Cyber Weapon Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: cyber-weapon
Cyber Weapon Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Cyber Weapon market, focusing on market size, trends, regional insights, and forecasts for the period 2023 to 2033. Insights include market capitalization, growth rates, and an overview of key players shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
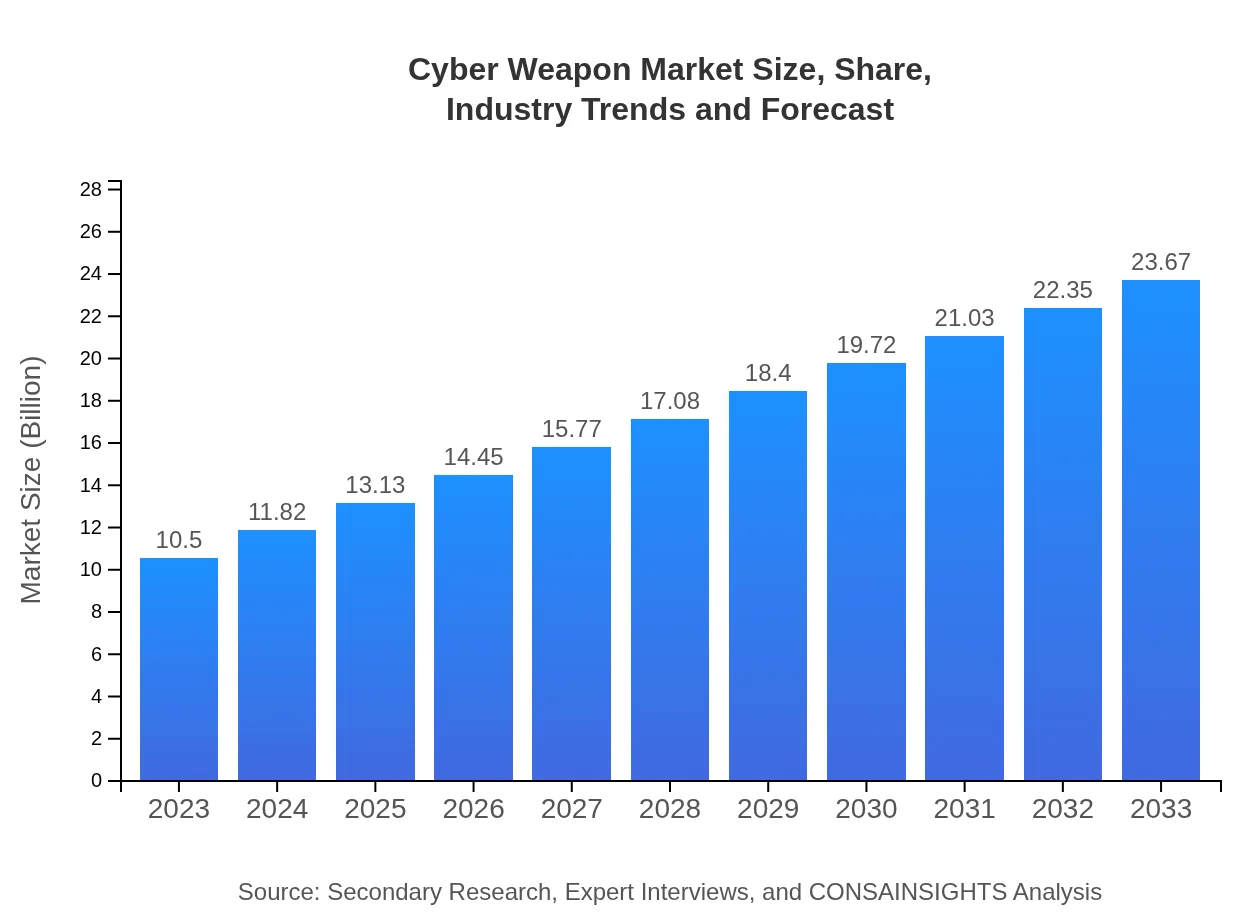
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $23.67 Billion |
| Top Companies | Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, Cisco Systems, FireEye, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Cyber Weapon Market Overview
Customize Cyber Weapon Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cyber Weapon market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cyber Weapon's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cyber Weapon
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cyber Weapon market in 2023?
Cyber Weapon Industry Analysis
Cyber Weapon Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cyber Weapon Market Report:
Europe's Cyber Weapon market was valued at $2.91 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand to $6.56 billion by 2033. European countries are increasingly prioritizing cybersecurity due to rising threats and the desire to protect sensitive data. Initiatives to foster collaborations among EU member states and develop common cybersecurity strategies are becoming critical components of national security policies.Asia Pacific Cyber Weapon Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Cyber Weapon market was valued at approximately $2.07 billion in 2023, with projections indicating growth to around $4.67 billion by 2033. This region faces unique challenges, including rising cyber threats from rival nation-states, necessitating a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Countries like China, India, and Japan are investing heavily in cyber capabilities, reflecting an increasing prioritization of national security strategies.North America Cyber Weapon Market Report:
North America leads the Cyber Weapon market, with a valuation of approximately $3.53 billion in 2023 and forecasted to reach $7.96 billion by 2033. The United States, as a significant player, emphasizes counter-cyber operations and invests substantially in both defensive and offensive cyber capabilities. This region demonstrates strong cooperation between governmental defense agencies and private sector technology developers, propelling innovation and market growth.South America Cyber Weapon Market Report:
South America’s Cyber Weapon market is currently valued at $1.02 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $2.29 billion by 2033. The region's investments in cybersecurity stem from a growing awareness of digital vulnerabilities and a response to increasing cybercrime. Governments are beginning to recognize the importance of robust cyber defense mechanisms to protect critical infrastructure and secure public safety.Middle East & Africa Cyber Weapon Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa experienced a market valuation of $0.97 billion in 2023, with expectations of growth to $2.18 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing an escalation in cyber threats linked to geopolitical tensions and is responding with expanded investments in cybersecurity infrastructures. Countries in this area are focusing on regional cooperation to develop effective strategies against cybercrime and terrorism.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
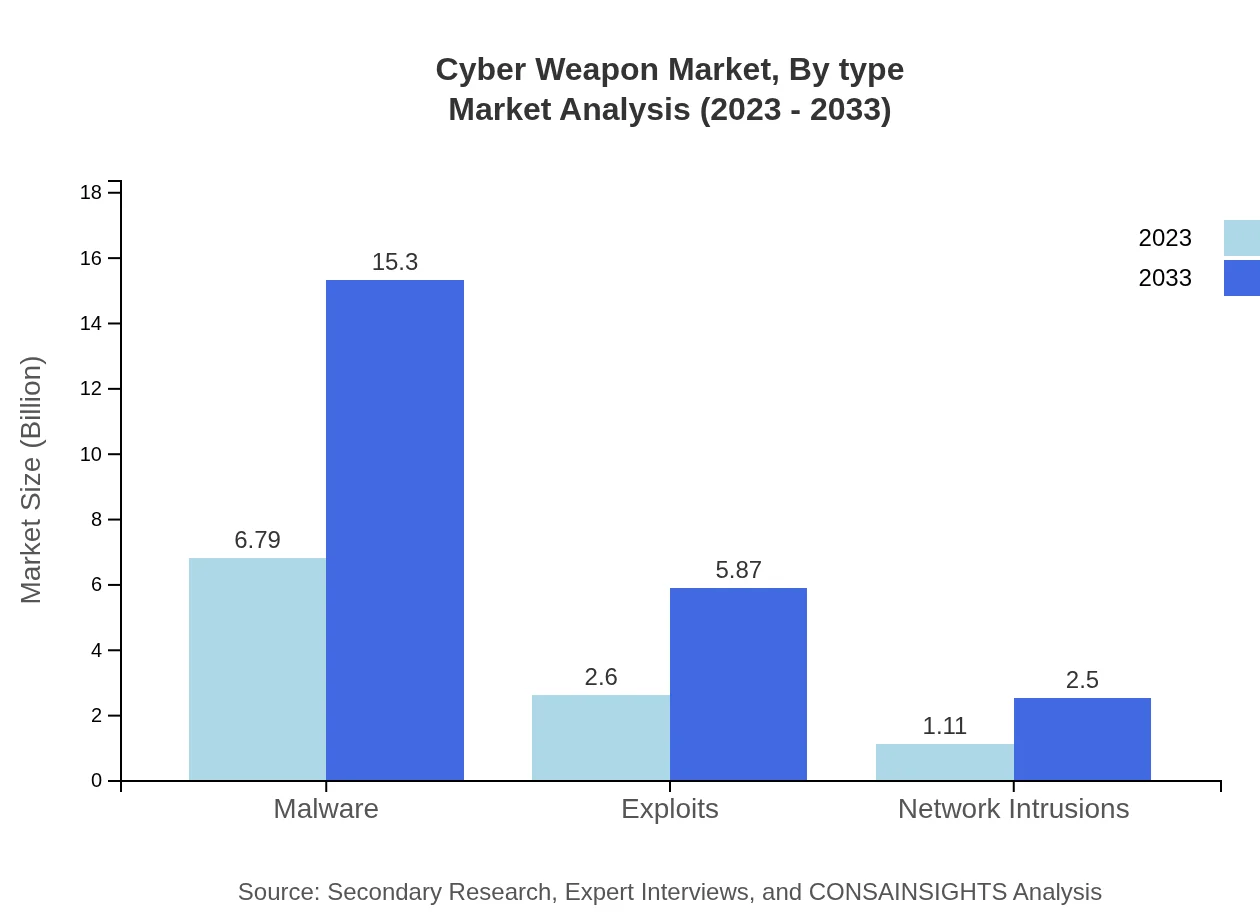
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis By Type
Malware continues to dominate the Cyber Weapon landscape, with a market size of approximately $6.79 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow significantly to $15.30 billion by 2033, holding a 64.65% market share. Exploits follow closely, with the market size rising from $2.60 billion in 2023 to $5.87 billion in 2033, maintaining a share of approximately 24.8%. Other segments like Network Intrusions are essential but represent a smaller portion of the market.
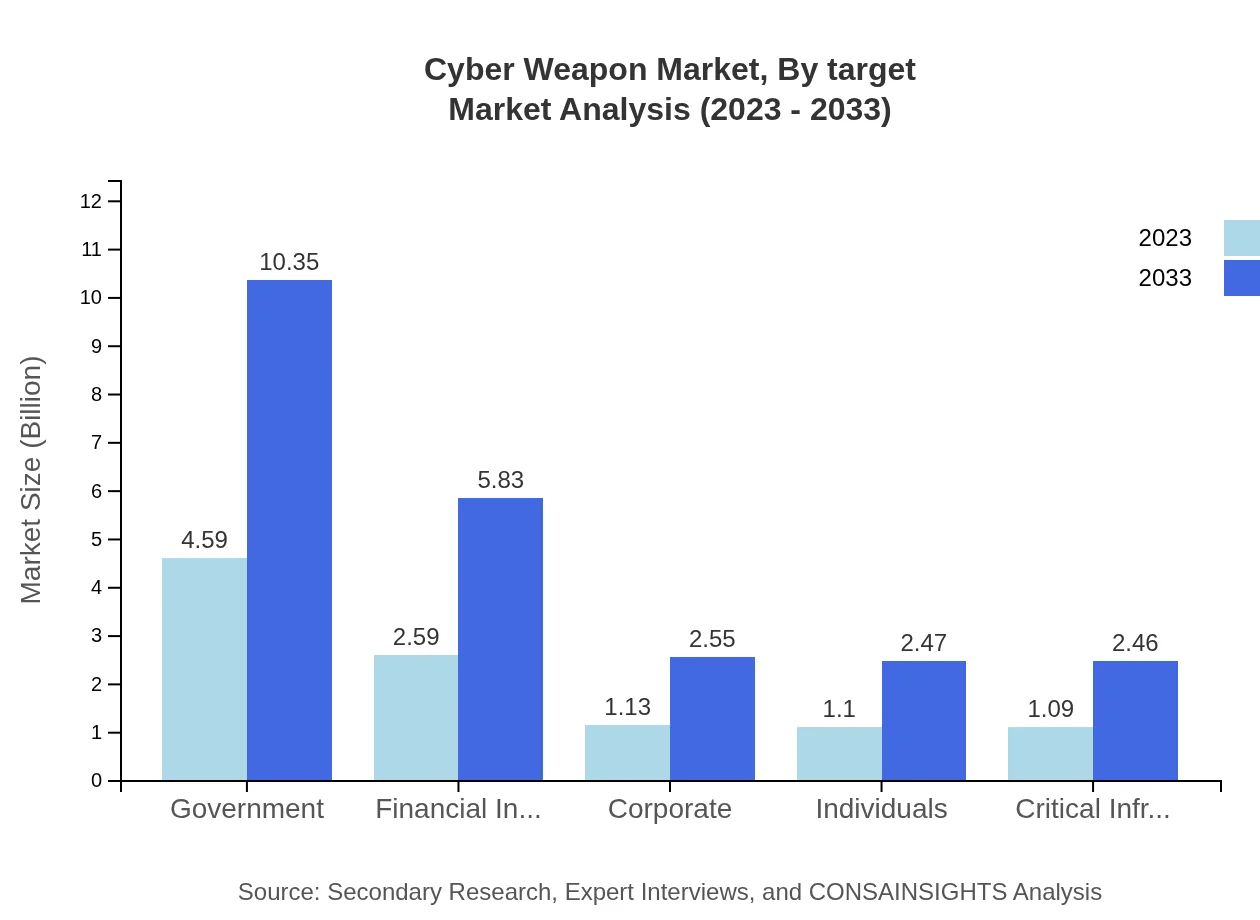
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis By Target
The targets of cyber weapons can include government entities, financial institutions, corporations, and individuals. The Government segment is notable, growing from $4.59 billion in 2023 to $10.35 billion by 2033, representing 43.72% of the total share. Financial institutions follow, increasing from $2.59 billion to $5.83 billion, accounting for 24.65%. Corporate and individual targets remain smaller but still vital components of the overall strategy.
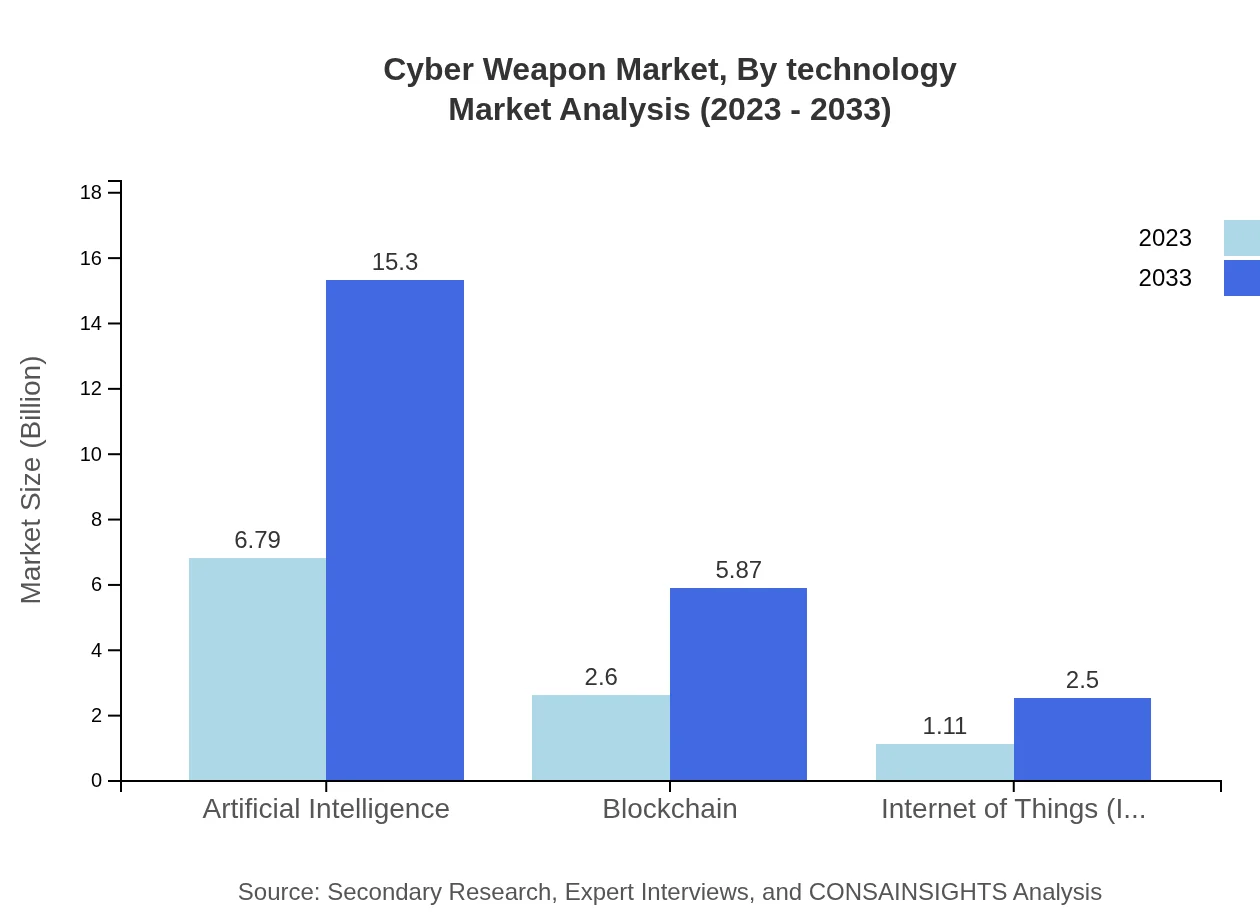
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are a defining factor in the Cyber Weapon market. Artificial Intelligence (AI) leads with a substantial market size growth from $6.79 billion in 2023 to $15.30 billion in 2033. Other technologies, such as Blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT), while smaller in their share, are also gaining traction, emphasizing the importance of innovative technologies in driving market growth.
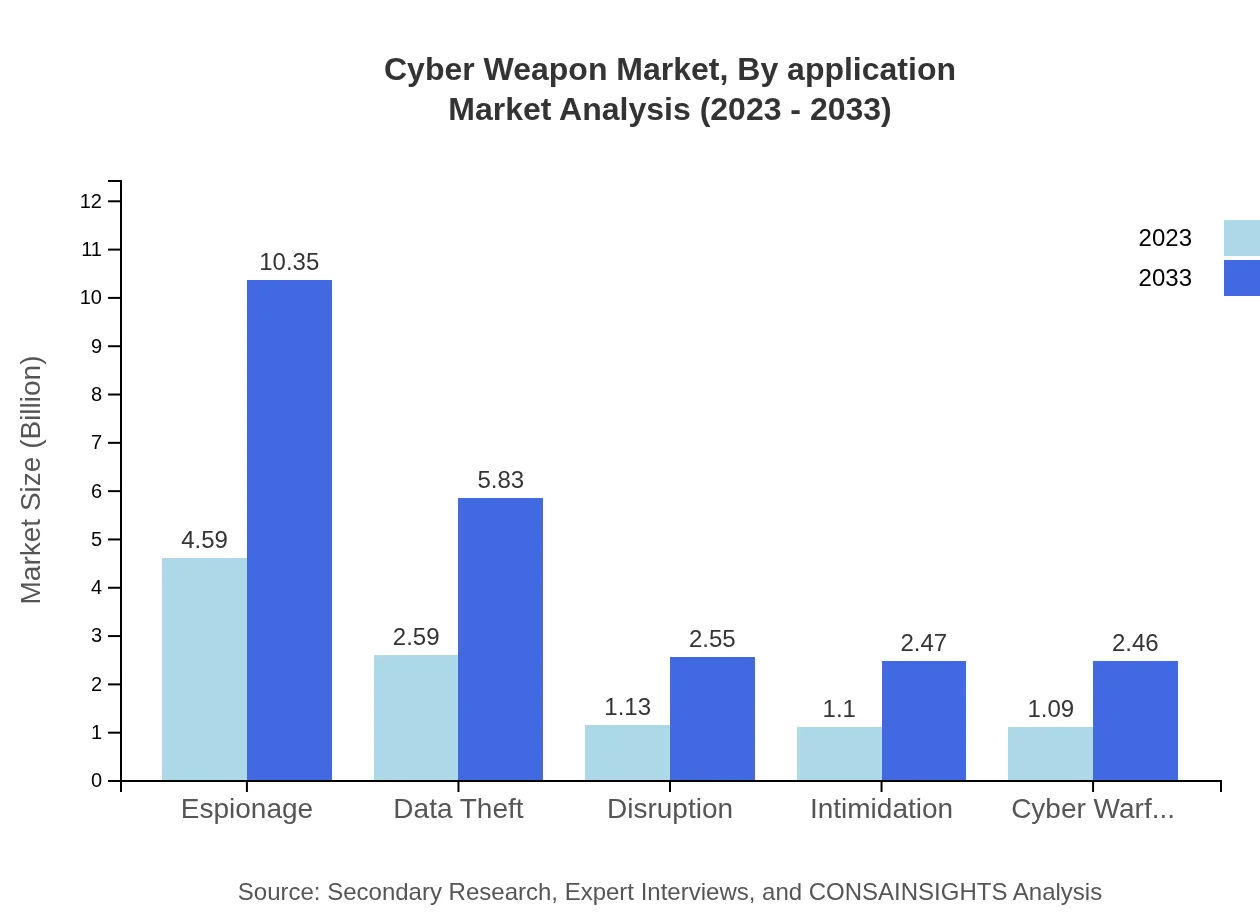
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis By Application
Applications of cyber weapons extend across espionage, data theft, disruption, intimidation, and cyber warfare. Espionage commands a significant market presence, projected to grow from $4.59 billion in 2023 to $10.35 billion by 2033. Data theft and disruption are also critical, with marked growth rates reflecting the increasing importance of safeguarding sensitive information.
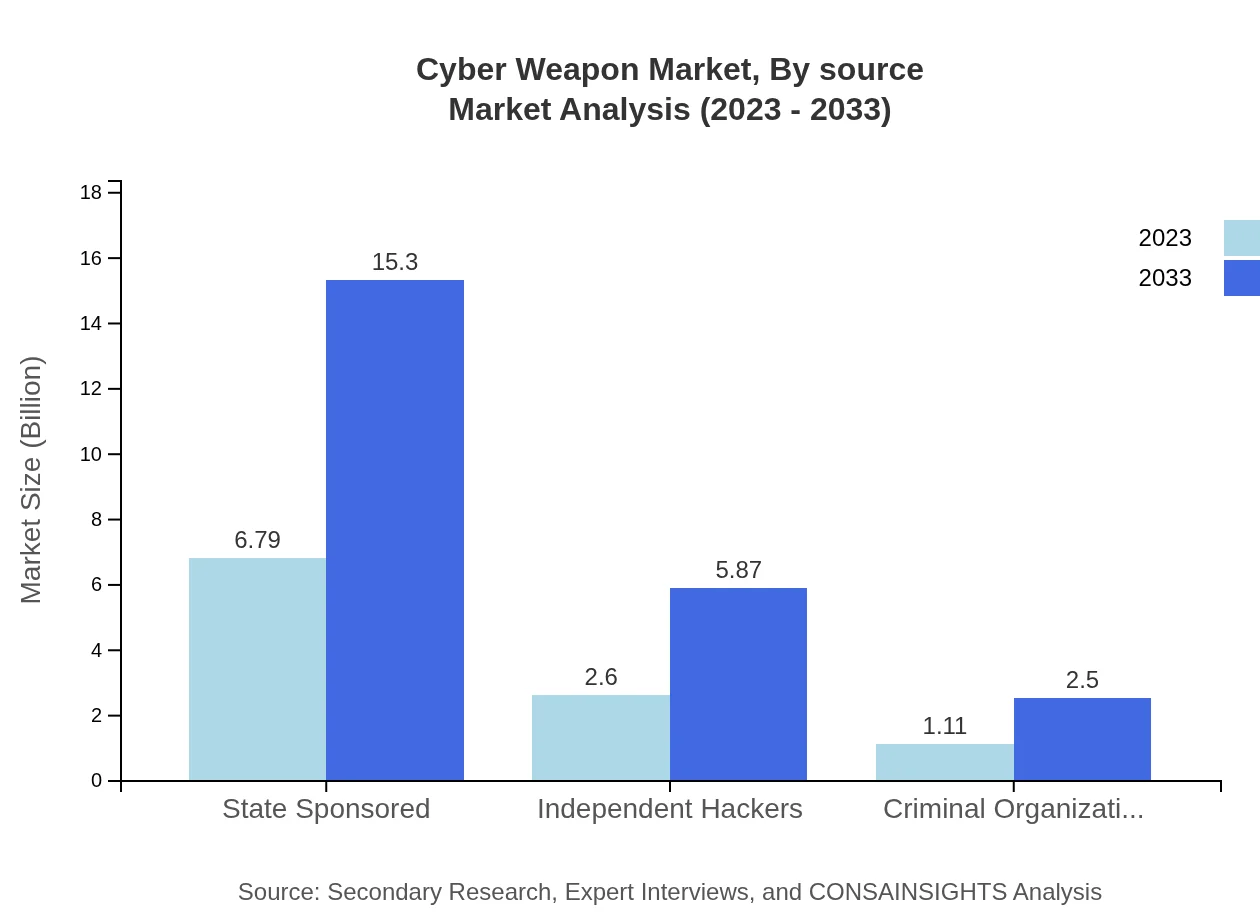
Cyber Weapon Market Analysis By Source
Sources of cyber weapons include state-sponsored, independent hackers, and criminal organizations. State-sponsored cyber weapons dominate, with shares representing approximately 64.65% of the overall market. This emphasizes the reliance on sophisticated technologies and methodologies employed by state actors in the cyber domain, further complicating the competitive landscape within the industry.
Cyber Weapon Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cyber Weapon Industry
Lockheed Martin:
Lockheed Martin is a global aerospace, defense, and security company that plays a significant role in developing cyber capabilities for military applications.Raytheon Technologies:
Raytheon Technologies focuses on delivering advanced technology solutions, including cyber defense, to enhance national security and protect critical infrastructures.Northrop Grumman:
Northrop Grumman is a leader in cyber solutions, providing innovative technologies that support defense measures against evolving cyber threats.Cisco Systems:
Cisco Systems specializes in networking and cybersecurity solutions, offering products designed to mitigate cyber threats and enhance digital resilience.FireEye, Inc.:
FireEye is known for its intelligence-driven security solutions, particularly in identifying and countering sophisticated cyber threats and weapons.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cyber Weapon?
The cyber-weapon market is currently valued at approximately $10.5 billion as of 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% through 2033. This growth reflects the rising reliance on digital infrastructure and ongoing security threats.
What are the key market players or companies in this cyber Weapon industry?
Key players in the cyber-weapon market include various defense contractors, cybersecurity firms, and state-sponsored entities. These companies focus on developing advanced malware, exploits, and network defense systems to protect national and corporate interests.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cyber Weapon industry?
The growth in the cyber-weapon industry is driven by increasing cyber threats, national security concerns, technological advancements, and the digital transformation of businesses. The escalation of cyber warfare tactics is pushing governments to enhance their defensive and offensive capabilities.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cyber Weapon market?
The fastest-growing region in the cyber-weapon market is North America, expected to expand from $3.53 billion in 2023 to $7.96 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by substantial investments in cybersecurity and defense technologies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cyber Weapon industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the cyber-weapon industry. Clients can receive insights based on specific parameters, including geographic focus, segment analysis, and targeted trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this cyber Weapon market research project?
From this market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports featuring market size data, CAGR forecasts, regional analysis, and competitive landscape details, as well as insights into current trends and future projections.
What are the market trends of cyber Weapon?
Current trends in the cyber-weapon market include an increased focus on AI-driven cyber defense solutions, growing state-sponsored cyber activities, and rising investments in advanced malware detection and protection technologies.