Distribution Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: distribution-automation
Distribution Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Distribution Automation market from 2023 to 2033, offering insights into market size, segmentation, technological advancements, regional performance, and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
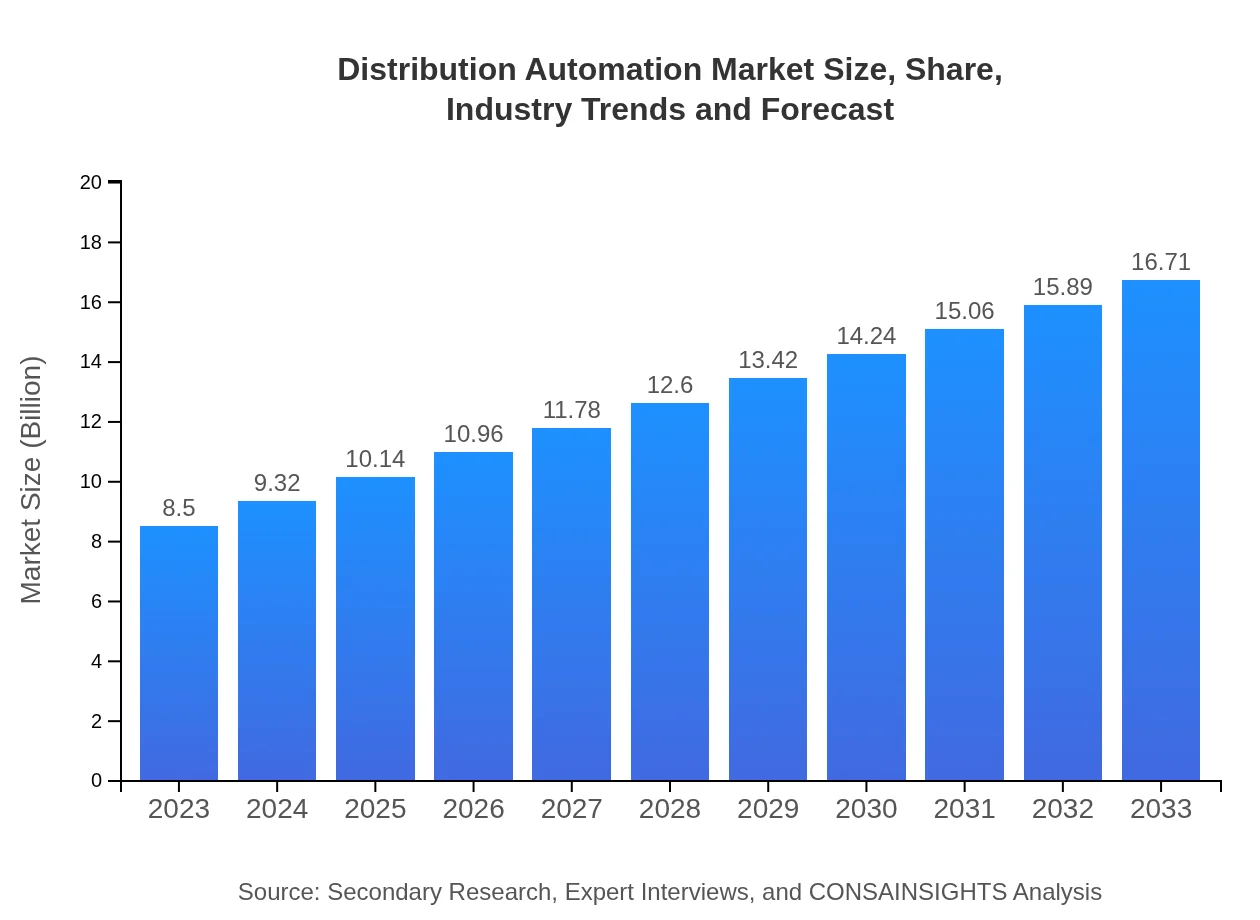
| 2023 Market Size | $8.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $16.71 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric Company, ABB Ltd., Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Distribution Automation Market Overview
Customize Distribution Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Distribution Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Distribution Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Distribution Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Distribution Automation market in 2023?
Distribution Automation Industry Analysis
Distribution Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
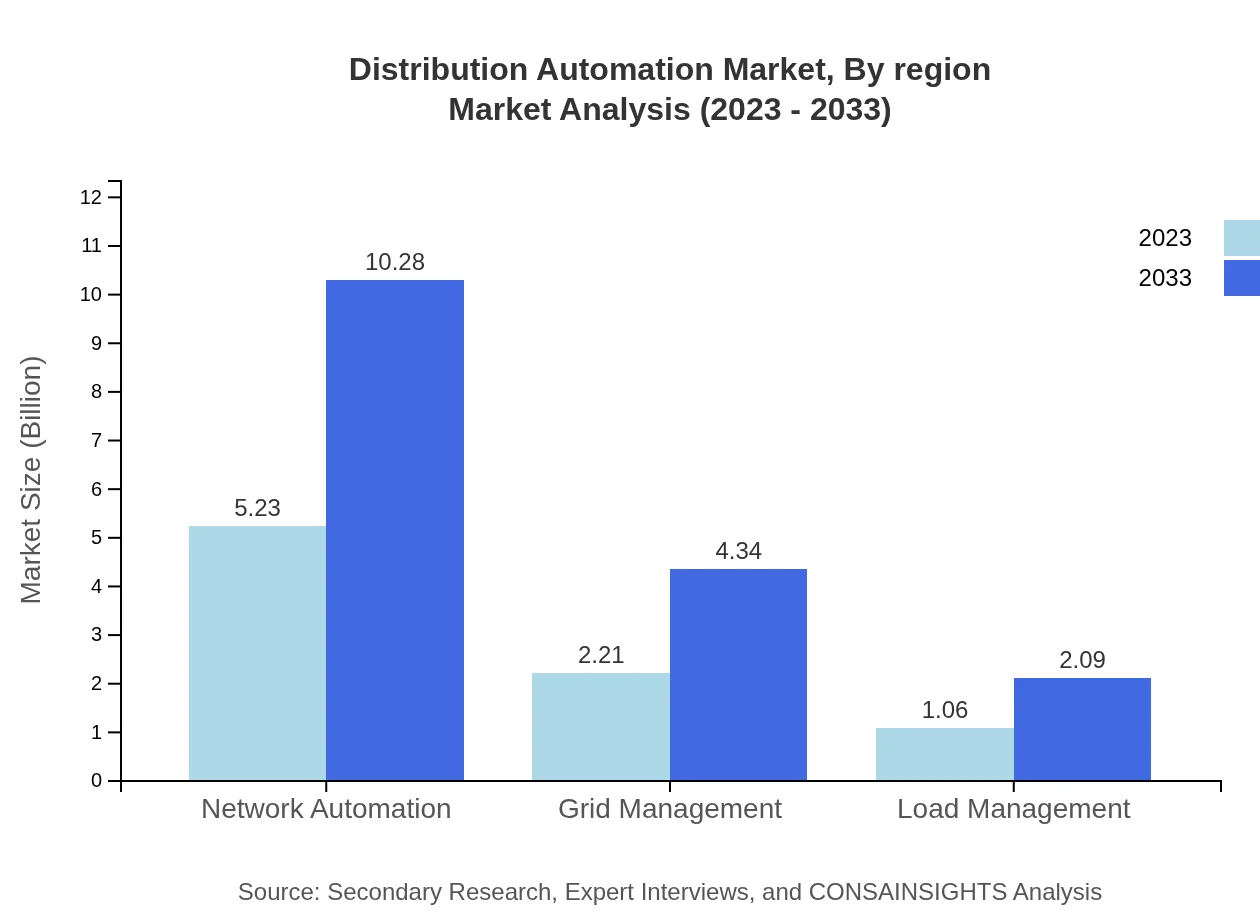
Distribution Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Distribution Automation Market Report:
Europe's Distribution Automation market is set to grow from $2.75 billion in 2023 to $5.41 billion by 2033. The region is a leader in adopting smart grids and renewable energy initiatives, with many countries pushing for sustainable energy solutions and regulatory support for grid evolution.Asia Pacific Distribution Automation Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Distribution Automation market is expected to grow from $1.59 billion in 2023 to $3.13 billion by 2033. Key drivers include rapid urbanization, increasing electricity demand, and government initiatives to enhance the grid. Countries like China and India are leading investments in smart grid technologies.North America Distribution Automation Market Report:
In North America, the market is projected to increase from $3.12 billion in 2023 to $6.13 billion by 2033. Factors such as aging infrastructure, regulatory mandates, and a shift towards renewable energy sources strongly influence market dynamics. Major investments in grid modernization are expected in the US and Canada.South America Distribution Automation Market Report:
The South America Distribution Automation market is forecasted to grow from $0.53 billion in 2023 to $1.05 billion by 2033. Growth factors include growing energy demand and the need for reliable electricity supplies amid socio-economic developments. Brazil and Argentina are leading the adoption of DA technologies.Middle East & Africa Distribution Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market will expand from $0.50 billion in 2023 to $0.99 billion by 2033. Despite being smaller, the market is gaining traction due to increased investments in energy infrastructure and initiatives aimed at integrating renewable energy sources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
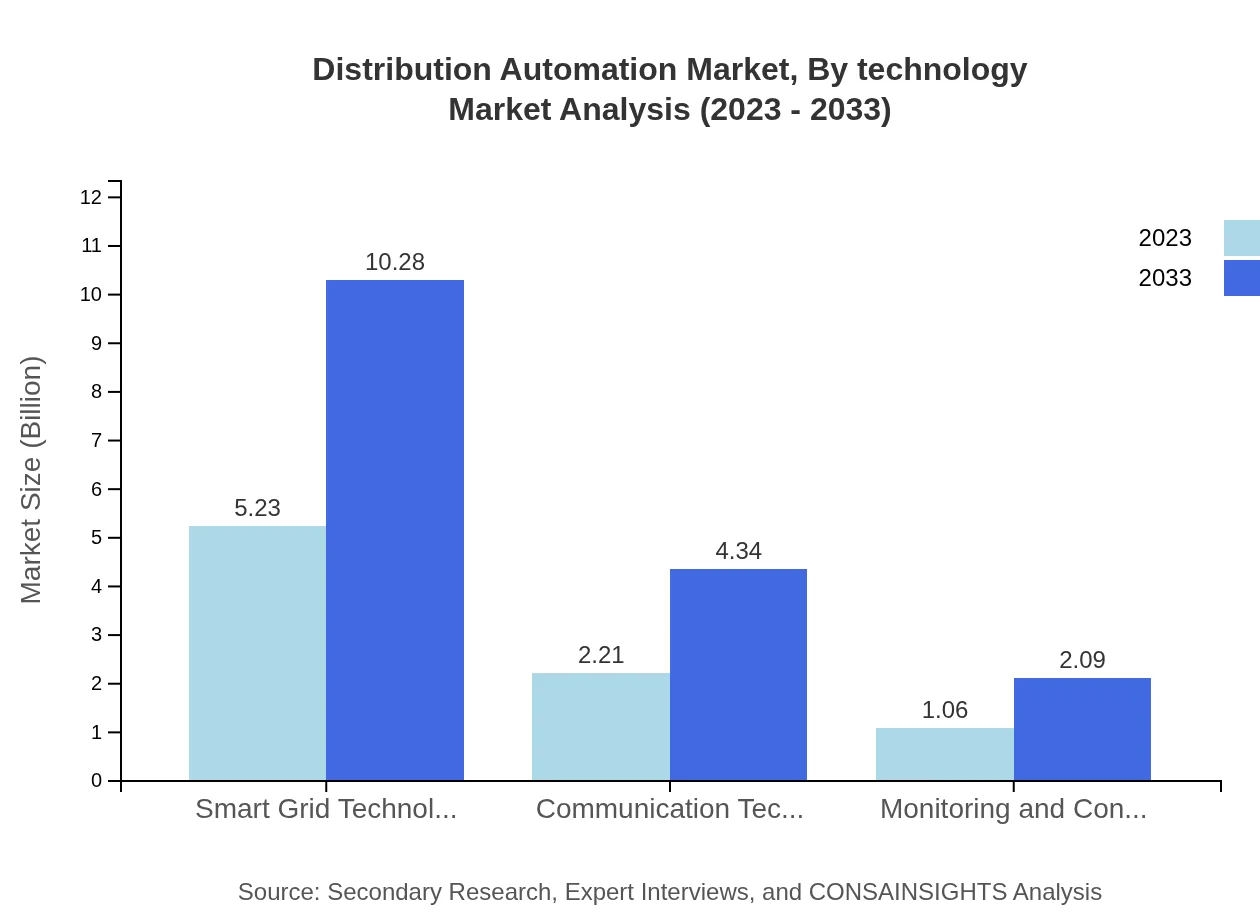
Distribution Automation Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment includes hardware components, software solutions, and services. Hardware components, leading the market with a share of 61.54% and valued at $5.23 billion in 2023, are critical for implementing automation solutions. Software solutions account for 25.97% of the market, providing vital integration for DA systems. Services contribute to implementation and maintenance, ensuring operational efficiency.
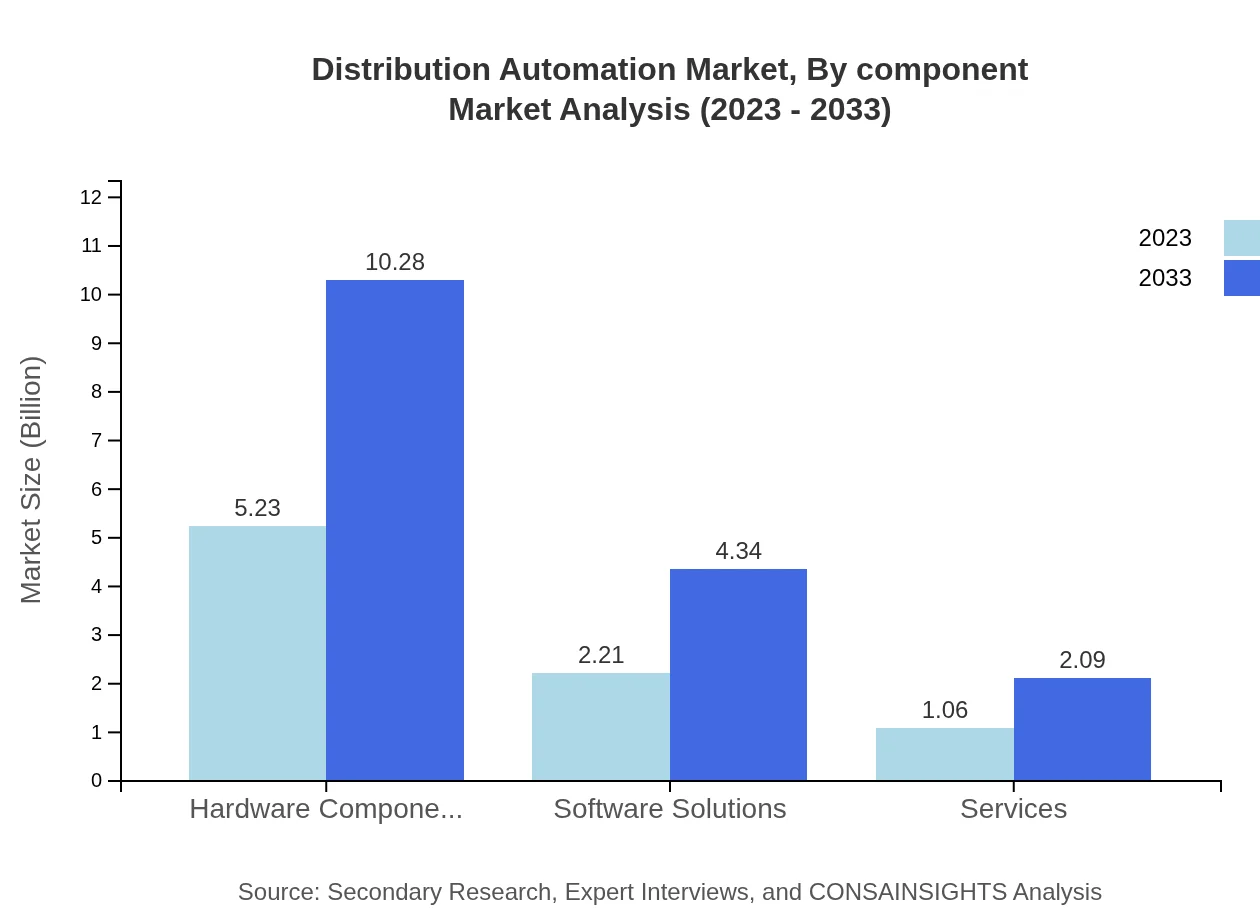
Distribution Automation Market Analysis By Component
In terms of components, the Distribution Automation market includes grid management, monitoring and control systems, communication technologies, and more. Grid management solutions are significant, accounting for approximately 25.97% of total market share. Monitoring and control systems, though smaller, grow steadily as utilities increasingly focus on operational reliability.
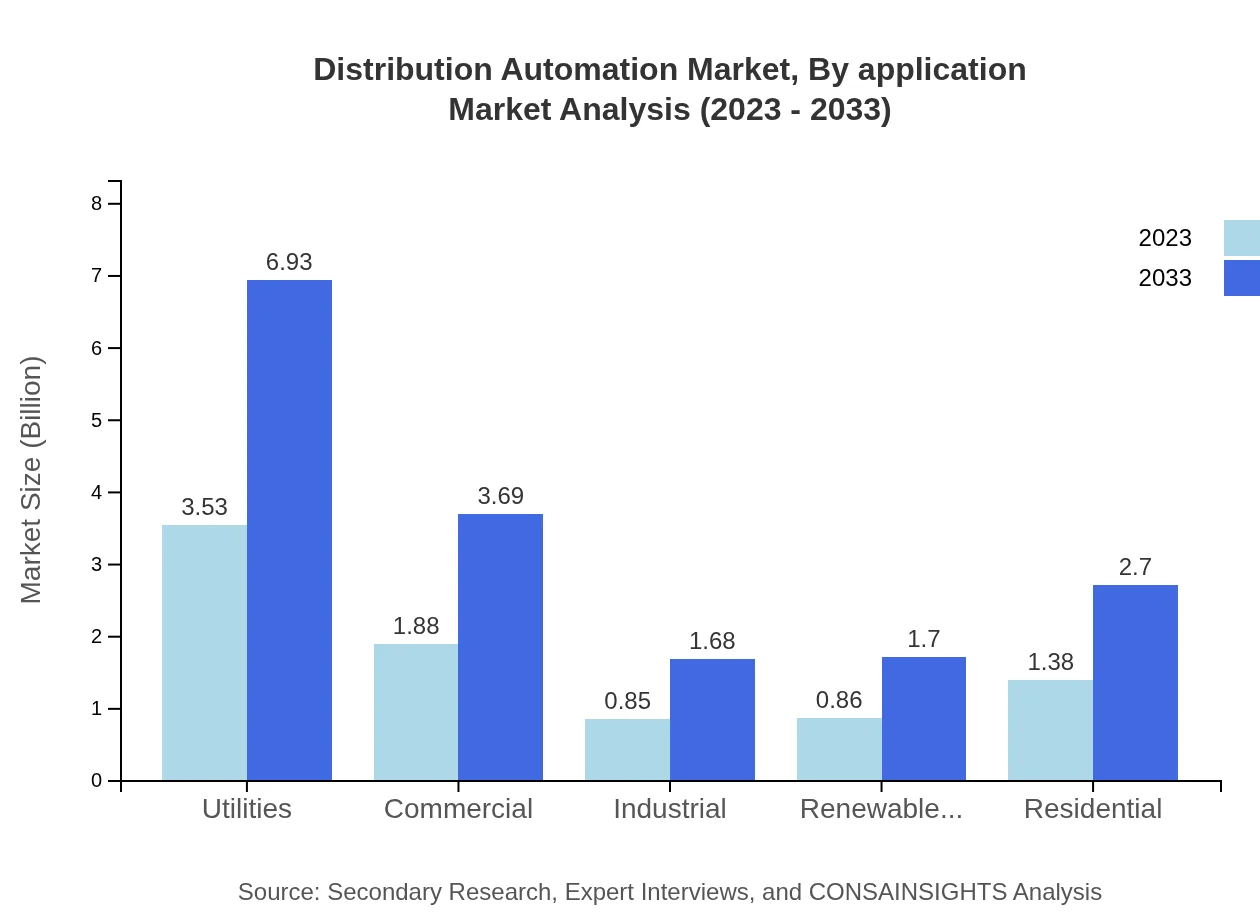
Distribution Automation Market Analysis By Application
The market is also segmented by application, focusing on utilities, commercial use, renewable energy integration, and residential applications. Utilities dominate, holding 41.51% of the market share in 2023 due to the critical need for efficiency improvements. Commercial applications are growing as businesses increasingly adopt automation to optimize energy use.
Distribution Automation Market Analysis By Region
The market's functionality segment shows growth across various applications, such as load management, crisis management, and energy distribution. Each functionality plays a crucial role in enhancing the operational aspects of electrical distribution, with significant roles in maintaining system reliability.
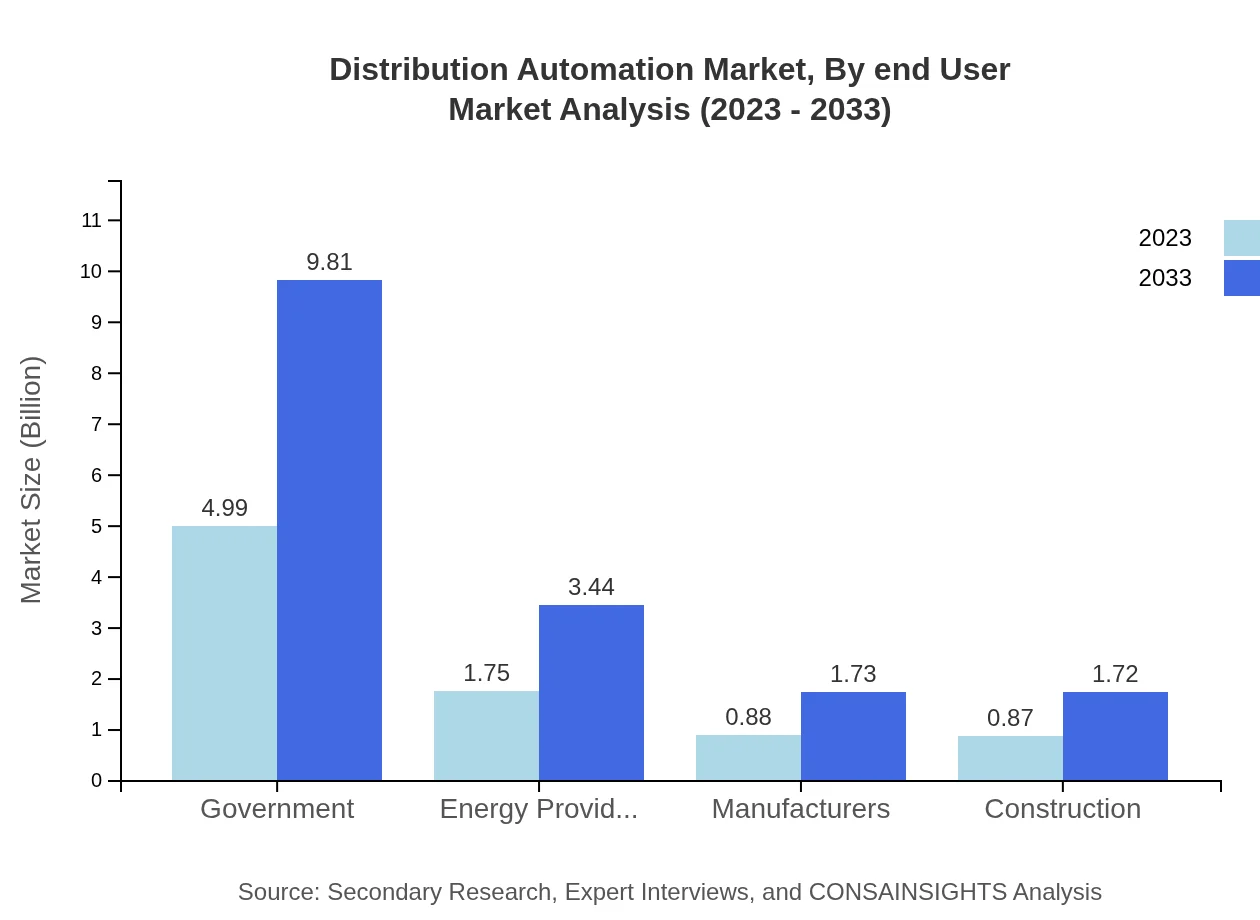
Distribution Automation Market Analysis By End User
Distribution Automation holds significance across various end-user industries, including energy providers, manufacturing and construction sectors, and government applications. Government implementations account for a large share due to increasing mandates for sustainable and resilient energy systems, marking a transformative shift in energy distribution.
Distribution Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Distribution Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a global engineering company that offers comprehensive solutions in automation and digitalization in energy, manufacturing, and transportation sectors, providing innovative DA technologies.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric specializes in digital transformation of energy management and automation solutions, driving efficiency and sustainability through its Distribution Automation services.General Electric Company:
General Electric is known for its diversified industrial operations, including comprehensive DA solutions enhancing grid performance and reliability.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a leader in electrification and automation, providing advanced technologies that enable the efficient operation of electrical distributions.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell delivers advanced solutions in automation and technology that serve the needs of dynamic energy and commercial sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of distribution Automation?
The global distribution automation market is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023. This growth signals increasing investments in technology to enhance grid reliability and efficiency.
What are the key market players or companies in this distribution Automation industry?
Key players in the distribution automation industry include Siemens, Schneider Electric, ABB, and General Electric. These companies are leaders in technology and innovation, providing various solutions that ensure efficient power distribution and smart grid integration.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the distribution Automation industry?
Growth drivers include advancements in smart grid technology, increasing demand for reliable power distribution, regulatory push for modernizing infrastructure, and the rise in renewable energy sources, necessitating improved distribution management and control systems.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the distribution Automation?
The North American region is the fastest-growing market in distribution automation, with its market expected to rise from $3.12 billion in 2023 to $6.13 billion by 2033. This growth showcases an urgent investment in infrastructure and technology upgrades.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the distribution Automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to client-specific needs in the distribution automation industry, ensuring they receive the most relevant and precise insights for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this distribution Automation market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports including market size, segmentation data, growth forecasts, regional analysis, competitive landscape, and strategic recommendations to help identify market opportunities and inform your business strategies.
What are the market trends of distribution automation?
Current trends include increased adoption of renewable energy integration, growth in smart grid technologies, and the rise in hardware and software solutions that improve grid management, ensuring operational efficiency and reliability in power distribution.