Dna Sequencing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: dna-sequencing
Dna Sequencing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides a comprehensive analysis of the DNA Sequencing market, focusing on insights, growth forecasts, and trends from 2023 to 2033, covering various segments, regional analyses, and key market leaders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
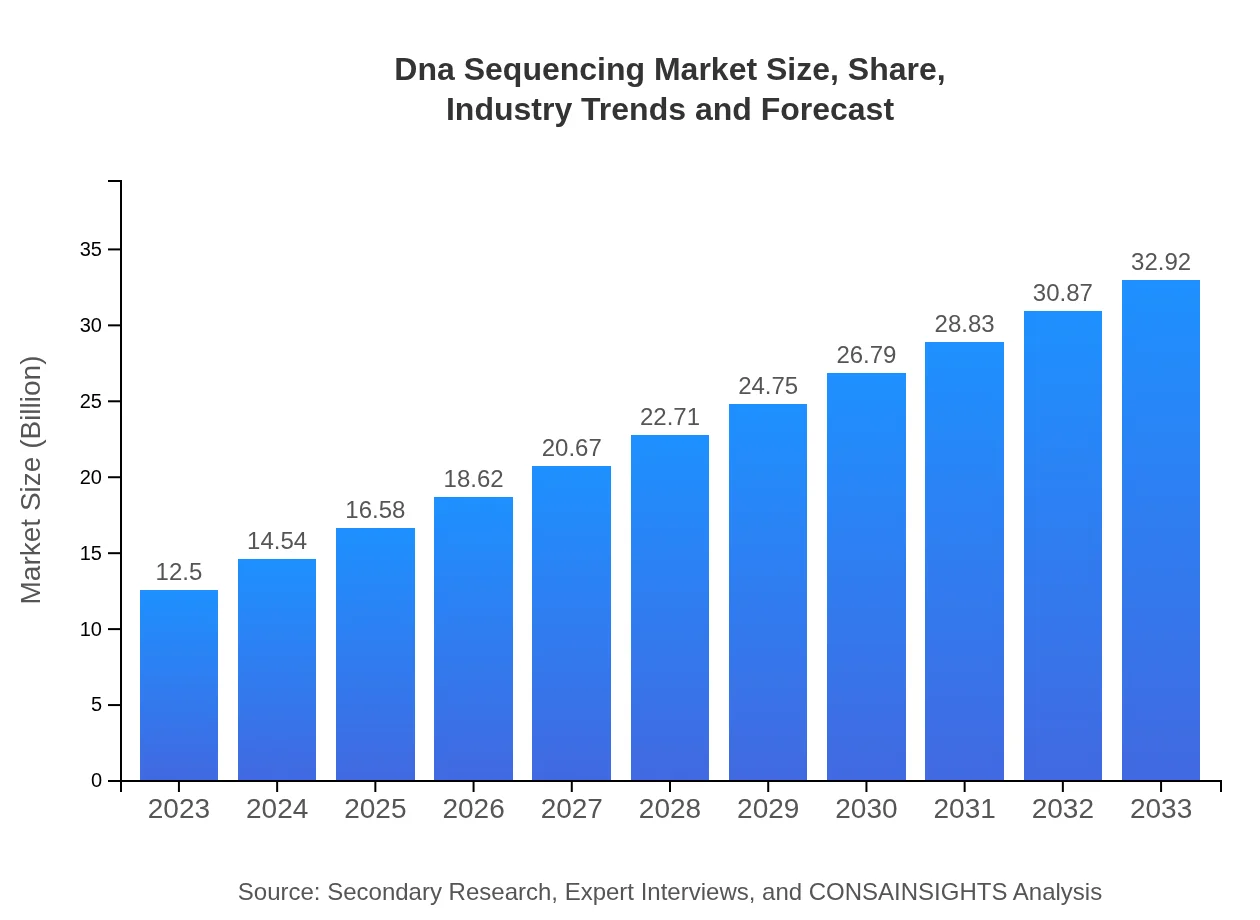
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | Illumina, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., BGI Group, Agilent Technologies, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Dna Sequencing Market Overview
Customize Dna Sequencing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Dna Sequencing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Dna Sequencing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Dna Sequencing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Dna Sequencing market in 2023?
Dna Sequencing Industry Analysis
Dna Sequencing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Dna Sequencing Market Report:
The European market for DNA sequencing is forecasted to expand from $3.68 billion in 2023 to $9.70 billion by 2033. Factors driving this growth include stringent regulatory frameworks promoting genetic research and enhanced healthcare solutions stemming from genomic technologies.Asia Pacific Dna Sequencing Market Report:
In Asia Pacific, the DNA sequencing market is expected to grow from $2.28 billion in 2023 to $6.01 billion by 2033, driven by increasing investments in biotechnology and a rising demand for genetic research. Countries like China and India have seen substantial governmental and private sector support aimed at advancing genomic analysis capabilities.North America Dna Sequencing Market Report:
North America dominates the DNA sequencing market, with a market size of $4.72 billion in 2023, projected to reach $12.44 billion by 2033. This region benefits from well-established healthcare infrastructure, high expenditures on R&D, and prominent players like Illumina and Thermo Fisher Scientific leading in innovation.South America Dna Sequencing Market Report:
South America’s DNA sequencing market, valued at approximately $0.62 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $1.64 billion by 2033. The growth is propelled by a burgeoning interest in genetic research and the implementation of sequencing technologies in clinical diagnostics.Middle East & Africa Dna Sequencing Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the DNA sequencing market is expected to grow from $1.19 billion in 2023 to $3.12 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by increasing awareness of genomic technologies and their potential applications in sectors like agriculture and healthcare.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
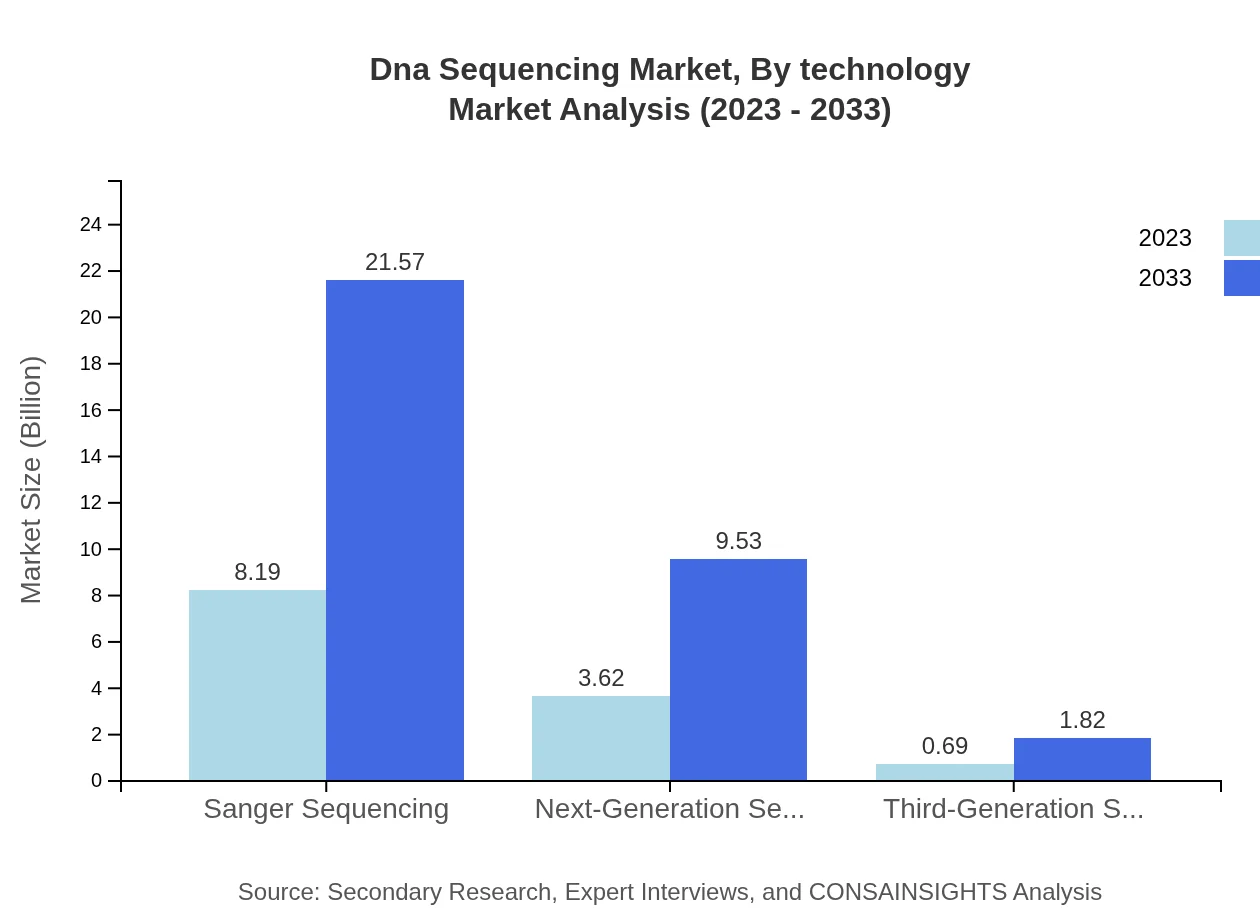
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis By Technology
In 2023, the Sanger Sequencing segment holds a market size of $8.19 billion, indicating a significant share of 65.53%. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), valued at $3.62 billion, accounts for 28.95%. Contrary, Third-Generation Sequencing, although growing, makes up a smaller portion at $0.69 billion (5.52%). As technological advancements continue, NGS is expected to lead the market with its extensive applications in diverse fields.
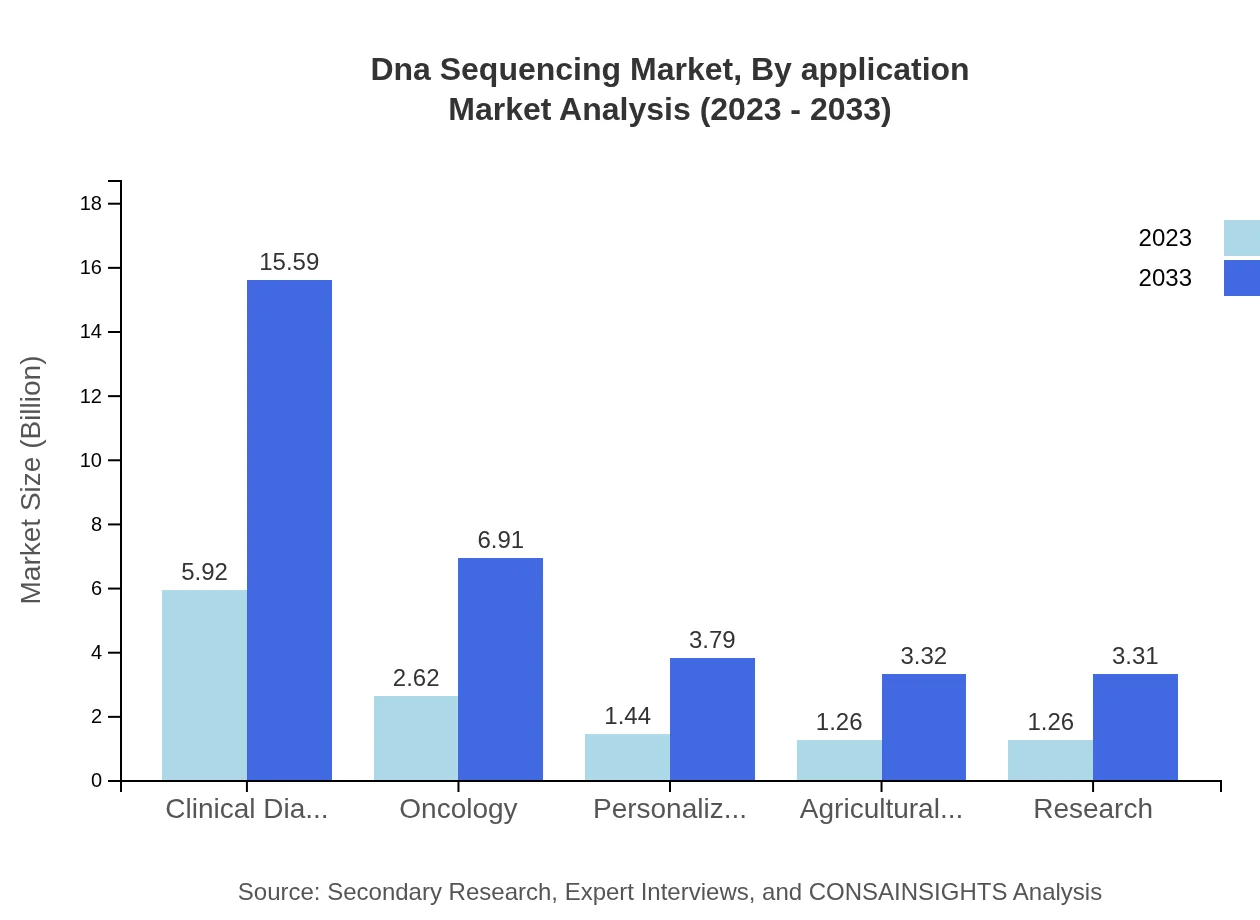
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis By Application
Clinical diagnostics is the leading application segment, valued at $5.92 billion in 2023 with a significant market share of 47.36%. The oncology application follows with a size of $2.62 billion (20.98%), while personalized medicine and agricultural biotechnology represent growing applications, valued at $1.44 billion (11.51%) and $1.26 billion (10.10%), respectively. As personalized healthcare grows, these segments are expected to see enhanced investments and developments.
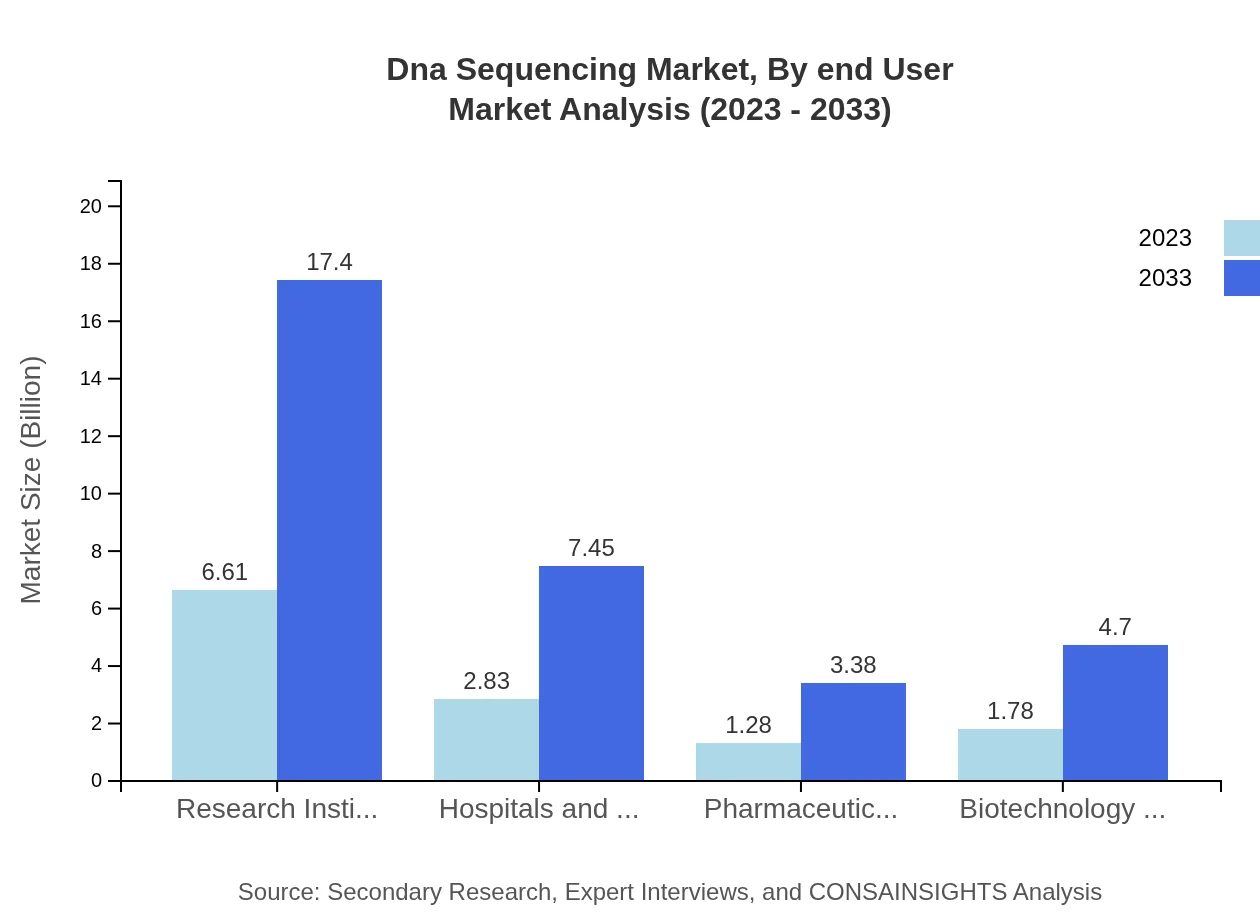
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis By End User
Research institutions dominate the end-user segment, estimated at $6.61 billion in 2023 and holding a stable share of 52.85%. Hospitals and Clinics follow with a size of $2.83 billion (22.62%), complemented by pharmaceutical companies at $1.28 billion (10.26%). The collaborative efforts between these sectors in genomics research will further enhance the adoption of sequencing technologies.
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis By Region
Global DNA Sequencing Market, By Region Market Analysis (2023 - 2033)
Regional segmentation shows North America as the leader, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific, each presenting unique growth drives. North America’s established infrastructure and extensive sequencing applications reaffirm its leading status, while Europe pursues robust regulations that encourage innovative genetic research. The Asia Pacific region is marked by rapid development in research capabilities, enhancing the global potential.
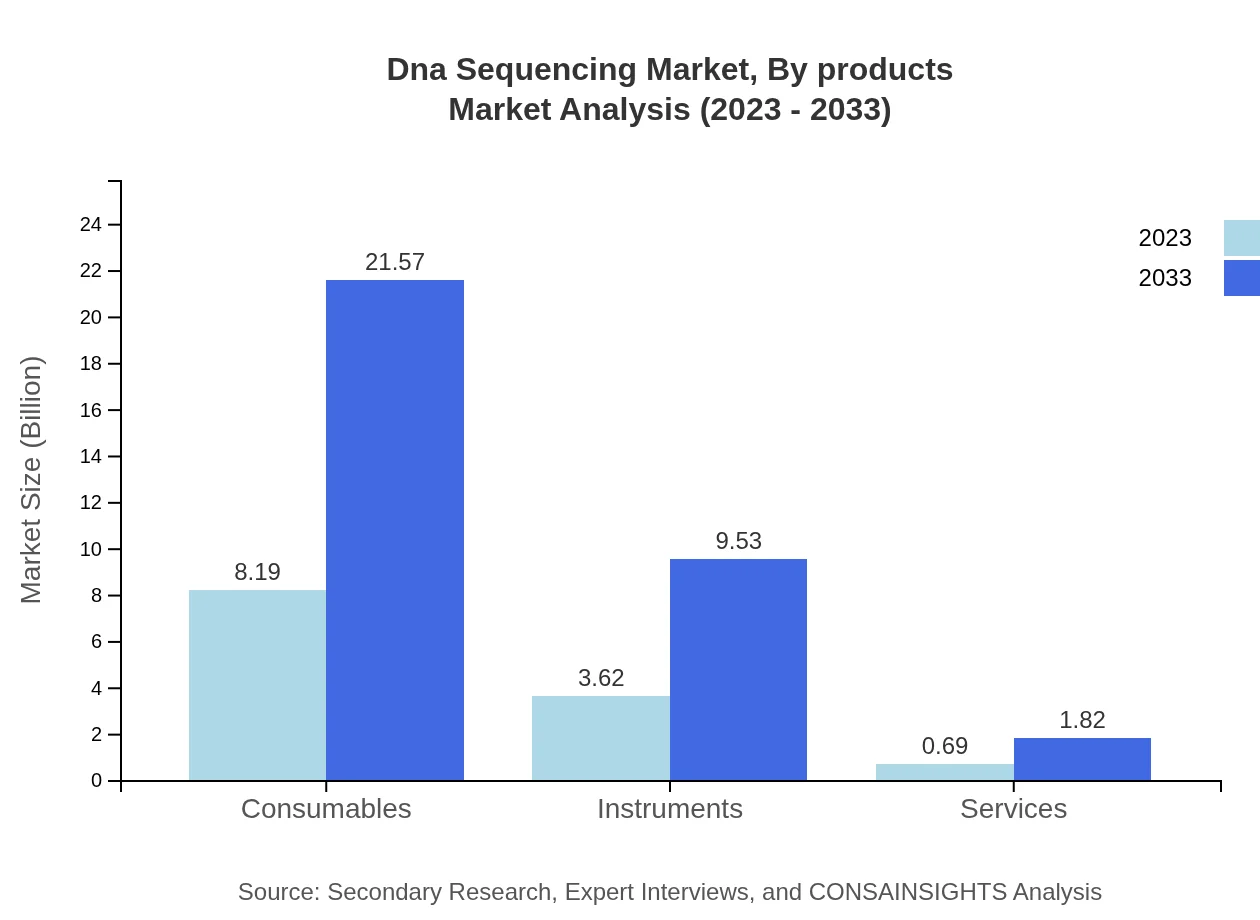
Dna Sequencing Market Analysis By Products
The product categories include consumables, instruments, and services. Consumables lead the market with a size of $8.19 billion (65.53%), highlighting the manufacturing demands for reagents and kits. Instruments, critical for performing sequencing tasks, represent $3.62 billion (28.95%), while services account for a smaller segment at $0.69 billion (5.52%). This distribution underlines the importance of consumable sales driving overall market revenues.
Dna Sequencing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Dna Sequencing Industry
Illumina, Inc.:
A market leader in DNA sequencing technology, Illumina specializes in NGS platforms that are extensively used in various genomic applications, including oncology and hereditary disease research.Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.:
Thermo Fisher offers a wide range of products and services related to DNA sequencing, including consumables and instruments, underscoring its critical role in genetic research.BGI Group:
A prominent genomics organization from China, BGI is a globally recognized entity contributing to technological advancements in NGS and providing large-scale genomic services.Agilent Technologies, Inc.:
Agilent provides comprehensive genomic solutions and instruments, playing a significant role in the DNA sequencing landscape through innovative products.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of dna Sequencing?
The global DNA sequencing market is estimated to be approximately $12.5 billion in 2023, with a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.8%. Projections suggest significant expansion, with an expected market size of $34.5 billion by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this dna Sequencing industry?
Key market players in the DNA sequencing industry include Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Roche, BGI, and Genomatix. These companies lead in innovation, technology development, and market share within this rapidly evolving sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the dna Sequencing industry?
Growth in the DNA sequencing industry is driven by technological advancements, increasing applications in healthcare, expanding genomics research, demand for personalized medicine, and rising investments in research and development across regions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the dna Sequencing?
The Asia Pacific region is poised to be the fastest-growing in the DNA sequencing market, expanding from $2.28 billion in 2023 to $6.01 billion by 2033, demonstrating the highest growth potential within the global landscape.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the dna Sequencing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the DNA sequencing industry, enabling clients to obtain tailored insights that meet their specific research needs and business objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this dna Sequencing market research project?
Deliverables from the DNA sequencing market research project typically include comprehensive reports, market analyses, segmented insights, competitive landscape evaluations, and forecasts outlining future trends and opportunities.
What are the market trends of dna Sequencing?
Current market trends in DNA sequencing include increasing adoption of next-generation sequencing technologies, greater emphasis on personalized medicine, enhanced efficiency in sequencing processes, and growth in applications across clinical diagnostics and agricultural biotechnology.