Dna Testing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: dna-testing
Dna Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the DNA Testing market, covering insights on market size, trends, technological advancements, and forecasts for the period from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
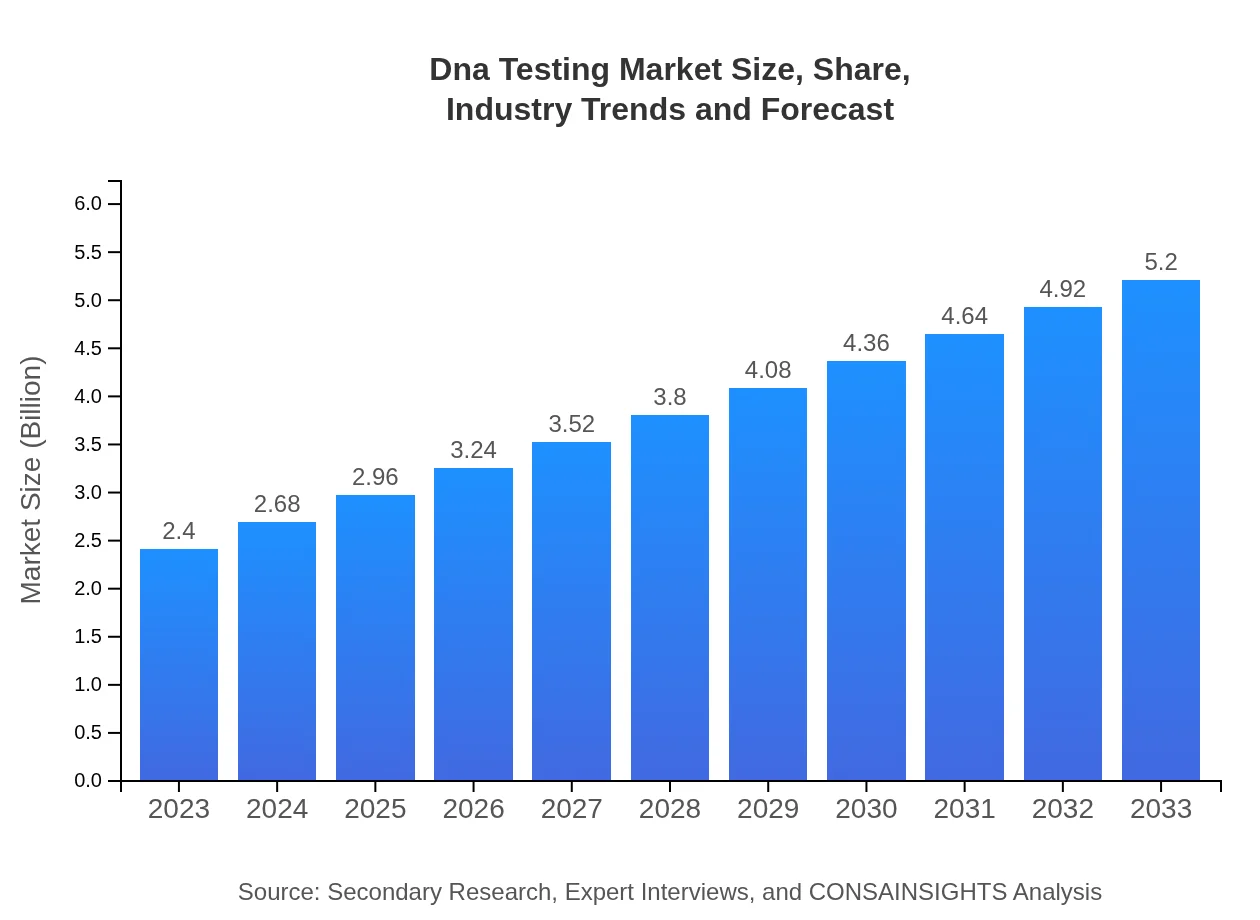
| 2023 Market Size | $2.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $5.20 Billion |
| Top Companies | 23andMe, Ancestry.com, Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
DNA Testing Market Overview
Customize Dna Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Dna Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Dna Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Dna Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of DNA Testing market in 2023?
DNA Testing Industry Analysis
DNA Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
DNA Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Dna Testing Market Report:
In Europe, the market is anticipated to grow from $0.61 billion in 2023 to $1.31 billion by 2033, propelled by advanced healthcare infrastructure and a strong focus on preventative healthcare measures.Asia Pacific Dna Testing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific DNA Testing market is projected to grow significantly from $0.47 billion in 2023 to $1.03 billion by 2033, driven by increased healthcare spending and rising awareness of genetic disorders in countries such as China and India.North America Dna Testing Market Report:
North America held a market size of $0.84 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1.82 billion by 2033, led by technological innovations and favorable government policies supporting genetic research and testing.South America Dna Testing Market Report:
The South American market, valued at $0.17 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $0.37 billion by 2033, indicating growing demand primarily in Brazil and Argentina, where awareness of genetic testing is on the rise.Middle East & Africa Dna Testing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa DNA Testing market is expected to grow from $0.31 billion in 2023 to $0.67 billion by 2033, assisted by rising health awareness and improvements in healthcare services in countries like South Africa and UAE.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
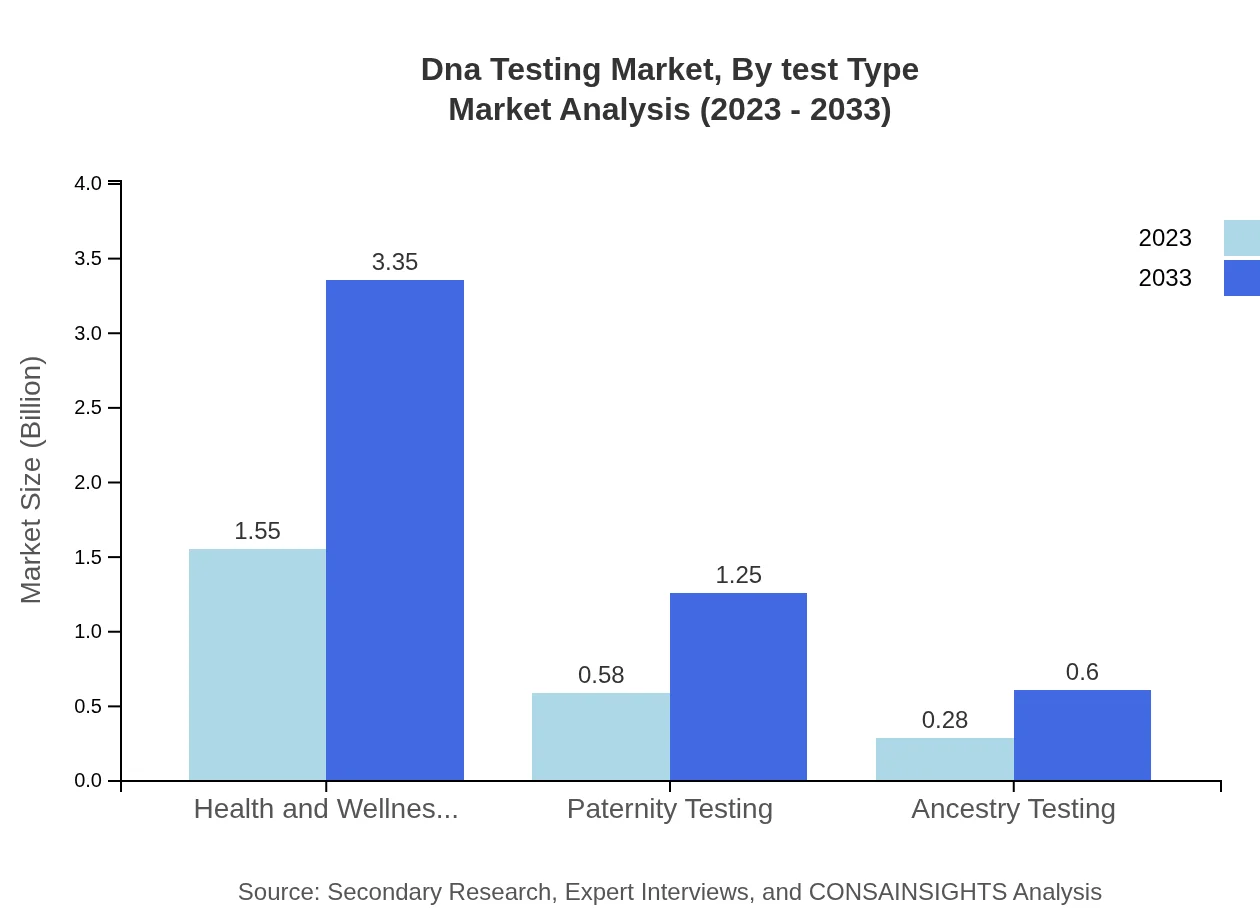
Dna Testing Market Analysis By Test Type
The Health and Wellness Testing segment dominates the market, growing from $1.55 billion in 2023 to $3.35 billion in 2033, capturing 64.38% market share. Other key segments include Paternity Testing and Ancestry Testing, which are also witnessing growth driven by increased consumer engagement in health-related decisions.
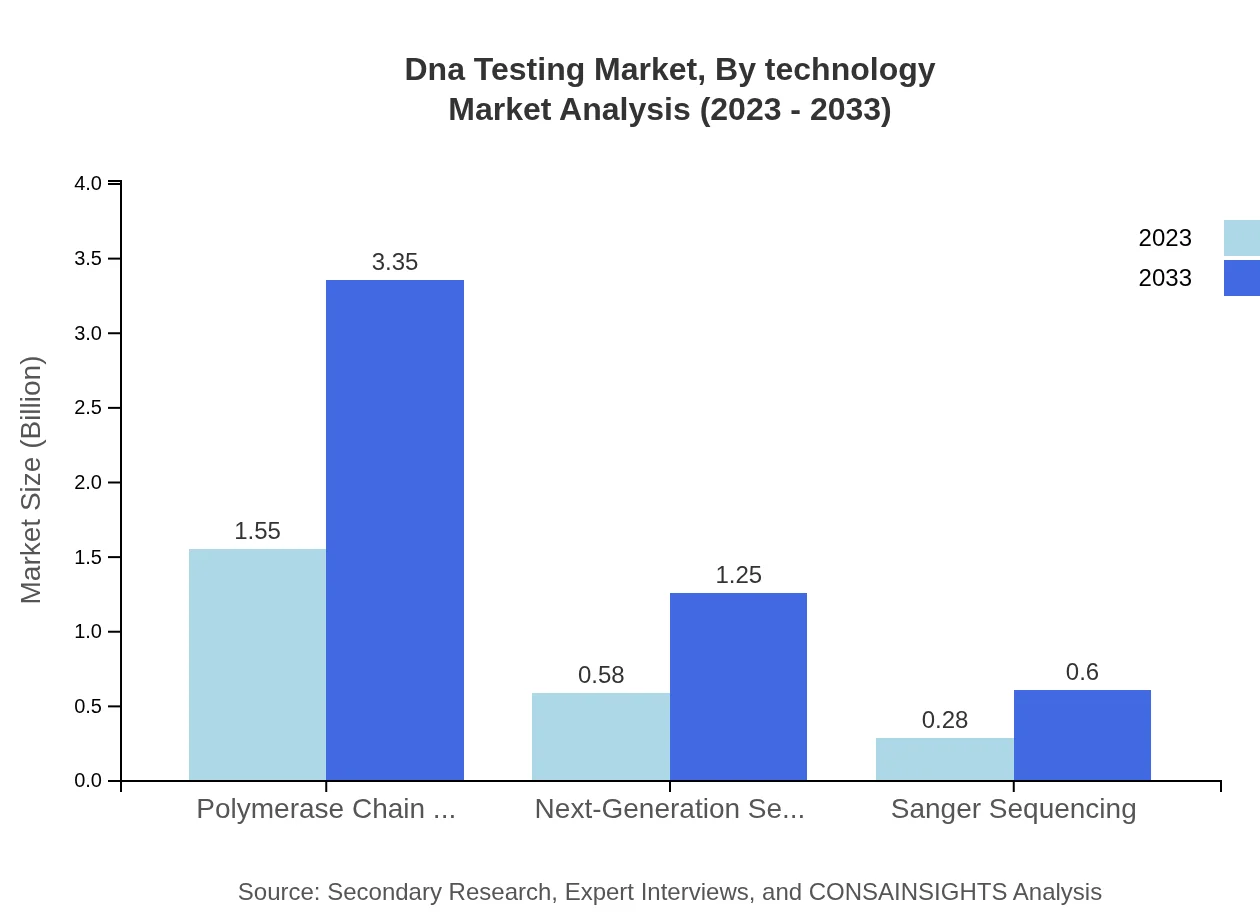
Dna Testing Market Analysis By Technology
Technologies such as PCR and NGS lead the DNA Testing market, accounting for 64.38% and 24% market shares, respectively. PCR is expected to grow from $1.55 billion in 2023 to $3.35 billion in 2033, while NGS is anticipated to rise from $0.58 billion in 2023 to $1.25 billion by 2033.
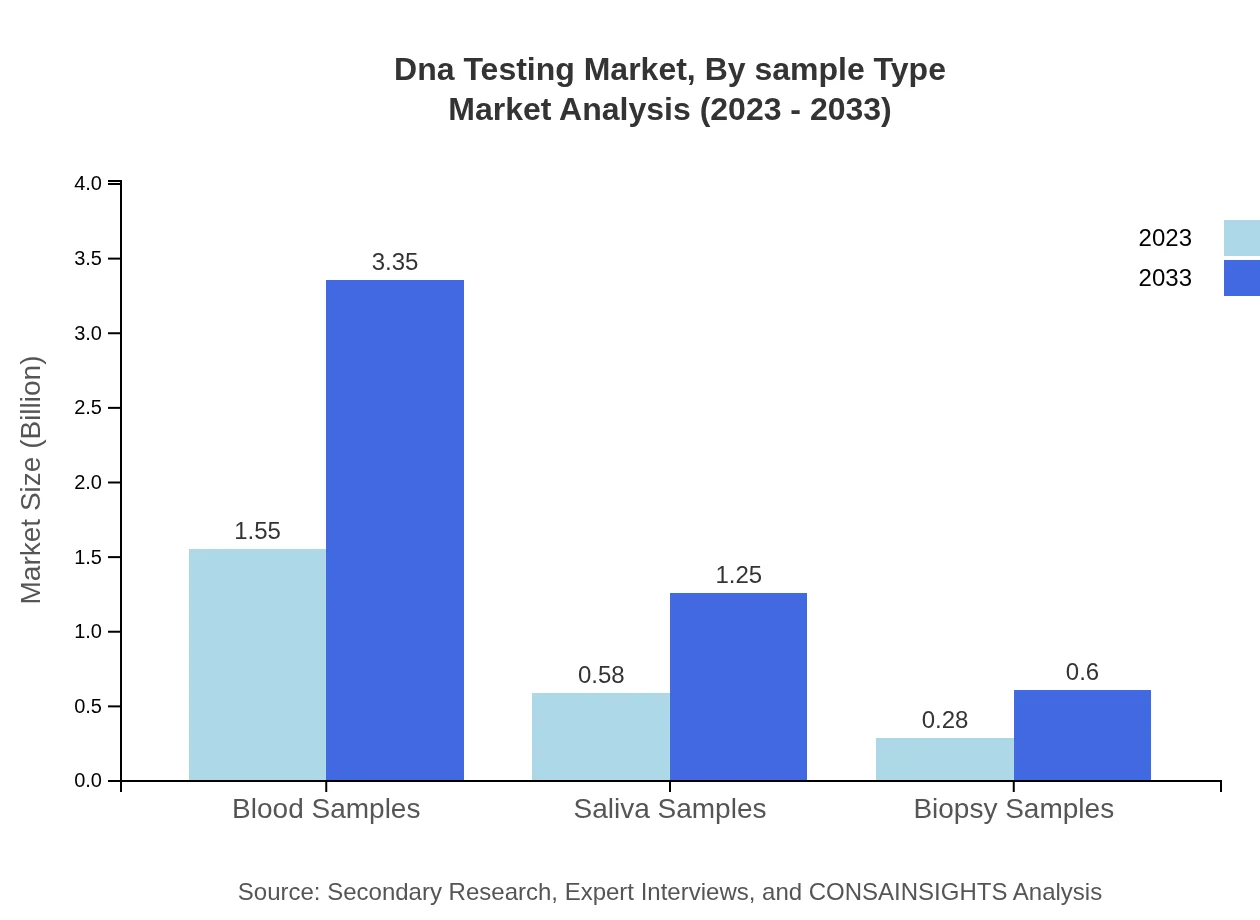
Dna Testing Market Analysis By Sample Type
Blood samples remain the dominant sample type, representing 64.38% market share and projected to grow from $1.55 billion in 2023 to $3.35 billion in 2033. Saliva samples and biopsy samples also show promising growth trajectories.
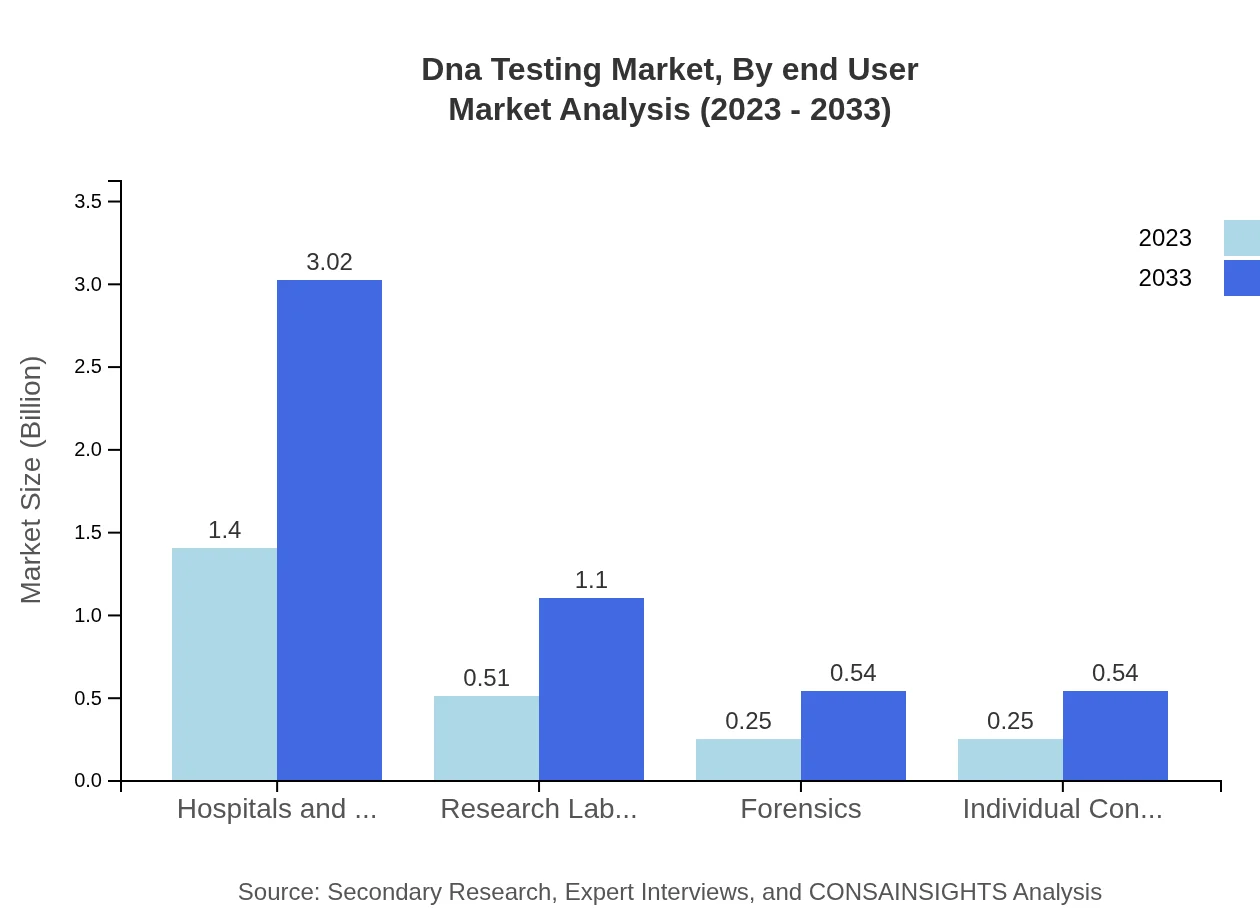
Dna Testing Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals and clinics remain the predominant end-users, accounting for 58.14% market share, expected to grow from $1.40 billion in 2023 to $3.02 billion in 2033, driven by increasing healthcare investments and rising laboratory capabilities.
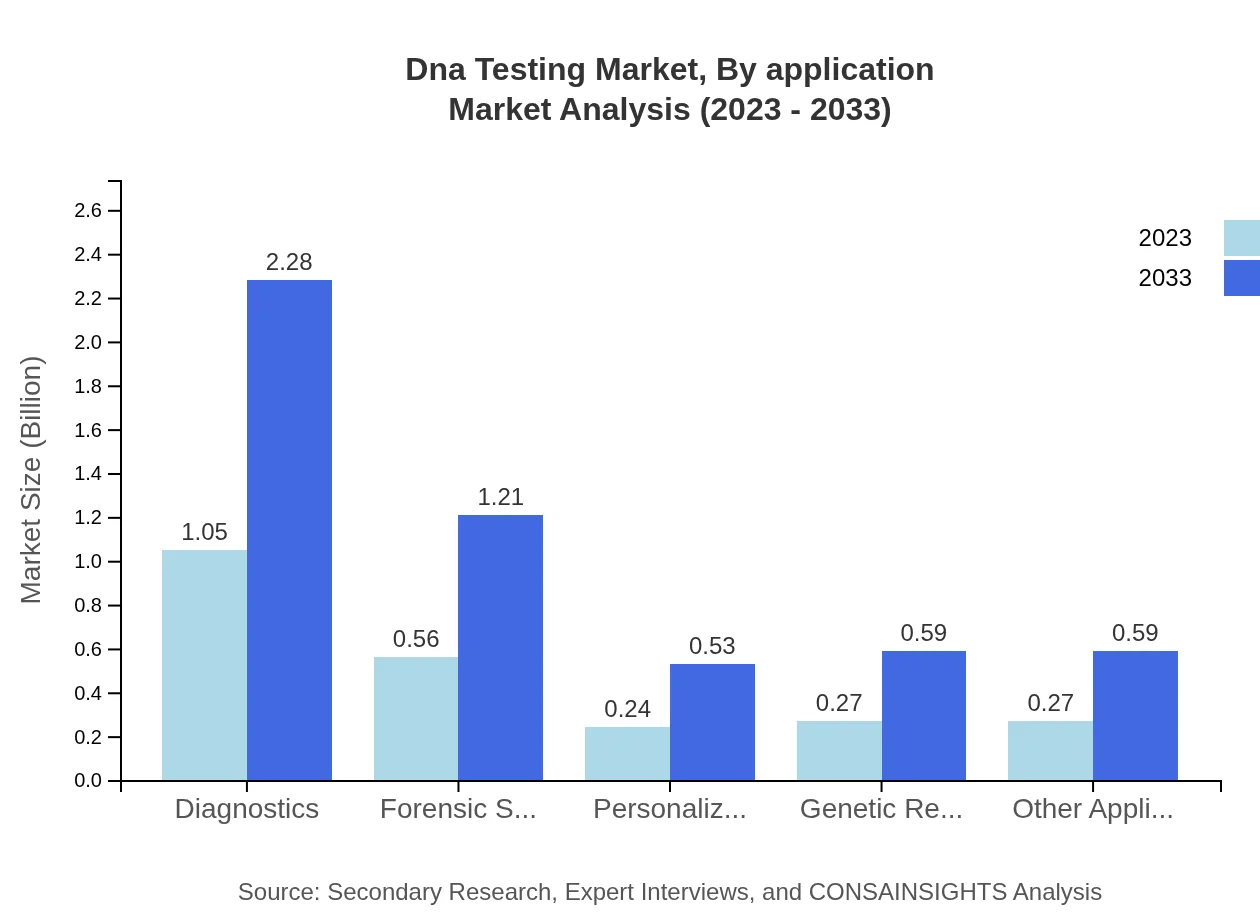
Dna Testing Market Analysis By Application
The diagnostics application segment leads the market with a 43.87% share, projected to grow from $1.05 billion in 2023 to $2.28 billion by 2033, fueled by the growing need for accurate disease screening and preventive healthcare.
DNA Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in DNA Testing Industry
23andMe:
23andMe offers genetic testing services that provide insights into ancestry and health traits with user-friendly at-home kits.Ancestry.com:
Ancestry.com specializes in genealogy-related DNA testing services, focusing on ancestry and ethnicity composition.Illumina:
Illumina is a leader in genomic sequencing and the development of NGS solutions for clinical and research applications.Thermo Fisher Scientific:
A global leader in serving science, the company provides various medical and research technologies including DNA testing solutions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of DNA testing?
The DNA testing market is currently valued at approximately $2.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8%, reaching around $4.5 billion by 2033, driven by increasing demand for genetic testing services.
What are the key market players or companies in the DNA testing industry?
Key players in the DNA testing market include 23andMe, Ancestry.com, MyHeritage, Illumina, and Thermo Fisher Scientific, among others, which lead in innovation and technology for genetic analysis.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the DNA testing industry?
Growth factors for the DNA testing industry are increasing consumer interest in ancestry and health insights, advances in biotechnology, decreasing costs of genetic testing, and rising prevalence of genetic disorders.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the DNA testing market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for DNA testing, expected to see increased size growth from $0.47 billion in 2023 to $1.03 billion by 2033, reflecting rising health awareness and testing demand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the DNA testing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs within the DNA testing industry, providing in-depth data and insights for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this DNA testing market research project?
Deliverables from the DNA testing market research project will include comprehensive market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape reviews, and insights into consumer behavior trends in various segments.
What are the market trends of DNA testing?
Key trends in the DNA testing market include increasing interest in personalized medicine, the rise of at-home testing kits, heightened privacy concerns, and collaborative research in genomics to enhance testing accuracy.