Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: electric-vehicle-supply-equipment
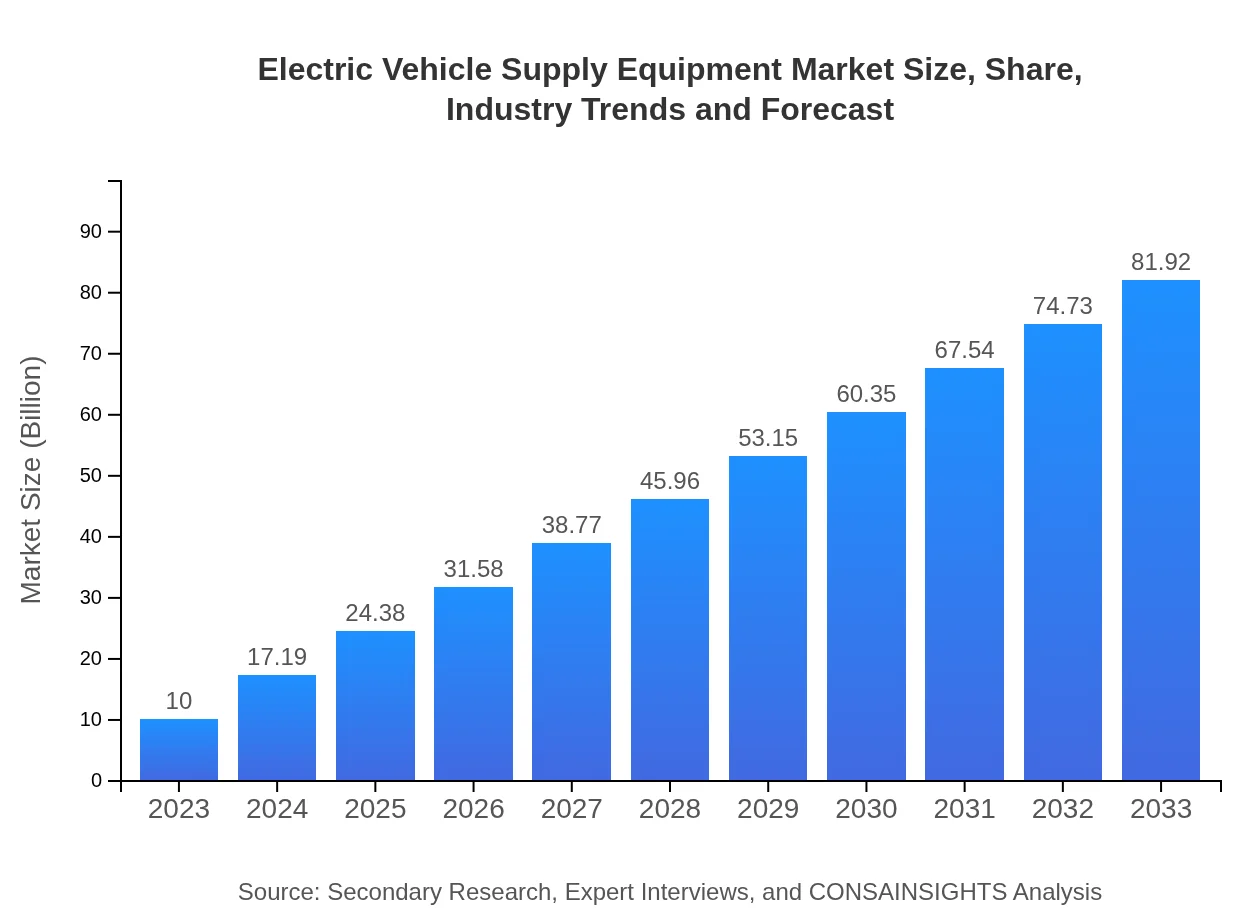
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment market, exploring market size, growth projections, and regional dynamics from 2023 to 2033. Insights include industry trends, segmentation, and competitive landscape information.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 22% |
| 2033 Market Size | $81.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | ChargePoint, ABB, Tesla, Siemens , EVBox |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Overview
Customize Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment market in 2023 and 2033?
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Industry Analysis
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report:
In Europe, the EVSE market is projected to increase from $2.58 billion in 2023 to an impressive $21.16 billion by 2033. The European Union's aggressive emission reduction targets and incentives for electric vehicles are propelling investments in charging infrastructure.Asia Pacific Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report:
The Asia Pacific EVSE market is projected to grow significantly, from $2.19 billion in 2023 to $17.91 billion by 2033. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are leading the way in electric mobility and charging infrastructure development, driven by government policies and initiatives to promote electric vehicles.North America Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report:
The North American market is anticipated to grow from $3.56 billion in 2023 to $29.18 billion by 2033. The strong presence of automotive manufacturers and rapidly expanding charging networks in the U.S. and Canada are significant drivers in this region.South America Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report:
The South American market for Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment is expected to expand from $0.69 billion in 2023 to $5.63 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing electric vehicle adoption and government support for charging station deployment.Middle East & Africa Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is set to grow from $0.98 billion in 2023 to $8.04 billion by 2033, as regional governments start prioritizing electric vehicle adoption and necessitate the establishment of charging infrastructure.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
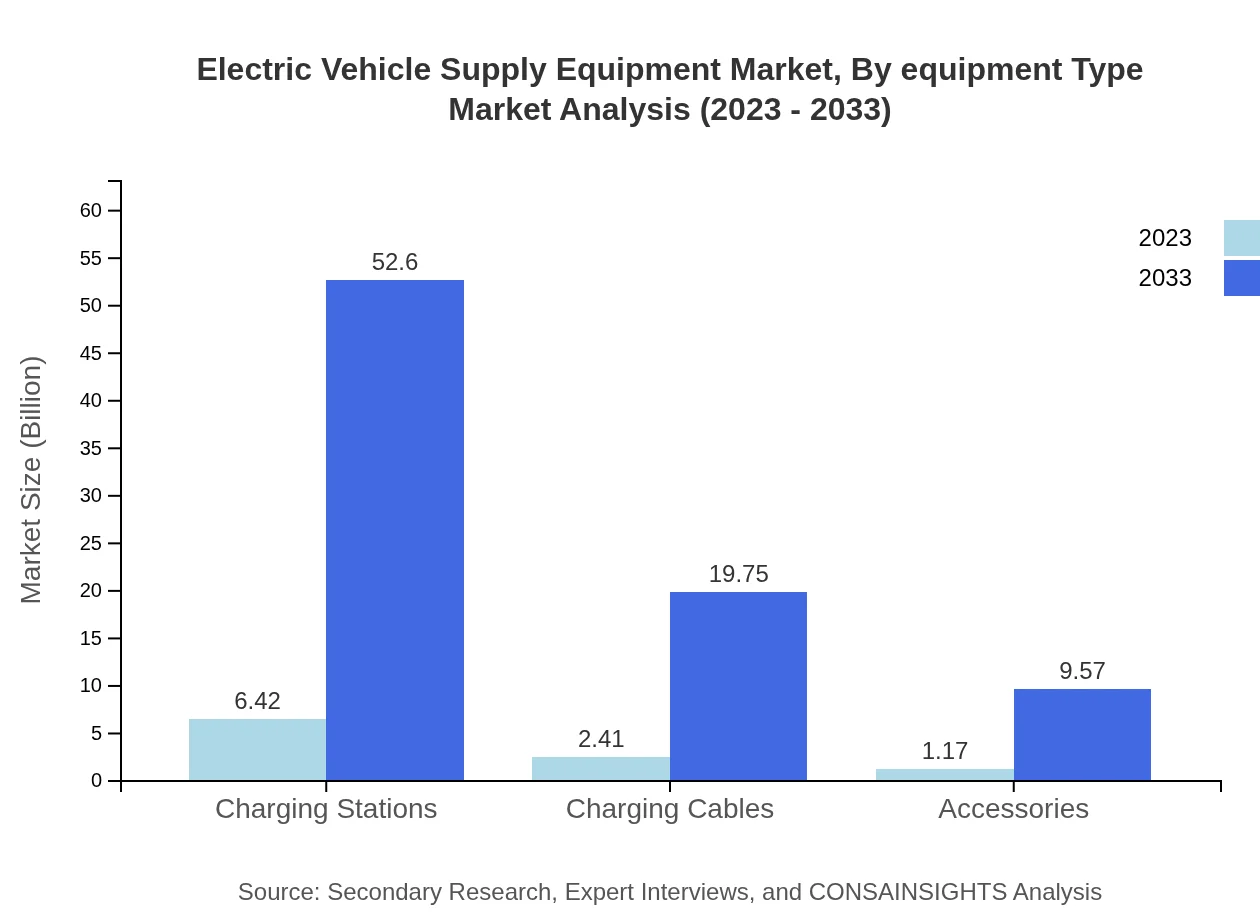
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis By Equipment Type
The market is dominated by various equipment types such as wiring and connectors, charging cables, charging stations, and smart chargers. Wired charging holds the highest market share, constituting about 88.62% in 2023, with projections to maintain similar trends through 2033.
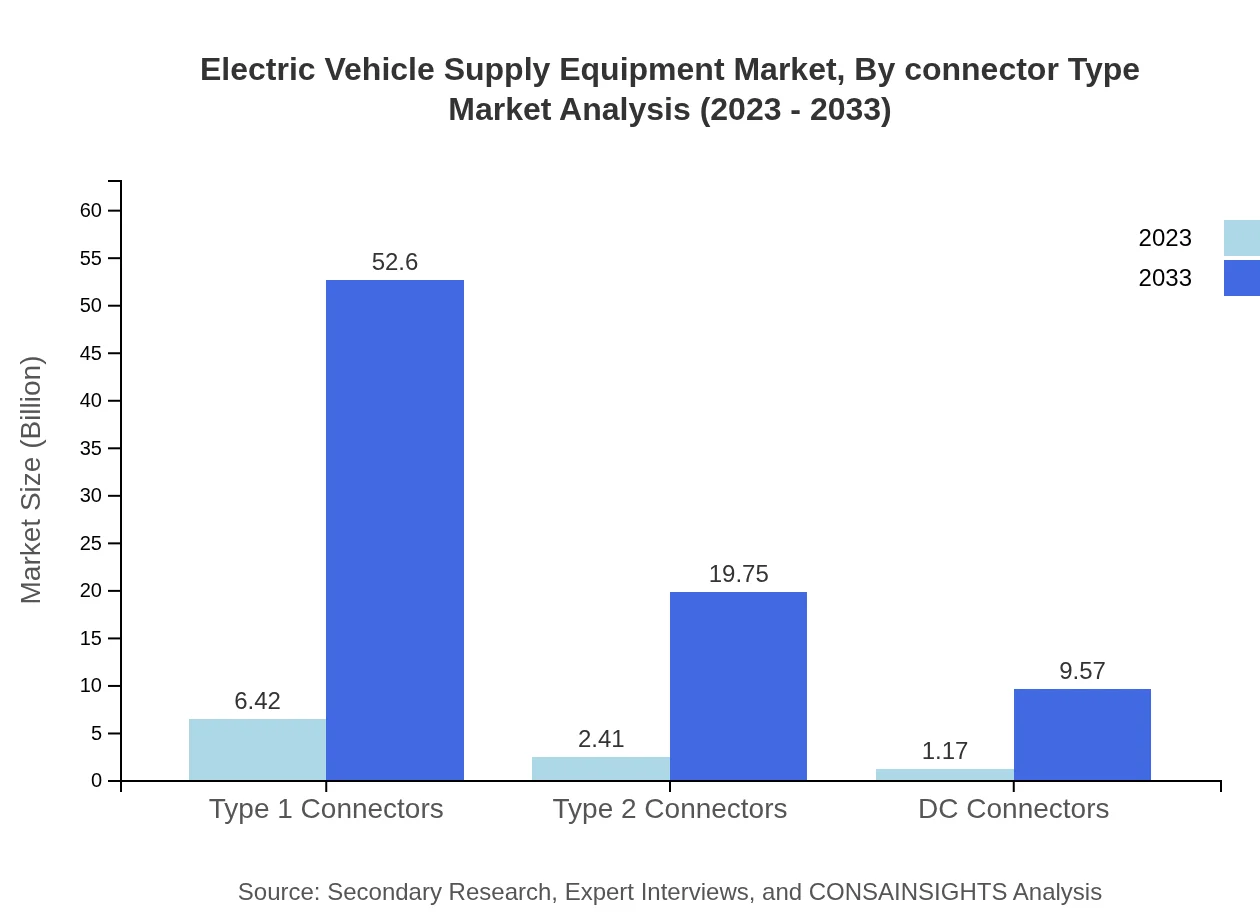
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis By Connector Type
In terms of connector types, Type 1 and Type 2 connectors are the prevalent configurations in the market, representing 64.21% and 24.11% market shares, respectively, driven by their compatibility with numerous vehicle models.
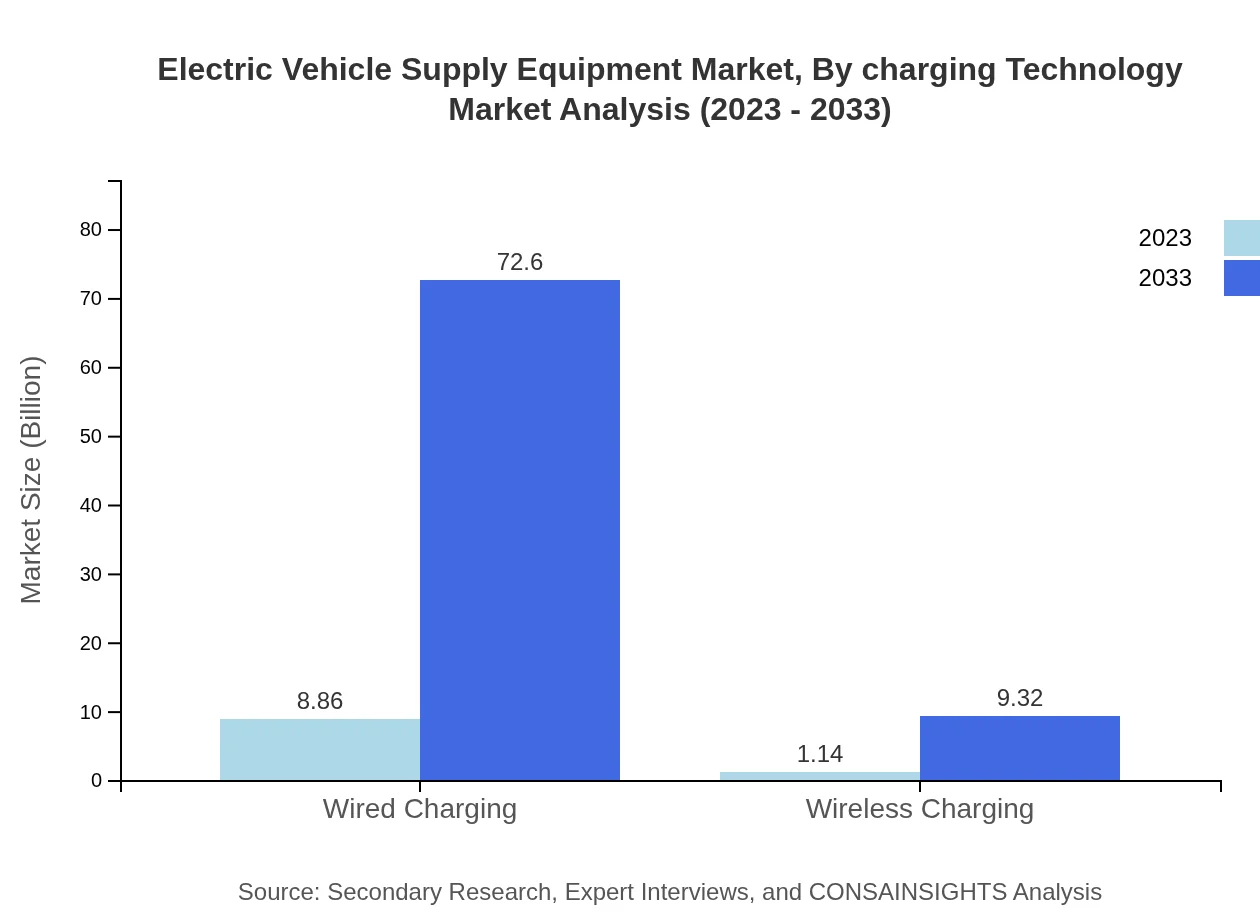
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis By Charging Technology
The market for wired charging technology is significantly larger compared to wireless charging technology, estimated at 88.62% market share in 2023 due to the reliability and efficiency of wired connections for EVs.
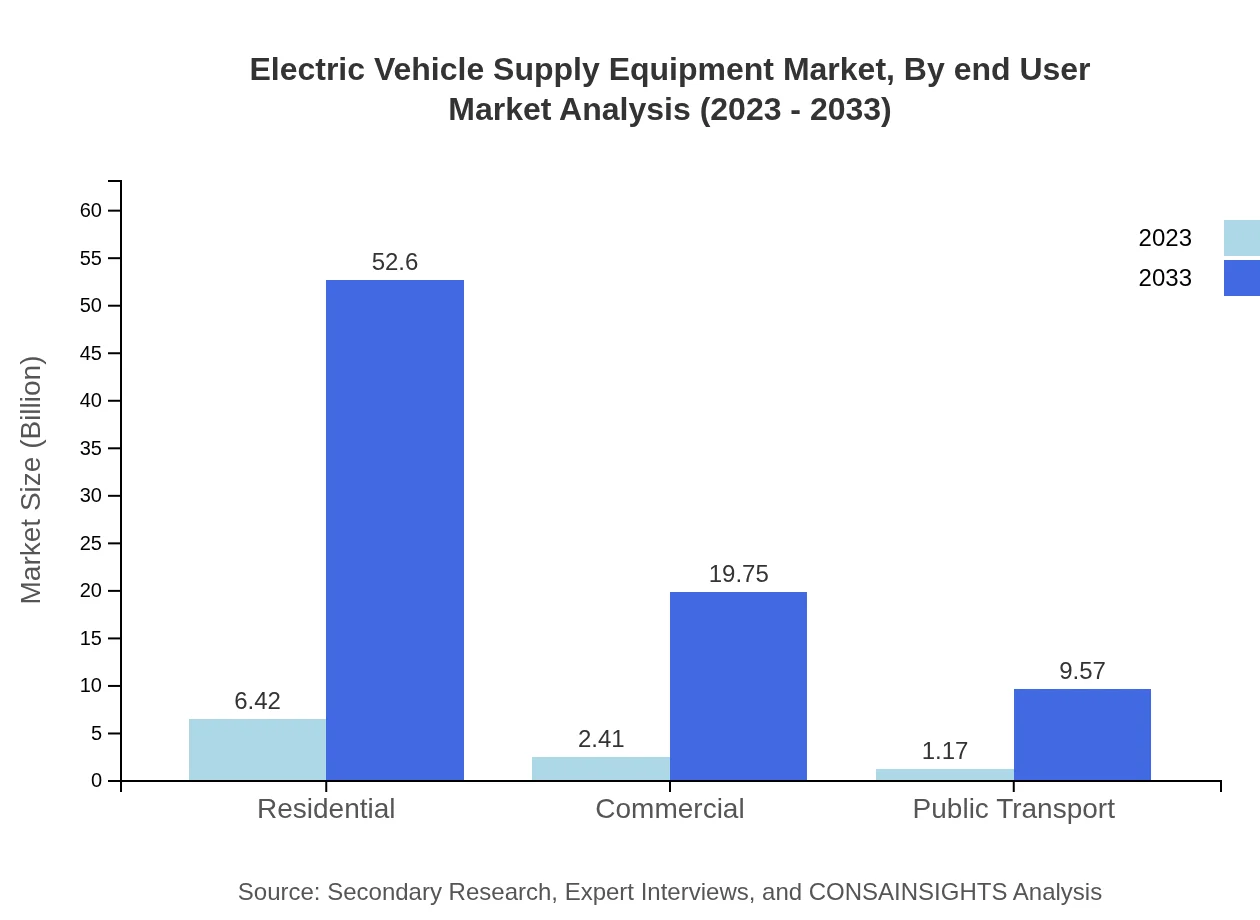
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis By End User
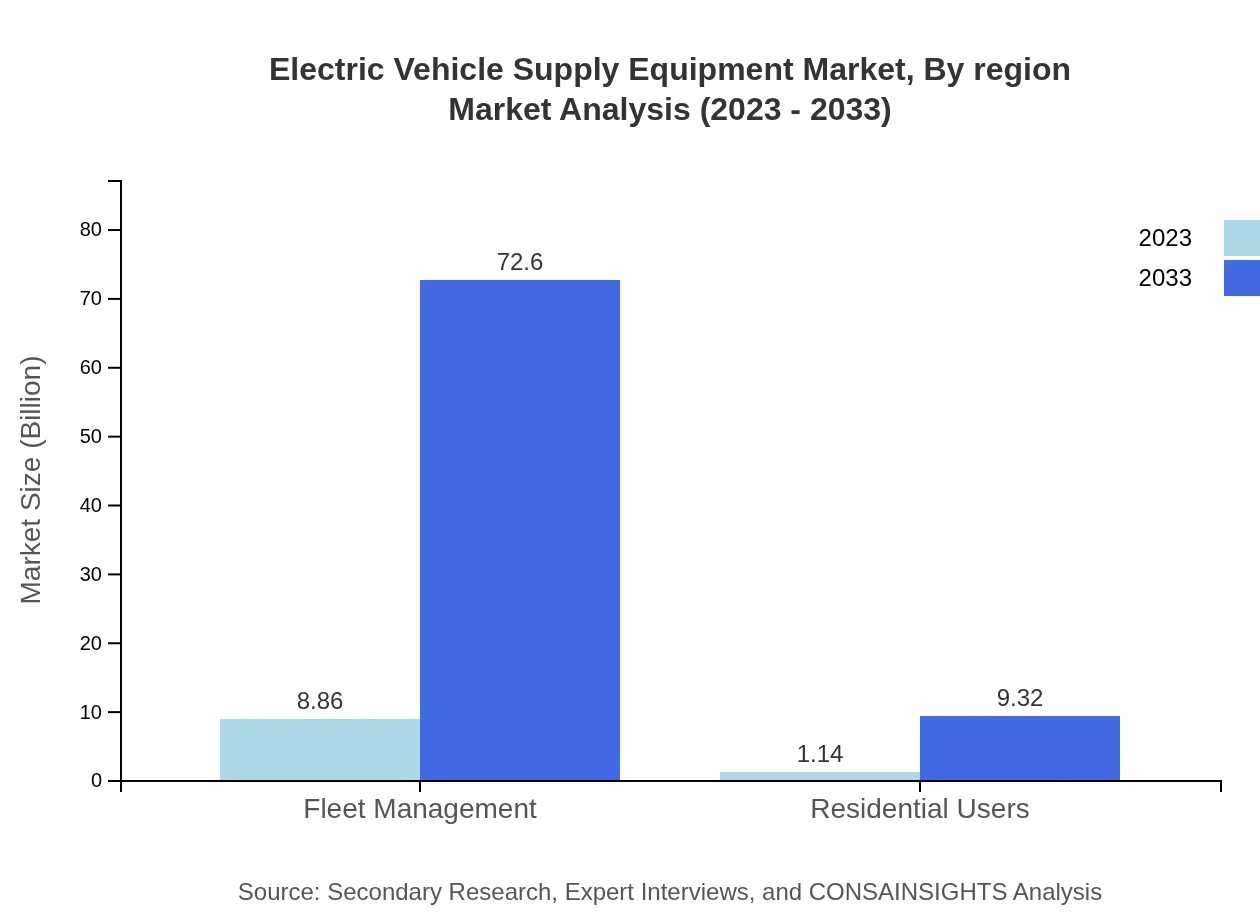
Fleet Management emerges as the largest segment, expected to expand from $8.86 billion in 2023 to $72.60 billion by 2033. This is followed by significant contributions from residential users, public transport, and commercial users.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Analysis By Region
The regional diversity illustrates robust growth in charging infrastructure needs, with North America commanding a significant market share and the Asia Pacific region emerging as a powerhouse due to rapid EV adoption.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment Industry
ChargePoint:
ChargePoint is a pioneering EV charging network providing charging stations for a range of electric vehicles. The company leads in per-session pricing with software solutions that optimize charging operations.ABB:
ABB is a global technology company known for its expertise in electrification and automation. The company offers a range of EV charging solutions, including fast chargers and support in developing charging infrastructure.Tesla:
Tesla has established itself as a leader in the EV market with its proprietary Supercharger network. The company continues to expand its charging infrastructure while promoting electric vehicle sales.Siemens :
Siemens focuses on sustainable transportation solutions and invests heavily in EV charging technology, including innovative charging infrastructure that complements renewable energy.EVBox:
EVBox is prominent in providing smart charging solutions designed for businesses and municipalities, aiming to support the rapid growth of electric vehicle adoption worldwide.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of electric Vehicle Supply Equipment?
The global electric vehicle supply equipment market is projected to reach approximately $10 billion by 2033, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 22%. This significant growth reflects increased adoption of electric vehicles worldwide.
What are the key market players or companies in the electric Vehicle Supply Equipment industry?
Key players in the electric vehicle supply equipment market include ChargePoint, ABB, Siemens, and Schneider Electric, among others. These companies are driving innovation and expanding infrastructure to support the growing demand for electric vehicles.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the electric Vehicle Supply Equipment industry?
Primary factors include increasing government regulations for emissions, rising demand for electric vehicles, advancements in charging technologies, and heightened consumer awareness of sustainability. These elements collectively enhance the infrastructure needed for electric vehicles.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the electric Vehicle Supply Equipment?
The fastest-growing region is North America, with the market size expected to grow from $3.56 billion in 2023 to $29.18 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also demonstrate robust growth, reflecting global trends.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the electric Vehicle Supply Equipment industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to clients' specific needs. Clients can receive detailed insights into regional markets, segments, and player dynamics in the electric vehicle supply equipment industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this electric Vehicle Supply Equipment market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, competitor assessments, growth forecasts, and detailed regional insights, allowing clients to make informed decisions based on the latest data.
What are the market trends of electric Vehicle Supply Equipment?
Market trends include an increasing focus on fast-charging technologies, growth in public and residential charging stations, and a shift towards wireless charging solutions. These trends indicate a progressive evolution in electric vehicle infrastructure.