Cyber Security Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: cyber-security
Cyber Security Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report presents an in-depth analysis of the Cyber Security market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, trends, segmentation, and insights into regional dynamics and technologies shaping this vital sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
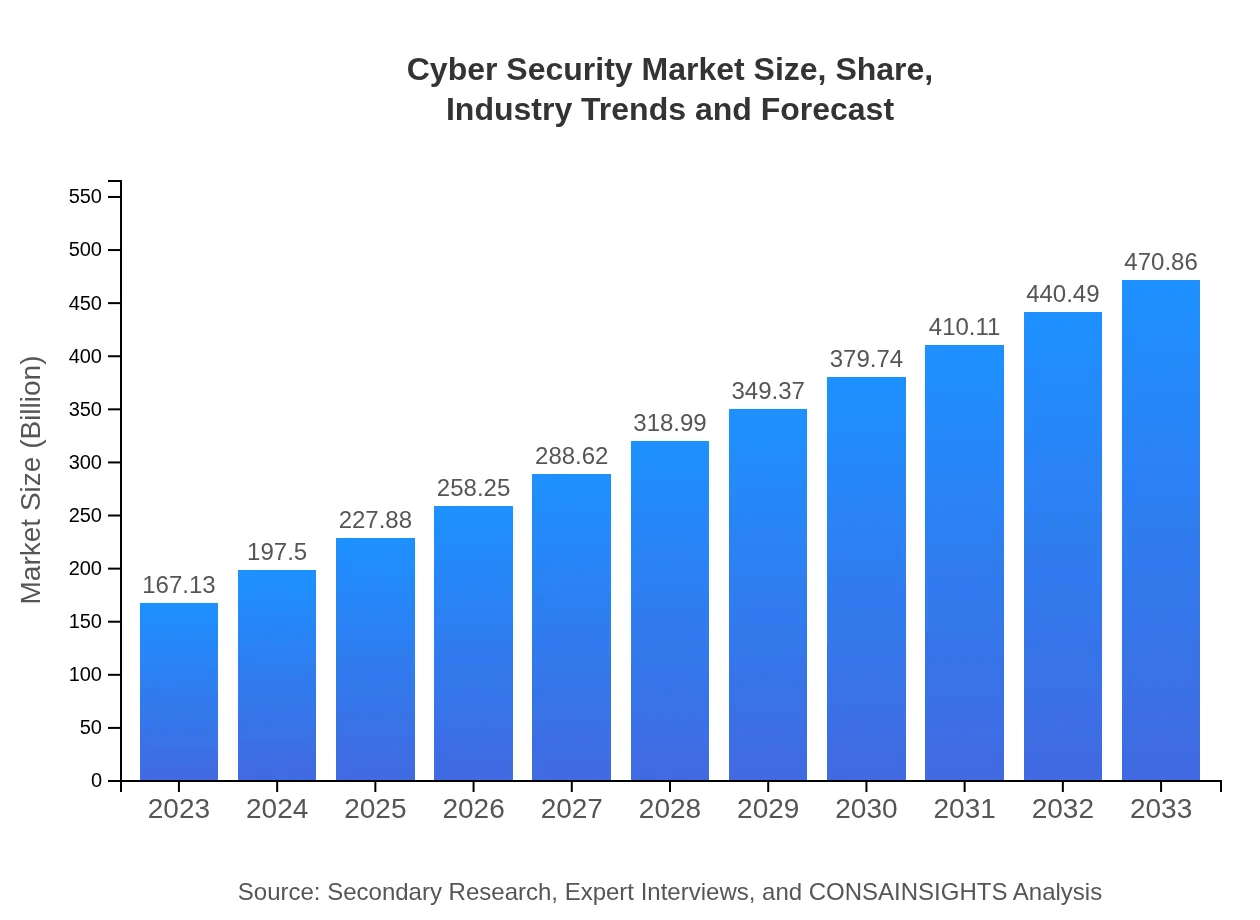
| 2023 Market Size | $167.13 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $470.86 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, IBM, CrowdStrike |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Cyber Security Market Overview
Customize Cyber Security Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Cyber Security market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Cyber Security's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Cyber Security
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Cyber Security Market in 2023?
Cyber Security Industry Analysis
Cyber Security Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Cyber Security Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Cyber Security Market Report:
The European Cyber Security market is set to rise from $53.87 billion in 2023 to $151.76 billion by 2033. Regulatory frameworks such as the GDPR and increasing cyber threats are pushing organizations to enhance their cybersecurity measures substantially.Asia Pacific Cyber Security Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Cyber Security market is projected to grow from $30.45 billion in 2023 to approximately $85.79 billion by 2033. Factors such as rapid digitalization, increased cyber threat awareness, and significant government initiatives aimed at enhancing national security are propelling market growth.North America Cyber Security Market Report:
North America leads the global Cyber Security market, which is anticipated to expand from $57.94 billion in 2023 to $163.25 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by high cybersecurity investment opportunities, a strong focus on regulatory compliance, and the presence of major cybersecurity firms in the region.South America Cyber Security Market Report:
The Cyber Security market in South America is expected to grow from $7.30 billion in 2023 to $20.58 billion by 2033. The increasing reliance on technology and cloud services among enterprises in this region is driving demand for comprehensive Cyber Security solutions.Middle East & Africa Cyber Security Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Cyber Security market size is expected to increase from $17.57 billion in 2023 to $49.49 billion by 2033. Growing awareness of the importance of digital security, coupled with rising adoption of mobile and cloud technologies in several industries, supports significant growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
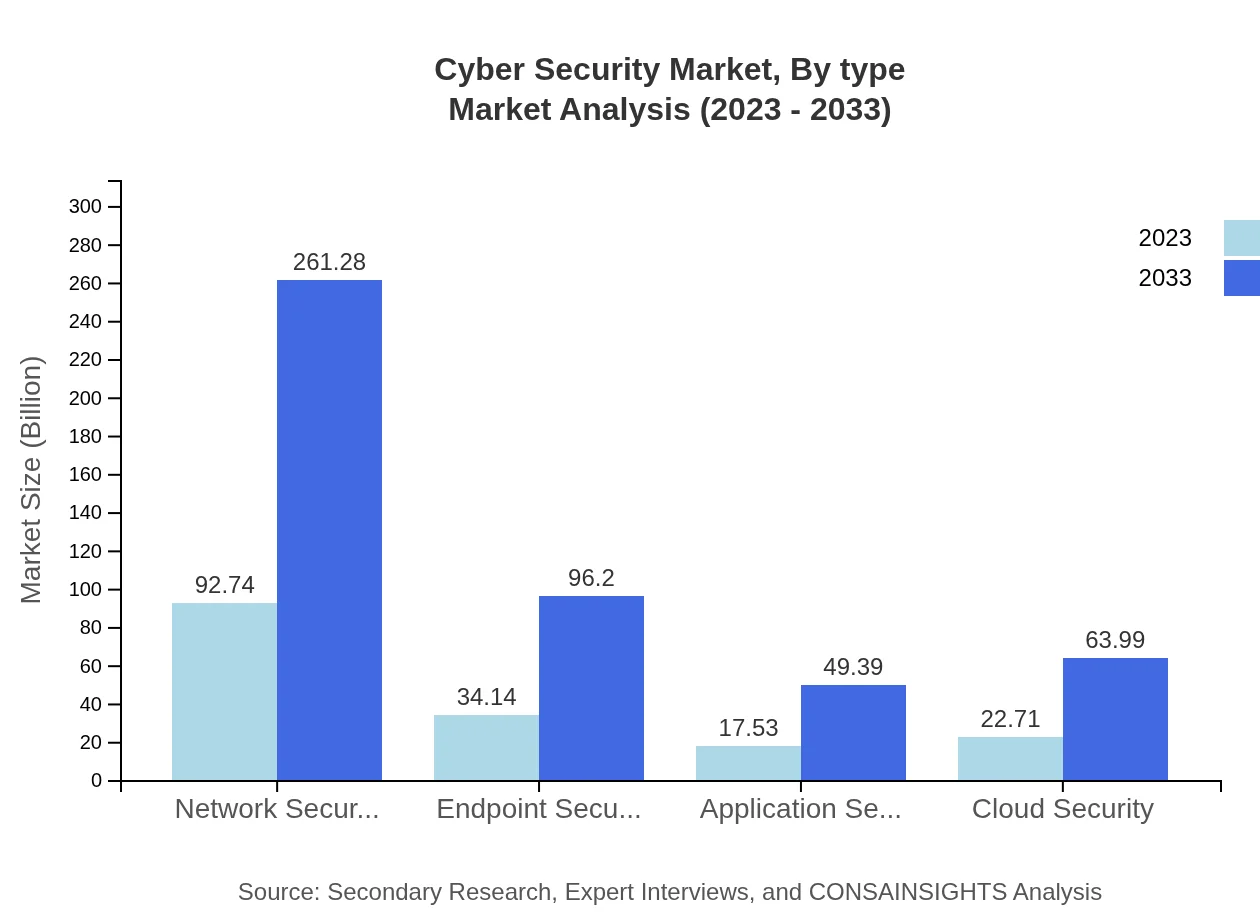
Cyber Security Market Analysis By Type
Network Security is anticipated to dominate the Cyber Security segment, growing from $92.74 billion in 2023 to $261.28 billion by 2033, representing a substantial market share. Endpoint Security is also gaining traction, expected to grow from $34.14 billion to $96.20 billion. Both Application Security and Cloud Security play critical roles, with respective growth from $17.53 billion to $49.39 billion, and $22.71 billion to $63.99 billion.
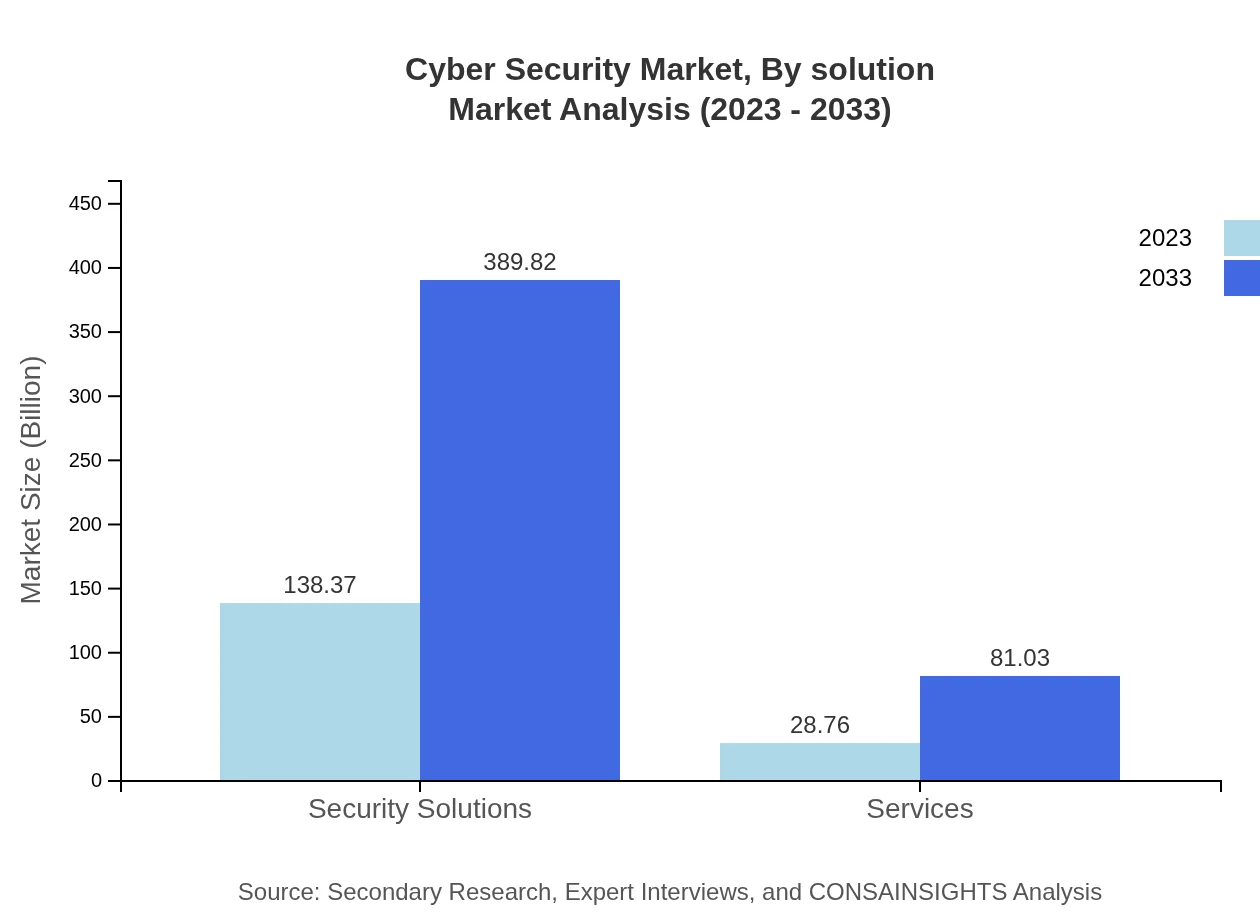
Cyber Security Market Analysis By Solution
Within the solution segment, Security Solutions are key contributors, expected to enhance from $138.37 billion to $389.82 billion. Service solutions are witnessing growth as well, projected to rise from $28.76 billion to $81.03 billion by 2033. These segments point to the industry's trend of integrated and holistic security approaches.
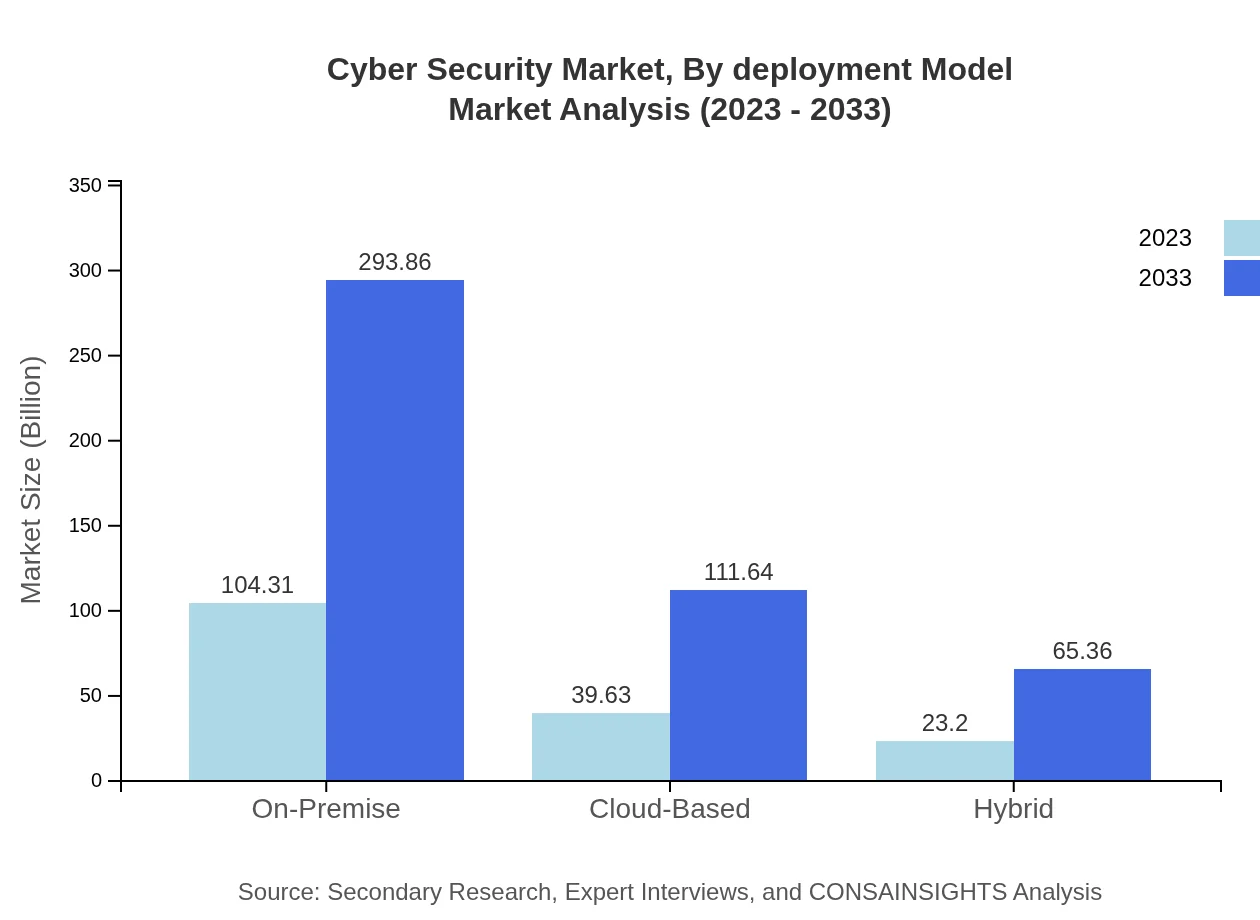
Cyber Security Market Analysis By Deployment Model
In terms of deployment, the On-Premise model remains prevalent, expected to grow from $104.31 billion to $293.86 billion, while Cloud-Based solutions are on the rise, projected to increase from $39.63 billion to $111.64 billion. The Hybrid model capitalizes on both, with growth from $23.20 billion to $65.36 billion.
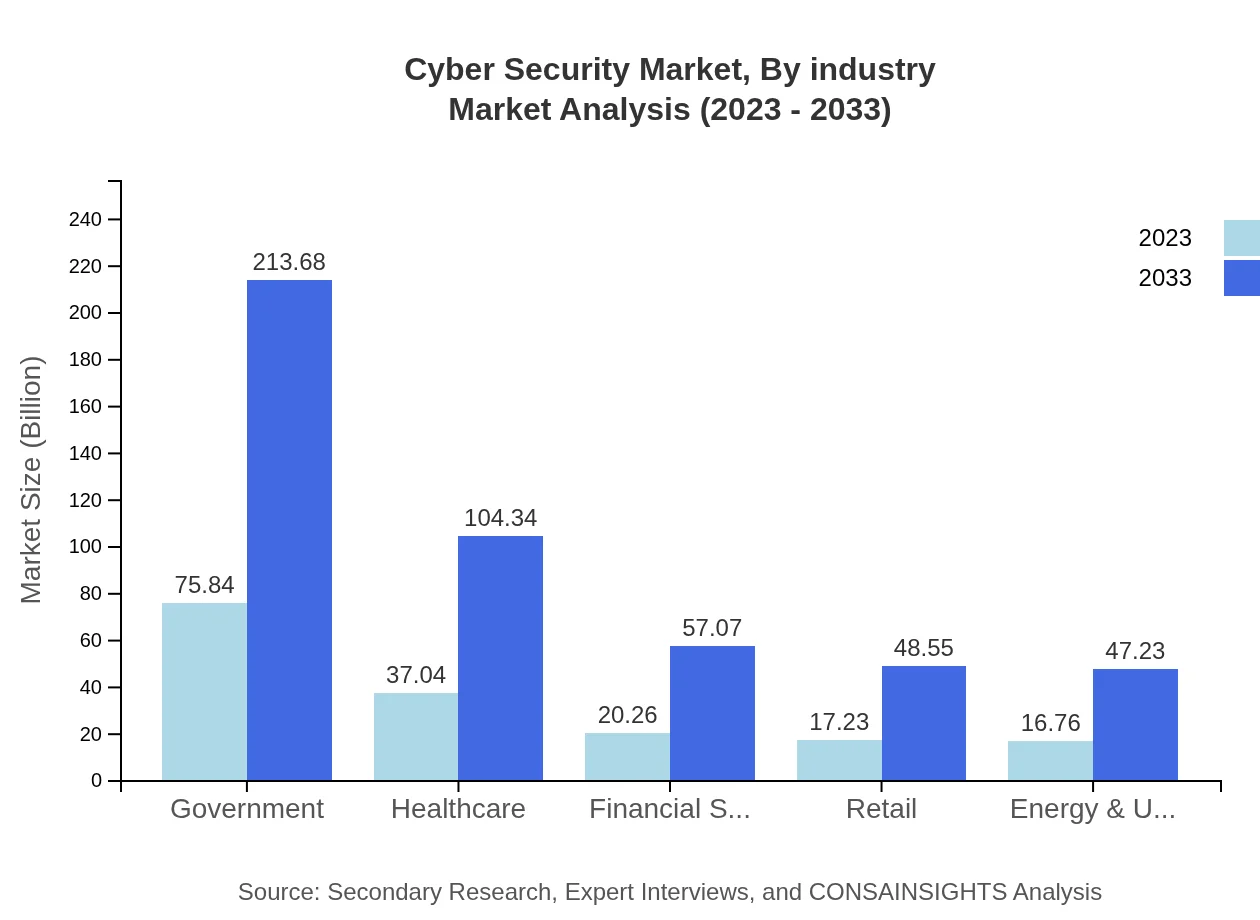
Cyber Security Market Analysis By Industry
The Government sector leads the market, with cyber security spending enhancing from $75.84 billion to $213.68 billion, driven by heightened national security requirements. The Healthcare sector follows suit, expect to grow from $37.04 billion to $104.34 billion, underscoring the critical need for protecting sensitive health data.
Cyber Security Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Cyber Security Industry
Cisco:
Cisco is a leader in IT, networking, and cybersecurity solutions. Their comprehensive portfolio includes advanced threat protection and network security.Palo Alto Networks:
Palo Alto Networks specializes in cybersecurity solutions, providing advanced firewalls and cloud-based security services that help safeguard businesses.Fortinet:
Fortinet is known for its cutting-edge security technology, offering integrated security solutions that protect networks, applications, and endpoints.IBM:
IBM provides a wide array of cybersecurity services, focusing on AI-driven security frameworks that enhance threat intelligence and incident response.CrowdStrike:
CrowdStrike is recognized for its cloud-native endpoint security platform, which leverages AI to protect against sophisticated cyber threats.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of cyber Security?
The global cyber-security market was valued at $167.13 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.5% through 2033, showcasing significant demand for security solutions across industries.
What are the key market players or companies in the cyber Security industry?
Key players in the cyber-security industry include major firms such as Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, and McAfee, specializing in various segments like network security, cloud protection, and endpoint security, contributing to market innovation.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the cyber Security industry?
The growth of the cyber-security industry is driven by increasing cyber threats, regulatory compliance needs, digital transformation initiatives, and the rise of IoT devices, necessitating robust security frameworks for both businesses and consumers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the cyber Security market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the cyber-security market, projected to grow from $30.45 billion in 2023 to $85.79 billion by 2033, reflecting increasing investments in technology and rising cybersecurity awareness.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the cyber Security industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client specifications in the cyber-security industry, providing unique insights, trend analysis, and strategic recommendations to support business decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this cyber Security market research project?
Deliverables from the cyber-security market research project typically include comprehensive reports, market forecasts, competitive analysis, segment insights, and actionable recommendations, designed to assist strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of cyber Security?
Current market trends in cyber-security include a shift towards cloud-based solutions, increased focus on AI and machine learning for threat detection, and the rising importance of privacy regulation compliance, influencing industry strategies.