Dredging Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: dredging
Dredging Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the dredging market, covering insights into market size, segmentation, industry trends, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
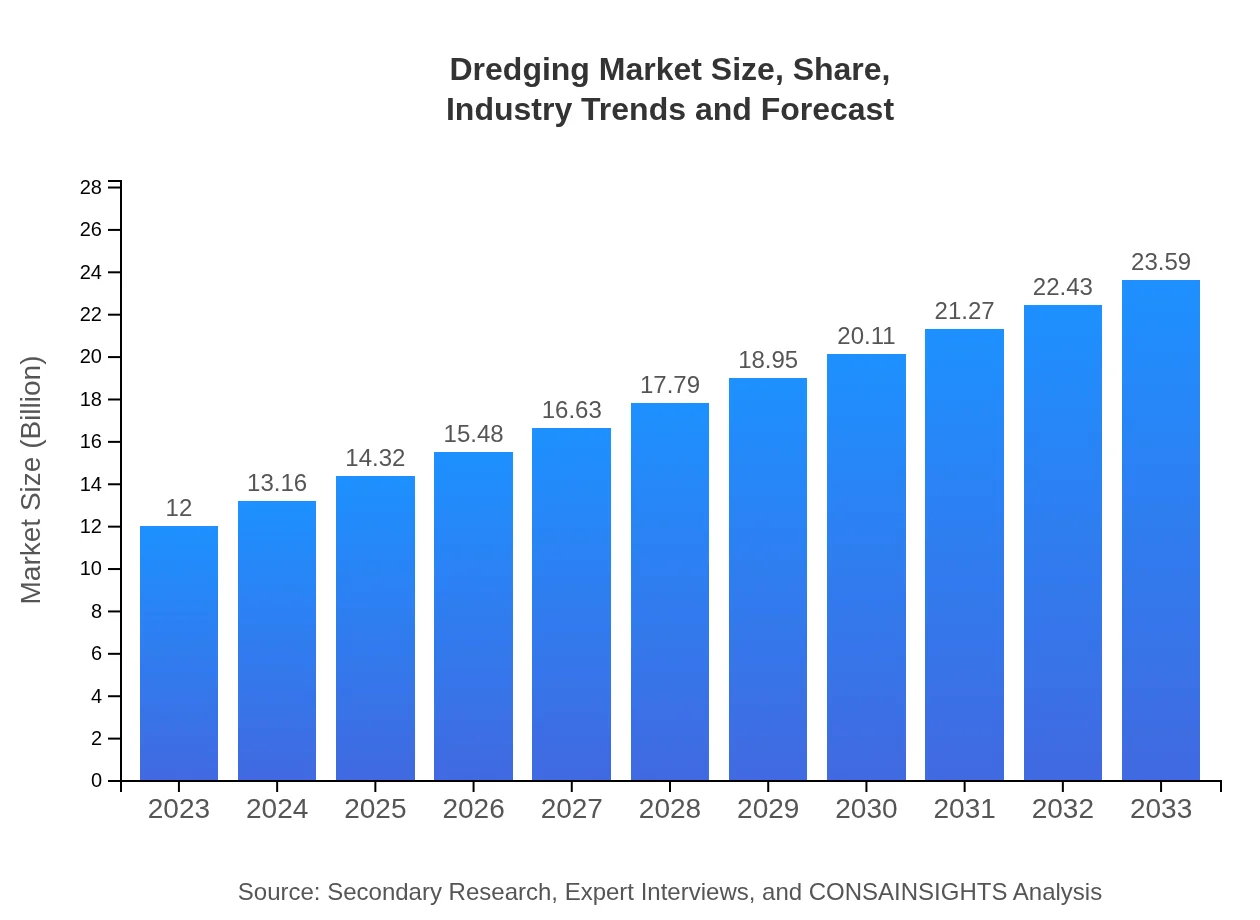
| 2023 Market Size | $12.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $23.59 Billion |
| Top Companies | Royal IHC, Jan De Nul Group, Boskalis Westminster, Dredging International |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Dredging Market Overview
Customize Dredging Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Dredging market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Dredging's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Dredging
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Dredging market in 2023?
Dredging Industry Analysis
Dredging Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Dredging Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Dredging Market Report:
In Europe, the dredging market is robust, with a value of USD 3.64 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 7.15 billion by 2033. The European Union's push for sustainable marine practices and funding for climate resilience projects significantly contributes to this growth. The region's extensive port network also requires regular maintenance dredging.Asia Pacific Dredging Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the dredging market is projected to grow from USD 2.28 billion in 2023 to USD 4.48 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization and increased port construction activities are significant growth factors. Environmental dredging initiatives are also rising due to stricter regulations regarding water quality and habitat restoration.North America Dredging Market Report:
The North American market is valued at USD 4.26 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach USD 8.38 billion by 2033. The region's robust infrastructure investment and maintenance projects, coupled with increasing environmental regulations, are driving market growth. Technological advancements boosting dredging efficiency further support this trend.South America Dredging Market Report:
South America's dredging market is expanding, with a size of USD 0.31 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 0.61 billion by 2033. The focus is on improving existing port facilities and addressing environmental issues related to mining and agriculture, which significantly contribute to sedimentation.Middle East & Africa Dredging Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is expected to grow from USD 1.51 billion in 2023 to USD 2.97 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by infrastructure development initiatives and increasing investments in port expansion, particularly in Gulf countries. Environmental concerns are also pushing for eco-friendly dredging practices.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
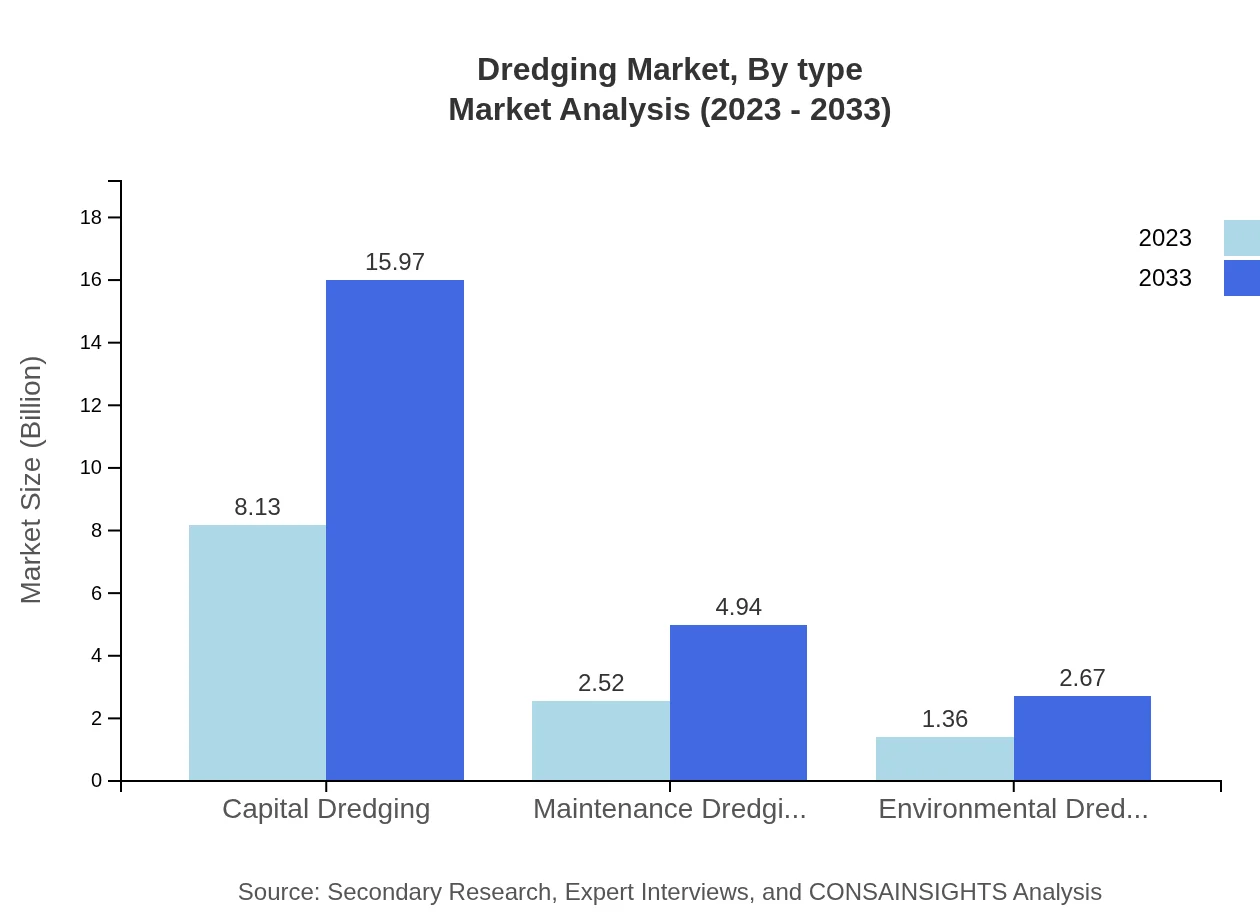
Dredging Market Analysis By Type
The key segments in the dredging market by type include: Capital Dredging, valued at USD 8.13 billion in 2023 and expected to reach USD 15.97 billion by 2033. It holds a significant market share of 67.72%. Maintenance Dredging is valued at USD 2.52 billion with a forecast of USD 4.94 billion by 2033, representing a market share of 20.96%. Environmental Dredging, valued at USD 1.36 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to USD 2.67 billion by 2033 with an 11.32% market share.
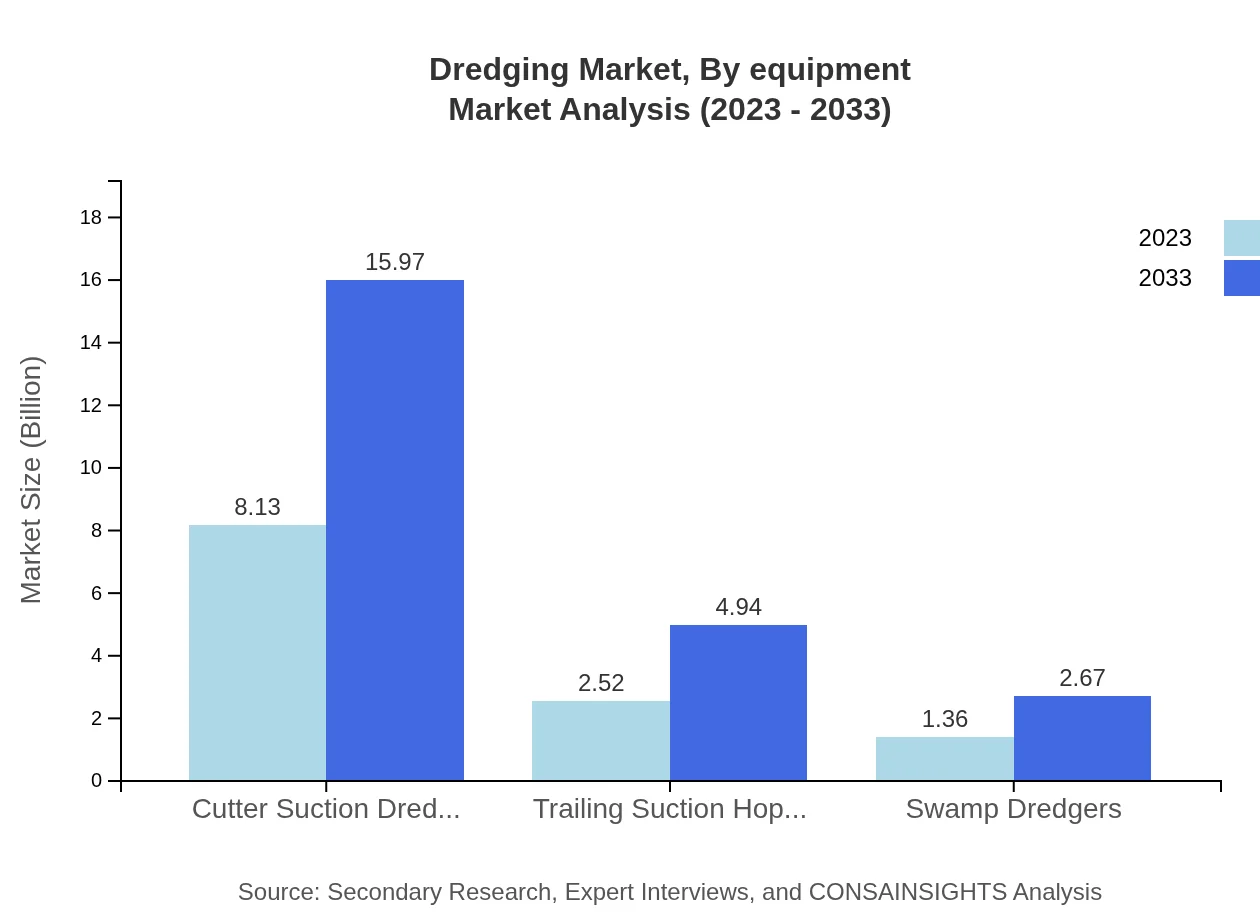
Dredging Market Analysis By Equipment
The dredging market's equipment segment showcases key technologies like Cutter Suction Dredgers and Trailing Suction Hopper Dredgers. Cutter Suction Dredgers represent a market size of USD 8.13 billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 15.97 billion in 2033, securing a 67.72% market share. Trailing Suction Hopper Dredgers, with anticipated growth from USD 2.52 billion to USD 4.94 billion, account for 20.96% market share. Swamp Dredgers cater to niche markets, valued at USD 1.36 billion and expected to increase to USD 2.67 billion.
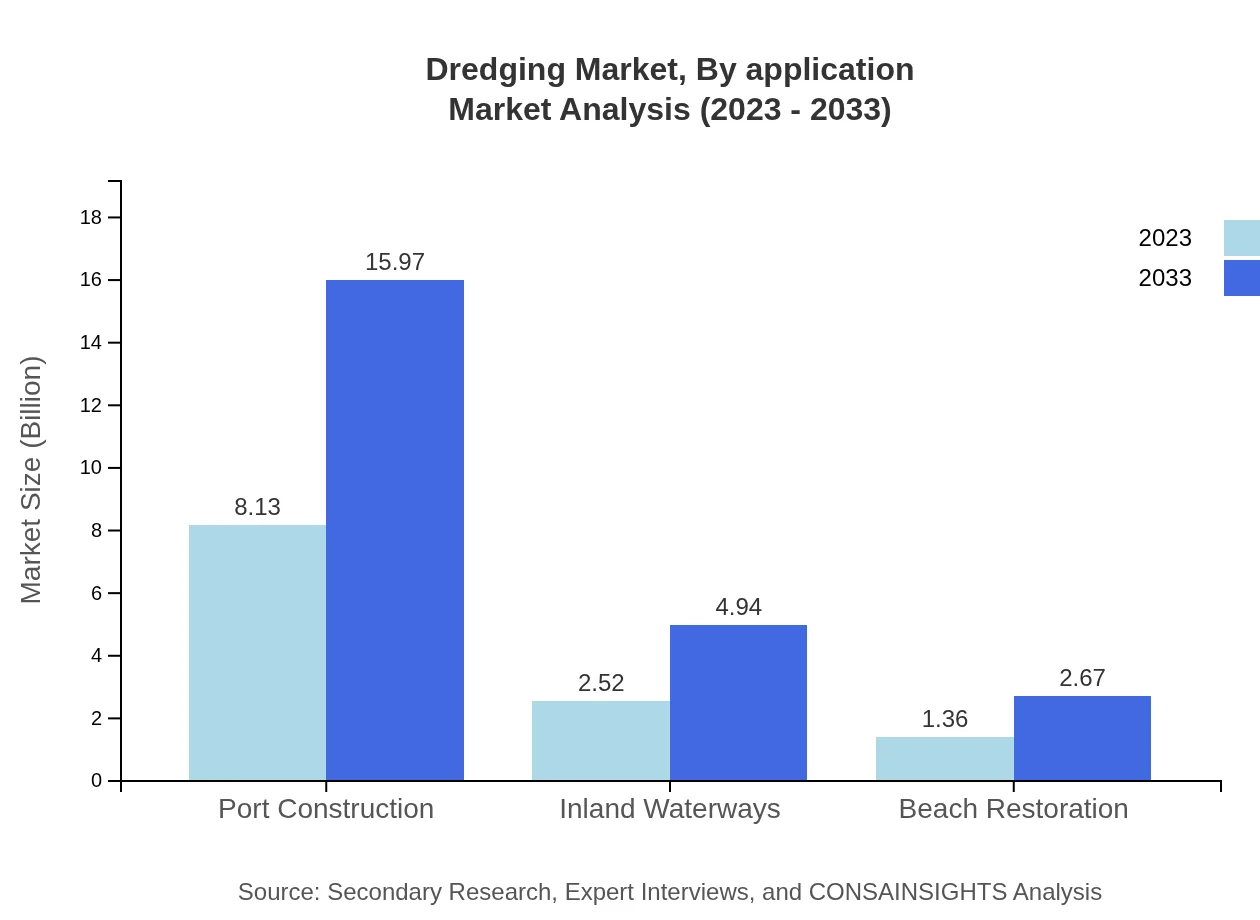
Dredging Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, segments such as Port Construction and Inland Waterways are prominent. Port Construction stands at USD 8.13 billion and is forecasted to reach USD 15.97 billion by 2033, dominating with a 67.72% share, while Inland Waterways, currently at USD 2.52 billion, is expected to reach USD 4.94 billion by 2033, holding 20.96% market share. This emphasizes the critical infrastructure role played by dredging activities.
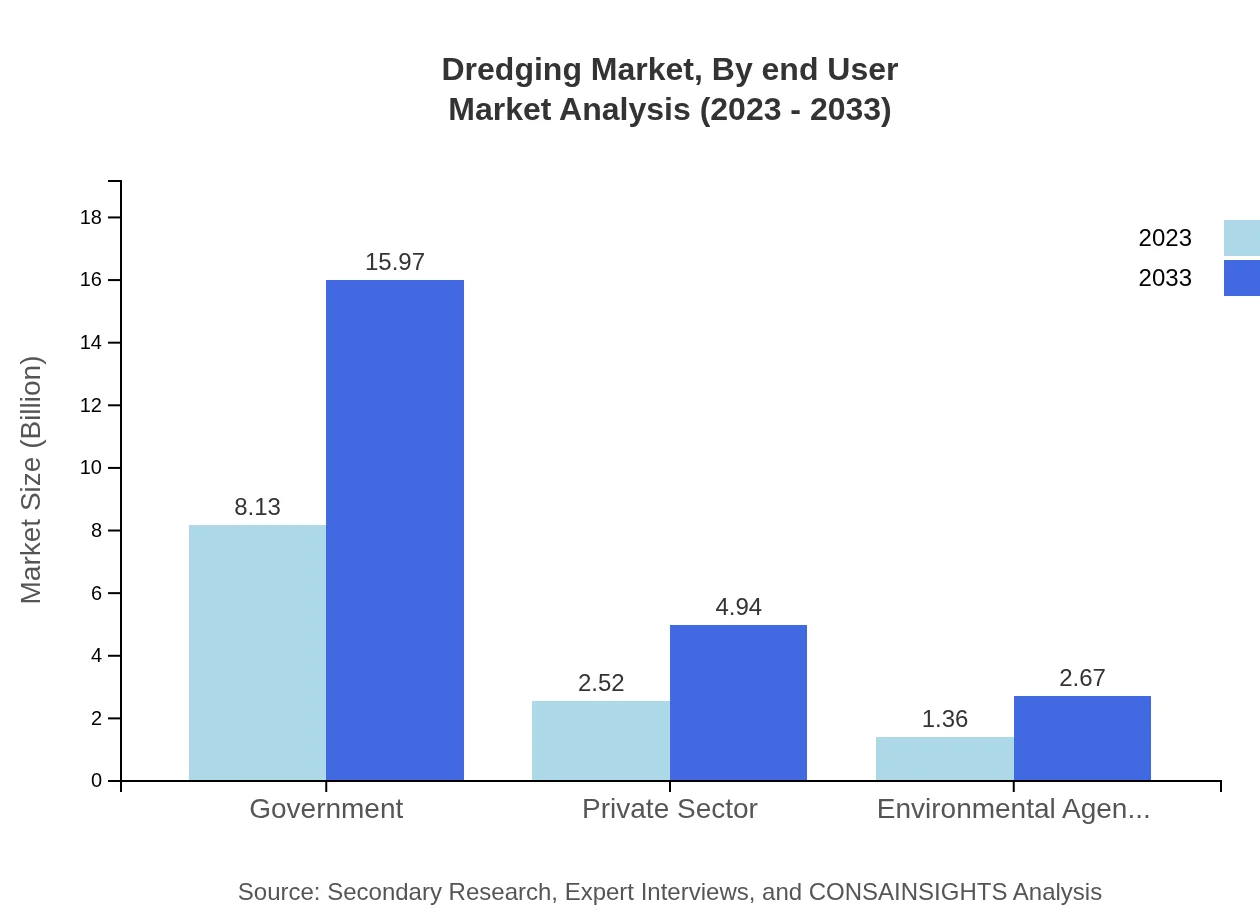
Dredging Market Analysis By End User
End-user segmentation reveals that government entities are the largest consumers in the dredging market, reflecting a size of USD 8.13 billion in 2023, seeking to address navigational and environmental issues. The private sector follows, valued at USD 2.52 billion, focusing on commercial development projects. Environmental agencies also show a keen interest, with a value of USD 1.36 billion, emphasizing environmental restoration initiatives.
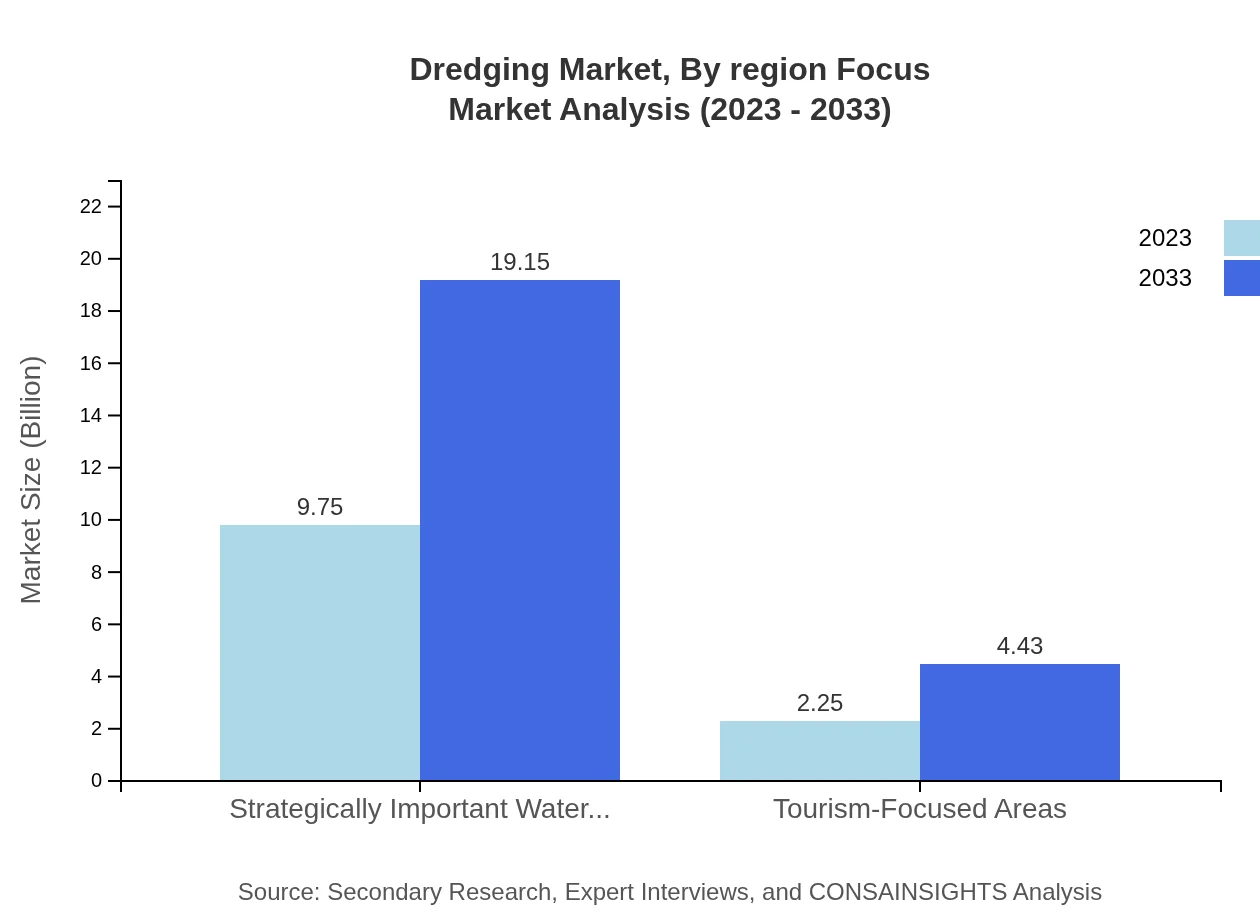
Dredging Market Analysis By Region Focus
Segments focusing on unique initiatives include strategically important waterways and tourism-focused areas. Strategically Important Waterways are forecasted to grow rapidly from USD 9.75 billion to USD 19.15 billion by 2033, constituting a market share of 81.21%. Tourism-Focused Areas, valued at USD 2.25 billion in 2023, anticipate an increase to USD 4.43 billion, signifying a growing investment in recreational and eco-tourism infrastructure.
Dredging Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Dredging Industry
Royal IHC:
A leading supplier of dredging equipment and services, Royal IHC stands out for advancing innovative solutions in dredging technology.Jan De Nul Group:
A prominent global dredging contractor known for complex dredging projects, Jan De Nul places emphasis on environmental sustainability and operational efficiency.Boskalis Westminster:
Boskalis is recognized for its extensive experience in dredging and marine services, involved in various infrastructure and environmental projects globally.Dredging International:
A key player in the dredging industry, Dredging International specializes in large scale dredging and reclamation projects with a strong focus on environmental care.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of dredging?
The global dredging market is currently valued at $12 billion with a CAGR of 6.8%. This growth reflects an increasing demand for dredging services across multiple sectors, significantly expanding from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this dredging industry?
Key players in the dredging industry include renowned companies such as Boskalis, Deme Group, and Jan De Nul Group. These firms lead in innovative dredging solutions and expansive project portfolios worldwide.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the dredging industry?
The main drivers of growth include rising global trade, the expansion of ports, and infrastructure development. Additionally, environmental projects aimed at cleaning waterways contribute significantly to the industry's expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the dredging market?
North America is the fastest-growing region, with market growth from $4.26 billion in 2023 to $8.38 billion by 2033, driven by port developments and waterway projects.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the dredging industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data in the dredging industry, allowing clients to obtain focused insights based on specific interests and regional demands.
What deliverables can I expect from this dredging market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports containing market analysis, regional breakdowns, competitor assessments, and forecasts, ensuring a detailed understanding of the dredging industry landscape.
What are the market trends of dredging?
Current trends include increased investment in sustainable dredging practices, growing demand for maintenance dredging, and expansion into environmental dredging projects, reflecting an evolving market landscape.