Depression Drugs Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: depression-drugs
Depression Drugs Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the depression drugs market, covering market size, growth rates, industry trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It offers insights into key segments, regional performances, and market leaders shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
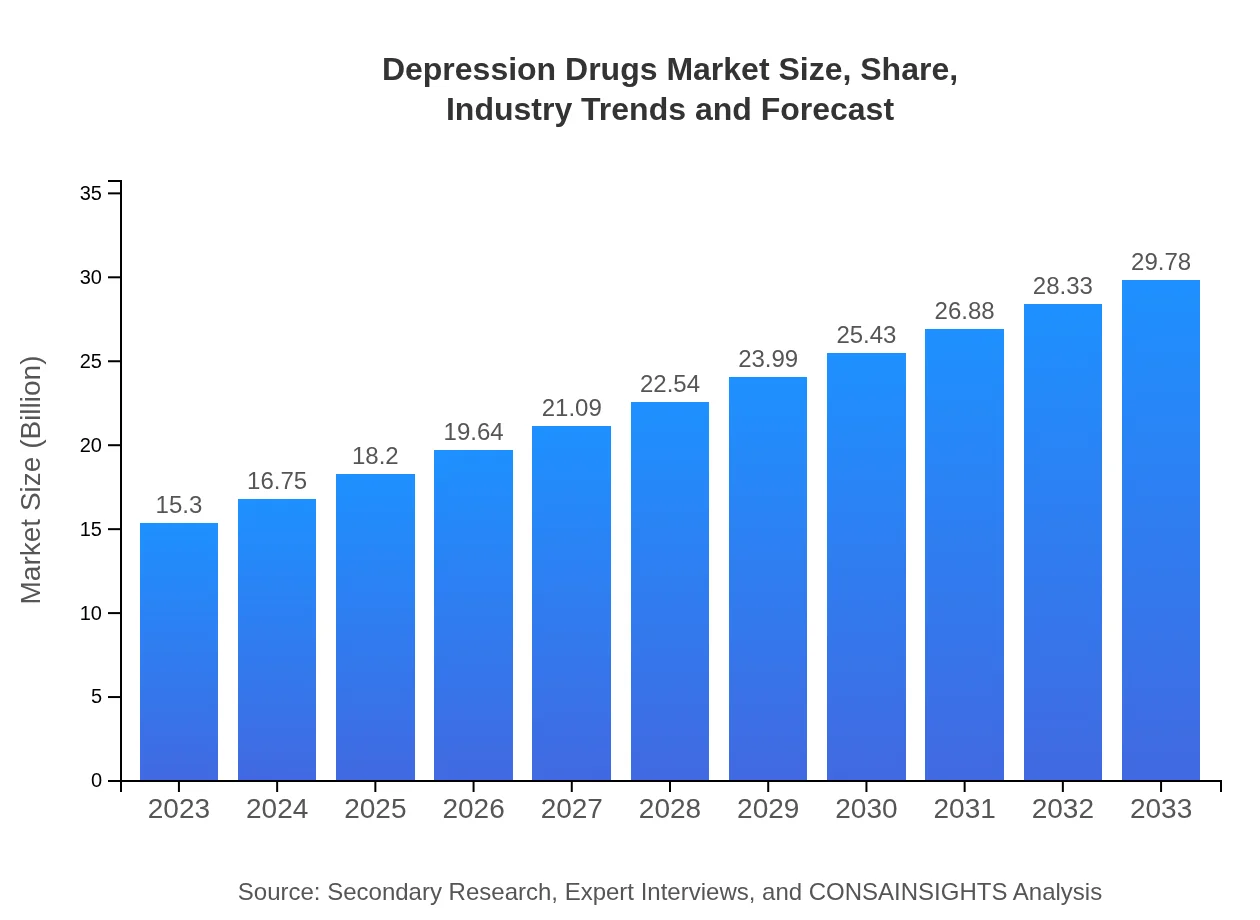
| 2023 Market Size | $15.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $29.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | Pfizer Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Johnson & Johnson, GlaxoSmithKline |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Depression Drugs Market Overview
Customize Depression Drugs Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Depression Drugs market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Depression Drugs's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Depression Drugs
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Depression Drugs market in 2023?
Depression Drugs Industry Analysis
Depression Drugs Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Depression Drugs Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Depression Drugs Market Report:
The European region encompasses a market size of USD 5.34 billion in 2023, projected to flourish to USD 10.39 billion by 2033. Factors such as rapid adoption of novel treatment protocols and high expenditure on mental health support significantly contribute to this growth.Asia Pacific Depression Drugs Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific depression drugs market is valued at USD 2.55 billion, projected to reach USD 4.97 billion by 2033. The growth in this region is driven by increasing awareness of mental health, government initiatives promoting mental health, and expanding healthcare access.North America Depression Drugs Market Report:
North America is one of the largest markets for depression drugs, with a 2023 valuation of USD 5.20 billion anticipated to grow to USD 10.12 billion by 2033. High prevalence rates of depression, strong healthcare financing, and ongoing innovations in medication contribute to this impressive market growth.South America Depression Drugs Market Report:
South America recorded a market size of USD 0.80 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow to USD 1.55 billion by 2033. Economic advancements and investment in healthcare infrastructure are essential drivers for market growth in this region.Middle East & Africa Depression Drugs Market Report:
The depression drugs market in the Middle East and Africa is valued at USD 1.41 billion in 2023, expected to rise to USD 2.74 billion by 2033. Increased investment in healthcare and the growing need for mental health services are key growth drivers in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Depression Drugs Market Analysis By Drug Class
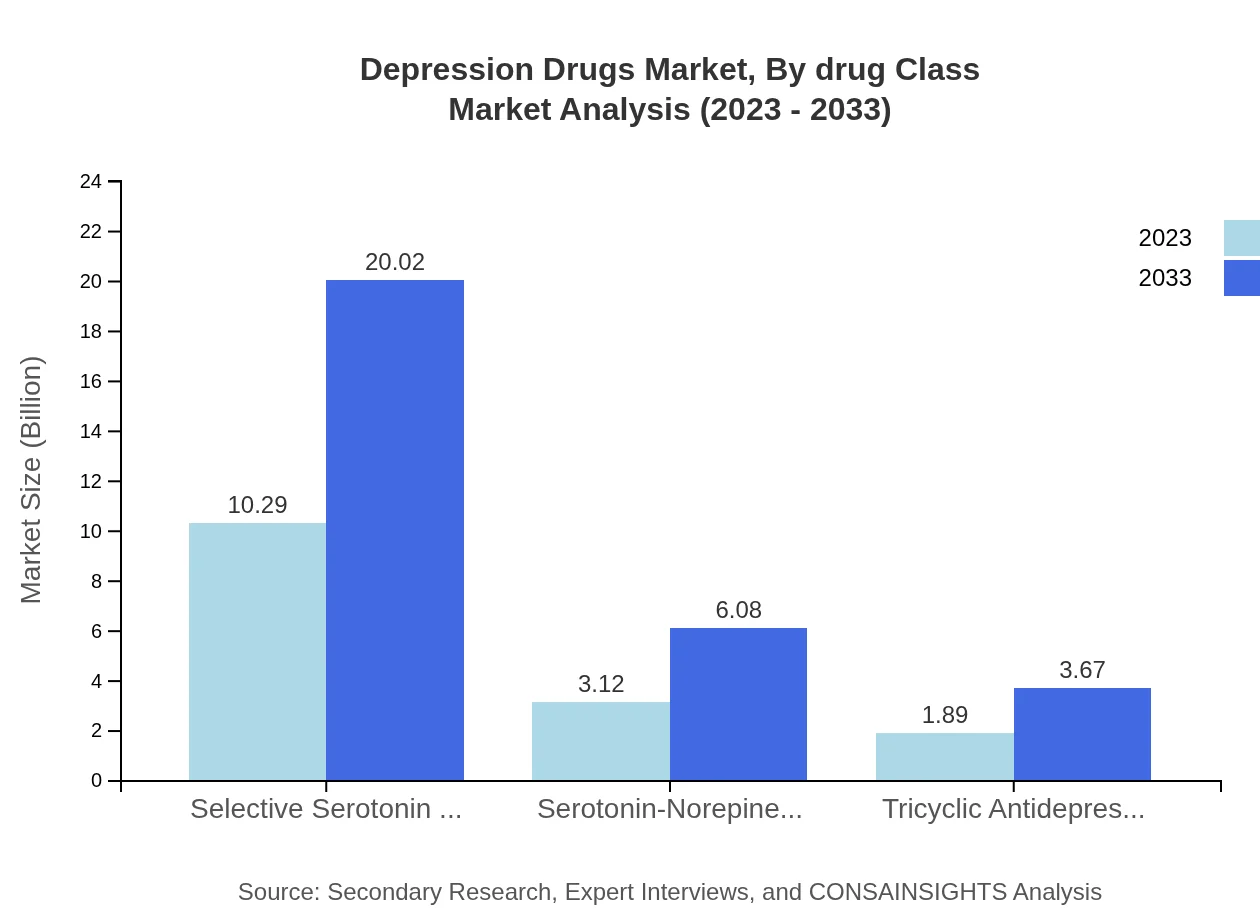
The major drug classes in the depression drugs market include SSRIs, SNRIs, and TCAs. SSRIs dominate the market with a size of USD 10.29 billion in 2023, projected to increase to USD 20.02 billion by 2033, capturing a 67.24% market share. In contrast, SNRIs also show substantial growth from USD 3.12 billion to USD 6.08 billion, holding a 20.42% market share. TCAs follow with market sizes of USD 1.89 billion in 2023, expanding to USD 3.67 billion by 2033, comprising a 12.34% market share.
Depression Drugs Market Analysis By Administration Route
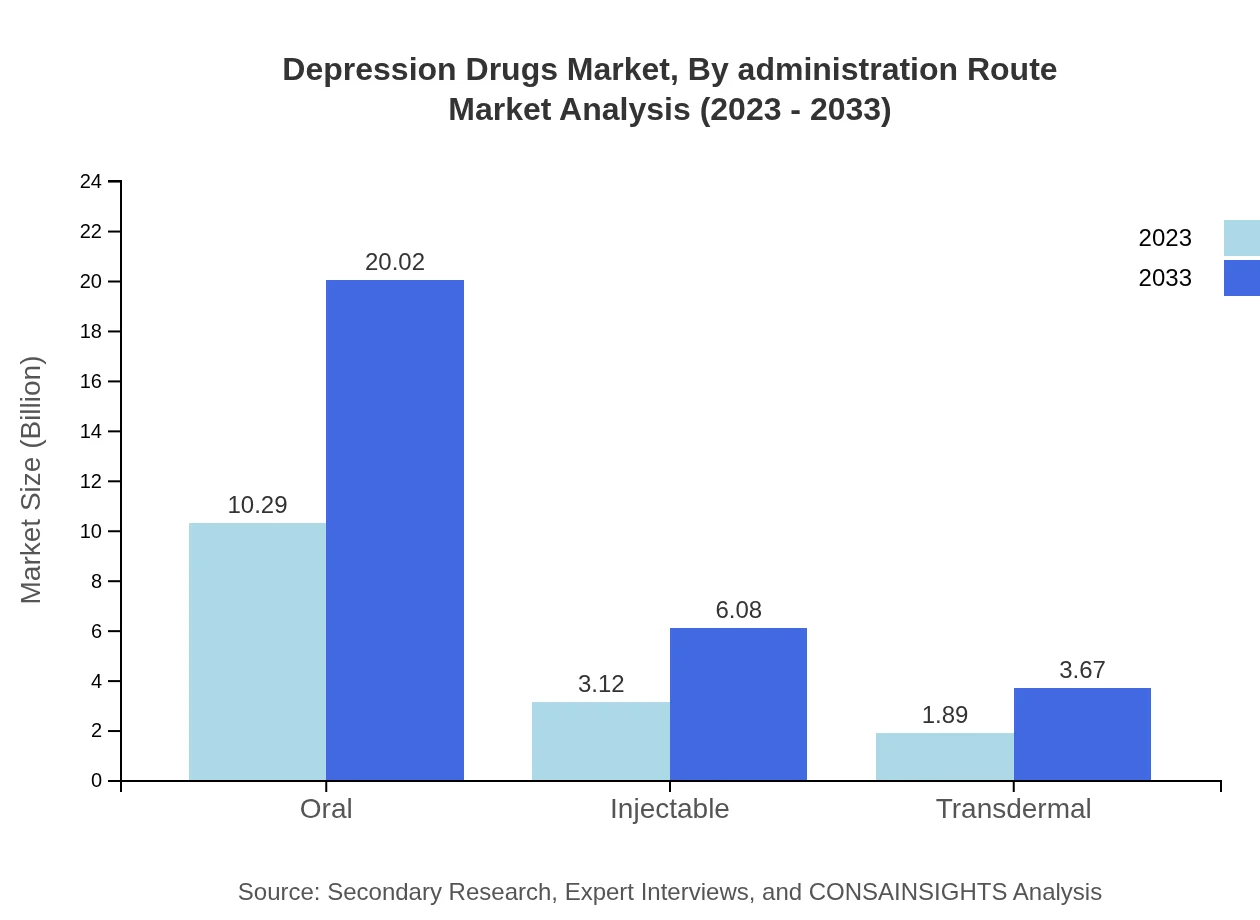
In terms of administration routes, oral medications lead the market, valued at USD 10.29 billion in 2023 and projected to rise to USD 20.02 billion by 2033. Injectable alternatives comprise a smaller yet growing segment, currently at USD 3.12 billion and expected to reach USD 6.08 billion. Transdermal routes, though currently the smallest, show steady growth from USD 1.89 billion to USD 3.67 billion, indicating an evolving delivery method landscape.
Depression Drugs Market Analysis By Age Group
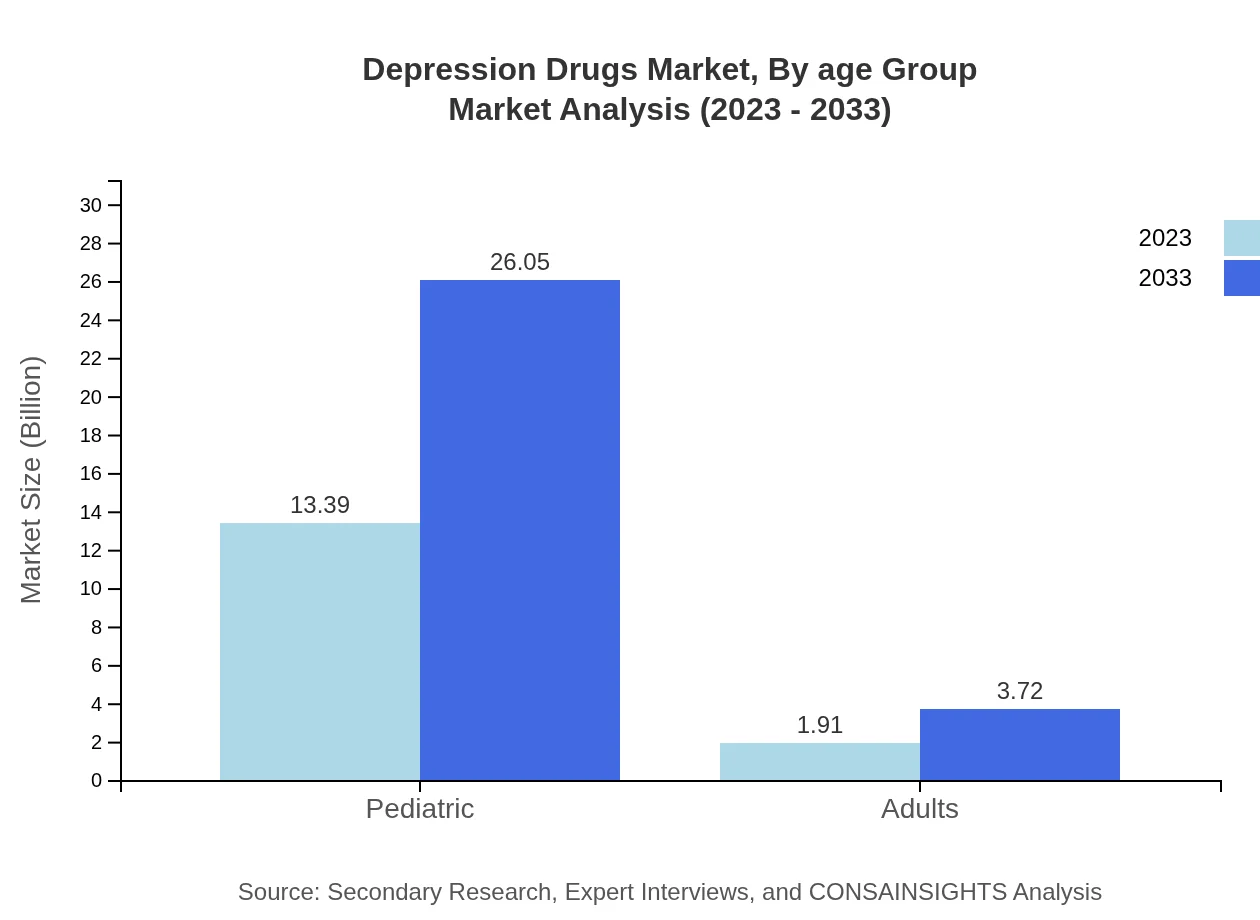
The pediatric segment significantly outweighs the adult segment in market size. In 2023, pediatric-related depression drugs are valued at USD 13.39 billion, forecast to grow to USD 26.05 billion by 2033, maintaining an 87.5% market share. The adult segment, while growing, remains smaller with market sizes increasing from USD 1.91 billion to USD 3.72 billion, capturing a 12.5% market share.
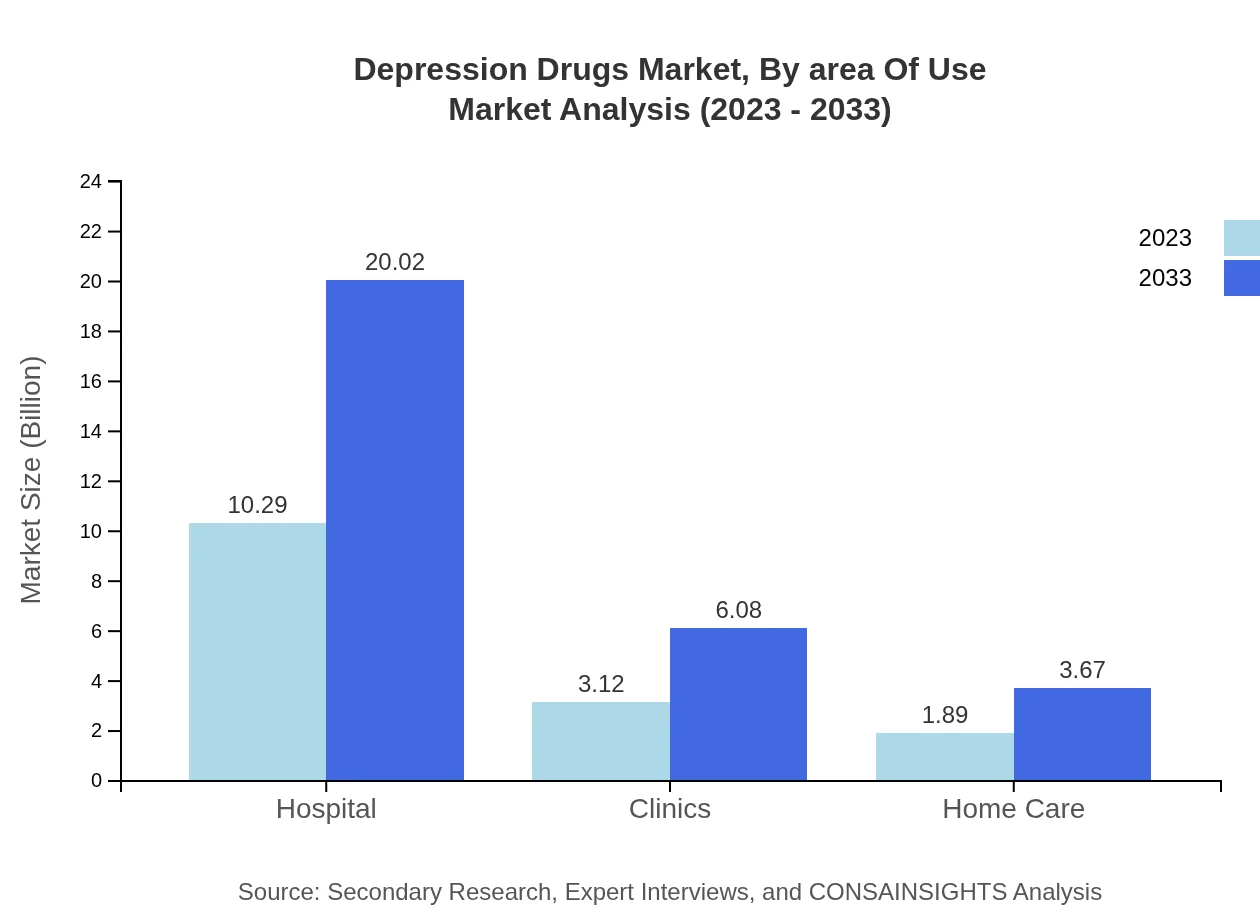
Depression Drugs Market Analysis By Area Of Use
The area of use analysis reveals significant market sizes in healthcare settings. Hospitals account for a dominant market size of USD 10.29 billion in 2023, expected to increase to USD 20.02 billion by 2033, holding a 67.24% share. Clinics serve a substantial market as well, with sizes expanding from USD 3.12 billion to USD 6.08 billion, while home care segments grow from USD 1.89 billion to USD 3.67 billion.
Depression Drugs Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Depression Drugs Industry
Pfizer Inc.:
A leading pharmaceuticals company, Pfizer develops commonly used SSRIs and is known for its significant R&D investment in mental health medications.Eli Lilly and Company:
Eli Lilly offers a broad portfolio of mental health treatments, including well-recognized antidepressants, and maintains a strong presence in global markets.Johnson & Johnson:
Johnson & Johnson produces a range of psychological medications, contributing significantly through innovations in treatment methodologies.GlaxoSmithKline:
Specializing in multiple therapeutic areas, GlaxoSmithKline enhances the depression drugs landscape with its diverse offerings tailored for patient needs.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of depression Drugs?
The global market for depression drugs is valued at approximately $15.3 billion in 2023, with an impressive CAGR of 6.7% projected through 2033, indicating growth in demand and innovation in therapeutic options.
What are the key market players or companies in this depression Drugs industry?
Key players within the depression-drugs market include major pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline, who are involved in research, development, and distribution of various antidepressants.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the depression Drugs industry?
Factors driving growth in the depression-drugs market include increasing awareness of mental health issues, advancements in drug formulation, and the rising prevalence of depression globally, resulting in greater demand for effective treatments.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the depression Drugs?
The fastest-growing region in the depression-drugs market is Europe, projected to expand from $5.34 billion in 2023 to $10.39 billion by 2033, reflecting an increasing focus on mental health services and treatment accessibility.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the depression Drugs industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the depression-drugs industry, tailored to meet client-specific requirements, including detailed market analysis, trends, and competitive landscapes.
What deliverables can I expect from this depression Drugs market research project?
Deliverables from the depression-drugs market research project include comprehensive market reports, trend analysis, segmentation insights, and forecasts with supporting data visualizations and actionable recommendations.
What are the market trends of depression Drugs?
Current trends in the depression-drugs market include the growth of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), increasing use of alternative therapies, and innovation in drug delivery methods, boosting patient adherence and treatment effectiveness.