Edible Fungus Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: edible-fungus
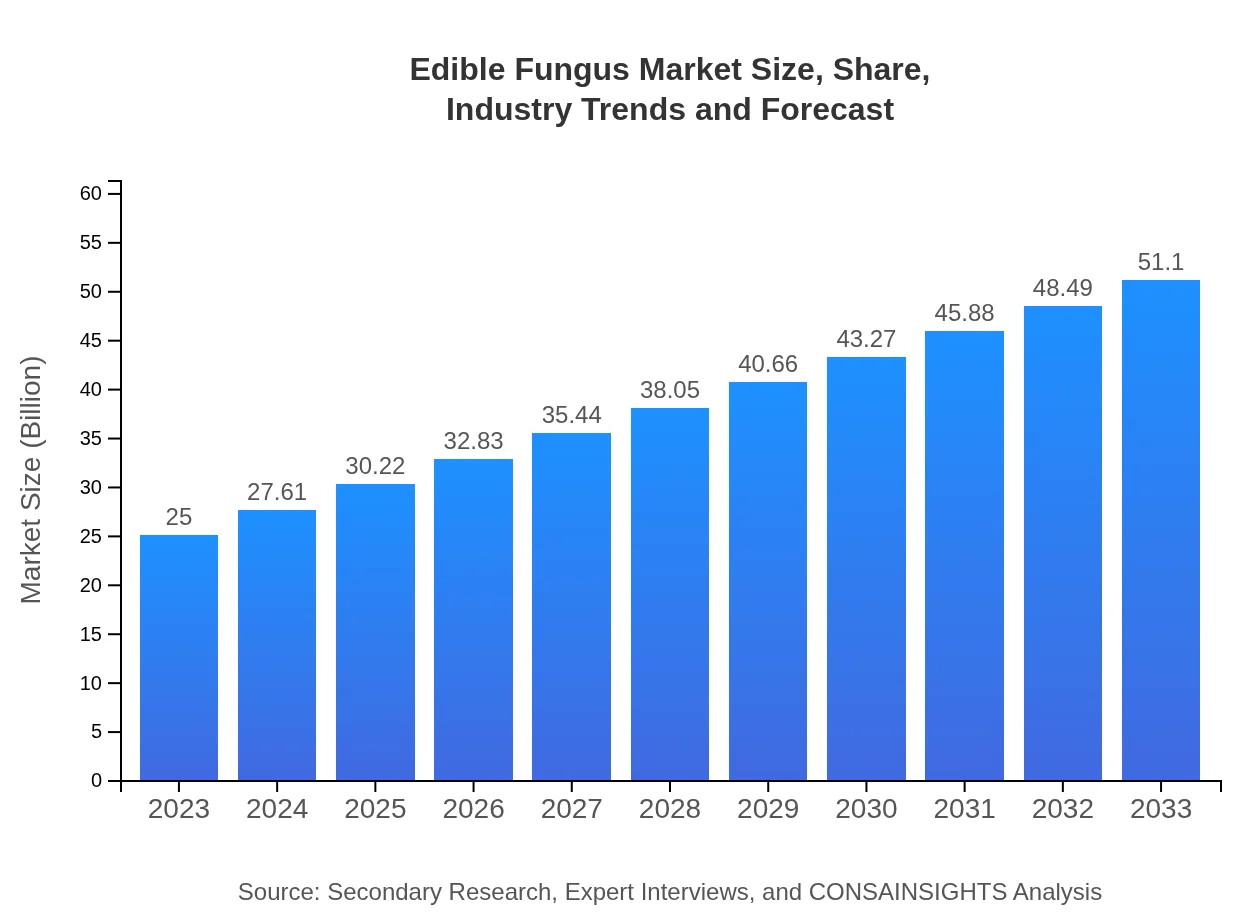
Edible Fungus Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the edible fungus market from 2023 to 2033, focusing on market trends, segmentation, regional dynamics, and forecasts, enriched with data-driven insights and industry analysis.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $25.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $51.10 Billion |
| Top Companies | Oyster Mushroom Company, Mushroom World Ltd., Fungi Fresh Inc., Green Earth Mushrooms |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Edible Fungus Market Overview
Customize Edible Fungus Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Edible Fungus market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Edible Fungus's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Edible Fungus
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Edible Fungus market in 2033?
Edible Fungus Industry Analysis
Edible Fungus Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Edible Fungus Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Edible Fungus Market Report:
Europe shows a consistent increase in edible fungus consumption, starting at $7.20 billion in 2023 and forecasted to reach $14.71 billion by 2033. The prevalence of organic food trends and gourmet cuisine prominent in countries like Italy and France are significant growth contributors.Asia Pacific Edible Fungus Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region held a prominent share of the market in 2023, with a market value of $4.79 billion and is projected to reach approximately $9.79 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, increased disposable income, and the cultural significance of mushrooms in Asian cuisines significantly drive demand.North America Edible Fungus Market Report:
North America dominated the edible fungus market in 2023 with a valuation of $9.20 billion. Expected to grow to $18.80 billion by 2033, the region benefits from a high trend towards health and wellness, boosting mushroom consumption both in households and foodservice.South America Edible Fungus Market Report:
In South America, the market for edible fungus was valued at around $0.35 billion in 2023. With projections indicating growth reaching $0.71 billion by 2033, increasing interest in gourmet cooking and natural foods is fostering market expansion.Middle East & Africa Edible Fungus Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market was valued at $3.47 billion in 2023, with projections indicating a rise to $7.09 billion by 2033. Factors like evolving culinary practices and increased focus on nutritional food sources underpin this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
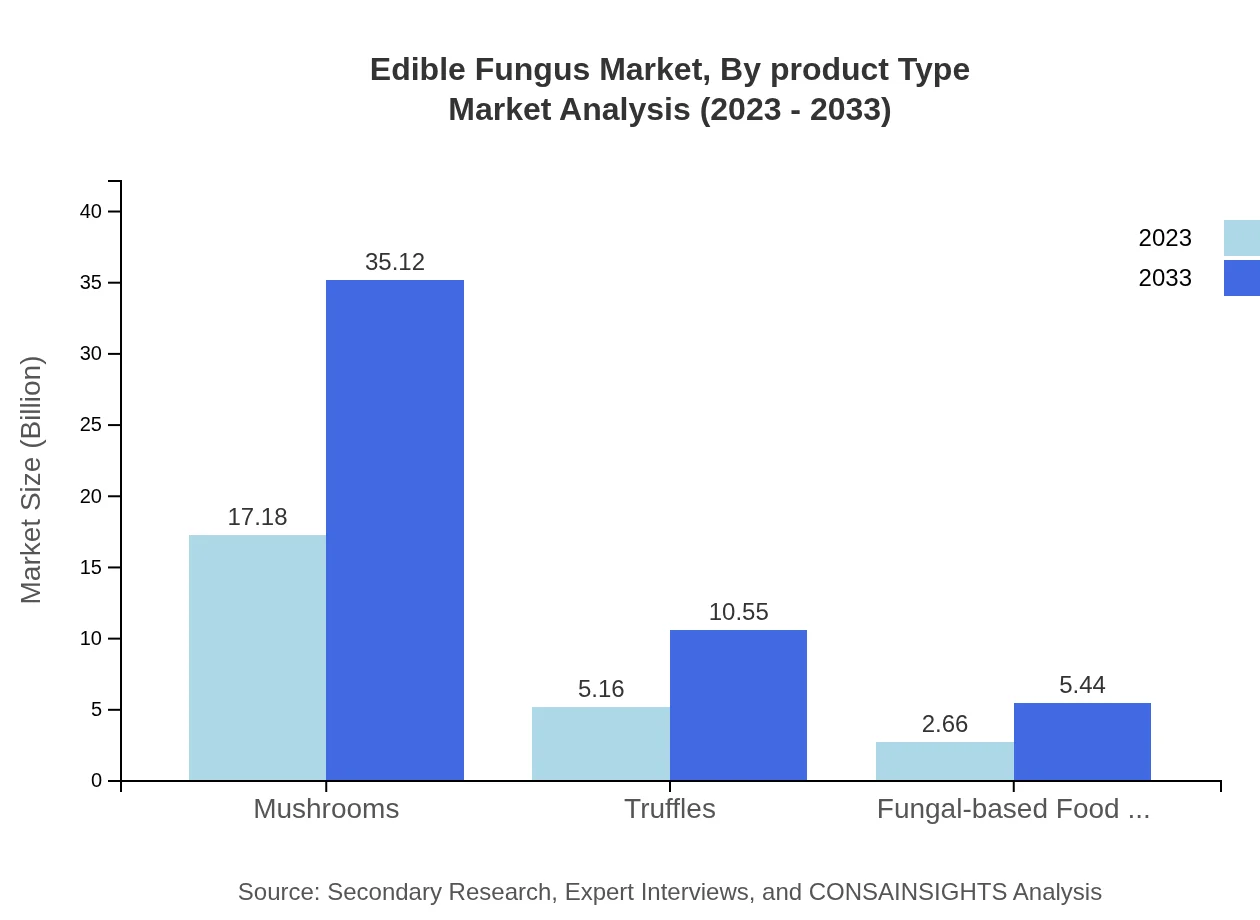
Edible Fungus Market Analysis By Product Type
The product segmentation indicates that fresh edible fungi dominated the market with a size of $17.18 billion in 2023, expected to soar to $35.12 billion by 2033, holding a steady market share of 68.72%. Dried fungi followed with a 2023 valuation of $5.16 billion, predicting a rise to $10.55 billion. Processed fungi and their niche markets also projected strong growth trajectories.
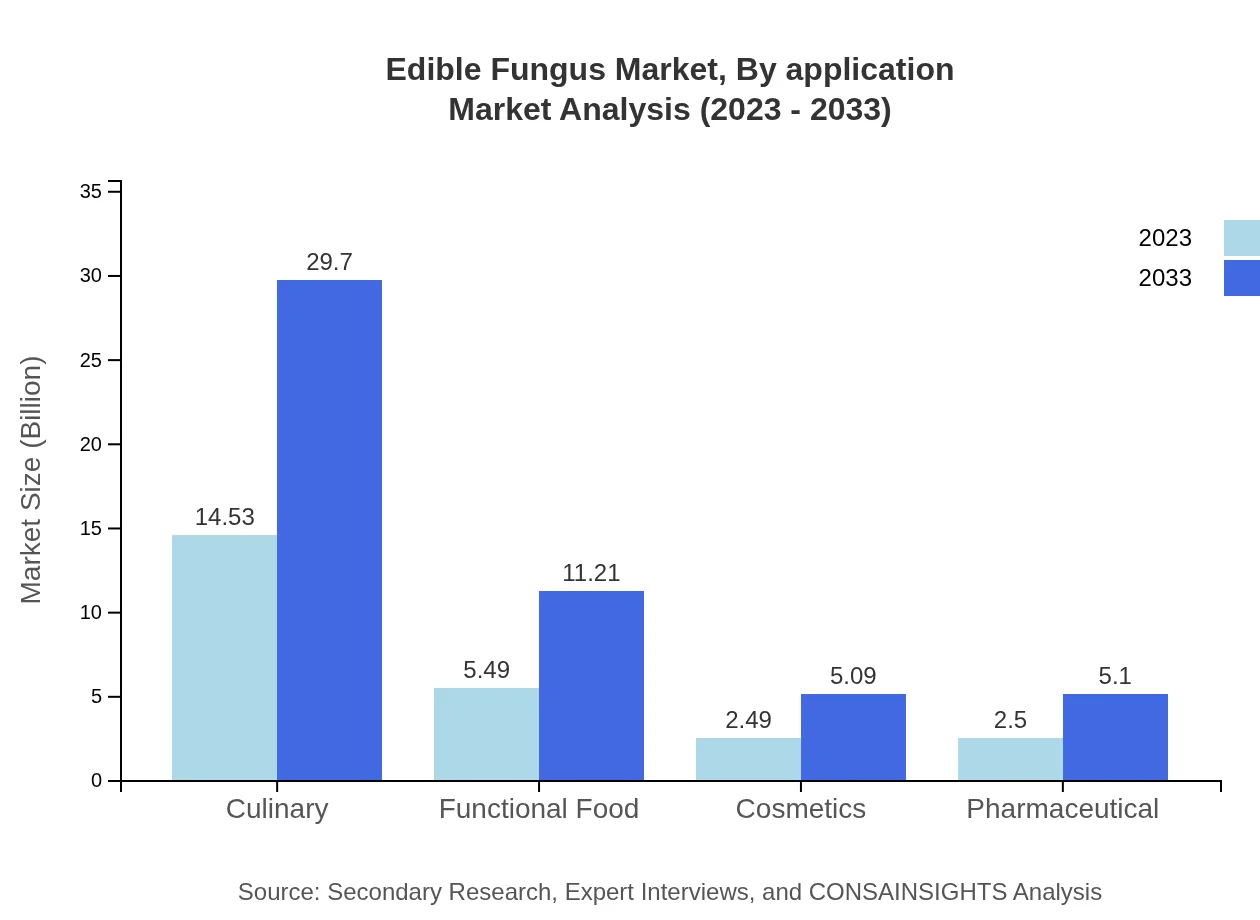
Edible Fungus Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, culinary integration remains the top segment with a market size of $14.53 billion in 2023, set to achieve $29.70 billion by 2033. The food processing industry also contributes significantly, growing from $2.66 billion to $5.44 billion, highlighting the sector's growing utilization of edible fungi for nutritional enhancement.
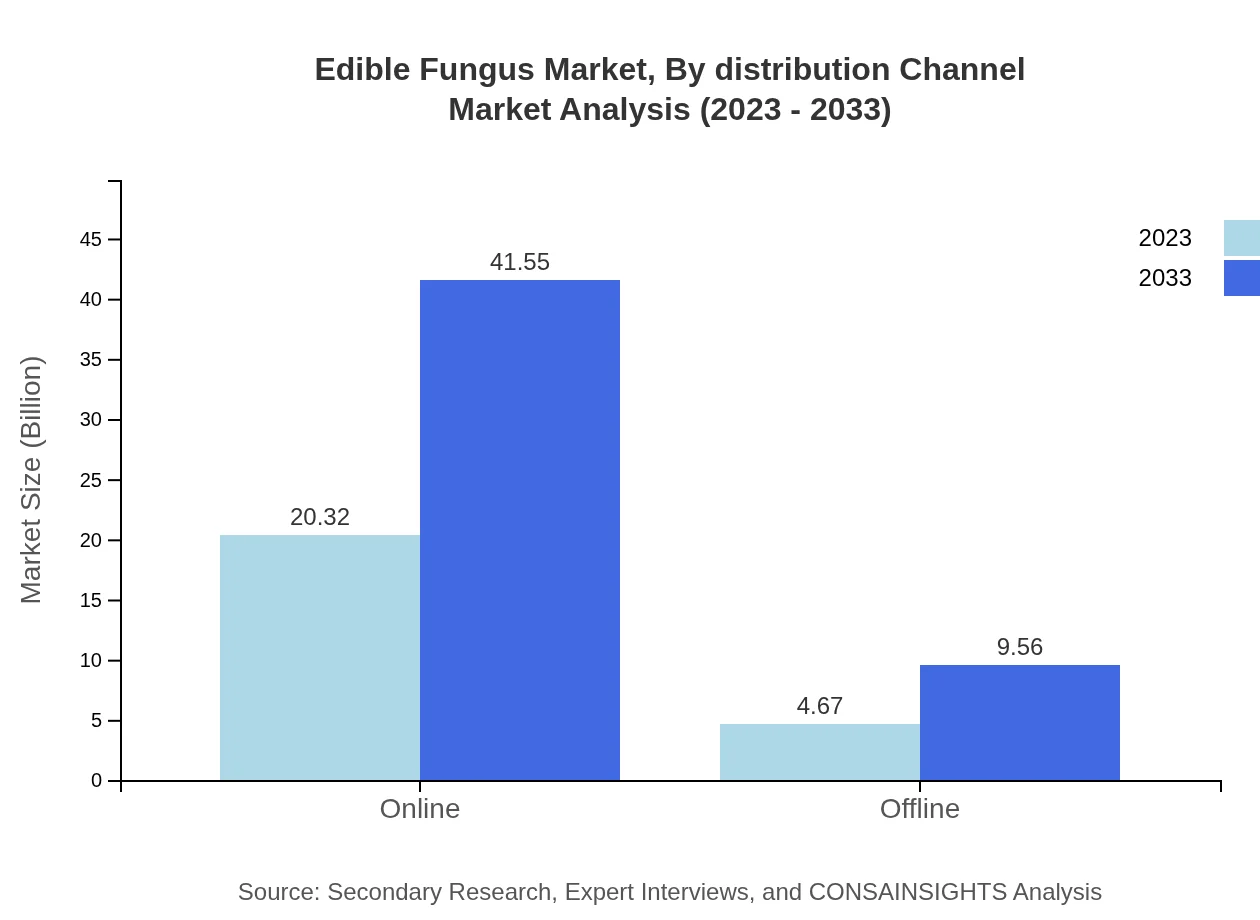
Edible Fungus Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution dynamics are shifting towards online channels marked by a $20.32 billion valuation in 2023, anticipated to peak at $41.55 billion by 2033. The offline segment continues to play a vital role but is growing at a slower pace, expected to reach $9.56 billion in 2033.
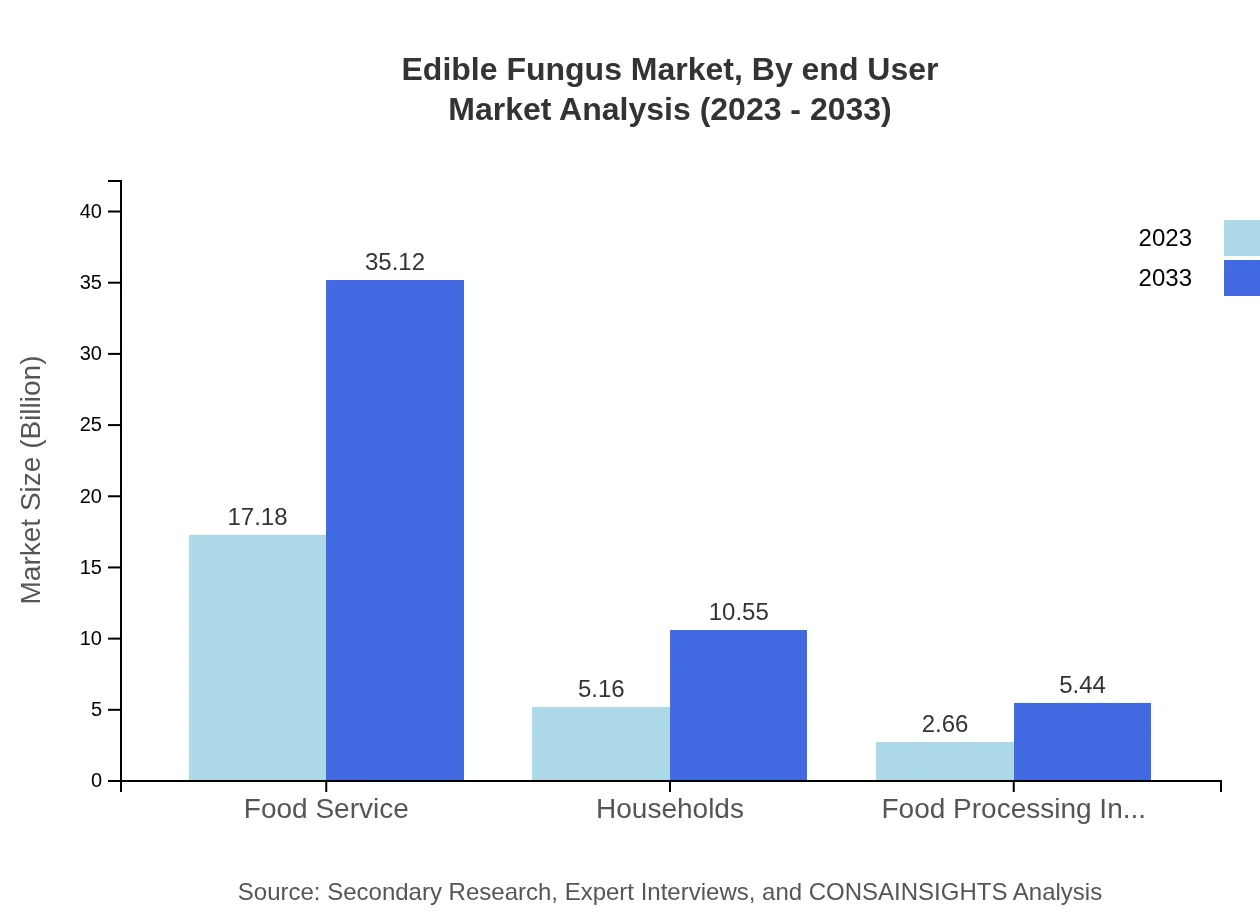
Edible Fungus Market Analysis By End User
The food service sector remains a heavyweight in edible fungus consumption, poised to maintain its position through predicted sales of $35.12 billion by 2033. Households are also significant contributors, especially in gourmet cooking, moving from $5.16 billion in 2023 to $10.55 billion by 2033.
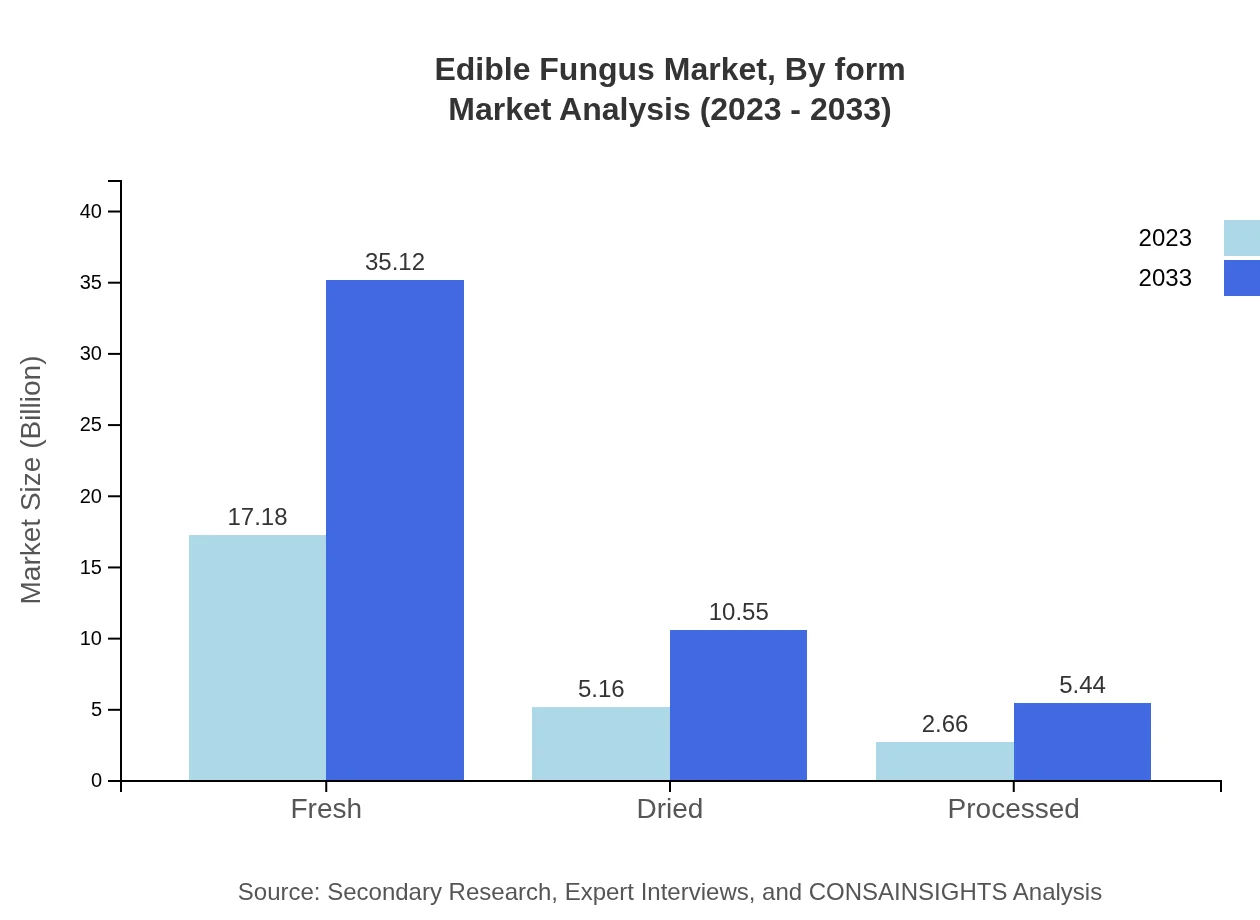
Edible Fungus Market Analysis By Form
The various forms of edible fungi available in the market, particularly fresh mushrooms, are projected to uphold dominance due to their popularity, while dried forms also present a promising segment. The significance of processed forms is rising, especially in the context of the food service sector looking to enhance dish quality.
Edible Fungus Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Edible Fungus Industry
Oyster Mushroom Company:
A leading cultivator of oyster mushrooms known for innovative farming practices focused on sustainability and quality.Mushroom World Ltd.:
A prominent player specializing in a wide range of mushroom products, catering to both consumers and food service providers.Fungi Fresh Inc.:
This company innovates with fresh fungi sourcing and offers an extensive distribution network across North America and Europe.Green Earth Mushrooms:
Focuses on organic mushroom production and has a robust online presence, making fungi accessible for health-conscious consumers.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of edible Fungus?
The global edible fungus market is projected to reach approximately $25 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023. This growth reflects increasing consumer demand and awareness of the nutritional benefits.
What are the key market players or companies in the edible Fungus industry?
Key players in the edible fungus market include prominent producers and suppliers who focus on organic and cultivated varieties. These include companies specializing in mushrooms, truffles, and fungal-based food products, although specific names were not disclosed.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the edible Fungus industry?
Growth in the edible fungus industry is primarily driven by increasing health consciousness, rising demand for vegetarian and vegan options, and the growing popularity of mushrooms as functional foods. Innovations in cultivation and processing technologies are also significant contributors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the edible Fungus market?
The fastest-growing region for the edible fungus market is North America, where the market is expected to increase from $9.20 billion in 2023 to $18.80 billion by 2033. Asia Pacific also exhibits considerable growth potential, reflecting changing dietary preferences.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the edible Fungus industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights provides tailored market research reports for the edible fungus industry. These customized reports can include specific data points, regional insights, or segment-focused analyses based on client requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this edible Fungus market research project?
Deliverables from the edible fungus market research project typically include detailed reports featuring market size, growth forecasts, segment analyses, competitive landscape, regional insights, and consumer trends, all tailored to inform business strategies.
What are the market trends of edible Fungus?
Key trends in the edible fungus market include a shift towards organic and sustainable practices, expansion of e-commerce channels, and increased usage of mushrooms in functional foods and cosmetics, reflecting a broader trend towards health-oriented consumer choices.