Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: covid19-impact-on-5g-infrastructure
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This detailed report examines the significant effects of COVID-19 on 5G infrastructure markets worldwide, providing insights, data analysis, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
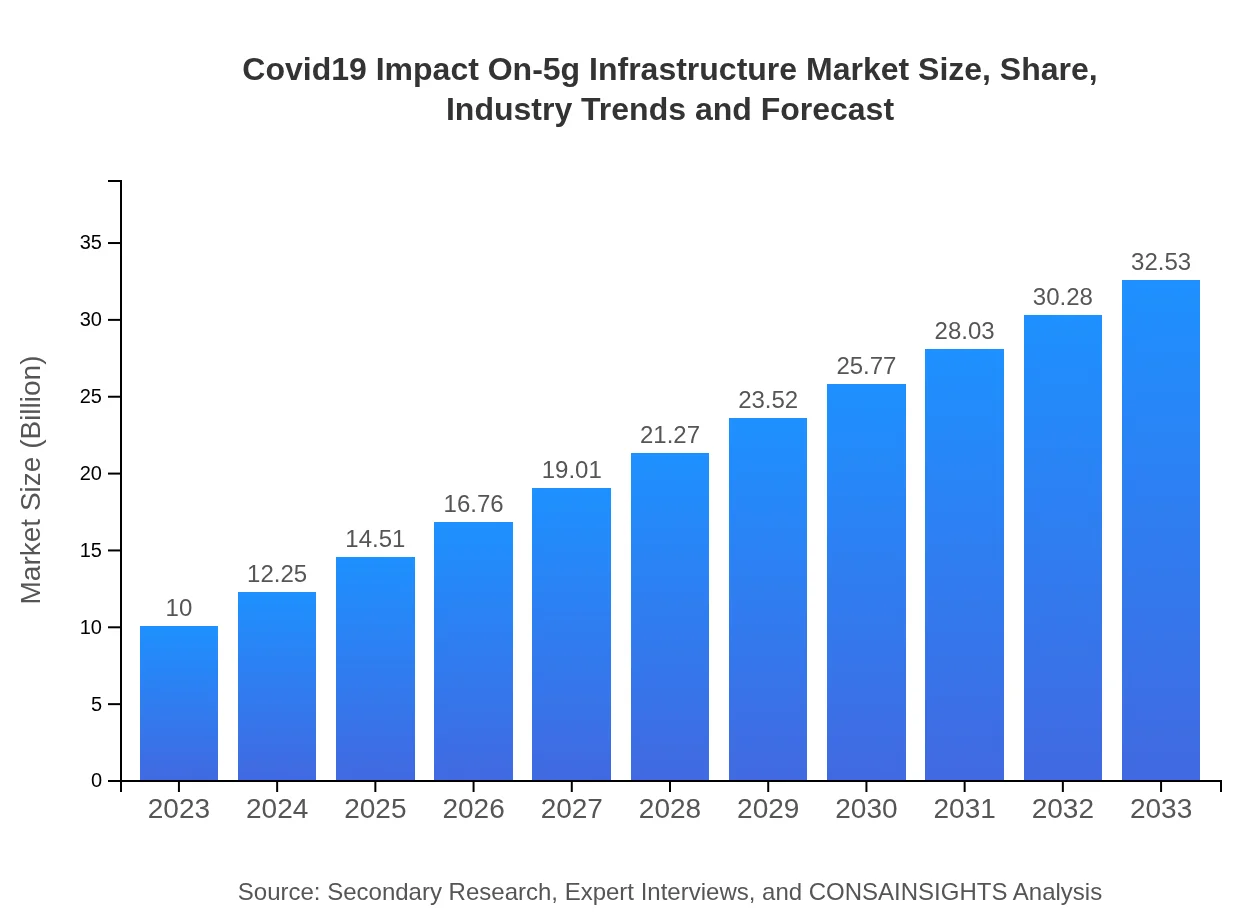
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.53 Billion |
| Top Companies | Ericsson , Nokia , Qualcomm , Huawei , Cisco Systems |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Overview
Customize Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure market in 2023?
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Industry Analysis
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report:
Europe's market is projected to increase from $2.47 billion in 2023 to $8.02 billion by 2033. COVID-19 has accelerated the rollout of 5G across European nations, with a strong emphasis on regulatory reforms and public-private partnerships aimed at achieving digital resilience in the post-pandemic era.Asia Pacific Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing significant growth in the 5G infrastructure market, projected to increase from $1.92 billion in 2023 to approximately $6.25 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by major investments in broadband expansion, government initiatives, and a high consumer demand for smart devices. Countries like China, India, and Japan are leading the charge, focusing on comprehensive digital transformation strategies.North America Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report:
North America stands as a robust market for Covid19 Impact On-5G Infrastructure, with anticipated growth from $3.74 billion in 2023 to $12.18 billion by 2033. The proliferation of 5G networks is essential for enhancing operational efficiency across industries, and technology giants are heavily investing in expanding their 5G capabilities to support emerging applications.South America Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report:
South America’s 5G infrastructure market is expected to grow from $0.53 billion in 2023 to $1.71 billion by 2033. The pandemic has highlighted the necessity for improved connectivity, and governments are increasingly supporting infrastructure development projects. The adoption of 5G is seen as a vital component for economic recovery in the region.Middle East & Africa Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are expected to see their 5G infrastructure market grow from $1.34 billion in 2023 to approximately $4.37 billion by 2033. Countries in this region are leveraging technology to enhance service delivery, and initiatives are underway to improve digital infrastructure as part of broader economic development strategies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
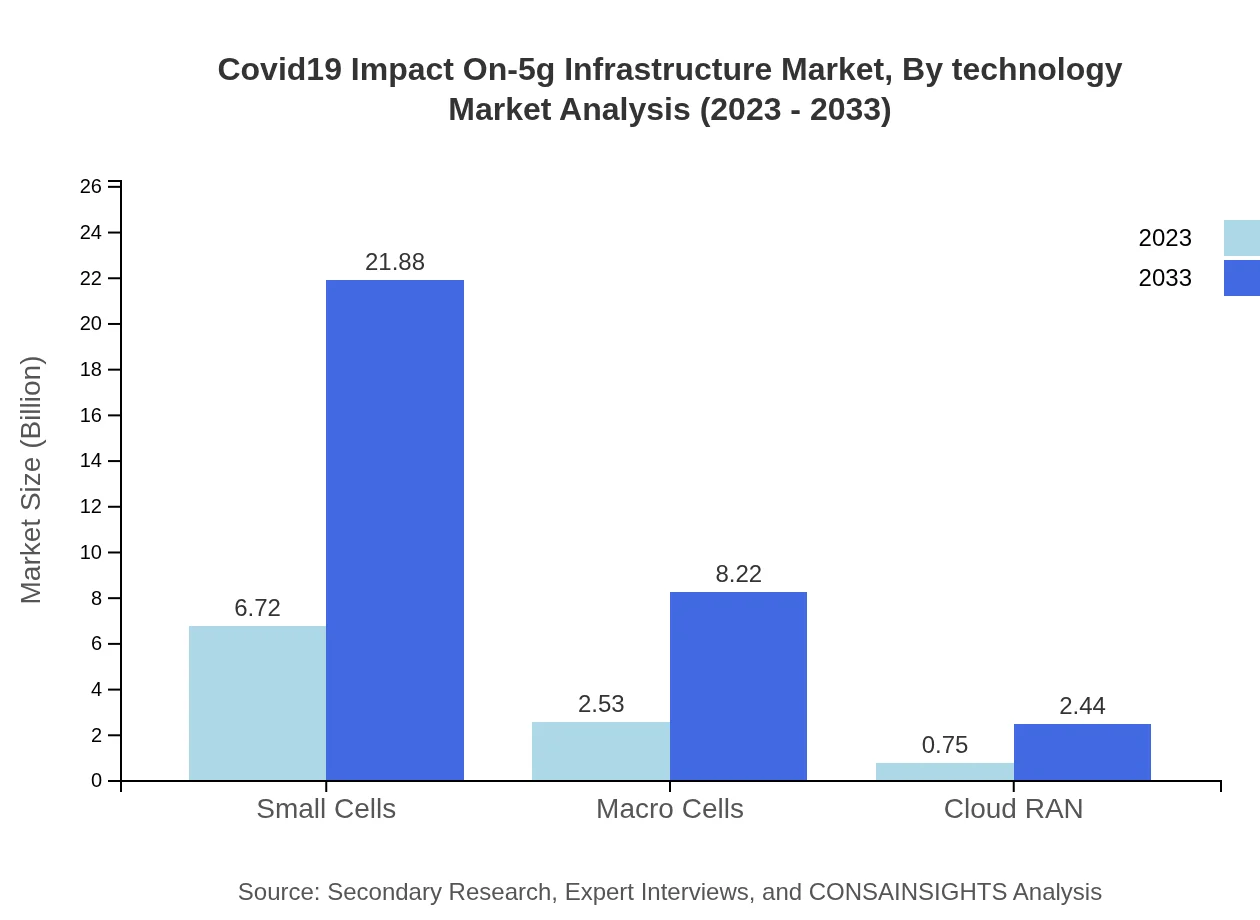
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Technology
Network Servers represent a significant segment in the technology category, increasing from $6.72 billion in 2023 to $21.88 billion by 2033, accounting for 67.25% share. Network Automation Tools are also growing significantly, with expected expansion from $2.53 billion to $8.22 billion, maintaining a 25.26% market share. Infrastructure as a Service is projected to rise from $0.75 billion to $2.44 billion, signifying a growing trend towards cloud-based solutions.
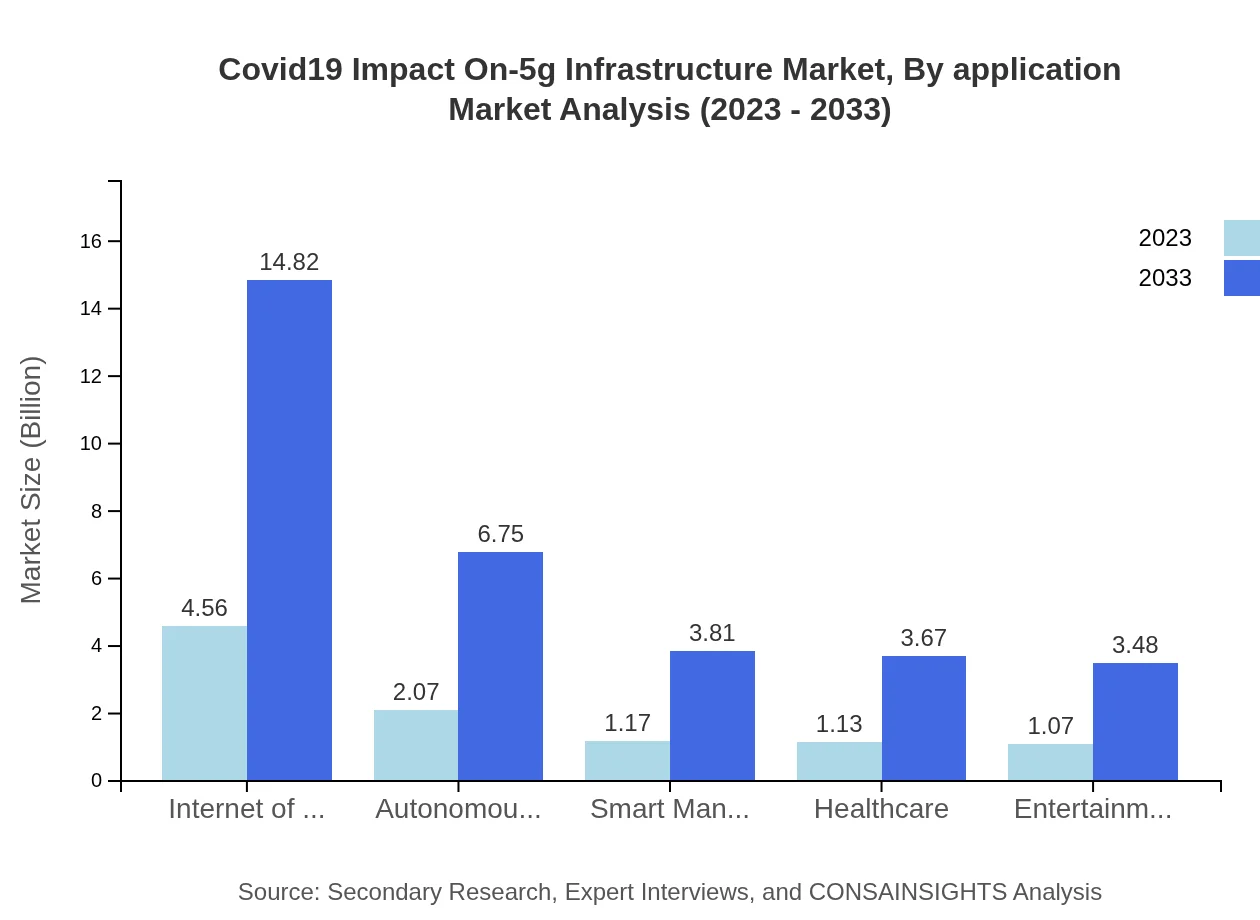
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Application
The Internet of Things (IoT) segment is pivotal, scaling from $4.56 billion in 2023 to $14.82 billion by 2033, maintaining a substantial 45.57% market share. Other notable applications include healthcare which sees growth from $1.13 billion to $3.67 billion and smart manufacturing expected to rise from $1.17 billion to $3.81 billion.
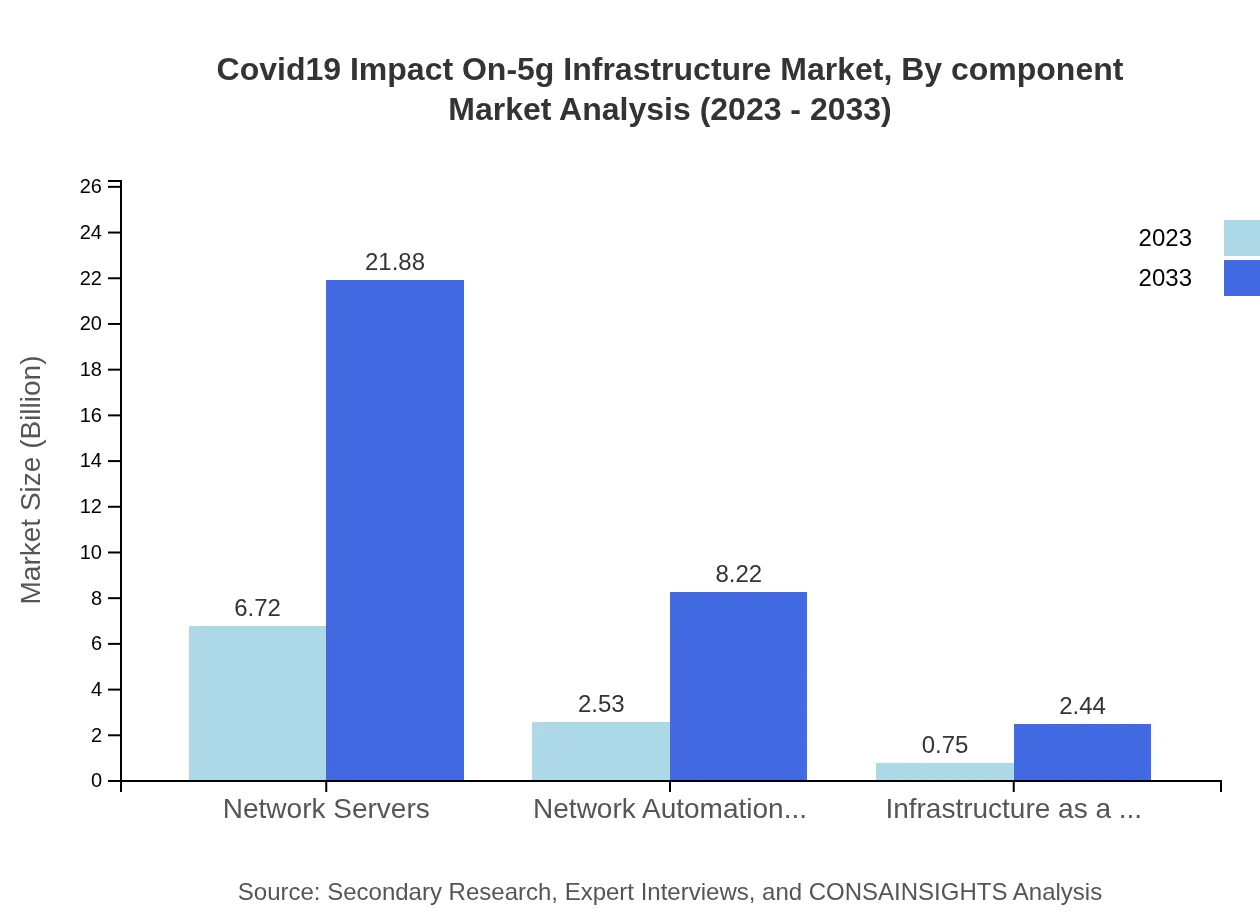
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Component
In terms of components, hardware remains the largest segment, expected to grow significantly, while software solutions, particularly in network management and automation, are projected to gain traction over the forecast period.
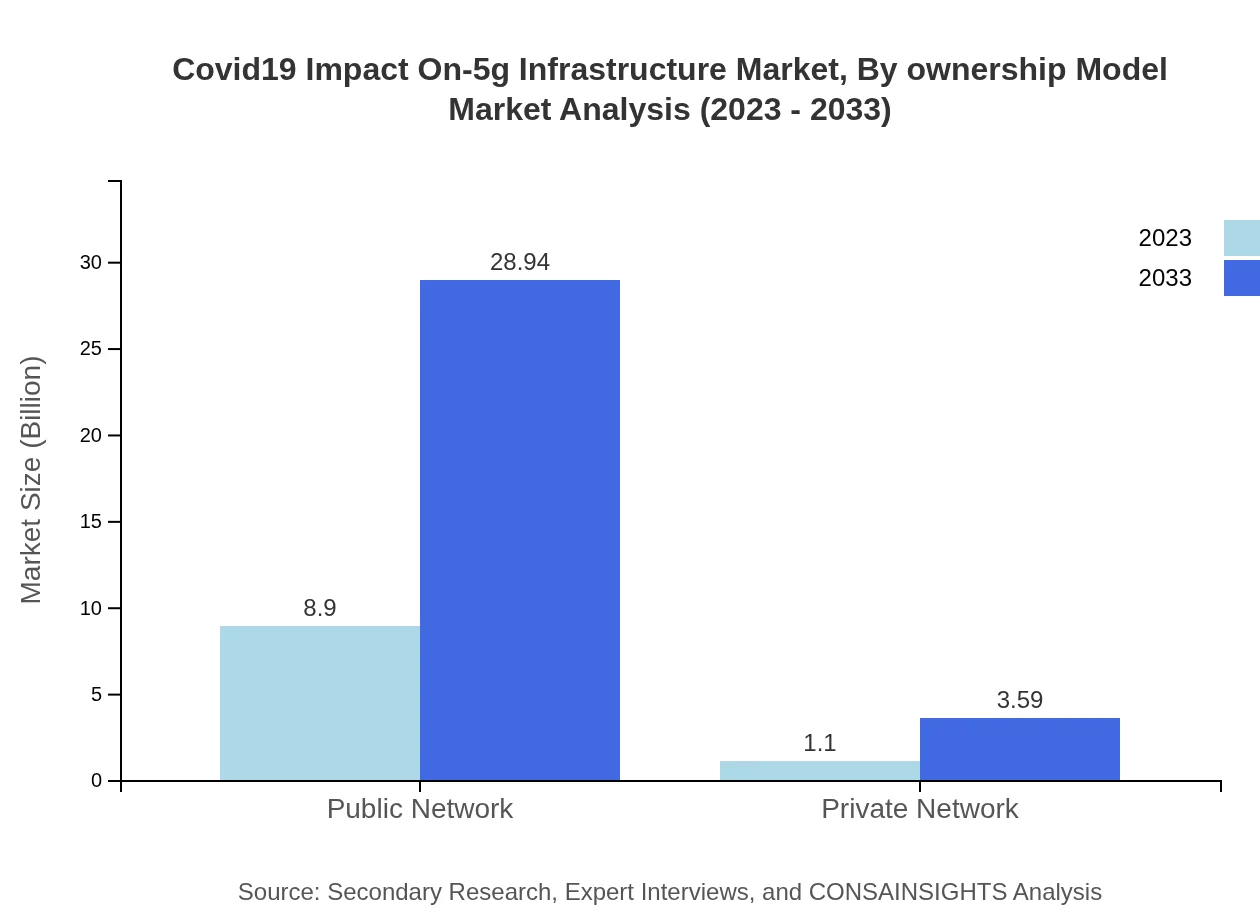
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Ownership Model
Public networks dominate the market, with growth expected from $8.90 billion in 2023 to $28.94 billion in 2033, representing an 88.97% market share. Private networks are also gaining ground, particularly among businesses focusing on security and data privacy, rising from $1.10 billion to $3.59 billion.
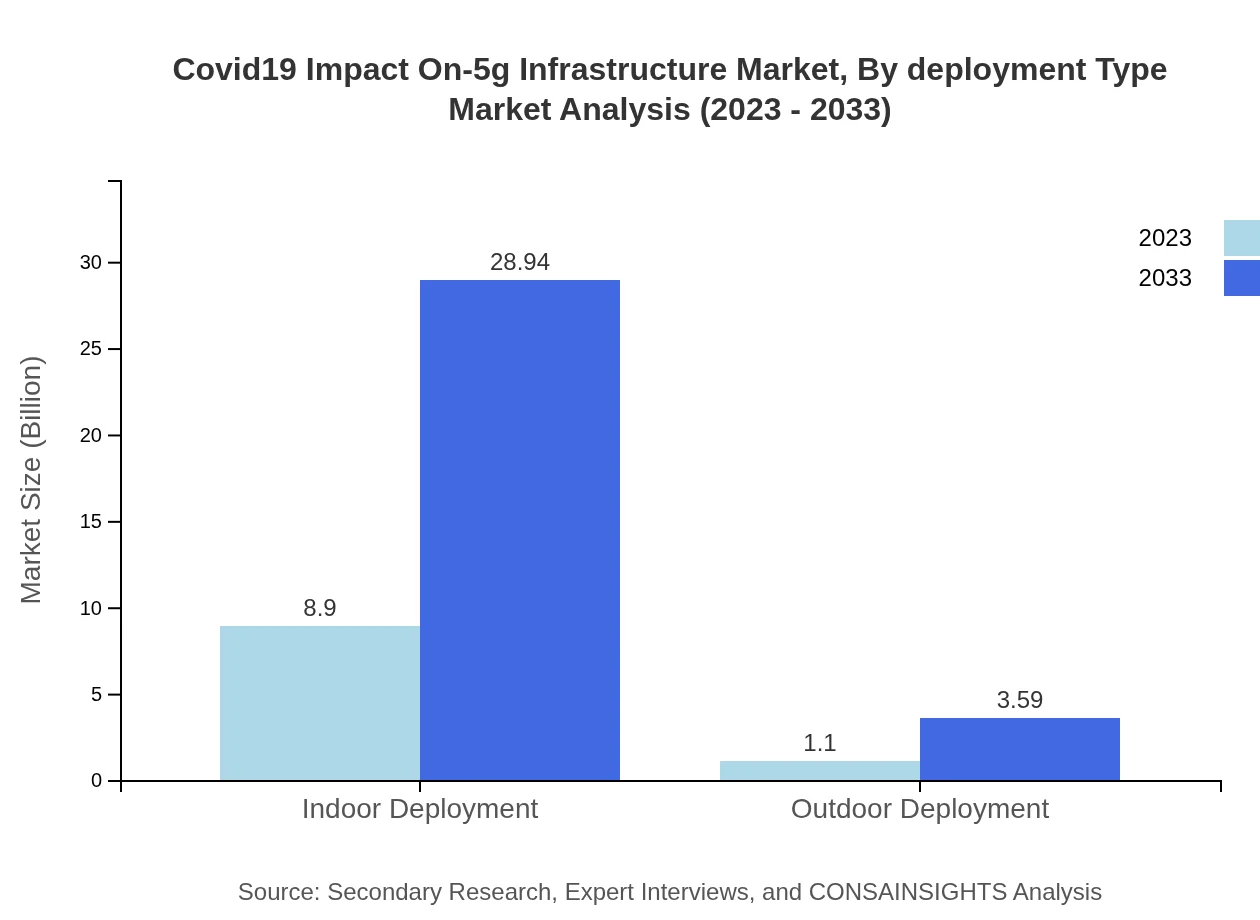
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Indoor deployment leads the market with significant investments leading to its growth from $8.90 billion to $28.94 billion. Outdoor deployments are essential for expanding coverage and are expected to grow from $1.10 billion to $3.59 billion, noting the strategic deployment of 5G towers.
Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Covid19 Impact On-5g Infrastructure Industry
Ericsson :
A prominent global provider of telecommunications equipment and services, Ericsson is leading the way in 5G innovation with comprehensive infrastructure solutions.Nokia :
Nokia has established a strong foothold in the 5G market, specializing in network infrastructure and paving the path for enhanced connectivity solutions worldwide.Qualcomm :
Renowned for its semiconductor and telecommunications equipment, Qualcomm plays a critical role in enabling 5G devices and technologies.Huawei :
A leading global technology company, Huawei has played a vital role in the development and deployment of 5G infrastructure, seeking to enhance connectivity globally.Cisco Systems:
Cisco provides networking solutions that support the 5G ecosystem, focusing on software-defined networking and security solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure?
The market size for the COVID-19 impact on 5G infrastructure is projected to reach 10 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12%. This growth demonstrates the increasing importance of 5G in the post-pandemic world.
What are the key market players or companies in the COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure industry?
Key players in the COVID-19 impact on the 5G infrastructure industry include major telecommunications companies, infrastructure providers, and technology developers. These companies are essential for deploying and enhancing 5G technology to meet future demands.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure industry?
The primary growth drivers in this industry include increased demand for high-speed internet, the rise of remote work, and heightened usage of IoT devices. During the pandemic, the need for robust 5G networks became crucial for various sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure?
The fastest-growing region for COVID-19 impact on 5G infrastructure is North America, projected to grow from 3.74 billion in 2023 to 12.18 billion by 2033. This region leads in 5G technology adoption and infrastructure development.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports for the COVID-19 impact on 5G infrastructure. Clients can receive tailored insights specific to their strategic needs and market requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure market research project?
Deliverables from the market research project on COVID-19 impact on 5G infrastructure include detailed market analysis, growth projections, segment data, and competitive landscape assessments to inform strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of COVID-19 Impact on 5G Infrastructure?
Current market trends in COVID-19 impact on 5G infrastructure include increased investment in network automation tools and small cells, with segments like IoT and indoor deployment experiencing significant growth as demand rises.