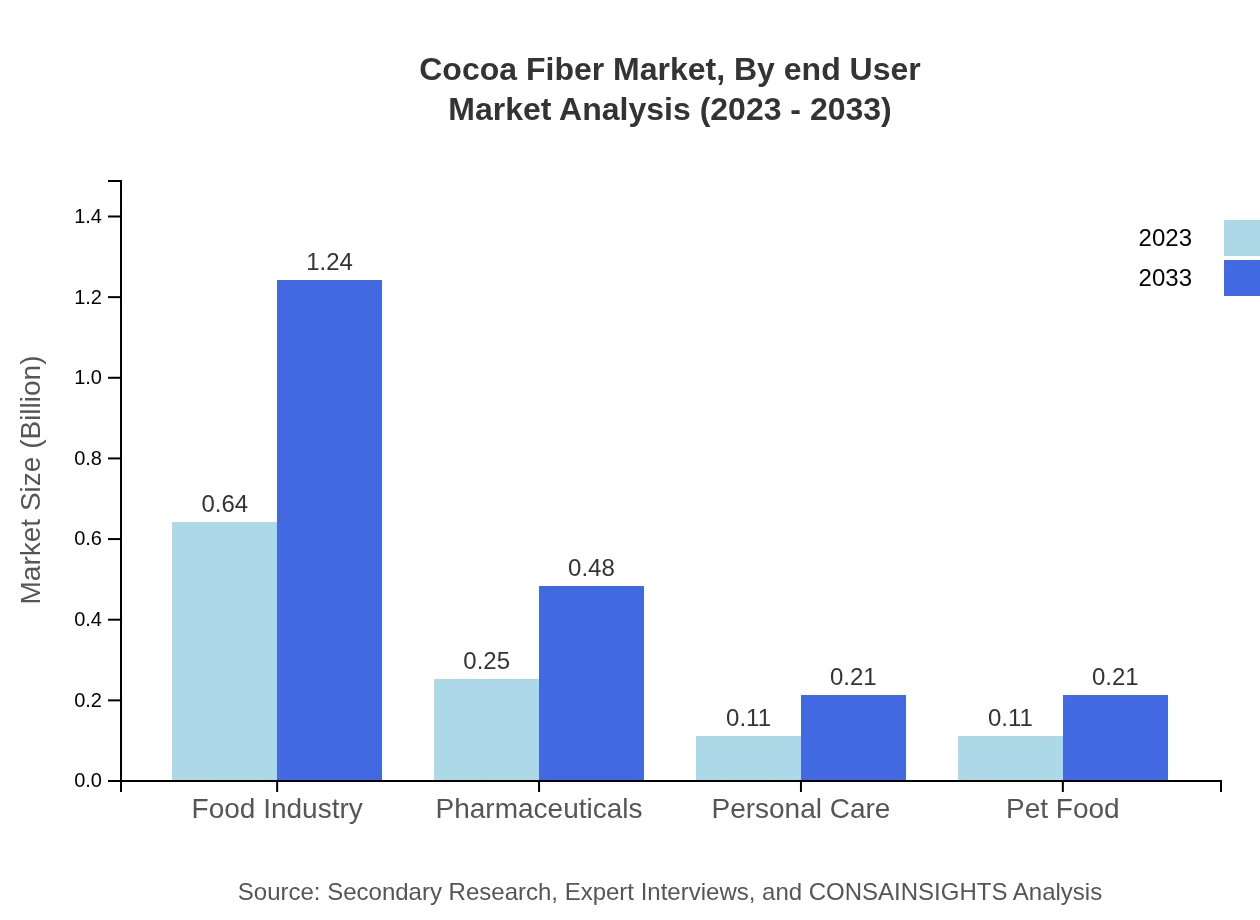
Cocoa Fiber Market Analysis By End User
Cocoa fiber's end-users include the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. It is extensively used in the food industry, where the market size expands from $0.68 billion to $1.32 billion. The pharmaceutical industry leverages cocoa fiber for its health benefits, and the cosmetic industry utilizes its natural properties to enhance product formulas.
Cocoa Fiber Market Analysis By Form
The cocoa fiber products are available in various forms such as powder, granules, and pellets. The powder form captures the largest market share, accounting for 61.58% in both 2023 and 2033 due to its versatility and ease of use in formulations.
Cocoa Fiber Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cocoa Fiber Industry
Cargill, Incorporated:
A global leader in food production, Cargill provides sustainable cocoa sourcing and processing solutions, contributing significantly to the cocoa fiber market.Barry Callebaut:
One of the largest chocolate manufacturers worldwide, Barry Callebaut also processes cocoa into various products, including cocoa fiber, focusing on quality and sustainability.The Hershey Company:
Known for its chocolate products, Hershey invests in sustainable cocoa farming, improving cocoa processing that supports cocoa fiber production.Olam Group:
Olam is a key player in the agricultural commodities sector, ensuring a robust supply chain for cocoa sourcing and cocoa fiber production.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cocoa Fiber?
The global cocoa fiber market is valued at approximately $1.1 billion in 2023, and it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7%, reaching a market size of around $2.2 billion by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the cocoa Fiber industry?
Key players in the cocoa-fiber market include companies that specialize in food products, cosmetics, and nutraceuticals. They focus on sustainable sourcing and innovative processing methods to enhance the fiber's application across various segments.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cocoa Fiber industry?
The growth drivers in the cocoa-fiber market include the increasing demand for vegan and gluten-free products, rising health consciousness among consumers, and the expanding applications of cocoa fiber in food, personal care, and pharmaceuticals.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cocoa Fiber market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing segment in the cocoa-fiber market. It's expected to grow from $0.24 billion in 2023 to $0.46 billion in 2033, driven by increasing consumer demand for healthier food alternatives.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the cocoa Fiber industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers tailored market report data for the cocoa-fiber sector, allowing clients to access specific insights and analyses based on their unique needs and market interests.
What deliverables can I expect from this cocoa Fiber market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, segmentation data, regional insights, competitive landscape reviews, and trends that provide actionable strategies for stakeholders in the cocoa fiber industry.
What are the market trends of cocoa Fiber?
Key trends in the cocoa-fiber market include an increasing focus on sustainable ingredient sourcing, product innovations in the food and beverage sector, and a rising awareness of the nutritional benefits of cocoa fiber in various applications.