Current Transducer Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: current-transducer
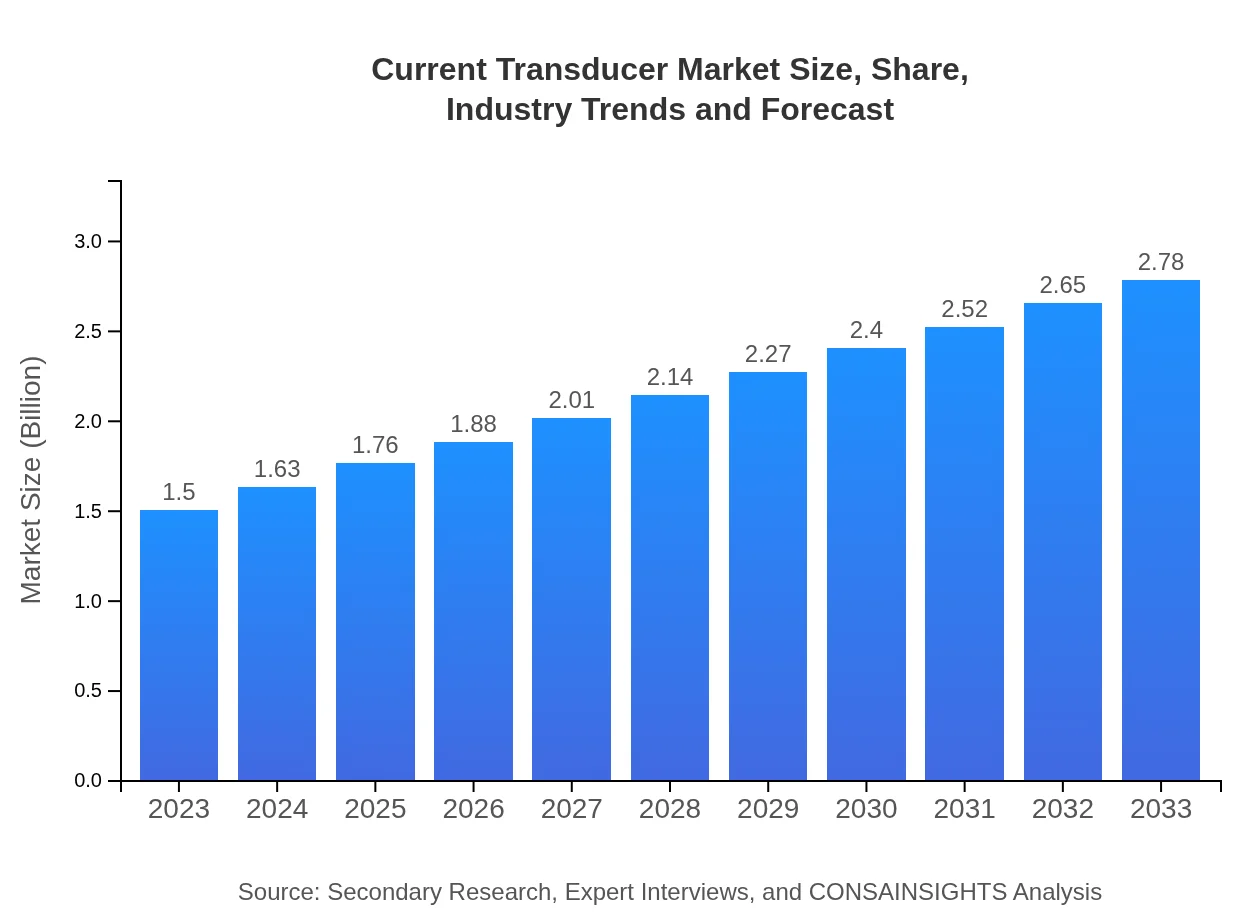
Current Transducer Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the Current Transducer market, providing insights on market size, segments, regional analysis, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | Texas Instruments, Honeywell International Inc., Infineon Technologies AG, Analog Devices, Inc., STMicroelectronics |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Current Transducer Market Overview
Customize Current Transducer Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Current Transducer market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Current Transducer's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Current Transducer
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Current Transducer market in 2023?
Current Transducer Industry Analysis
Current Transducer Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Current Transducer Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Current Transducer Market Report:
Europe's Current Transducer market recorded a size of $0.43 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $0.79 billion by 2033. Stricter regulations on energy efficiency and increased adoption of smart technologies boost demand in this region.Asia Pacific Current Transducer Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region held a market size of $0.30 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $0.55 billion by 2033. The rapid industrialization in countries like China and India boosts demand for current transducers, particularly in manufacturing and transportation sectors.North America Current Transducer Market Report:
North America's market reached $0.50 billion in 2023, anticipated to escalate to $0.93 billion by 2033. The region's focus on renewable energy and electric vehicles significantly contributes to this growth.South America Current Transducer Market Report:
In South America, the market was valued at $0.07 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $0.13 billion by 2033. Growth is driven by advancements in energy solutions and increased infrastructural investments.Middle East & Africa Current Transducer Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa current transducer market had a valuation of $0.20 billion in 2023, likely to expand to $0.38 billion by 2033. Growing investments in renewable energy sources are fostering market development in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
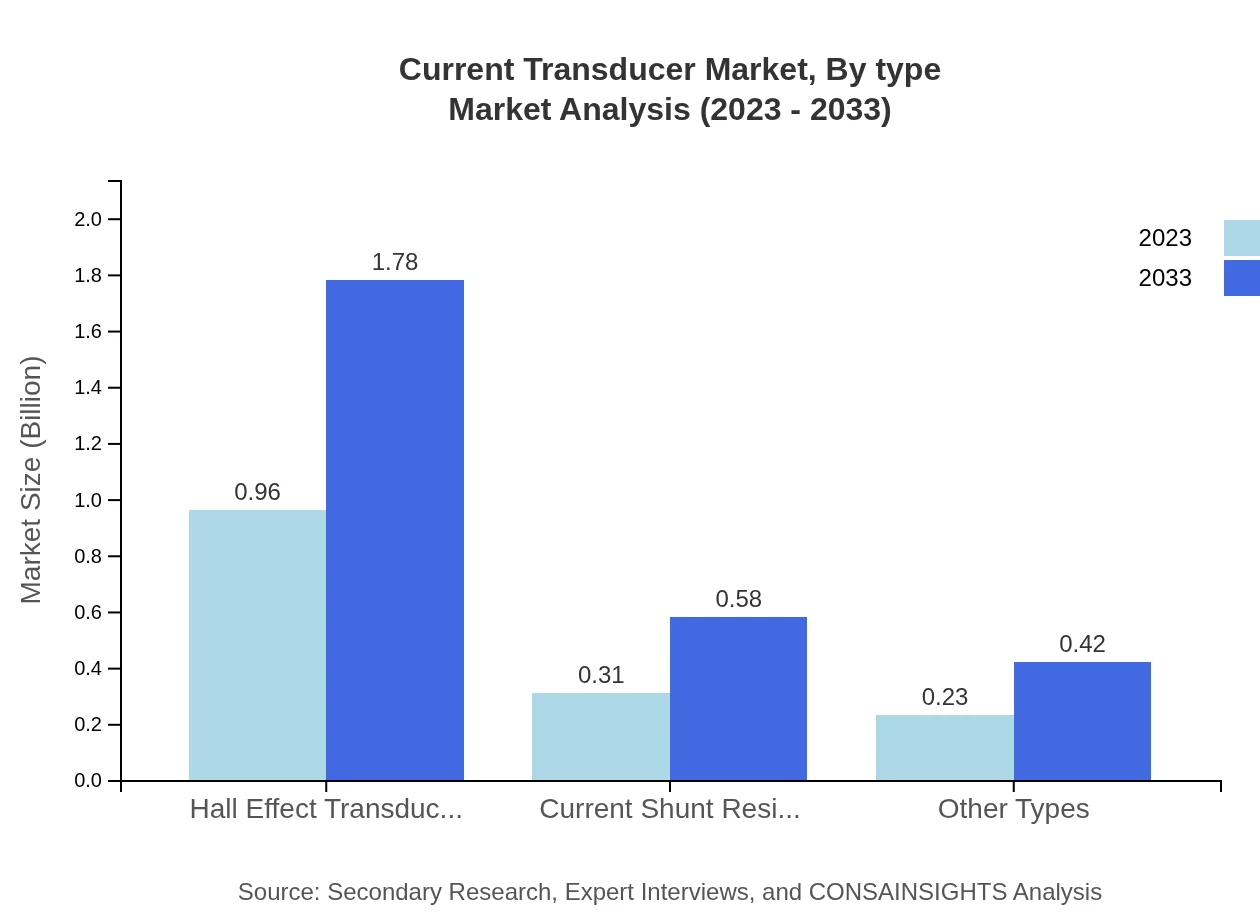
Current Transducer Market Analysis By Type
In 2023, Hall Effect Transducers dominated the market with a size of $0.96 billion and projected growth to $1.78 billion by 2033. Current shunt resistors and other transducer types followed with sizes of $0.31 billion and $0.23 billion in 2023, growing to $0.58 billion and $0.42 billion respectively by 2033.
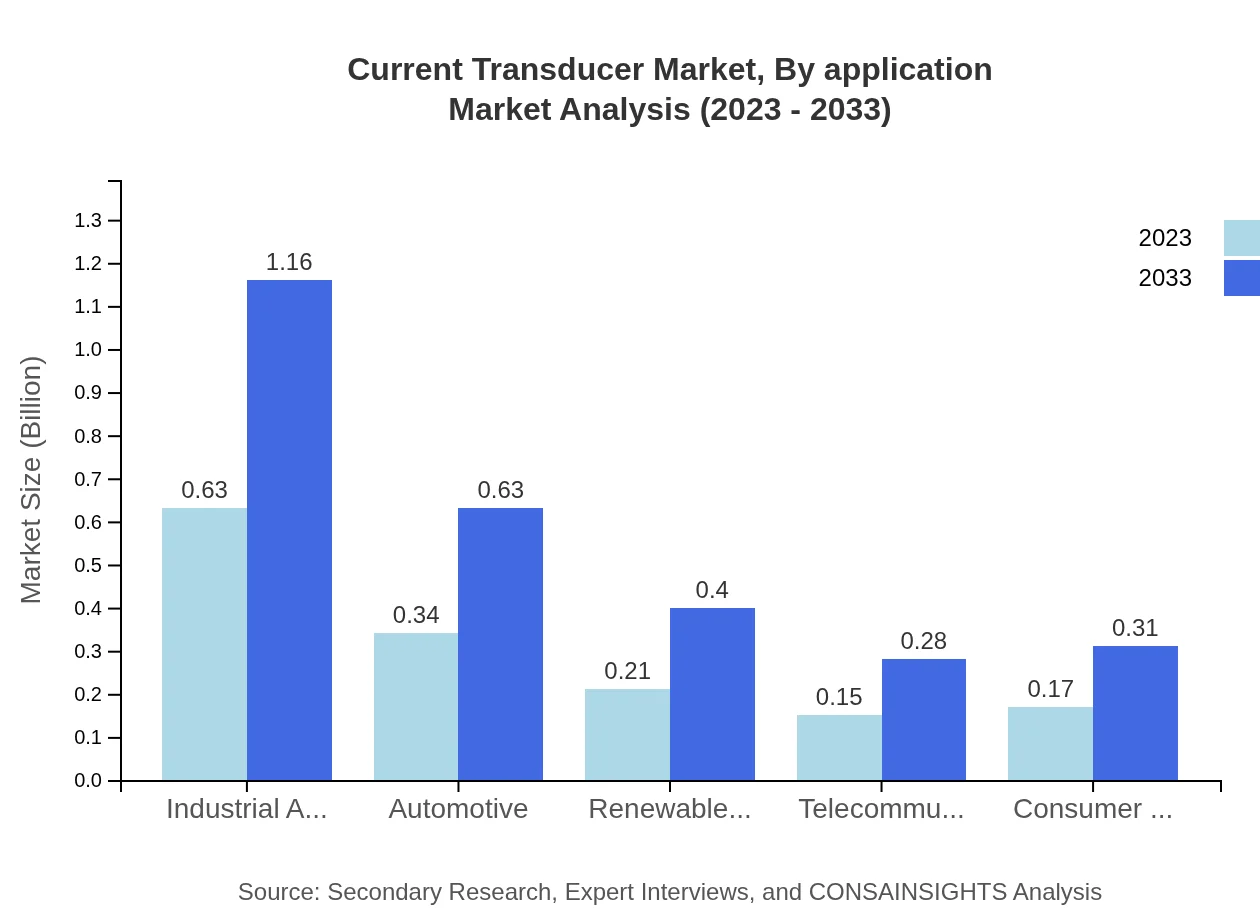
Current Transducer Market Analysis By Application
Energy and Utilities remain the leading application for current transducers, starting from $0.63 billion in 2023 to $1.16 billion in 2033. The automotive industry also plays a significant role, growing from $0.34 billion to $0.63 billion during the same period. Other key applications include consumer electronics and telecommunications.
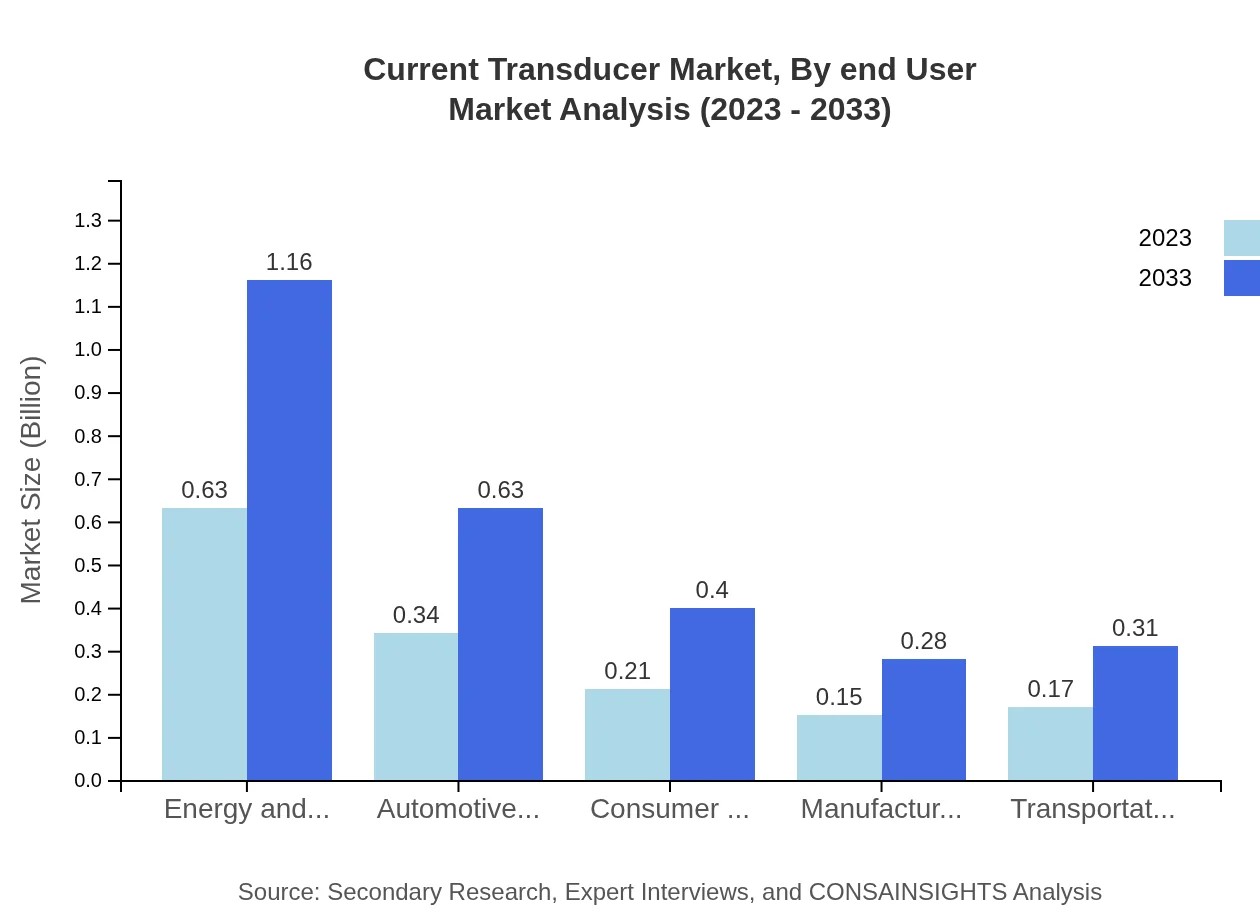
Current Transducer Market Analysis By End User
The industrial applications segment is a key player, valued at $0.63 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $1.16 billion by 2033. Other important end-user segments include automotive and renewable energy industries, which are also growing steadily.
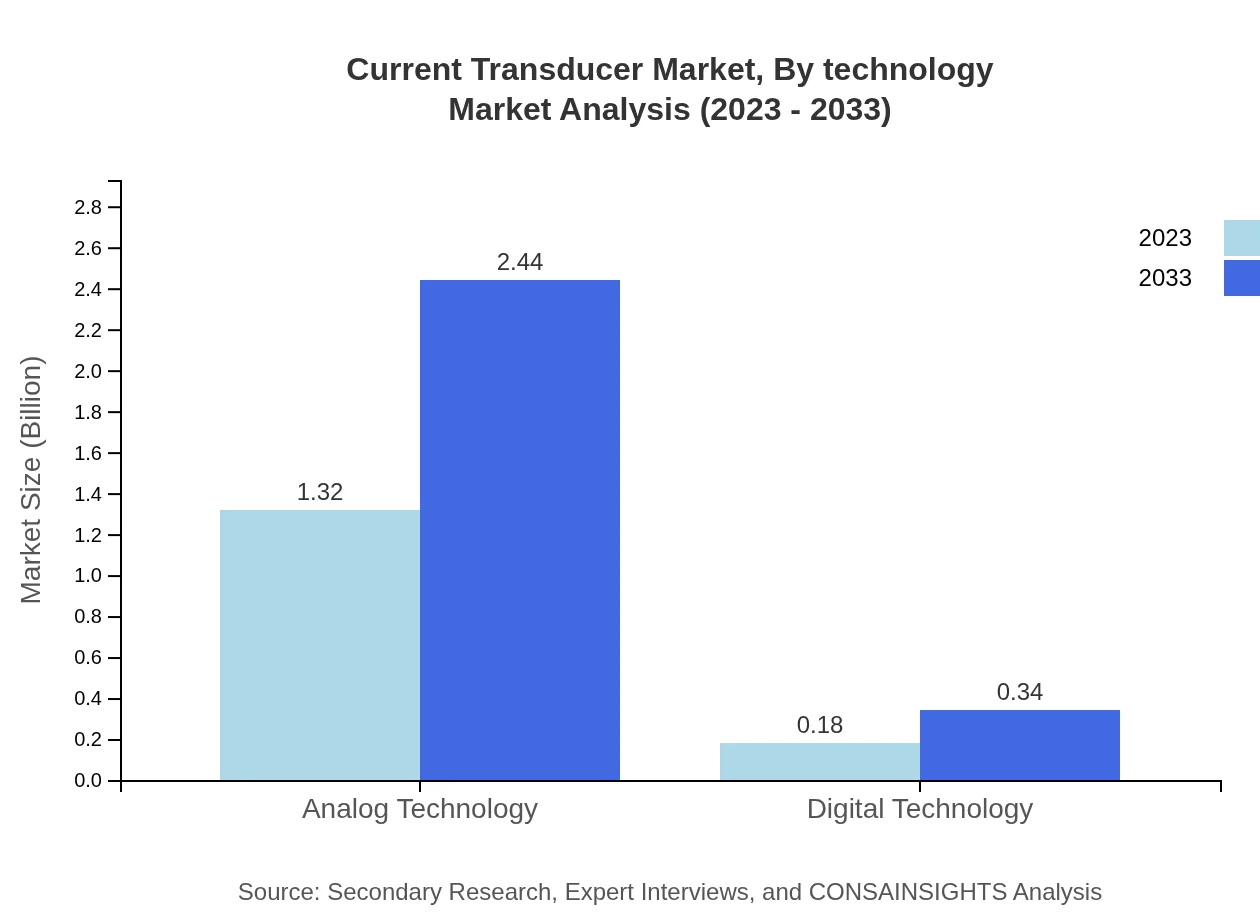
Current Transducer Market Analysis By Technology
Analog Technology represented a substantial market at $1.32 billion in 2023, aiming for $2.44 billion by 2033. In contrast, Digital Technology accounted for $0.18 billion in 2023 and is targeted to reach $0.34 billion, indicating a shift to modernized measurement technologies.
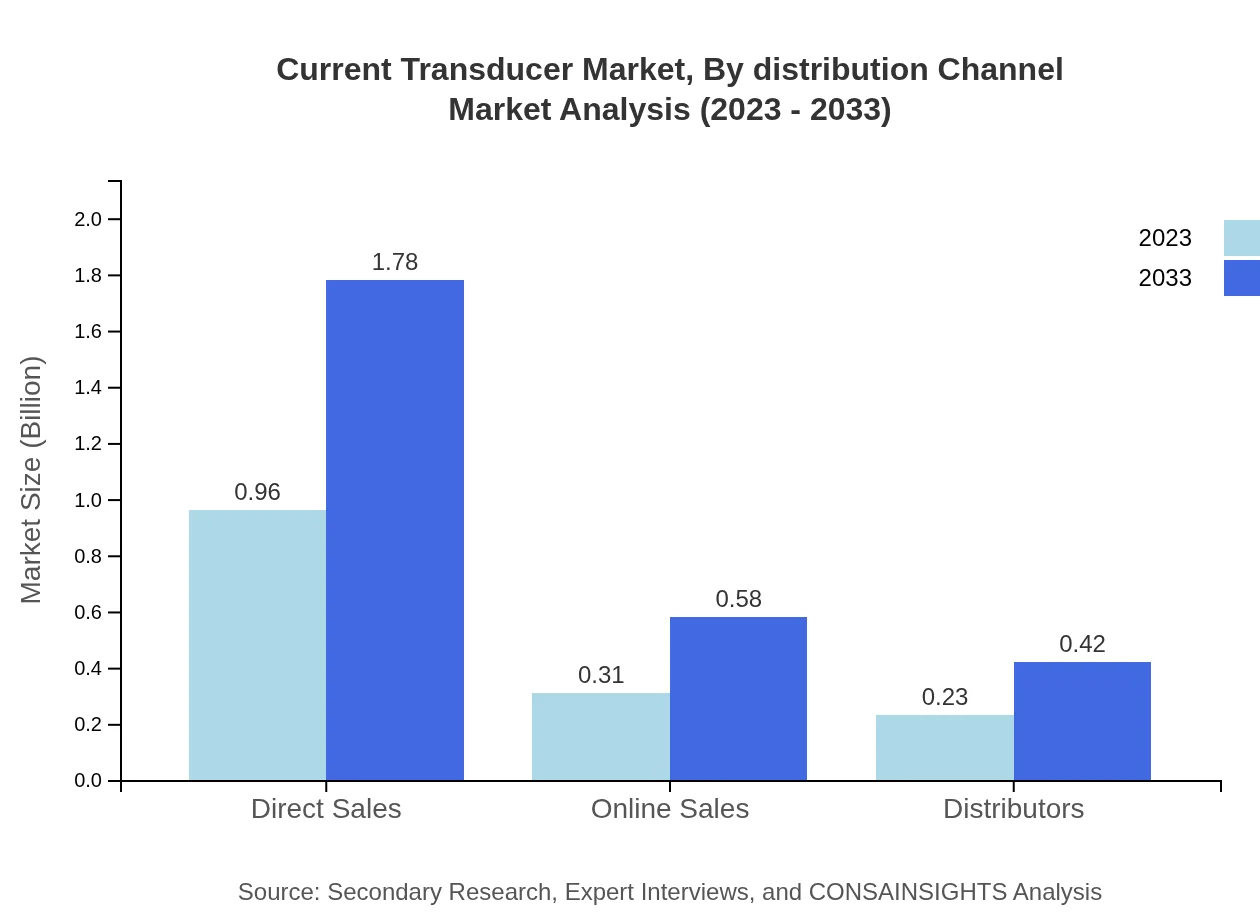
Current Transducer Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Direct Sales led distribution channels with a market size of $0.96 billion in 2023, forecast to grow to $1.78 billion. Online sales, valued at $0.31 billion, are anticipated to progress to $0.58 billion, showcasing a rising trend in e-commerce.
Current Transducer Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Current Transducer Industry
Texas Instruments:
A leading manufacturer of semiconductor products including current sensing devices used in various applications.Honeywell International Inc.:
Known for its innovative sensor technologies, Honeywell offers advanced current transducer solutions for industrial use.Infineon Technologies AG:
Specializes in semiconductor solutions that include current measurement systems suitable for automotive and industrial applications.Analog Devices, Inc.:
Provides high-performance analog, mixed-signal, and digital signal processing technologies, including current transducers.STMicroelectronics:
A global semiconductor company that delivers current transducer devices designed for automotive and energy applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Current Transducer?
The global market size for Current Transducer is projected to reach approximately $1.5 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the Current Transducer industry?
Some key players in the Current Transducer market include Texas Instruments, Allegro MicroSystems, and LEM International. These companies are major contributors due to their advanced technologies and extensive market reach.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Current Transducer industry?
The growth in the Current Transducer industry is driven by rising demand in renewable energy applications, increased automotive electrification, and the need for efficient energy management solutions across various industries.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Current Transducer?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the Current Transducer market, expected to grow from $0.30 billion in 2023 to $0.55 billion by 2033, indicating rapid expansion in this market segment.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Current Transducer industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs within the Current Transducer industry, including detailed data analysis and insights based on client requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this Current Transducer market research project?
Deliverables from the Current Transducer research project include comprehensive market reports, trend analysis, regional insights, competitor analysis, and tailored recommendations for strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of Current Transducer?
Market trends in Current Transducer indicate a shift towards digital technologies, increased reliance on automation in industrial applications, and growth in demand from the automotive and renewable energy sectors.