Embedded Sim Esim Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: embedded-sim-esim
Embedded Sim Esim Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the comprehensive analysis of the Embedded Sim (eSIM) market, providing insights into market size, growth trends, key players, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
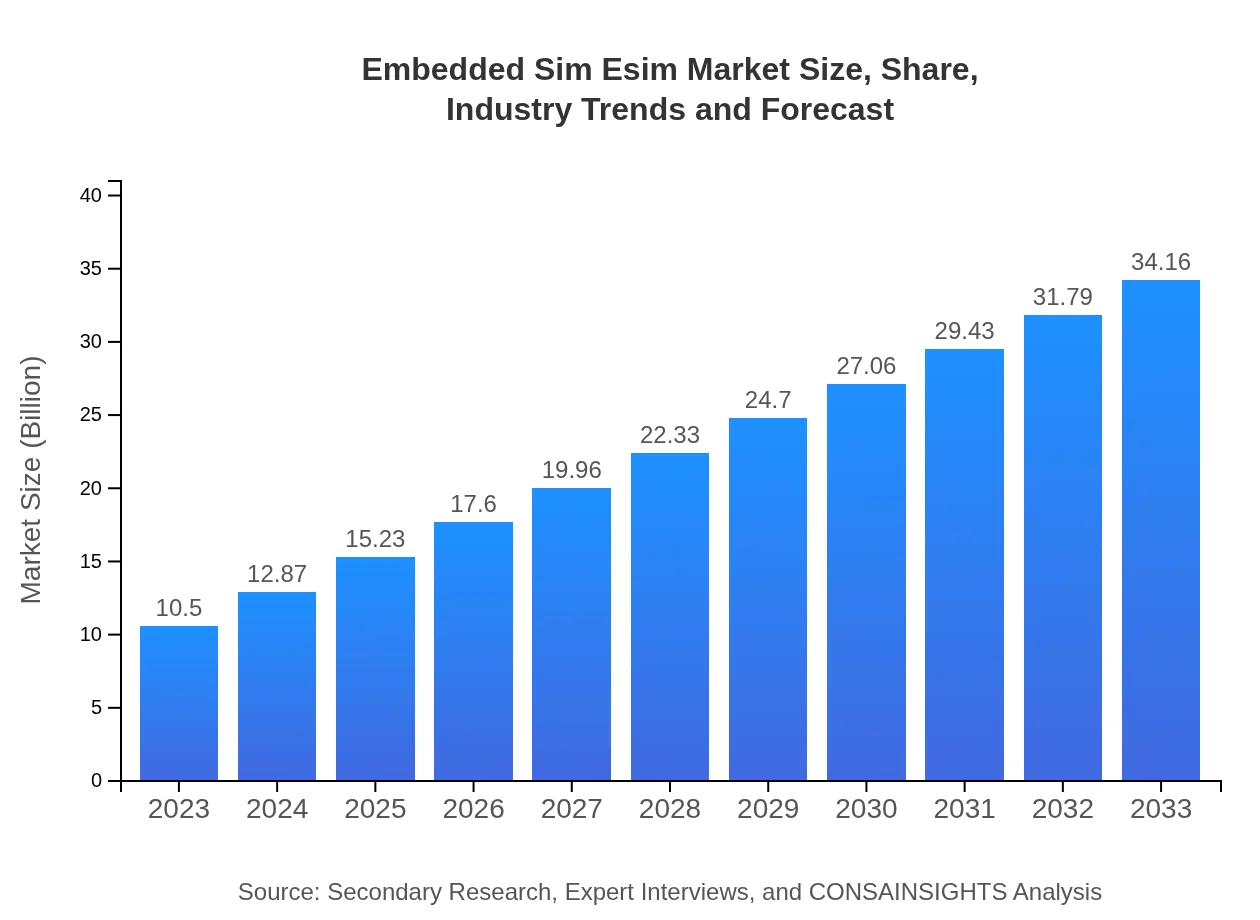
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12% |
| 2033 Market Size | $34.16 Billion |
| Top Companies | Apple , GSMA (GSM Association), STMicroelectronics, Vodafone |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Embedded Sim Esim Market Overview
Customize Embedded Sim Esim Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Embedded Sim Esim market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Embedded Sim Esim's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Embedded Sim Esim
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Embedded Sim Esim market in 2023 and 2033?
Embedded Sim Esim Industry Analysis
Embedded Sim Esim Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Embedded Sim Esim Market Report:
The European eSIM market is set to expand from $3.29 billion in 2023 to $10.72 billion by 2033, propelled by regulatory support for eSIM solutions, the integration of eSIMs in consumer electronics, and the automotive sector. Europe is at the forefront of adopting new mobile technologies.Asia Pacific Embedded Sim Esim Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the eSIM market is projected to expand from $2.02 billion in 2023 to $6.59 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by the proliferation of smartphones, IoT devices, and significant technological advancements in telecommunications. Countries like China and India are leading the charge due to their massive consumer base and increasing penetration of connected devices.North America Embedded Sim Esim Market Report:
North America exhibits a strong growth trajectory, with the market size projected to increase from $3.55 billion in 2023 to $11.56 billion by 2033. Factors driving this growth include strong investment in IoT solutions and a high adoption rate of connected devices. Leading telecommunications companies are actively pursuing eSIM innovations.South America Embedded Sim Esim Market Report:
The Embedded Sim market in South America is relatively nascent, with a size of $0.26 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $0.86 billion by 2033. The market is largely influenced by the demand for improved mobile connectivity and the adoption of advanced telecommunications infrastructure.Middle East & Africa Embedded Sim Esim Market Report:
The Embedded Sim market in the Middle East and Africa is projected to grow from $1.36 billion in 2023 to $4.43 billion by 2033. Market growth is influenced by increased mobile penetration and technological advancements in telecommunications. The region is gradually adopting eSIM technologies across various applications.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
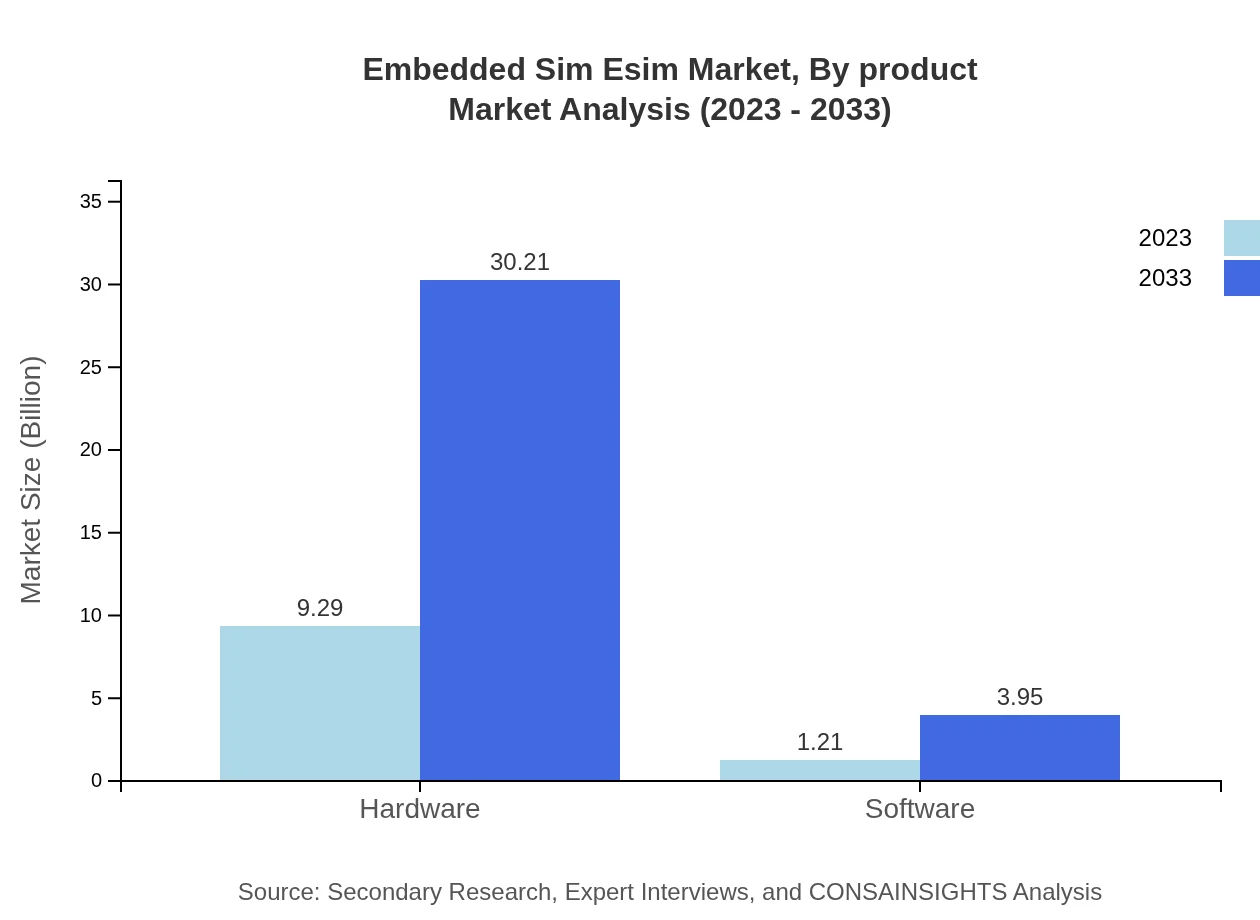
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis By Product
As of 2023, the hardware segment dominates the eSIM market with an estimated size of $9.29 billion, expected to reach $30.21 billion by 2033. The growth is attributed to increased demand for eSIM-enabled devices. Software solutions are also critical, expected to grow from $1.21 billion to $3.95 billion over the same period.
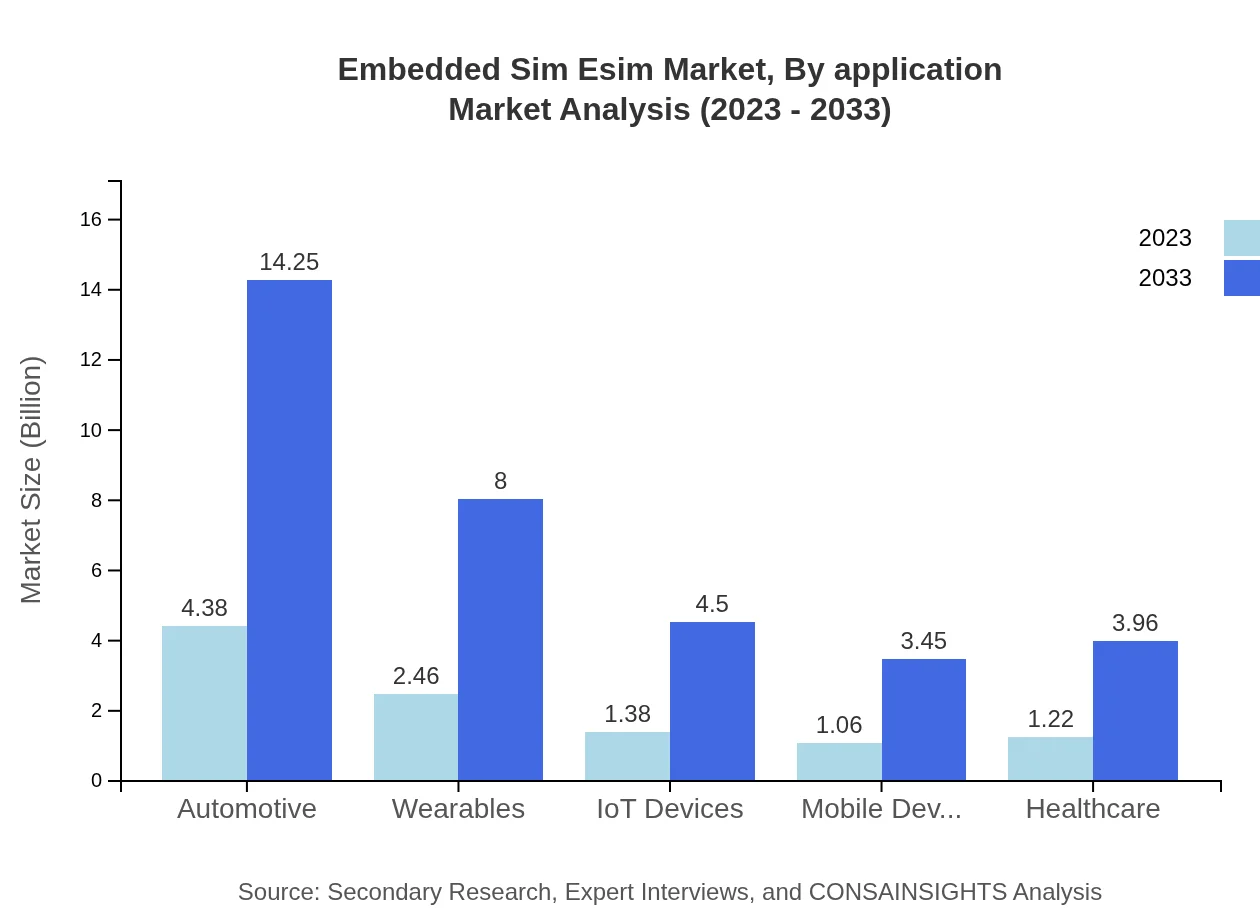
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis By Application
The telecommunications application segment leads the eSIM market with a size of $5.54 billion in 2023, predicted to reach $18.02 billion by 2033, contributing significantly to overall growth. Other applications like automotive and consumer electronics are also witnessing notable growth.
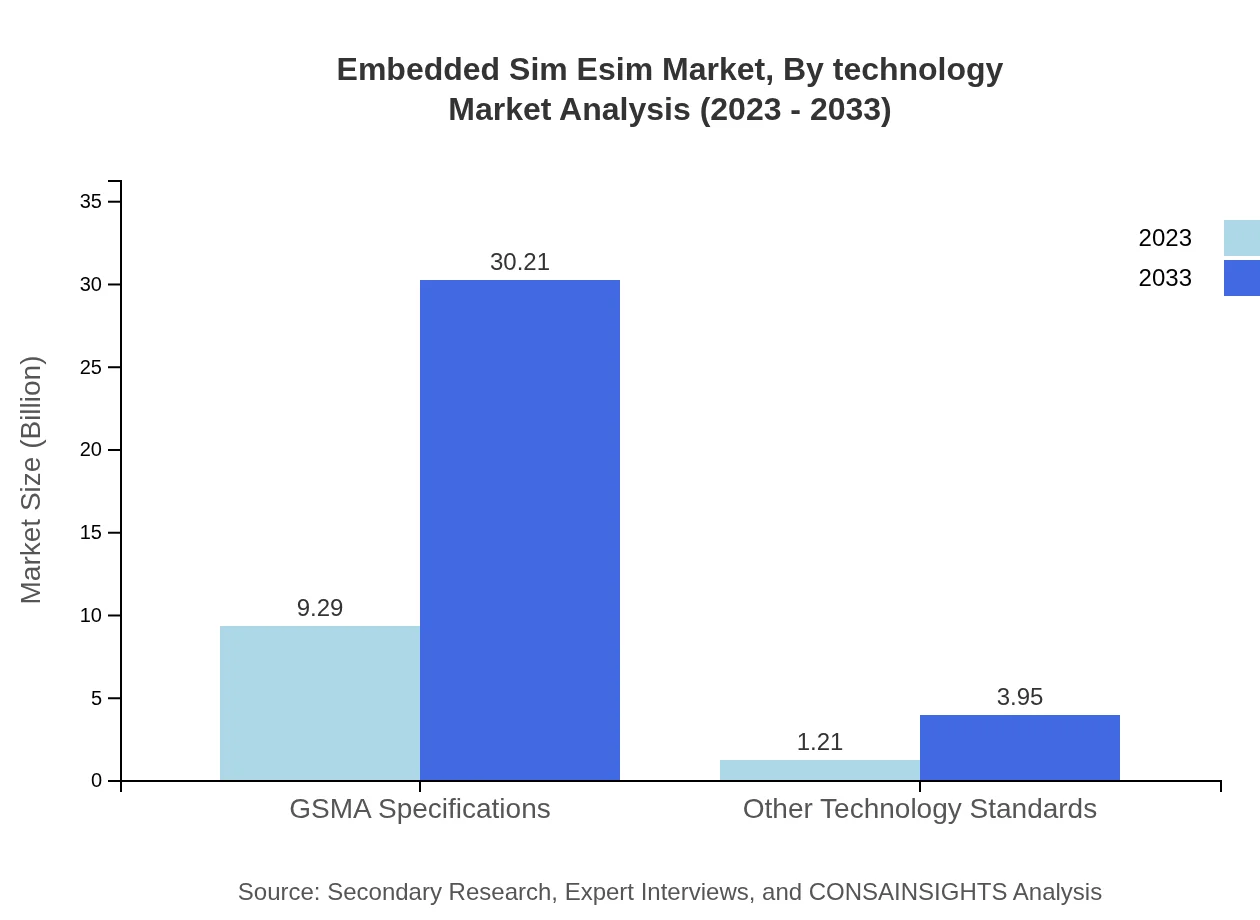
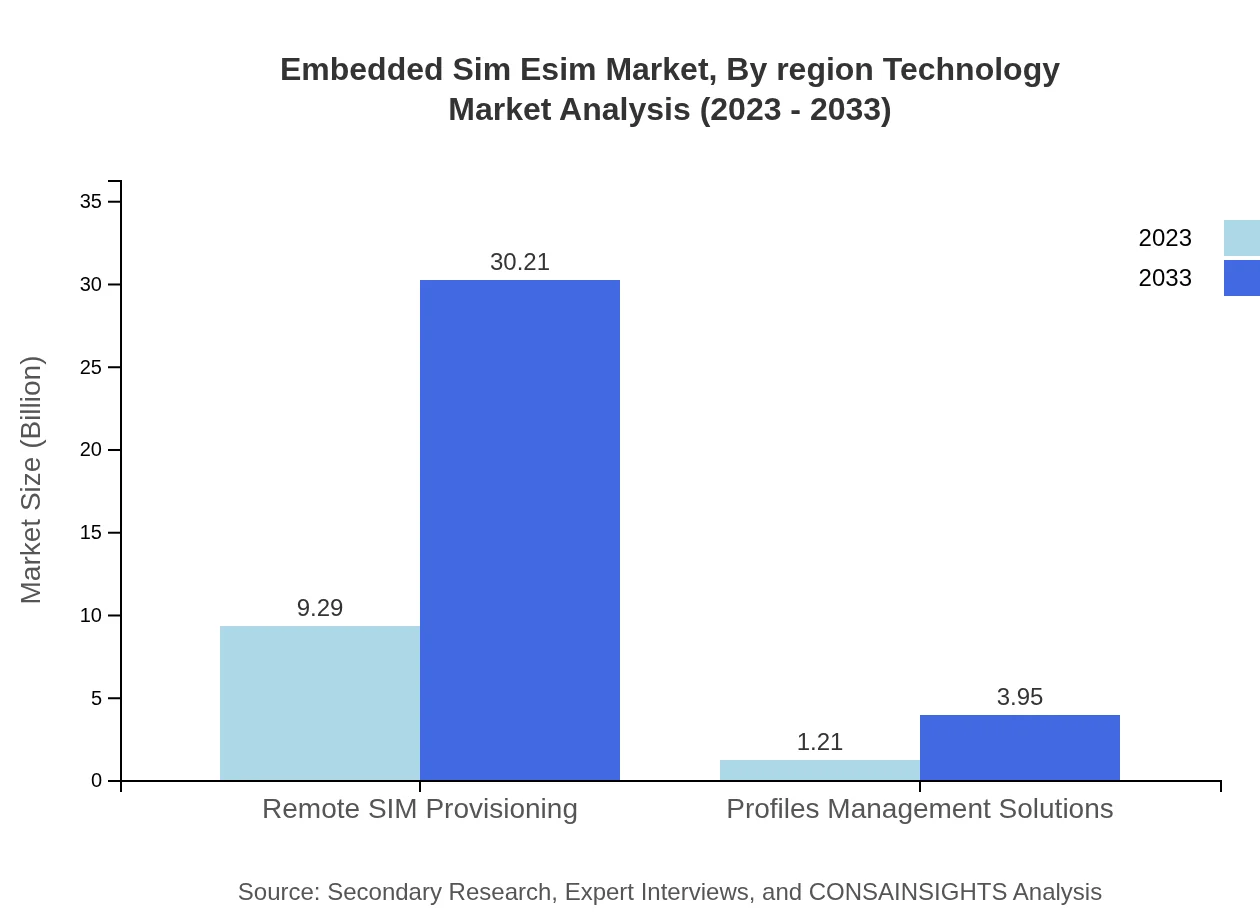
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis By Technology
The market for eSIM technology, particularly remote SIM provisioning solutions, is projected to expand significantly, exhibiting a growing demand. GSMA specifications will continue to underpin product development, with the market size anticipated to progress from $9.29 billion in 2023 to $30.21 billion by 2033.
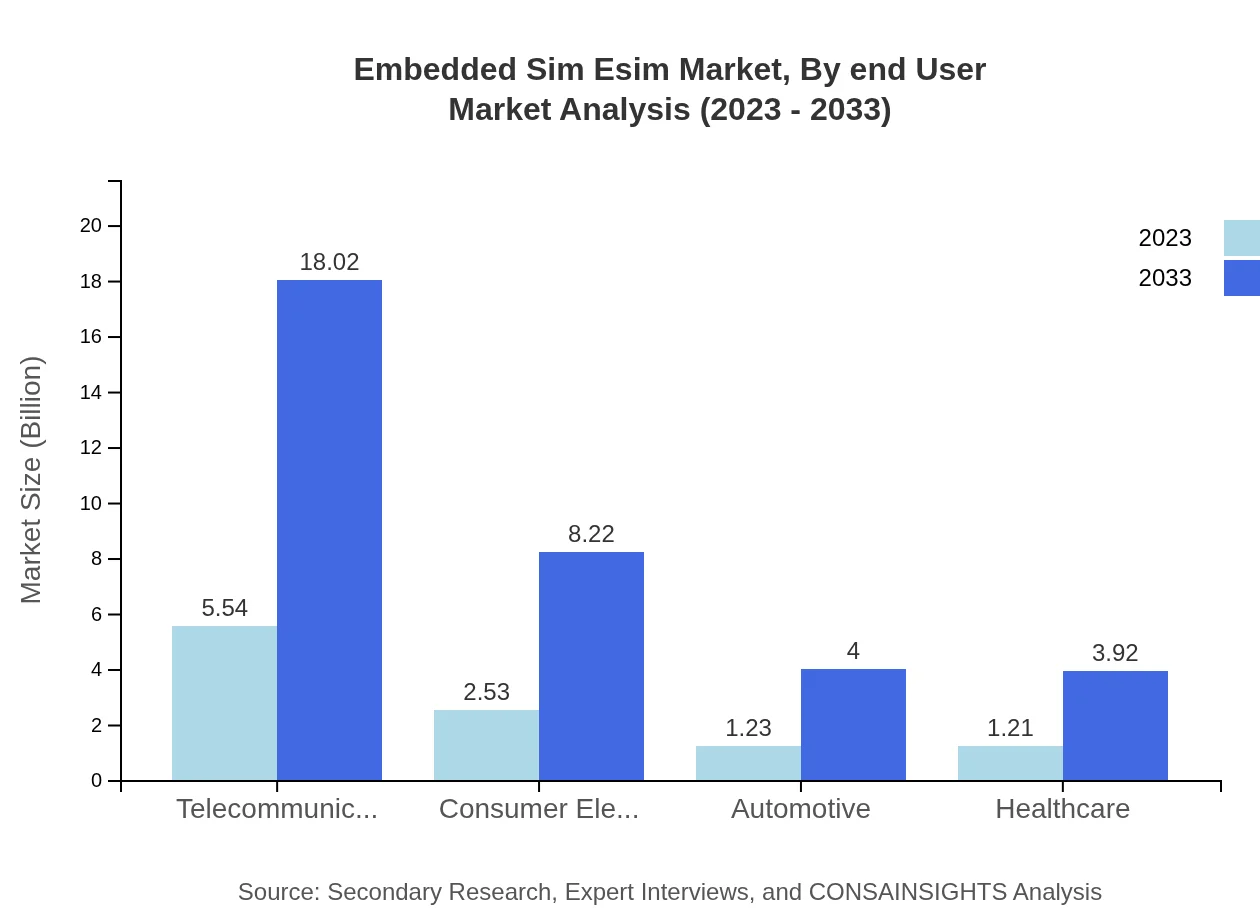
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis By End User
Different industries, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics, are increasingly adopting eSIM technologies, with automotive expected to grow from $1.23 billion to $4.00 billion by 2033, showcasing its potential in connected vehicles.
Embedded Sim Esim Market Analysis By Region Technology
The eSIM market's focus on emerging technologies like IoT and mobile devices is evident, with specific segments enjoying rapid growth due to the increasing need for connectivity and remote provisioning capabilities.
Embedded Sim Esim Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Embedded Sim Esim Industry
Apple :
Apple is a leading innovator in the eSIM space, integrating eSIM technology into devices like iPhones and iPads, allowing seamless connectivity for users around the globe.GSMA (GSM Association):
GSMA plays a crucial role in setting the standards for eSIM technology and facilitating industry collaboration for the widespread adoption of eSIM solutions.STMicroelectronics:
STMicroelectronics is a prominent semiconductor supplier, providing essential hardware components that support eSIM technology and its integration into various consumer devices.Vodafone:
As a global telecommunications leader, Vodafone is a key player in the eSIM market, offering services that leverage eSIM technology to enhance mobile connectivity.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of embedded Sim Esim?
The embedded SIM (eSIM) market is projected to grow from a market size of approximately $10.5 billion in 2023, with a CAGR of 12%, reaching new heights by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this embedded Sim Esim industry?
Key players in the embedded SIM industry include major technology companies such as Gemalto, Giesecke+Devrient, and STMicroelectronics, alongside network operators and telecommunications companies that drive innovation and deployment.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the embedded Sim Esim industry?
Growth in the eSIM market is driven by increased IoT adoption, demand for connected devices, and the flexibility offered by remote SIM provisioning, resulting in streamlined services for consumers and businesses.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the embedded Sim Esim?
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the embedded SIM market, with projected growth from $2.02 billion in 2023 to $6.59 billion by 2033, showcasing significant potential due to rising smartphone and IoT device adoption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the embedded Sim Esim industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the embedded SIM industry, ensuring precise insights and analytics for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this embedded Sim Esim market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscapes, and actionable insights, all designed to support strategic planning within the embedded SIM sector.
What are the market trends of embedded Sim Esim?
Current market trends include the rise of GSMA specifications, increased investments in remote SIM provisioning, and a shift towards hardware dominance, where hardware is projected to maintain an 88.43% market share through 2033.