Connected Ship Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: connected-ship
Connected Ship Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Connected Ship market's dynamics, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include market size, regional analyses, technology trends, and leading companies within the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
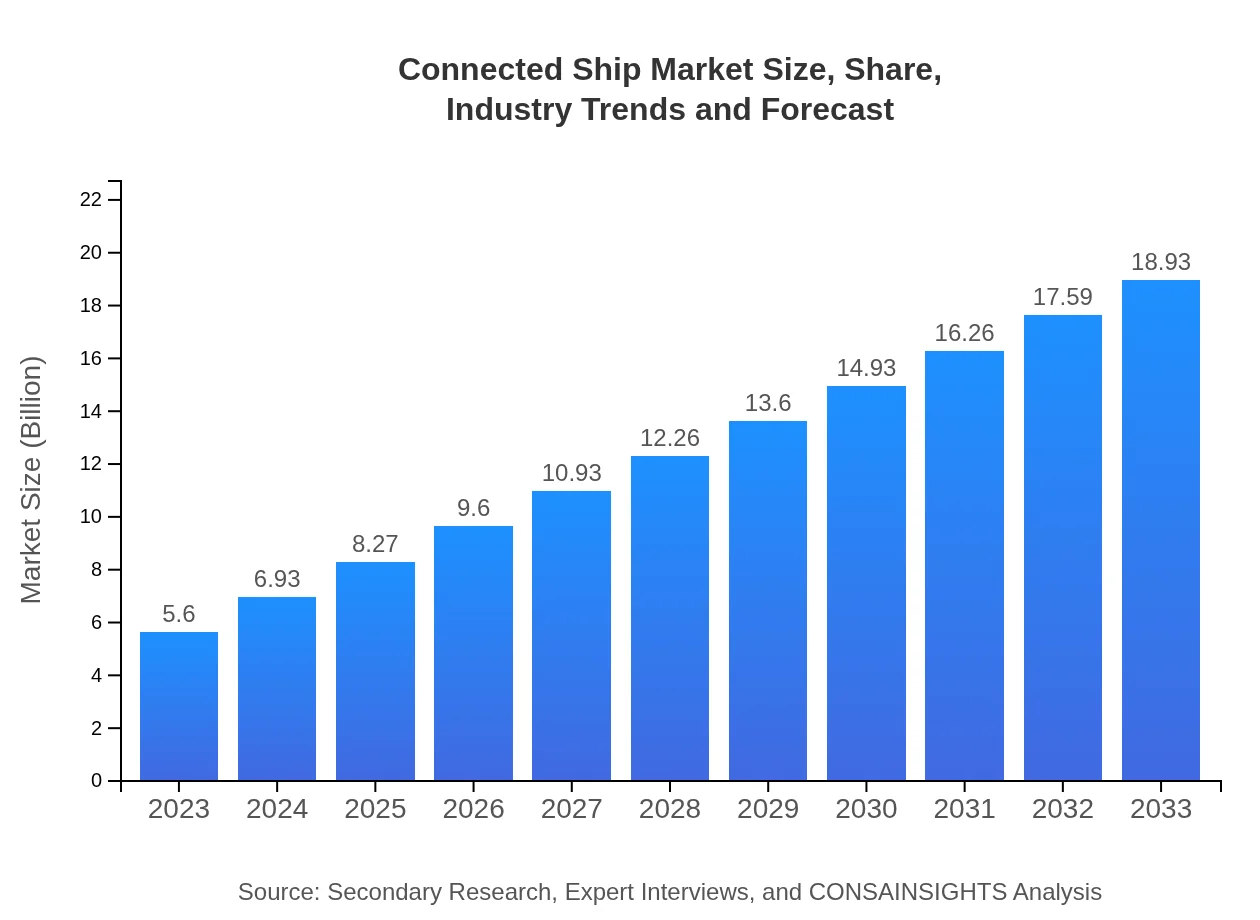
| 2023 Market Size | $5.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.93 Billion |
| Top Companies | ABB Ltd., Kongsberg Gruppen, Siemens AG, IBM Corporation, Wärtsilä Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Connected Ship Market Overview
Customize Connected Ship Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Connected Ship market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Connected Ship's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Connected Ship
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Connected Ship market in 2023?
Connected Ship Industry Analysis
Connected Ship Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
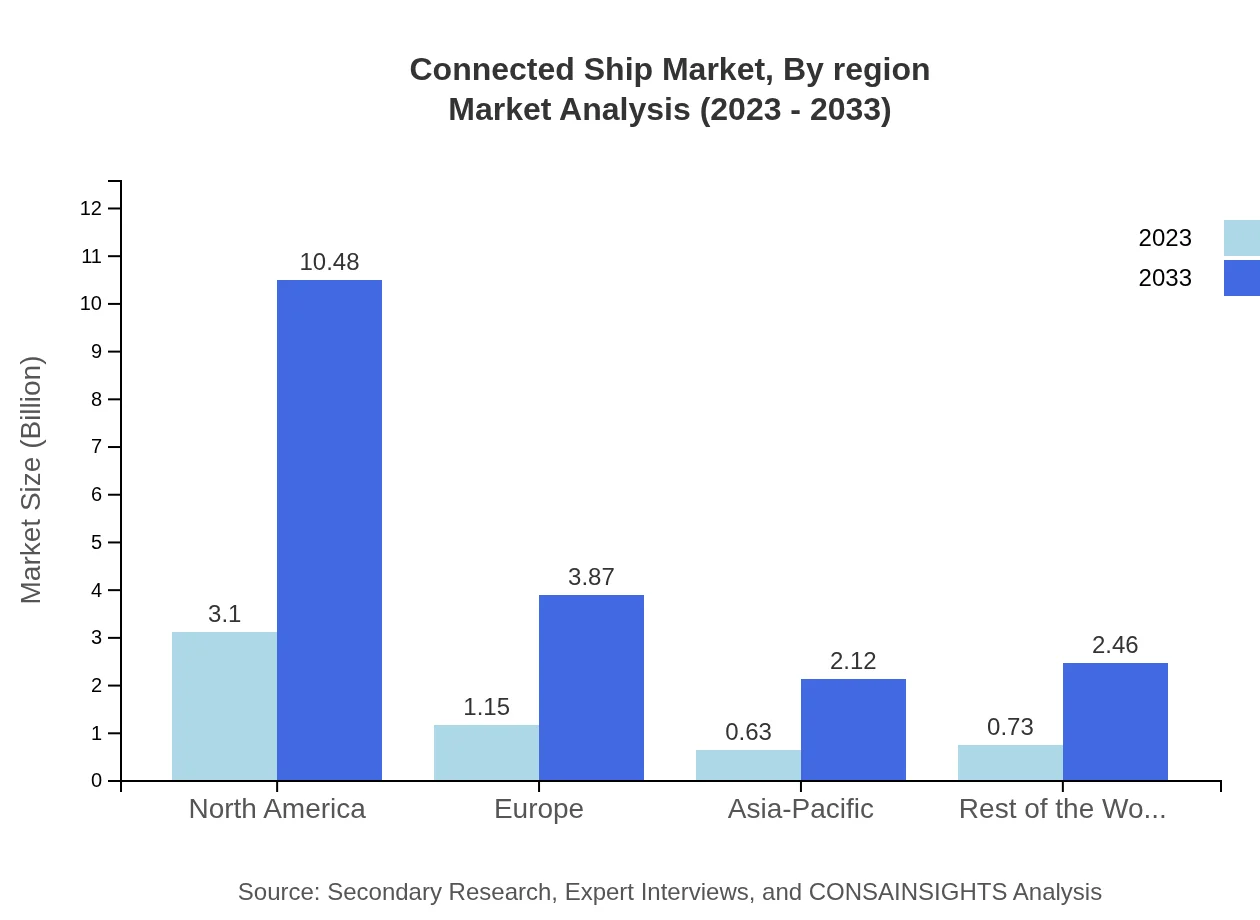
Connected Ship Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Connected Ship Market Report:
Europe's Connected Ship market is forecasted to grow from $1.92 billion in 2023 to $6.50 billion in 2033. The emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and the growth of smart shipping initiatives are pivotal to this growth.Asia Pacific Connected Ship Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing significant growth, with a market size projected to reach $3.12 billion by 2033, up from $0.92 billion in 2023. Factors contributing to this growth include rapid technological adoption, a rise in maritime commerce, and increasing investments in port infrastructure.North America Connected Ship Market Report:
North America stands out with a robust market size projected at $6.69 billion in 2033, up from $1.98 billion in 2023. The region's advancement in maritime technologies and increasing regulatory frameworks supporting digital transformation are contributing factors.South America Connected Ship Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to grow from $0.09 billion in 2023 to $0.29 billion in 2033. Growing trade activities and the focus on enhancing supply chain efficiency in the maritime sector are key drivers of this growth.Middle East & Africa Connected Ship Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is expected to increase from $0.69 billion in 2023 to $2.33 billion in 2033, driven by infrastructure development and the need for enhanced maritime security.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Connected Ship Market Analysis By Technology
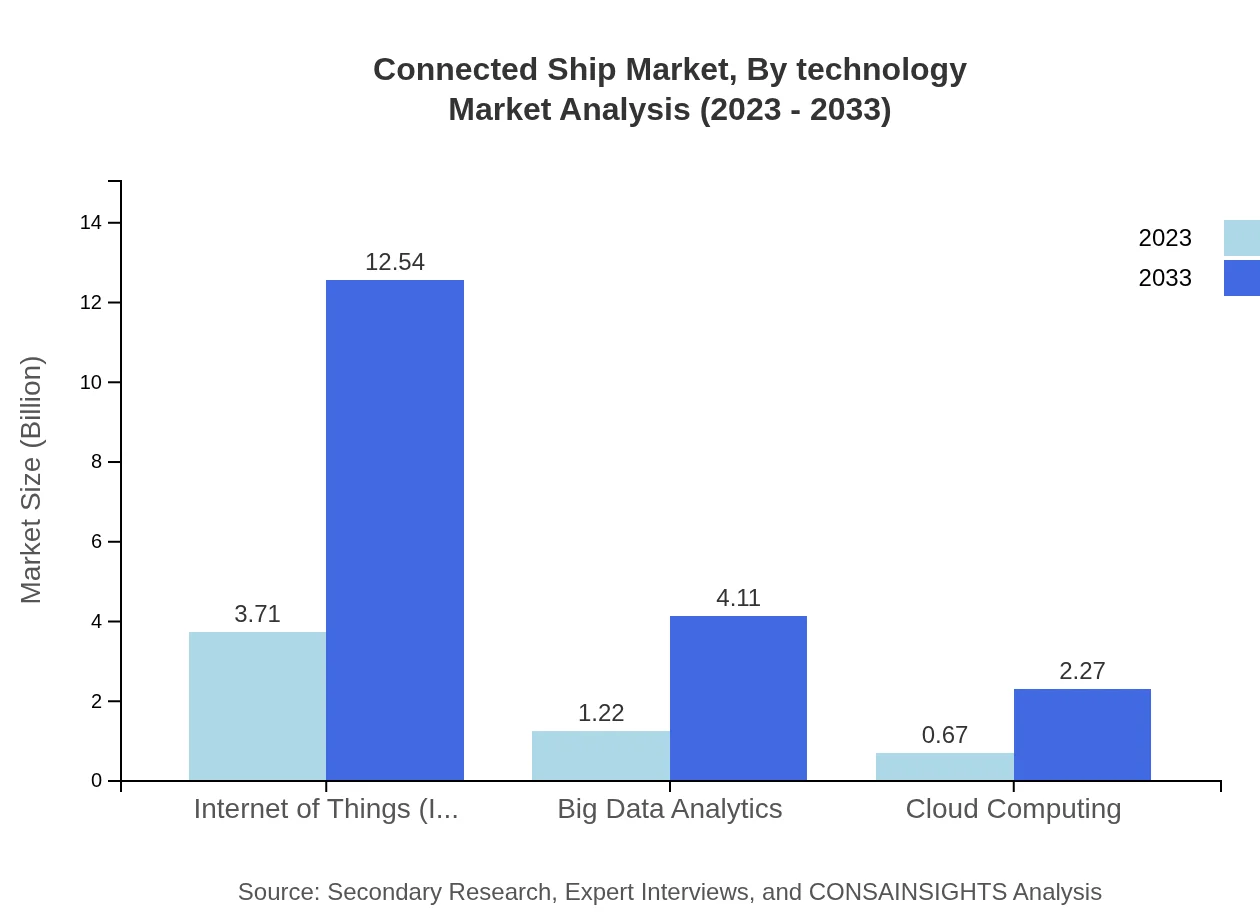
The market is prominently driven by advanced technologies such as IoT, which is expected to dominate the sector with a market size of $3.71 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of 66.26%. Big Data Analytics and cloud computing are also significant with projected sizes of $1.22 billion and $0.67 billion, respectively by 2033.
Connected Ship Market Analysis By Application
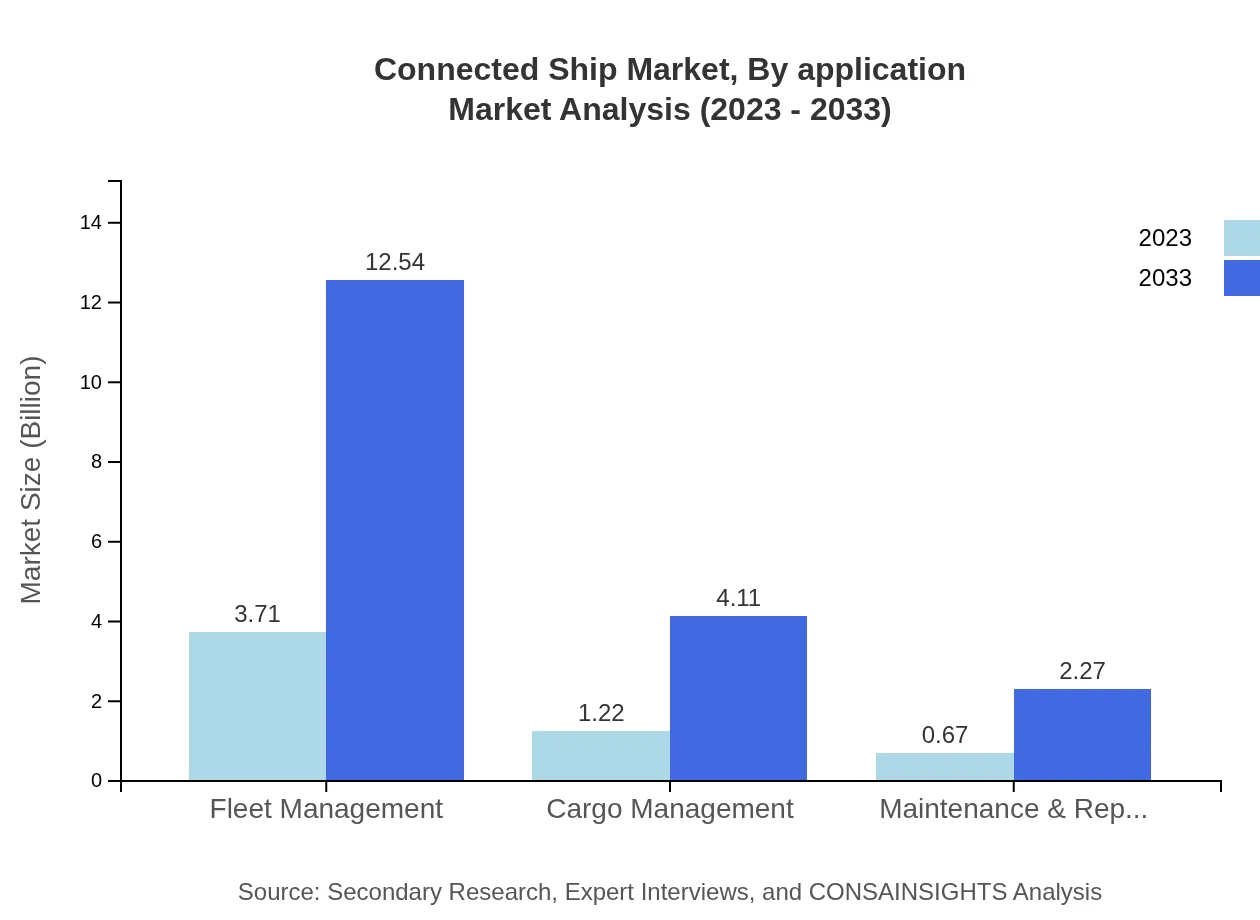
Applications such as fleet management and cargo management represent significant market segments. Fleet management specifically stands to gain a market size of $12.54 billion by 2033, maintaining its status as a pivotal application for shipping operators.
Connected Ship Market Analysis By End User
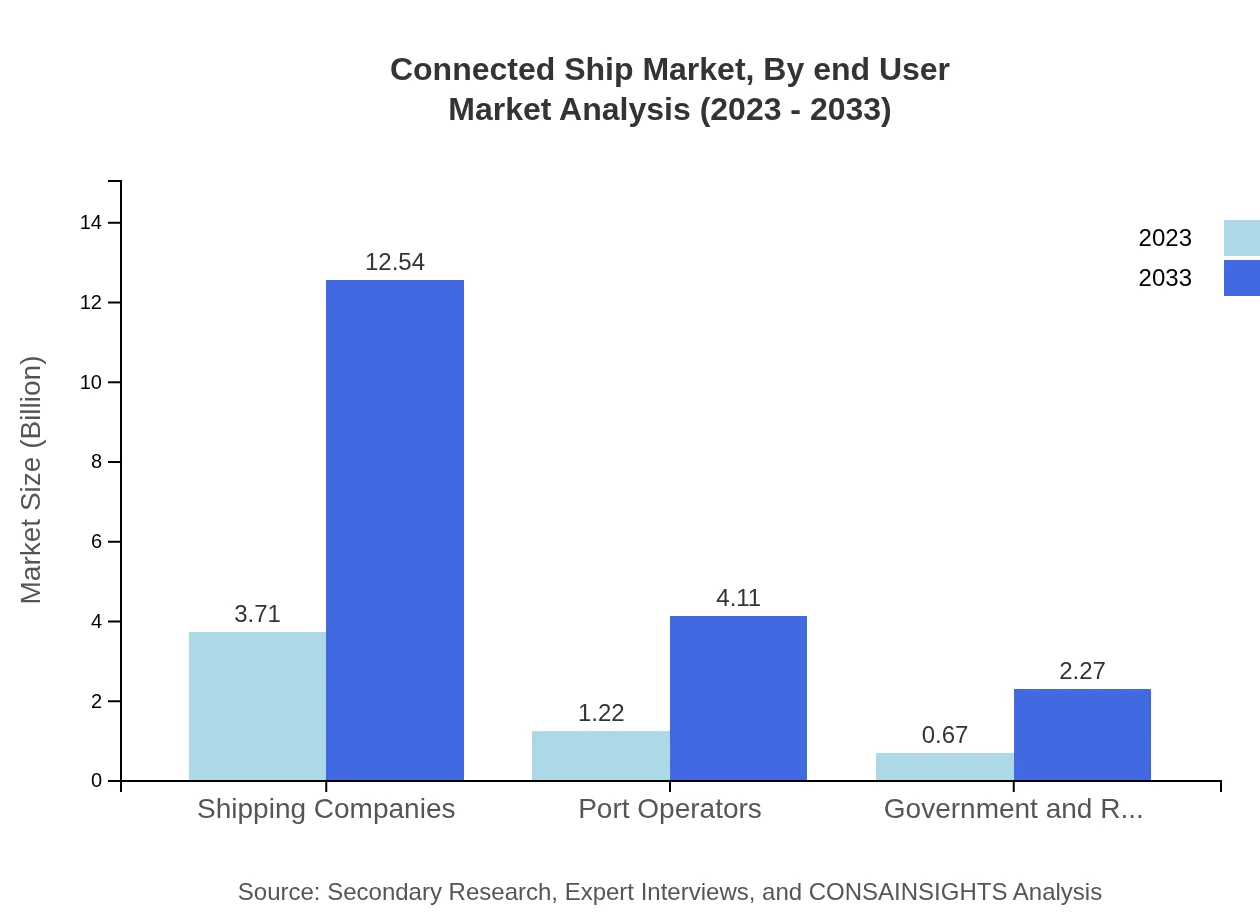
Shipping companies are major stakeholders, projected to have a market size of $12.54 billion in 2033, emphasizing their role in the adoption of connected ship technologies. Port operators also play a crucial role, with an expected market size of $4.11 billion.
Connected Ship Market Analysis By Region
Regional analysis shows North America leads with a 55.38% share, followed by Europe at 20.45%. Asia-Pacific holds an 11.18% share, while the Rest of the World accounts for about 12.99%.
Connected Ship Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Connected Ship Industry
ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a leading global technology company involved in the provision of power and automation solutions for the marine industry, including connected solutions.Kongsberg Gruppen:
Kongsberg is a well-established tech group that provides maritime automation technologies and solutions geared towards enhancing vessel connectivity.Siemens AG:
Siemens is actively involved in developing integrated digital solutions for the maritime industry, enhancing operational efficiency through connected ship technologies.IBM Corporation:
IBM provides innovative solutions using their cloud computing and data analytics capabilities to transform the shipping industry into a more connected ecosystem.Wärtsilä Corporation:
Wärtsilä focuses on sustainable technology, offering connected solutions that improve performance and operational efficiency in marine operations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of connected Ship?
The connected-ship market is valued at $5.6 billion in 2023, with a strong growth forecast of 12.4% CAGR, anticipated to significantly increase in the coming years.
What are the key market players or companies in this connected Ship industry?
The primary players in the connected-ship market include shipping companies, port operators, and technology firms specializing in IoT and big data solutions, driving innovation and collaboration within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the connected Ship industry?
Key growth drivers include advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technology, demands for operational efficiency, improved fleet management, and regulatory pressures promoting safer, more efficient shipping practices.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the connected Ship?
Europe is the fastest-growing region in the connected-ship market, expanding from $1.92 billion in 2023 to $6.50 billion by 2033, showcasing a robust annual growth trajectory.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the connected Ship industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the connected-ship industry, ensuring clients receive relevant insights aligned with their specific needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this connected Ship market research project?
Clients can expect detailed reports featuring market size, growth projections, segment analysis, competitive landscape information, and actionable recommendations.
What are the market trends of connected Ship?
Current trends in the connected-ship industry include increased adoption of advanced analytics, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and growing investments in sustainability technologies.
What is the projected market size of key segments in connected Ship?
By 2033, major segments like fleet management and IoT are projected to grow to $12.54 billion, showcasing significant investment and stakeholder interest.