Cocoa Products Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cocoa-products
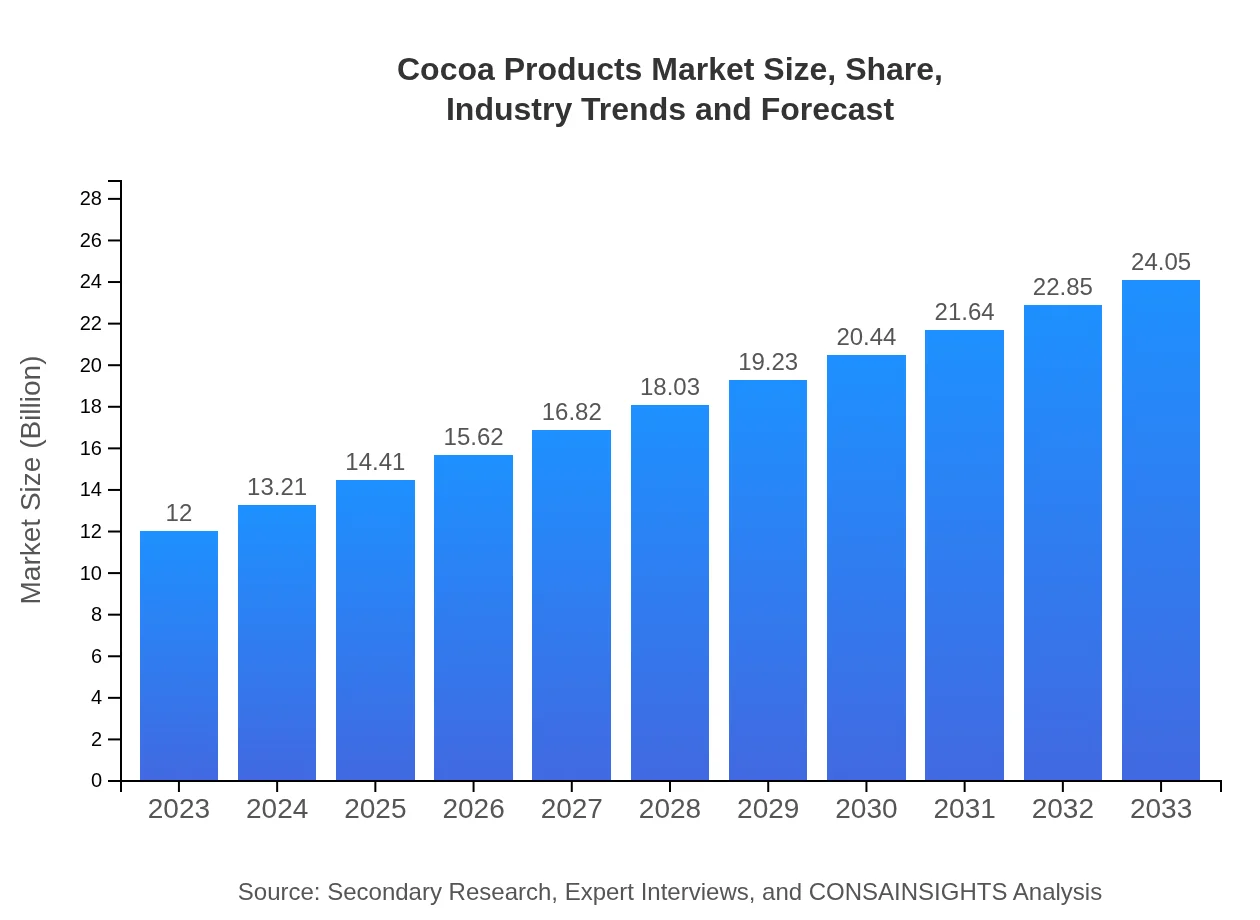
Cocoa Products Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cocoa Products market from 2023 to 2033, examining key insights, trends, and forecasts, alongside data on market size, regional performance, and competitive landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $12.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $24.05 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Incorporated, Barry Callebaut AG, The Hershey Company, Mondelez International, Inc., Nestlé S.A. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cocoa Products Market Overview
Customize Cocoa Products Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cocoa Products market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cocoa Products's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cocoa Products
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cocoa Products market in 2023?
Cocoa Products Industry Analysis
Cocoa Products Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cocoa Products Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cocoa Products Market Report:
The European market is set to grow from $3.75 billion in 2023 to $7.51 billion by 2033. With Germany, France, and the UK as key markets, the region is known for its sophisticated chocolate consumption patterns and innovative culinary applications of cocoa.Asia Pacific Cocoa Products Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's Cocoa Products market is valued at $2.34 billion, projected to grow to $4.68 billion by 2033, driven by rising urbanization, growing middle-class populations, and the increasing adoption of Western dietary preferences. Countries like China and India are experiencing a surge in chocolate consumption, alongside a growing bakery industry.North America Cocoa Products Market Report:
In 2023, the Cocoa Products market in North America is estimated at $3.85 billion, with projections to reach $7.71 billion by 2033. The region is characterized by high demand for premium chocolate and health-oriented cocoa products, driven by wellness trends and gourmet offerings.South America Cocoa Products Market Report:
The South American Cocoa Products market valued at $1.13 billion in 2023, is expected to rise to $2.26 billion by 2033. The region is a significant cocoa producer, influencing global supply. Enhanced focus on sustainable practices and organic cocoa will further bolster growth.Middle East & Africa Cocoa Products Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Cocoa Products market stands at $0.94 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $1.89 billion by 2033. Diversification efforts across product development in chocolate and confectionery sectors are aiding growth despite regional economic challenges.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
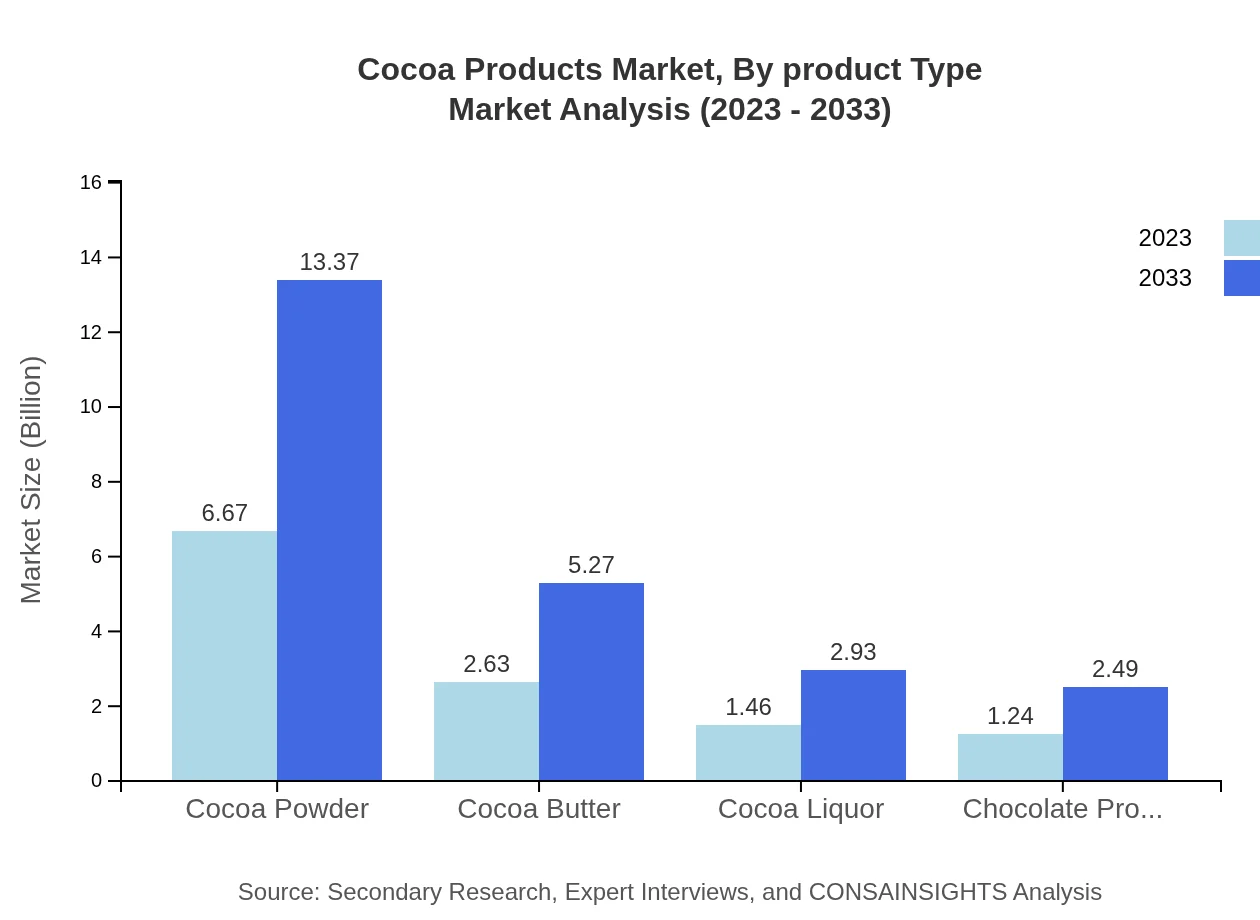
Cocoa Products Market Analysis By Product Type
The Cocoa Products market by product type is dominated by cocoa powder, which holds a significant share valued at $6.67 billion in 2023 and forecasted to be $13.37 billion by 2033. Cocoa butter follows, with a value of $2.63 billion in 2023, growing to $5.27 billion. Cocoa liquor and chocolate products also show positive growth trends, reflecting increasing applications across various industries.
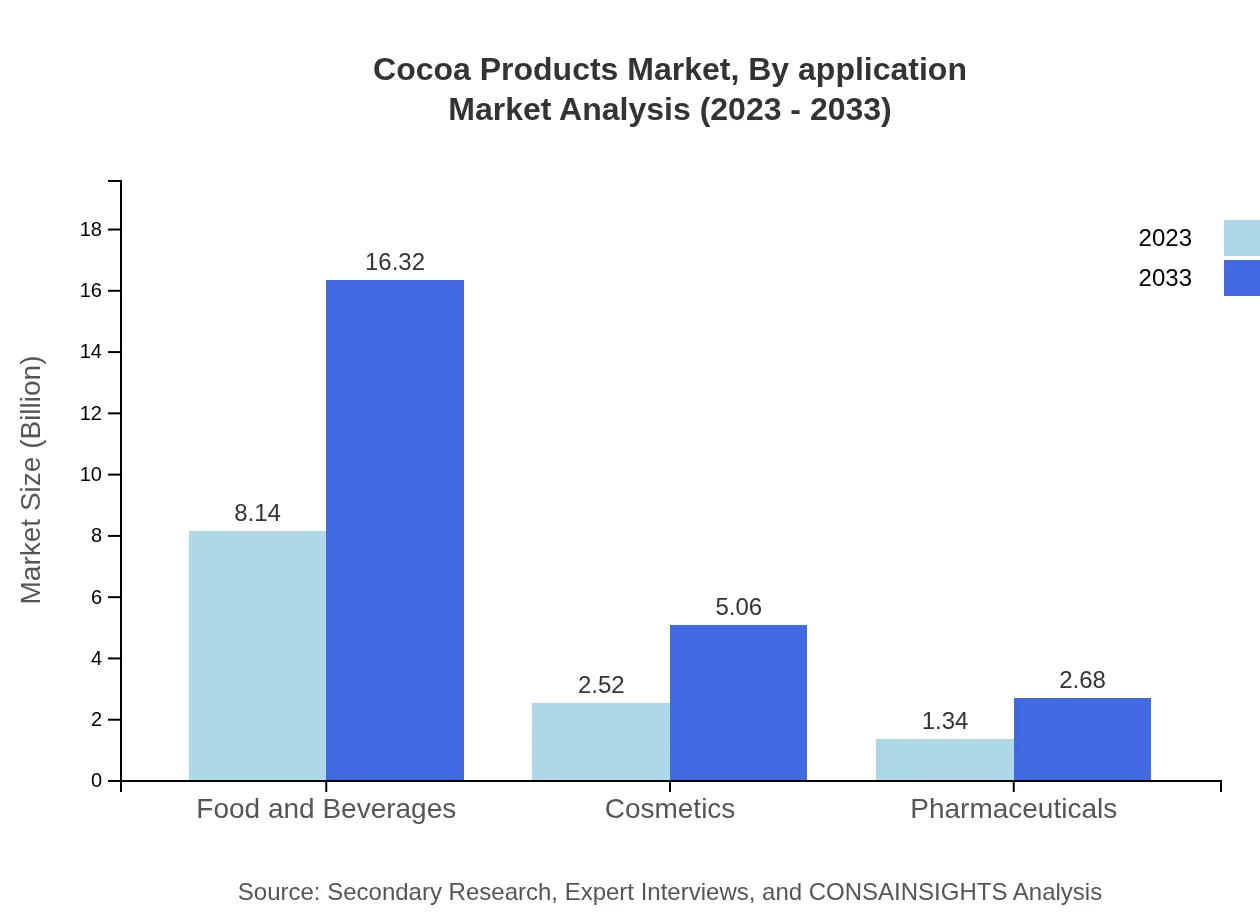
Cocoa Products Market Analysis By Application
The Cocoa Products market by application indicates the food and beverages sector as the largest segment, with a size of $8.14 billion in 2023, expected to reach $16.32 billion by 2033. The cosmetics sector is also notable, accounting for $2.52 billion and projected to double by 2033, driven by demand for organic and natural ingredients.
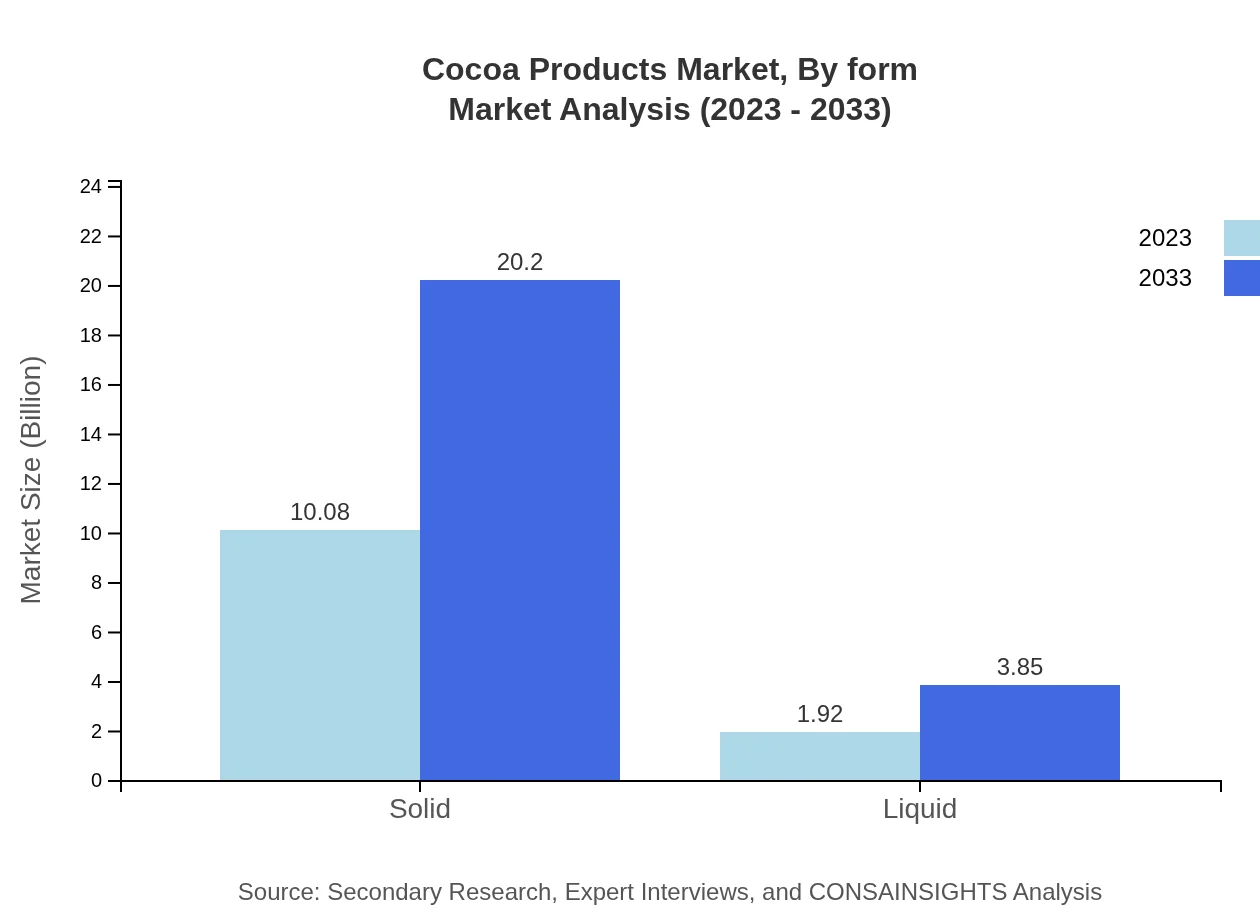
Cocoa Products Market Analysis By Form
The market is segmented into solid and liquid forms, with solid types comprising a considerable share at $10.08 billion in 2023 and projected to expand to $20.20 billion by 2033. Liquid forms exhibit steady growth as well, from $1.92 billion to $3.85 billion, driven by innovations in beverage applications.
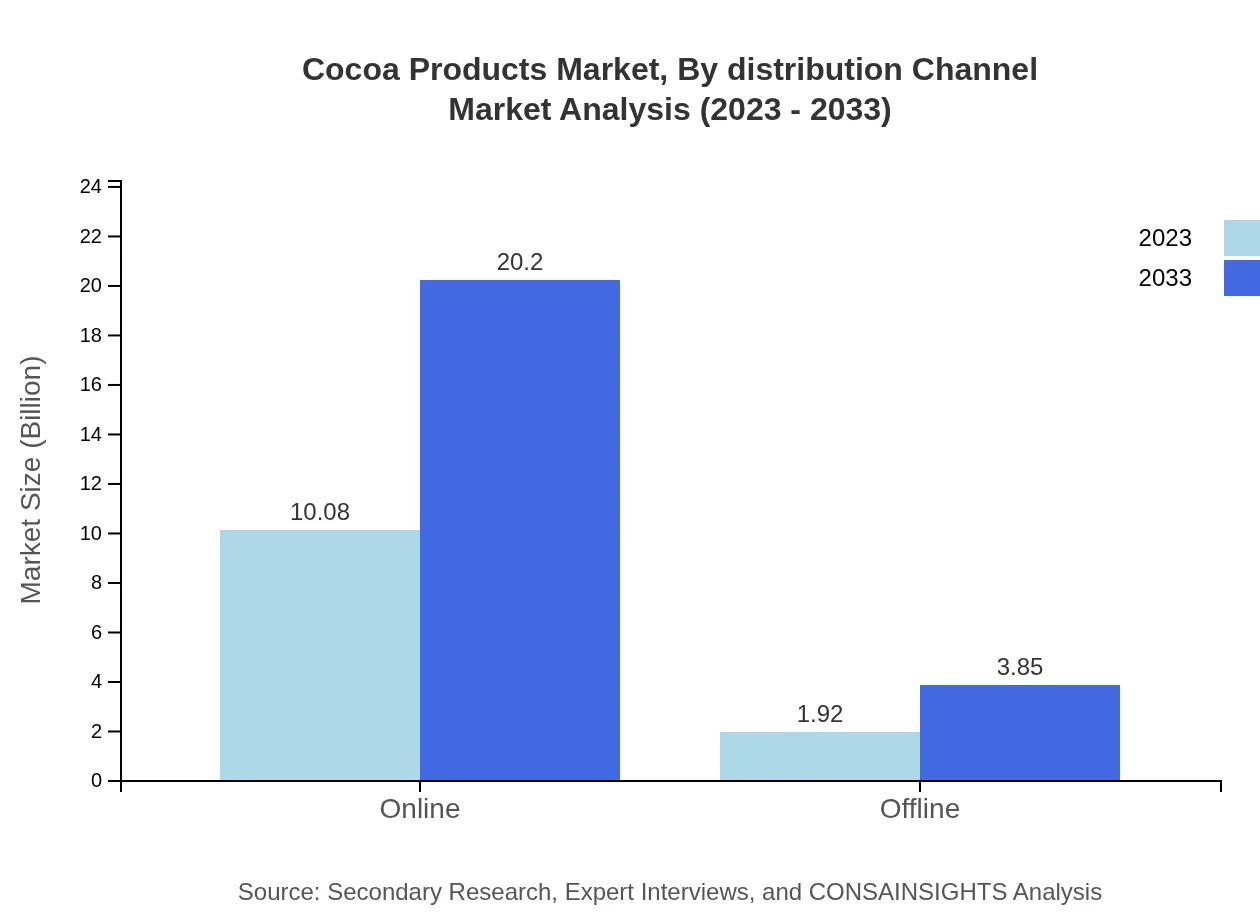
Cocoa Products Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Online distribution channels dominate the Cocoa Products market, with a size of $10.08 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $20.20 billion by 2033. Offline retail channels, although smaller, hold steady figures of $1.92 billion and forecasted growth to $3.85 billion, emphasizing the importance of various purchasing options.
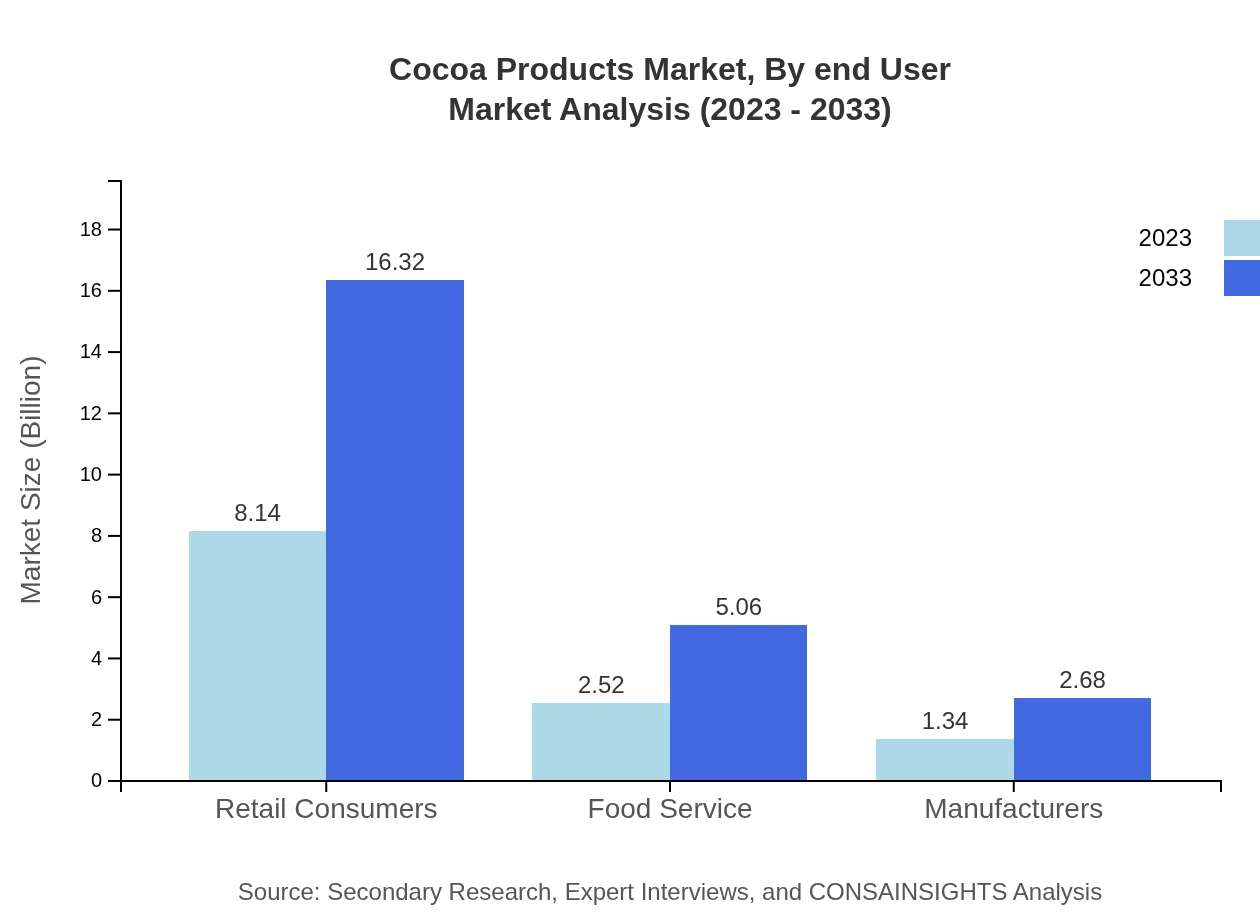
Cocoa Products Market Analysis By End User
The Cocoa Products market by end-user showcases retail consumers as the leading segment, with a market size of $8.14 billion in 2023 and growth anticipated to $16.32 billion by 2033. Food service and manufacturers also contribute significantly, with steadily increasing demand for high-quality cocoa ingredients.
Cocoa Products Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cocoa Products Industry
Cargill, Incorporated:
One of the largest global food companies, Cargill is a leader in cocoa processing and sourcing, committed to sustainable cocoa production practices, and driving innovation in cocoa products.Barry Callebaut AG:
A Swiss-based company and global leader in chocolate and cocoa products, Barry Callebaut provides quality cocoa ingredients to the food industry and is renowned for its focus on sustainability.The Hershey Company:
Known for its iconic chocolate products, Hershey is a major player in the cocoa products market, actively pursuing strategies for sourcing sustainable cocoa and expanding its product portfolio.Mondelez International, Inc.:
A leading snack company with a strong presence in the cocoa products segment, Mondelez focuses on creating innovative chocolate and confectionary items while committing to responsible sourcing.Nestlé S.A.:
Nestlé, as one of the largest food and beverage companies in the world, plays a significant role in the cocoa products market, focusing on health trends and innovative cocoa applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cocoa Products?
The global cocoa products market is estimated to reach $12 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2023. In 2023, the market size stands at approximately $6.72 billion, demonstrating significant growth potential in the coming decade.
What are the key market players or companies in this cocoa Products industry?
Key players in the cocoa products industry include major companies such as Barry Callebaut, Cargill, and Olam International. These firms lead in product innovation, maintaining significant market shares and contributing to the overall growth of the cocoa sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cocoa Products industry?
The growth of the cocoa products market is propelled by rising demand for chocolate and confectionery. Additionally, the increasing incorporation of cocoa in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals further boosts market expansion, appealing to a broader consumer base.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cocoa Products market?
The Asia Pacific region is identified as the fastest-growing market for cocoa products, projected to expand from $2.34 billion in 2023 to $4.68 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer preferences and developing economies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cocoa Products industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific requirements in the cocoa products industry. These reports can provide detailed insights into market trends, competitor analysis, and segment performance.
What deliverables can I expect from this cocoa Products market research project?
Deliverables from the cocoa products market research project may include a comprehensive report detailing market trends, growth forecasts, segment analysis, and actionable insights for strategic planning in the cocoa industry.
What are the market trends of cocoa Products?
Current trends in the cocoa products market include a rising demand for organic and sustainable cocoa, an expansion of specialty chocolate offerings, and the increasing integration of technology in production processes to improve efficiency.