Compound Isomaltitol Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: compound-isomaltitol
Compound Isomaltitol Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Compound Isomaltitol market, highlighting insights on market size, growth trends, regional analysis, and competitive landscape from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
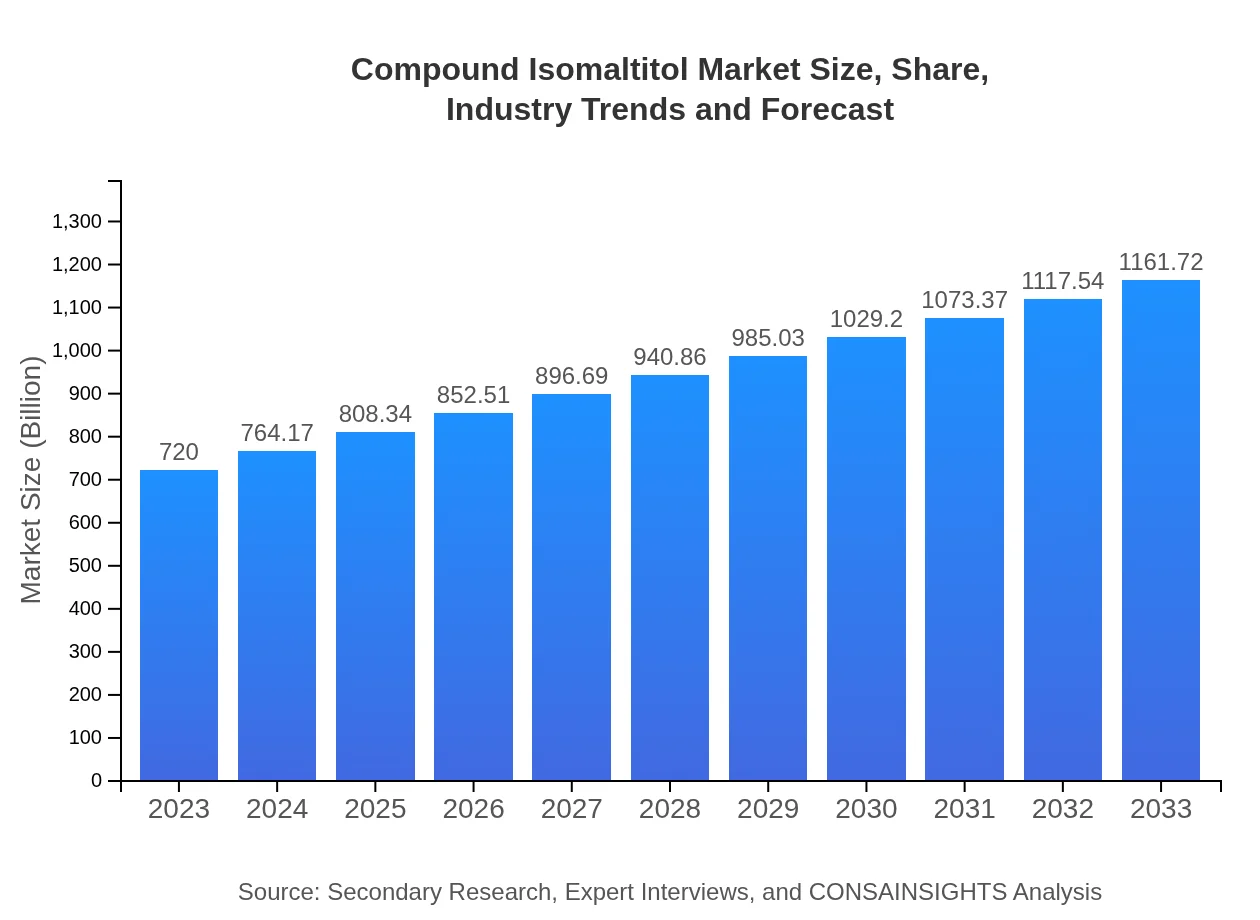
| 2023 Market Size | $720.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $1161.72 Million |
| Top Companies | Beneo, Mitsui Sugar Co., Ltd., Cargill, Incorporated, Eriksson Biochemicals |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Compound Isomaltitol Market Overview
Customize Compound Isomaltitol Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Compound Isomaltitol market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Compound Isomaltitol's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Compound Isomaltitol
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Compound Isomaltitol market in 2023?
Compound Isomaltitol Industry Analysis
Compound Isomaltitol Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Compound Isomaltitol Market Report:
Europe's market size for Compound Isomaltitol was valued at $221.47 million in 2023 and is expected to reach $357.34 million by 2033, with a CAGR of 5.0%. Notably, the food and beverage sector drives the majority of this growth, aligning with the increasing demand for low-calorie products.Asia Pacific Compound Isomaltitol Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Compound Isomaltitol market size was valued at $150.48 million in 2023 and is projected to grow to $242.80 million by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1%. The region's growth is driven by increasing demand from food and beverage industries, along with rising health awareness among consumers.North America Compound Isomaltitol Market Report:
The North America Compound Isomaltitol market is anticipated to expand from $240.05 million in 2023 to $387.32 million by 2033, demonstrating a robust CAGR of 5.0%. The region is poised for growth due to rising health consciousness, increased formulation innovation, and a robust food industry.South America Compound Isomaltitol Market Report:
South America is expected to see a modest growth in the Compound Isomaltitol market, with a size of $63.22 million in 2023 and a projected market size of $102 million by 2033, resulting in a CAGR of 5.0%. This growth will primarily stem from expanding pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors.Middle East & Africa Compound Isomaltitol Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market for Compound Isomaltitol is projected to grow from $44.78 million in 2023 to $72.26 million by 2033. This growth, with a CAGR of 5.0%, is bolstered by rising demand for health-focused products and investment in the cosmetics industry.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Analysis By Application
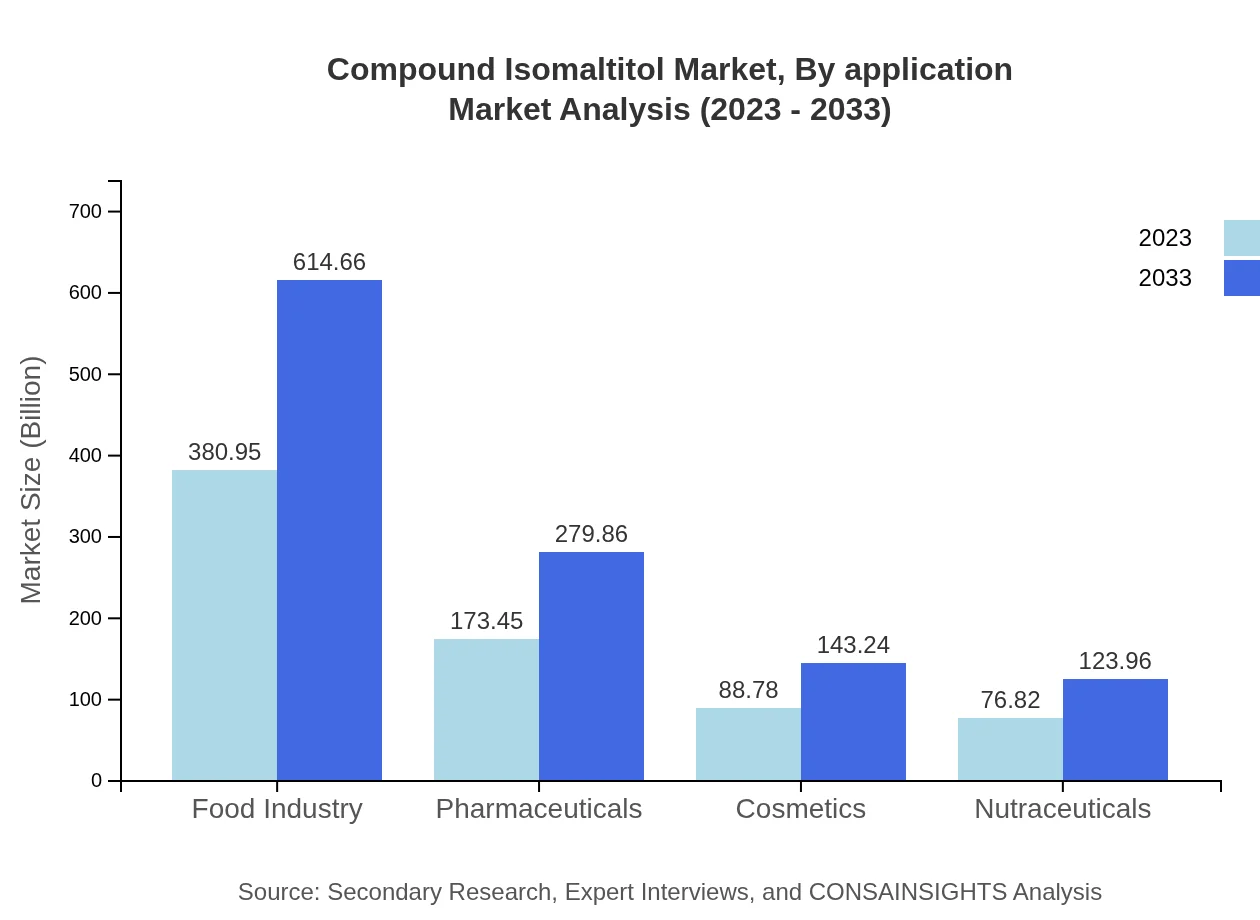
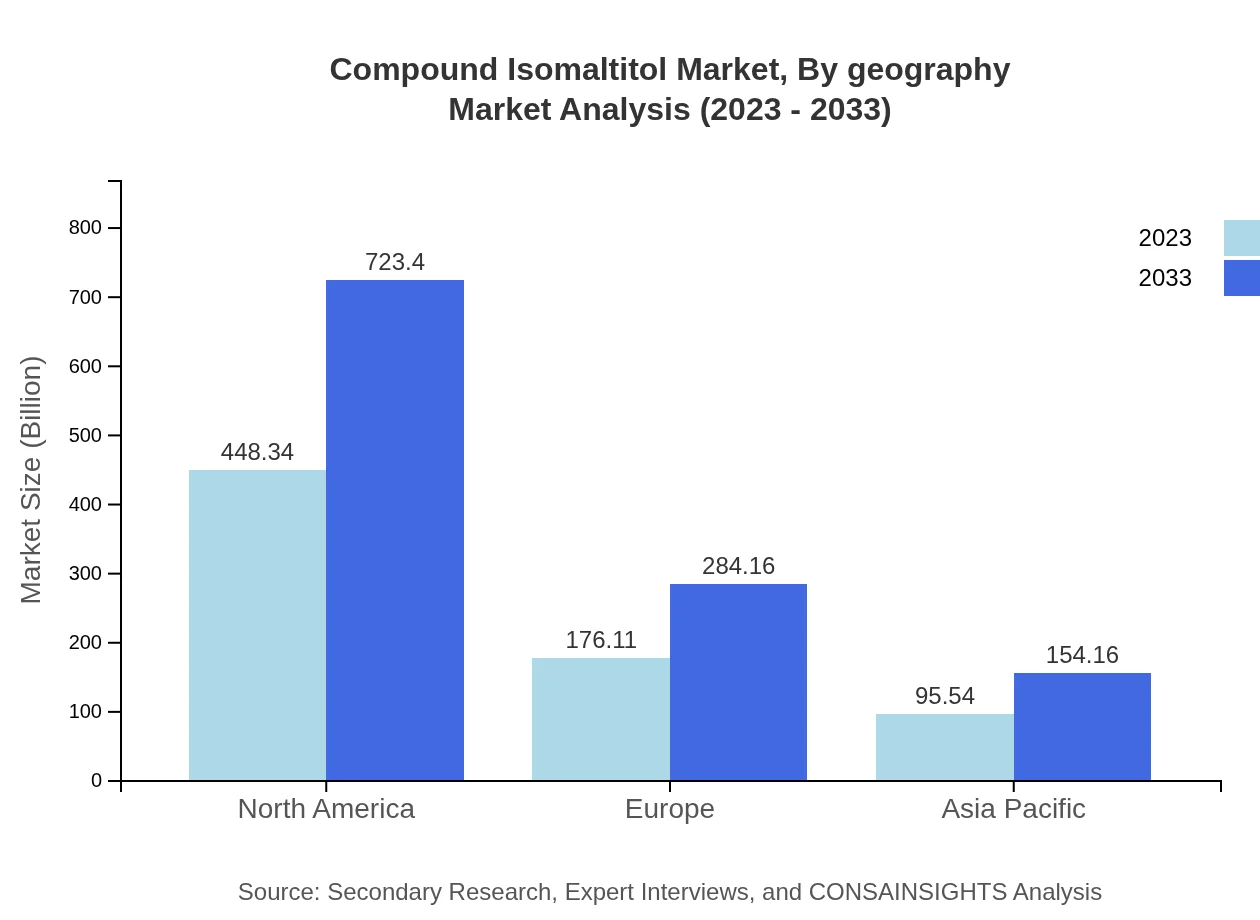
In 2023, food manufacturers accounted for the largest segment, with a market size of $448.34 million, set to grow to $723.40 million by 2033, maintaining a consistent market share of 62.27% throughout the period. The pharmaceutical segment also shows significant growth, increasing from $176.11 million in 2023 to $284.16 million by 2033, holding a steady share of 24.46%. Cosmetic manufacturers comprise a smaller segment but are vital, growing from $95.54 million to $154.16 million, maintaining a share of 13.27%.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Analysis By Formulation Type
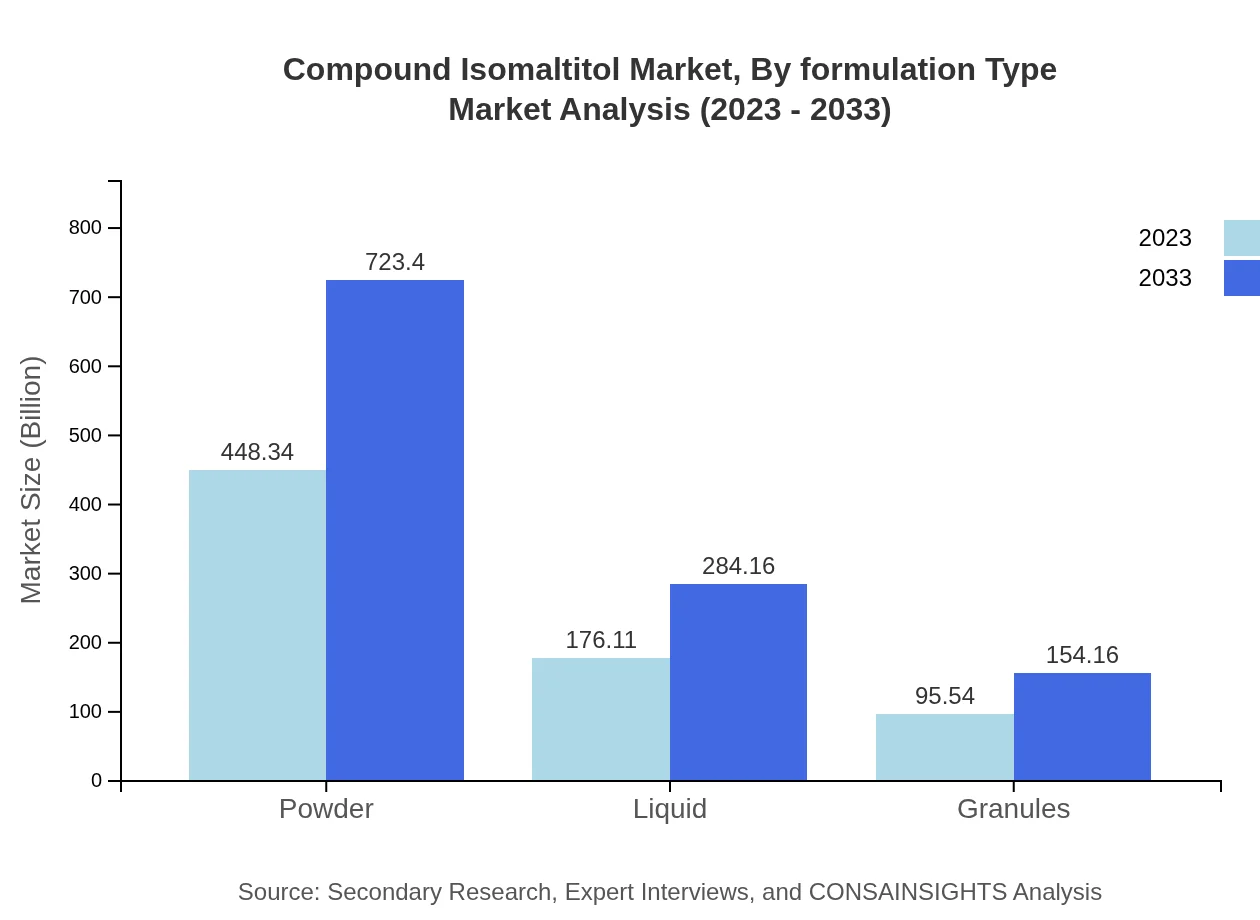
The powder formulation remains the most popular, growing from $448.34 million in 2023 to $723.40 million by 2033, representing a share of 62.27%. Liquid formulations, although smaller, show growth from $176.11 million to $284.16 million, capturing a 24.46% market share, while granules represent 13.27%, appreciating from $95.54 million to $154.16 million.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Analysis By End User
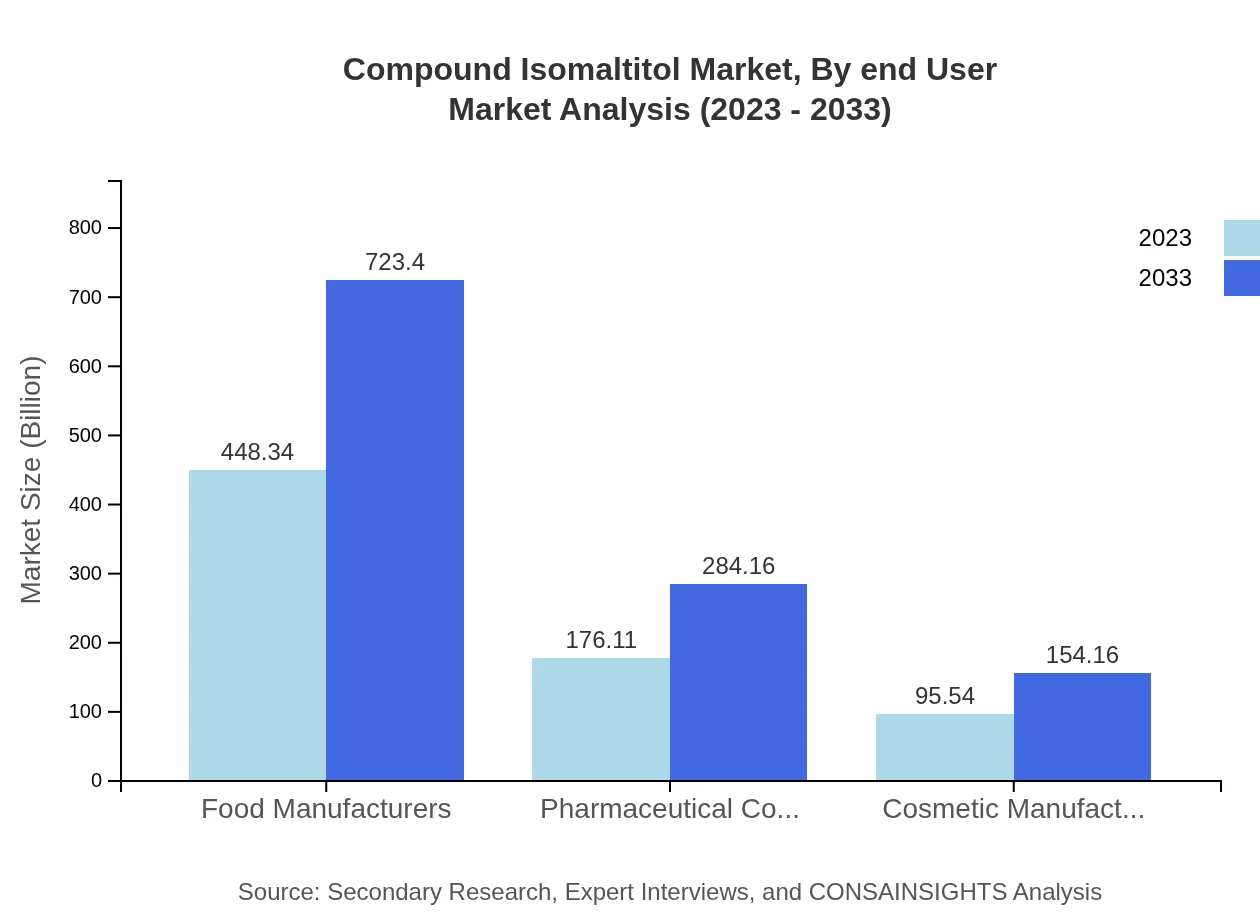
End-user industries such as food and beverage take center stage, with the overall market valued at approximately $380.95 million in 2023, forecasted to touch $614.66 million by 2033, representing 52.91% share. The pharmaceutical segment is also notable, valued at $173.45 million growing to $279.86 million through the decade, holding 24.09%, while cosmetic applications contribute 12.33%. In addition, the nutraceutical sector emerges with growth from $76.82 million to $123.96 million at 10.67%.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Analysis By Geography
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market, with North America's market projected to grow significantly. In contrast, Asia Pacific follows with robust growth predictions. South America has potential but lower market values. The Middle East and Africa present emerging opportunities, primarily driven by health-oriented technologies in formulation practices.
Compound Isomaltitol Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Compound Isomaltitol Industry
Beneo:
Beneo is a leading manufacturer specializing in functional ingredients and dietary fibers, offering premium-quality Isomaltitol products for the food and pharmaceutical industries.Mitsui Sugar Co., Ltd.:
Mitsui Sugar Co., Ltd. focuses on high-value-added products, contributing to the Compound Isomaltitol market by providing innovative applications and R&D support for dietary manufacturing.Cargill, Incorporated:
Cargill is a global leader in nutrition and food ingredients, actively investing in advanced formulations and organic growth in the Isomaltitol market.Eriksson Biochemicals:
Eriksson Biochemicals specializes in sweeteners and sugar-replacement solutions, playing a significant role in the distribution of Isomaltitol across multiple sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of compound Isomaltitol?
The global compound isomaltitol market is projected to reach approximately $720 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023, reflecting an increasing demand in various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in this compound Isomaltitol industry?
Key players in the compound isomaltitol industry include leading companies involved in food manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, although specific names are not enumerated.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the compound Isomaltitol industry?
Primary growth factors include rising health consciousness, increased demand for sugar alternatives, and the expanding application of isomaltitol in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the compound Isomaltitol?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for compound isomaltitol, with growth projected from $150.48 million in 2023 to $242.80 million by 2033, driven by demand in food and health sectors.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the compound Isomaltitol industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs within the compound isomaltitol industry, covering detailed insights and analyses.
What deliverables can I expect from this compound Isomaltitol market research project?
Expected deliverables from the compound isomaltitol market research include comprehensive reports, trend analyses, market data segmentation, and strategic recommendations.
What are the market trends of compound Isomaltitol?
Current market trends include a shift towards low-calorie sweeteners, increasing applications in nutraceuticals, and rising consumer interest in sustainable and healthy food ingredients.