Cold Storage Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cold-storage
Cold Storage Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cold Storage market, covering current trends, forecasts up to the year 2033, and insights into market size, segmentation, regional performance, and key players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
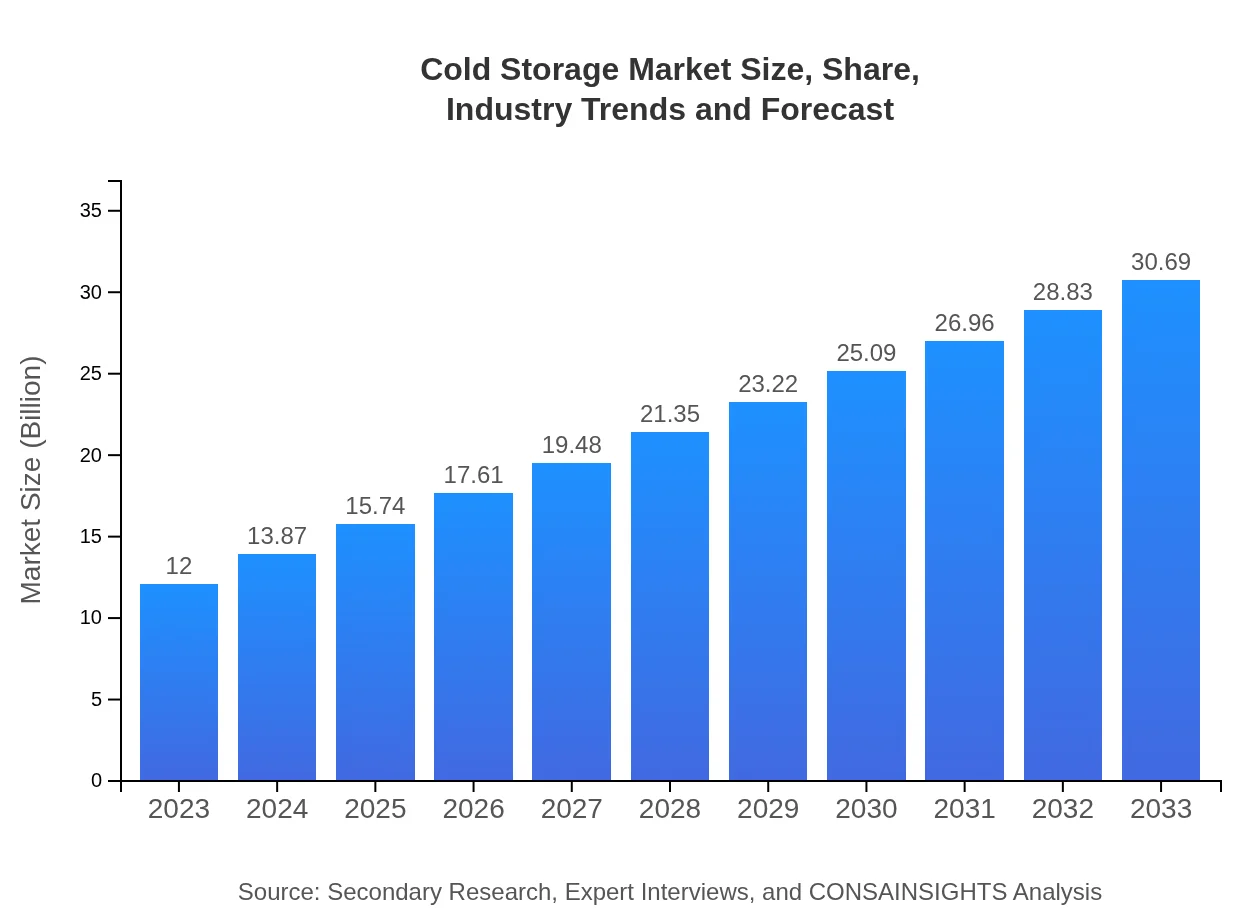
| 2023 Market Size | $12.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $30.69 Billion |
| Top Companies | Americold Realty Trust, Lineage Logistics, XPO Logistics, SWIRE Properties |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cold Storage Market Overview
Customize Cold Storage Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cold Storage market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cold Storage's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cold Storage
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cold Storage market in 2023?
Cold Storage Industry Analysis
Cold Storage Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cold Storage Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cold Storage Market Report:
The European cold storage market, estimated at $3.12 billion in 2023, is set to expand to $7.98 billion by 2033. Regulatory frameworks supporting food safety and innovative technologies for energy efficiency significantly drive growth in this region.Asia Pacific Cold Storage Market Report:
In 2023, the cold storage market in Asia Pacific is valued at $2.50 billion and is projected to reach $6.39 billion by 2033, fueled by the region's rapid urbanization, population growth, and increased demand for seafood, pharmaceuticals, and processed food.North America Cold Storage Market Report:
North America leads the cold storage market with a total value of $4.18 billion in 2023, projected to surge to $10.70 billion by 2033. The significant market growth is driven by advanced logistics infrastructure and an increasing trend towards online grocery shopping.South America Cold Storage Market Report:
The South American cold storage market, worth $1.20 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to $3.06 billion by 2033. Ongoing investments in agricultural production and the rise in exports of perishable goods drive growth in this region.Middle East & Africa Cold Storage Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the cold storage market is valued at $1.00 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $2.56 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increasing urbanization and demand for quality food products in developing economies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
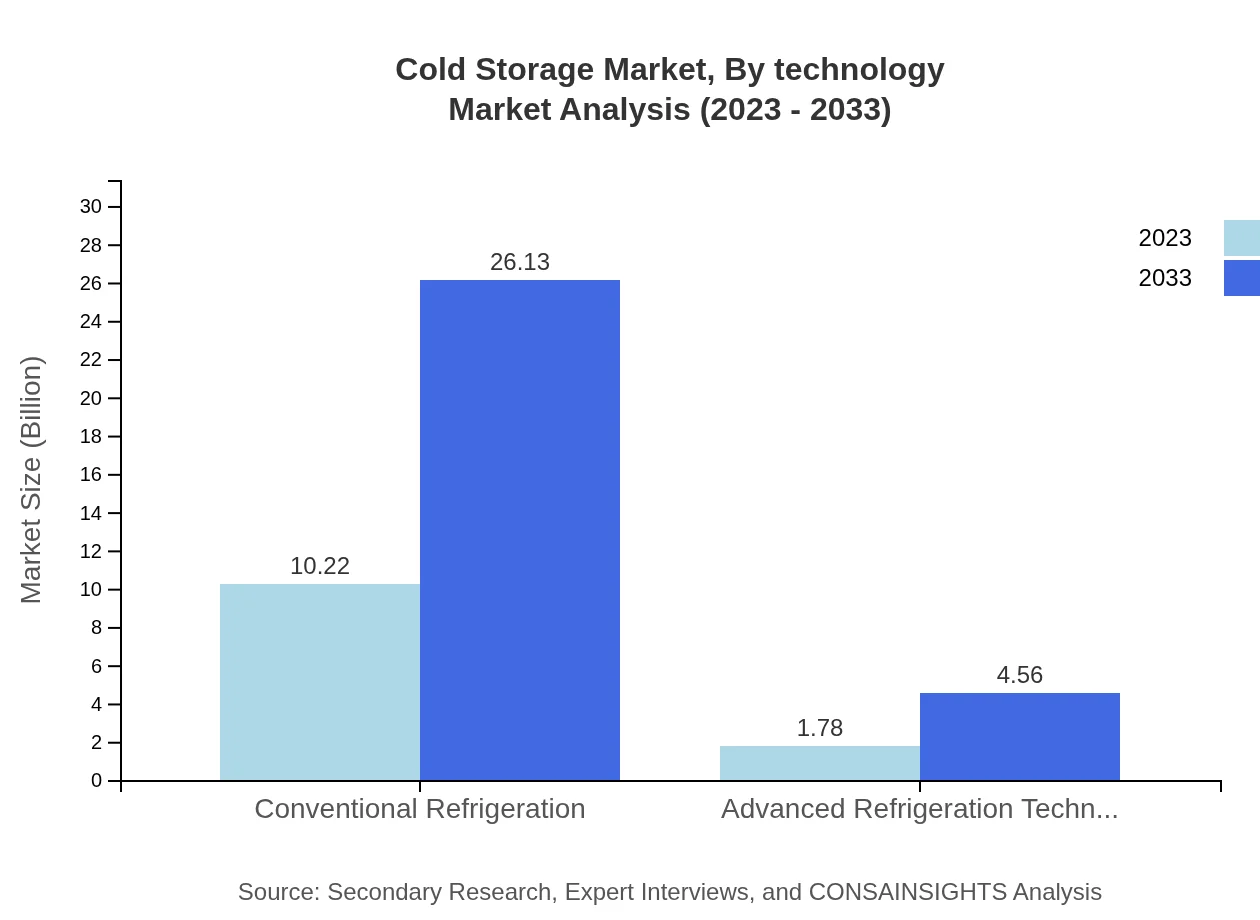
Cold Storage Market Analysis By Technology
The cold storage market, segmented by technology, includes conventional refrigeration, which currently dominates the market with a size of $10.22 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $26.13 billion by 2033. Advanced refrigeration technologies are also emerging, representing a growing market segment, valued at $1.78 billion in 2023 and forecasted at $4.56 billion by 2033.
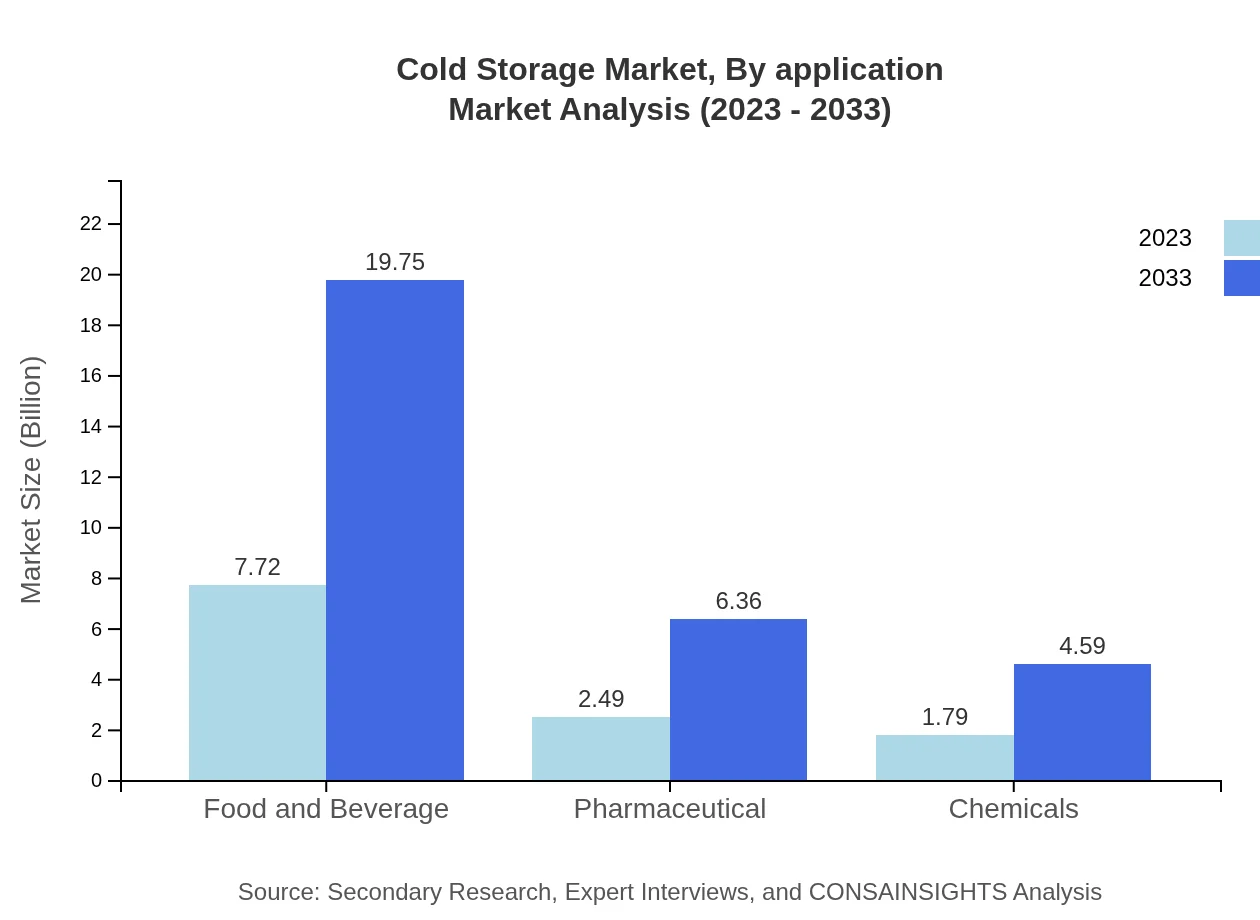
Cold Storage Market Analysis By Application
In terms of applications, the food and beverage sector contributes significantly to the cold storage market, with a size of $7.72 billion in 2023 and a forecasted growth to $19.75 billion by 2033. The pharmaceutical sector follows closely, currently valued at $2.49 billion and expected to grow to $6.36 billion.
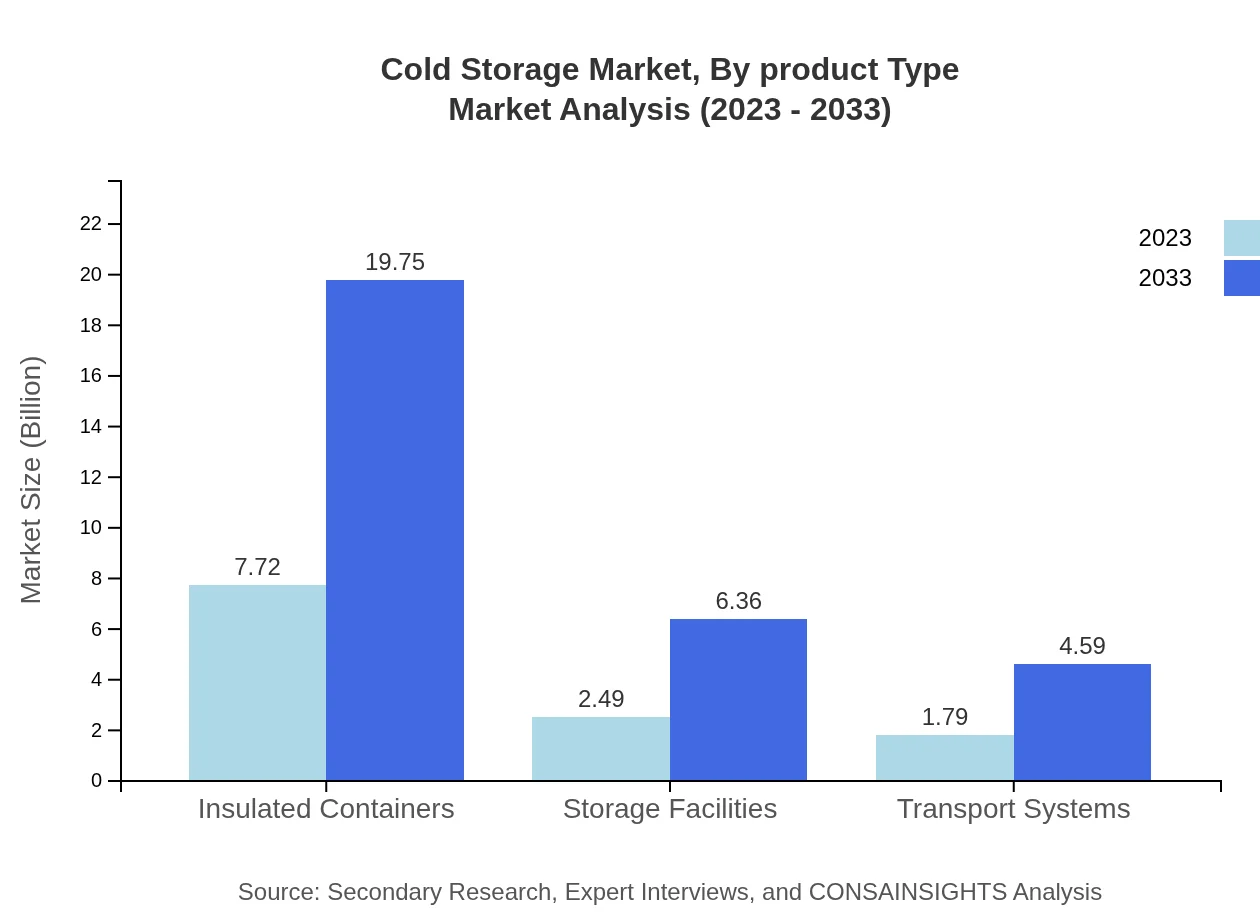
Cold Storage Market Analysis By Product Type
The product type segmentation includes insulated containers, which account for $7.72 billion in 2023, with growth to $19.75 billion by 2033. Storage facilities and transport systems are also vital segments, expected to increase in value as global logistics demand rises.
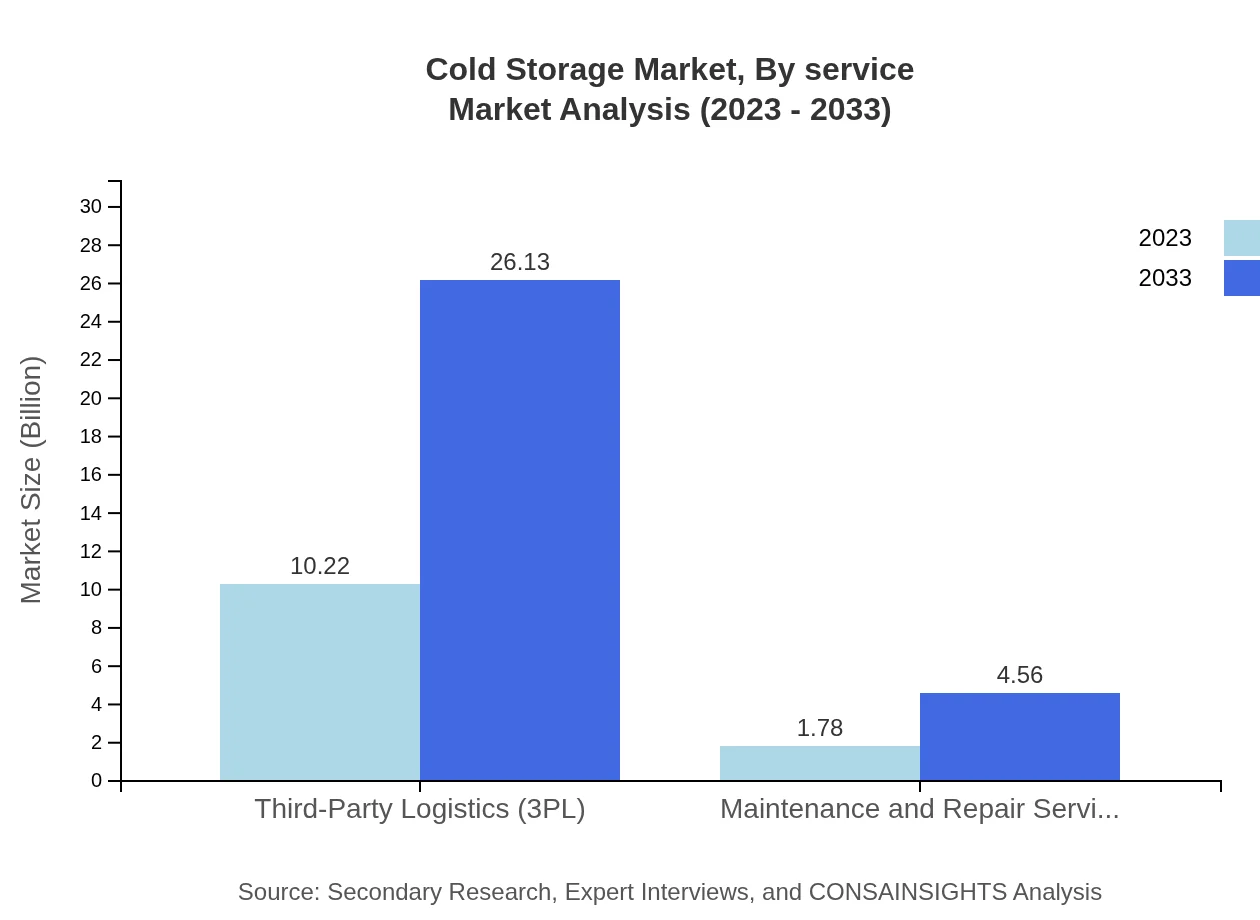
Cold Storage Market Analysis By Service
The services segment includes third-party logistics (3PL) which remains the largest service segment valued at $10.22 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $26.13 billion by 2033. Maintenance and repair services, although smaller at $1.78 billion in 2023, are also forecasted to grow substantially.
Cold Storage Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cold Storage Industry
Americold Realty Trust:
Americold Realty Trust is one of the largest operators of temperature-controlled warehouses, providing critical cold chain solutions across North America and beyond.Lineage Logistics:
Lineage Logistics operates a vast network of cold storage facilities and offers modern supply chain services, emphasizing technology and sustainability.XPO Logistics:
XPO Logistics is a prominent player in the logistics space, providing integrated cold storage solutions and transport services globally.SWIRE Properties:
SWIRE Properties specializes in the development of logistics facilities with advanced cold storage capabilities in Asia and Europe.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cold Storage?
The global cold storage market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 9.5% from 2023 to 2033. This growth is driven by increased demand for food safety and preservation, as well as technological advancements.
What are the key market players or companies in the cold Storage industry?
Key players in the cold storage market include major logistics companies and specialized storage solution providers. These entities are increasingly adopting advanced refrigeration technologies to meet the expanding needs of diverse sectors.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cold Storage industry?
The cold storage market is primarily driven by the rising demand for temperature-sensitive goods, increased globalization of food supply chains, and advancements in refrigeration technology, ensuring efficient storage and transportation.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cold Storage market?
The fastest-growing region in the cold storage market is North America, expected to expand from $4.18 billion in 2023 to $10.70 billion by 2033, fueled by significant investment in infrastructure and a rising demand for fresh products.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cold Storage industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the cold storage industry. This includes detailed analyses of market trends and regional growth opportunities to ensure actionable insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this cold Storage market research project?
Deliverables from the cold storage market research project will include comprehensive market analysis reports, growth forecasts, competitive landscape evaluations, and insights into regional trends and various segments of the market.
What are the market trends of cold Storage?
Current trends in the cold storage market include increasing investments in energy-efficient technologies, consolidation among service providers, and a focus on sustainability practices to improve supply chain resilience.