Embedded Software And Tools Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: embedded-software-and-tools
Embedded Software And Tools Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Embedded Software and Tools market from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, growth projections, competitive dynamics, regional insights, and trends influencing this sector, offering valuable insights for stakeholders.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
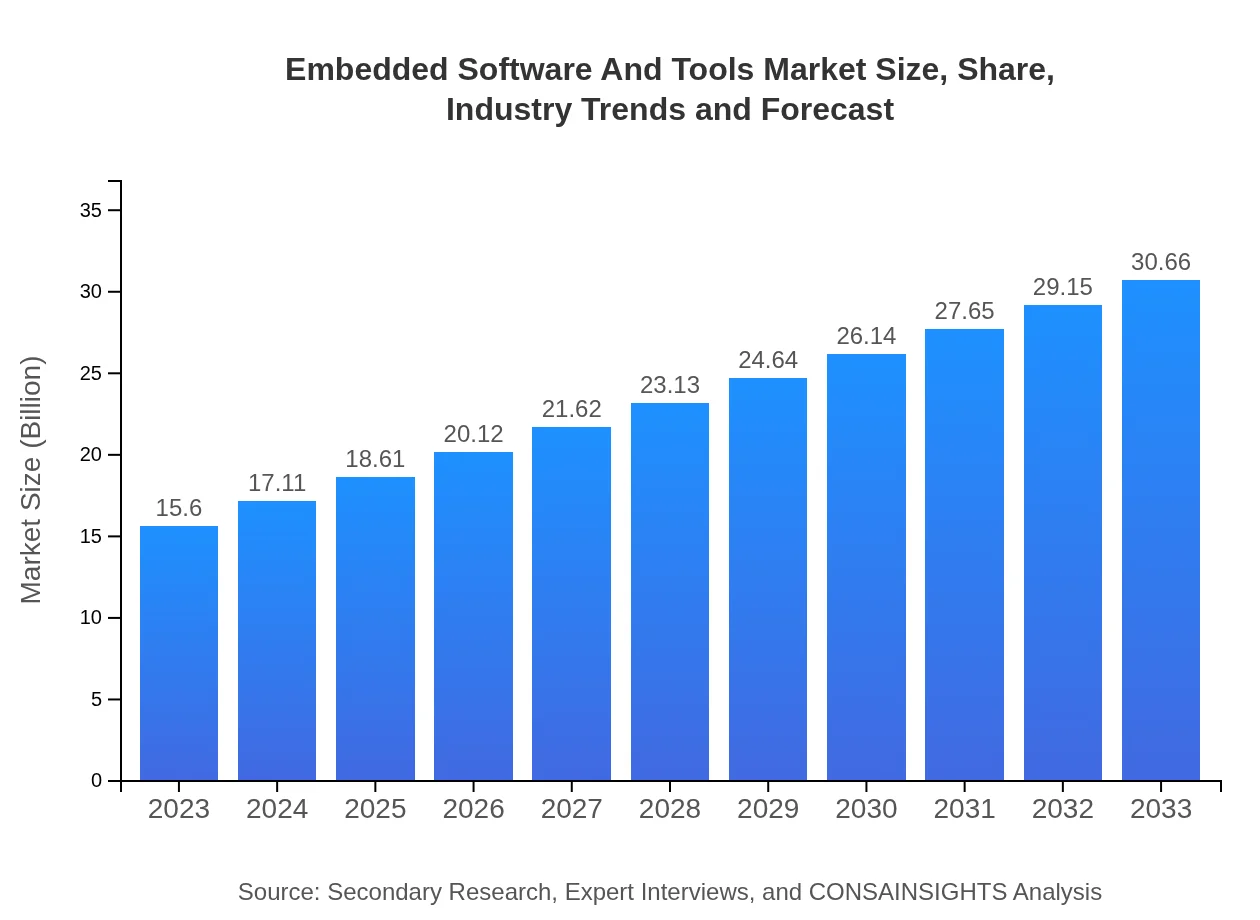
| 2023 Market Size | $15.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $30.66 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Microsoft Corporation, Intel Corporation, Wind River Systems, Inc., NXP Semiconductors |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Embedded Software And Tools Market Overview
Customize Embedded Software And Tools Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Embedded Software And Tools market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Embedded Software And Tools's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Embedded Software And Tools
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Embedded Software And Tools market in 2023 and 2033?
Embedded Software And Tools Industry Analysis
Embedded Software And Tools Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Embedded Software And Tools Market Report:
Europe is projected to see growth from $4.17 billion in 2023 to $8.19 billion by 2033. Focus on green and sustainable technologies, alongside stringent regulations addressing safety and efficiency, drives the demand for advanced embedded systems in various sectors including automotive and industrial.Asia Pacific Embedded Software And Tools Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market size is expected to grow from $2.99 billion in 2023 to $5.88 billion by 2033, driven by rising investments in smart technologies and a booming electronics manufacturing sector. Countries like China, Japan, and India are leading this demand surge, particularly in automotive and consumer electronics.North America Embedded Software And Tools Market Report:
The North American market, one of the largest, is poised to increase from $5.74 billion in 2023 to $11.27 billion by 2033. The strong presence of key industry players and increasing adoption of embedded systems in IoT applications are significant growth factors.South America Embedded Software And Tools Market Report:
South America shows a gradual increase in the Embedded Software and Tools sector, expanding from $1.30 billion in 2023 to $2.56 billion by 2033. The growth is majorly influenced by governmental initiatives focusing on technology adoption in various industries, particularly in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Embedded Software And Tools Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region will rise from $1.40 billion in 2023 to $2.76 billion by 2033, as investments in smart infrastructures increase. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are leading the charge with smart city projects and initiatives fostering digital transformation.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
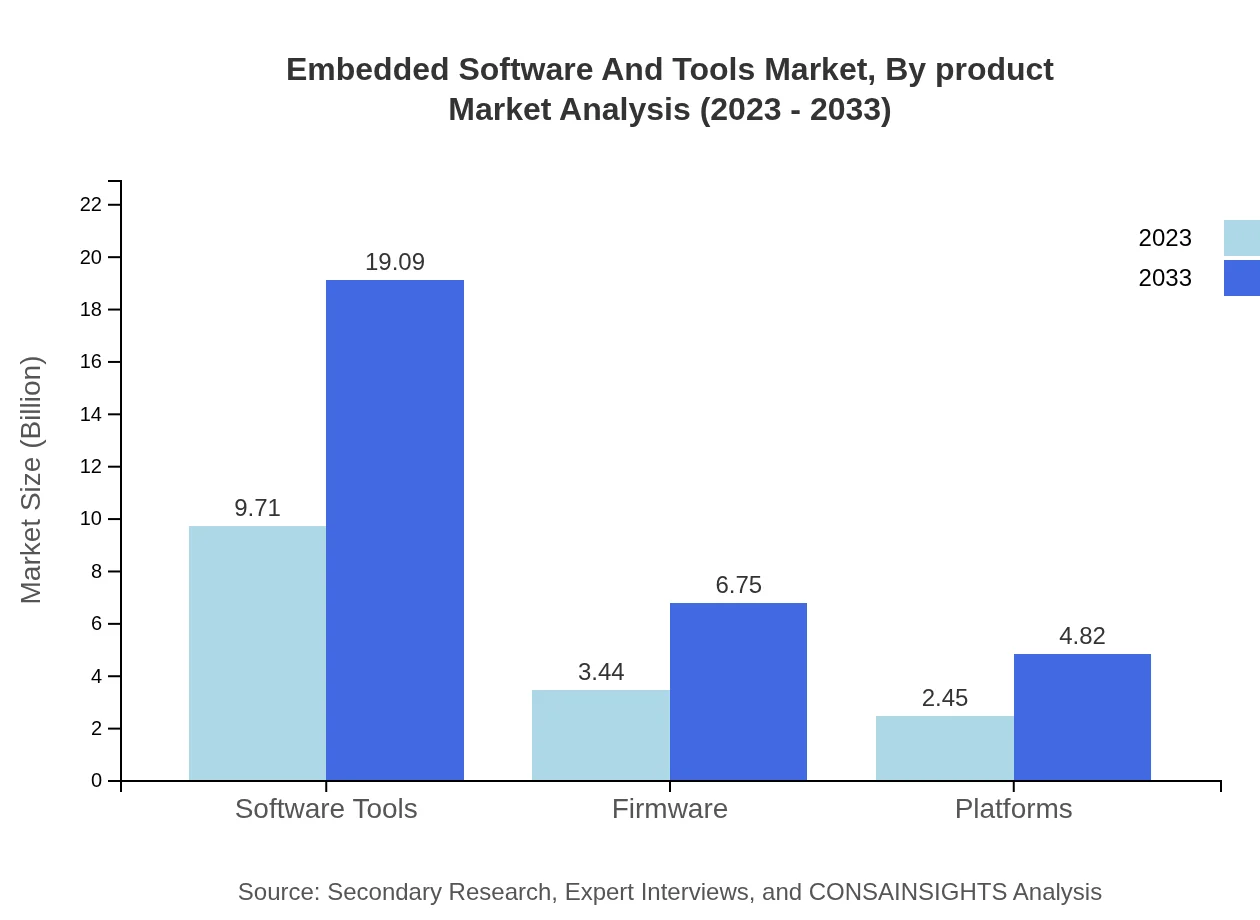
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis By Product
The software tools segment dominates the market, valued at $9.71 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $19.09 billion by 2033. Firmware, crucial to ensuring device efficiency, is valued at $3.44 billion in 2023, with an anticipated increase to $6.75 billion. Platforms also play a significant role with projections of growth from $2.45 billion to $4.82 billion, evidencing a trend toward integrated solutions.
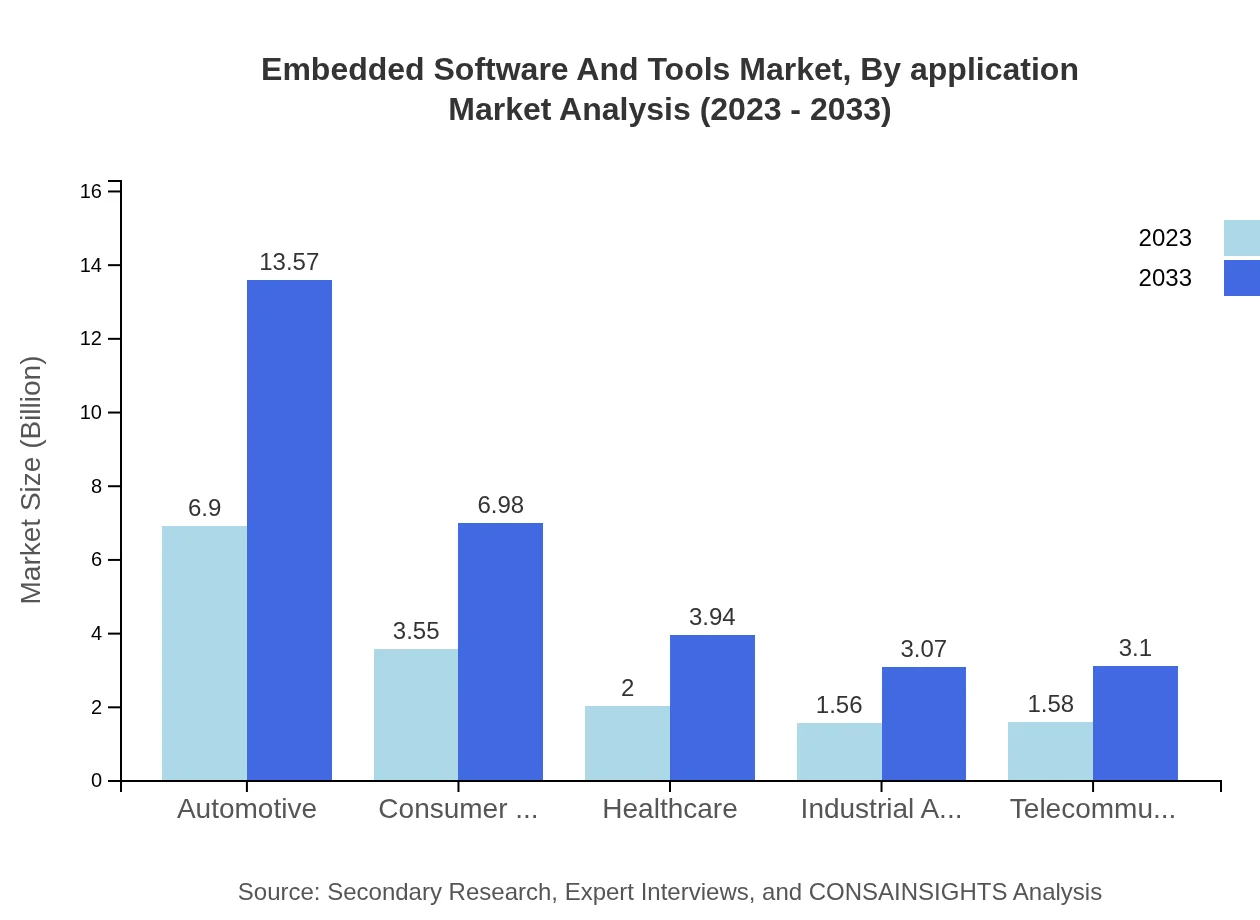
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis By Application
Applications across automotive, industrial automation, and consumer electronics are significant contributors to market growth. The automotive segment is dominated by a market share of 44.26% in 2023, indicating the substantial role of embedded systems in enabling enhanced vehicle functionalities. The consumer electronics and healthcare segments also show strong shares of 22.78% each, emphasizing the urgent need for innovation in product functionality and safety measures.
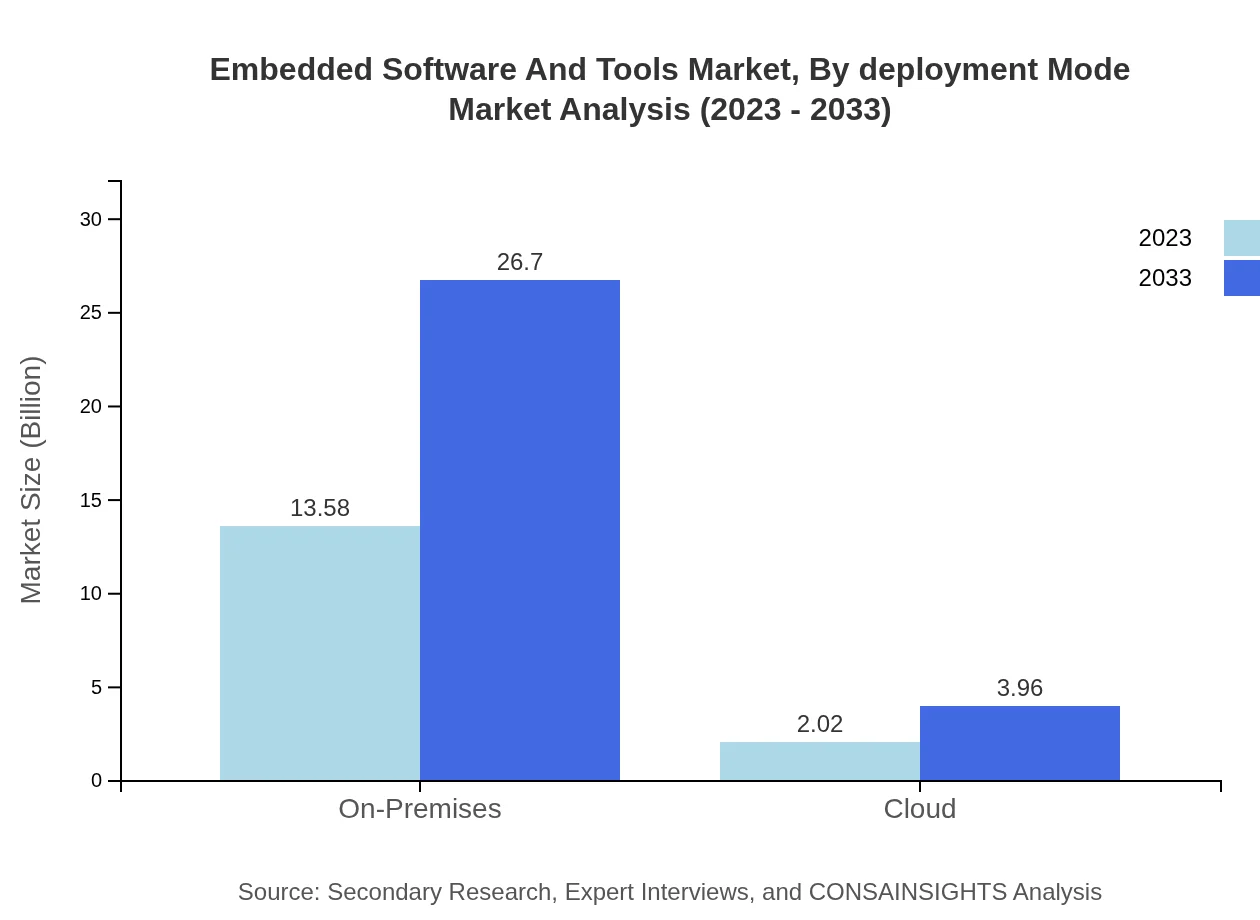
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
Deployment modes are categorized into On-Premises and Cloud solutions. The On-Premises segment dominates with a share of 87.08% currently, signifying a traditional inclination towards localized software solutions. Cloud solutions, however, are gaining traction, with a market size of $2.02 billion in 2023, growing substantially to $3.96 billion by 2033 as companies pivot towards flexible and scalable solutions.
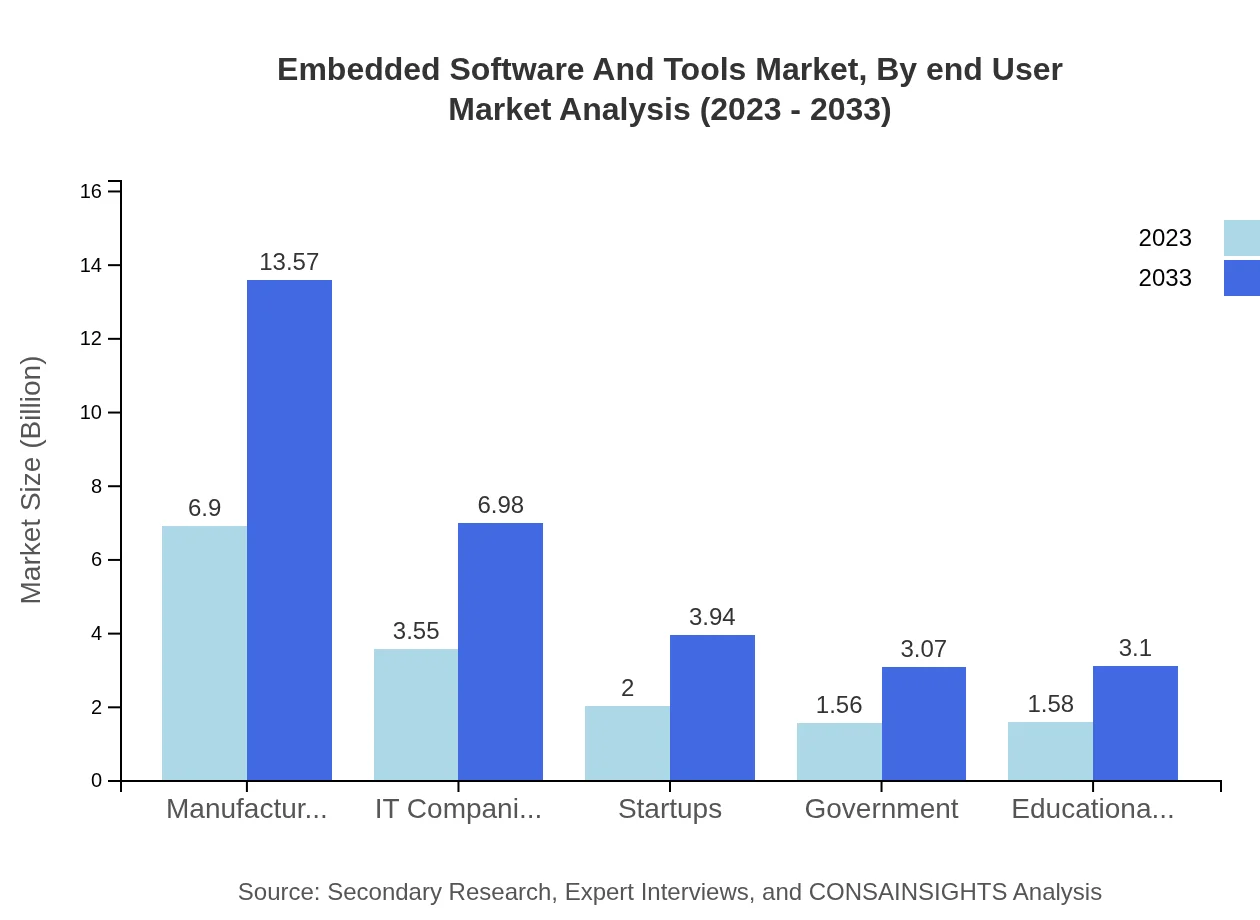
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, and healthcare are leading in embedded solutions. The automotive sector's increased focus on autonomous driving technology is a significant driver, while consumer electronics show a steady demand for innovative features. Healthcare's adoption of embedded systems for medical devices is also growing, projected to rise from $2.00 billion to $3.94 billion by 2033.
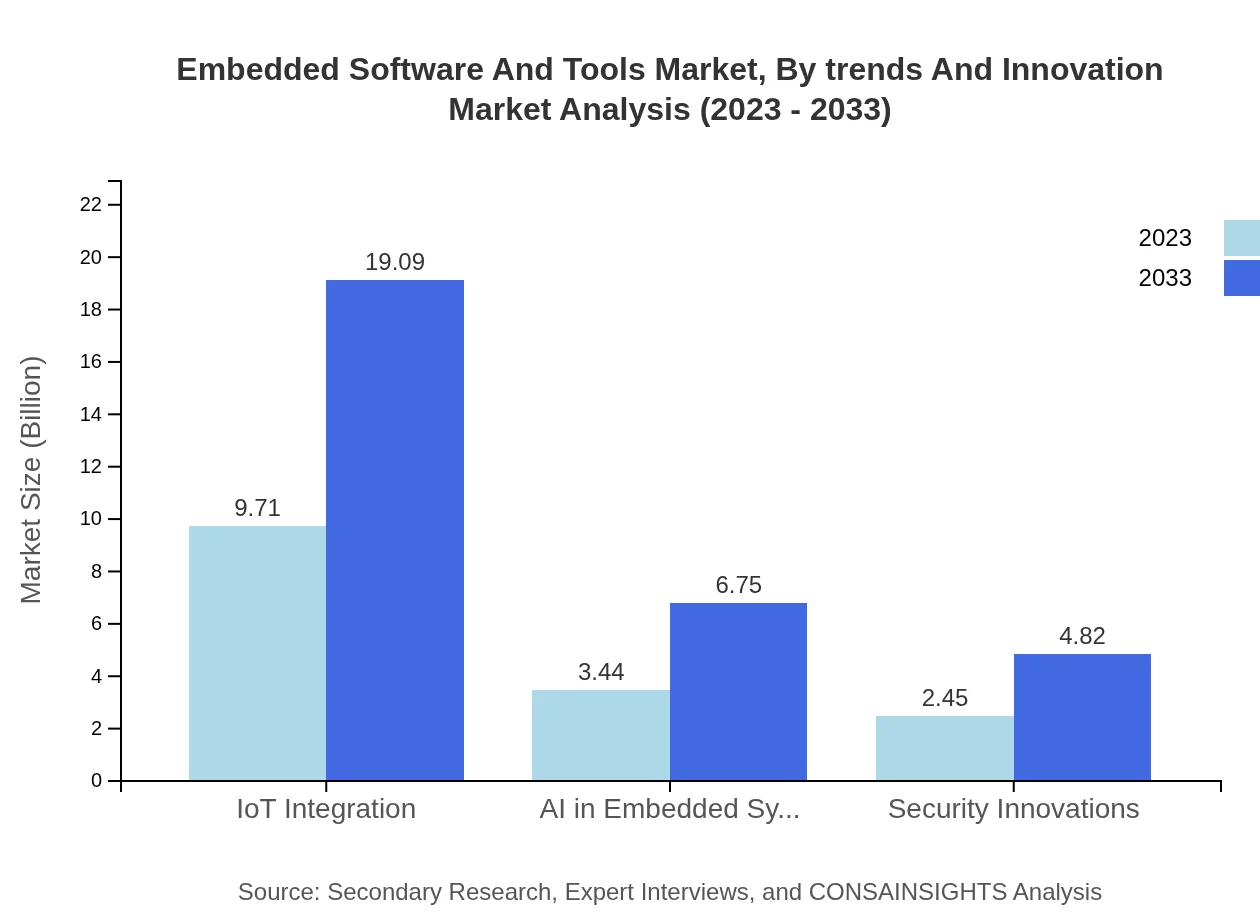
Embedded Software And Tools Market Analysis By Trends And Innovation
Technological trends such as IoT integration, advancements in AI, and innovations in security are transforming the Embedded Software and Tools market. Projections show that IoT integration will reach $9.71 billion in 2023, growing to $19.09 billion by 2033, illustrating a lucrative avenue as industries seek connected and smart systems.
Embedded Software And Tools Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Embedded Software And Tools Industry
Siemens AG:
A leading player in industrial automation and smart infrastructure, Siemens AG develops comprehensive embedded solutions for various industries.Microsoft Corporation:
Microsoft provides advanced embedded software tools that facilitate application development and integration, particularly in cloud and IoT tech.Intel Corporation:
Intel's focus on integrated systems and its development of software for embedded applications has positioned it as a key player in this sector.Wind River Systems, Inc.:
Specializes in providing software solutions tailored for embedded systems, focusing on performance, safety, and security.NXP Semiconductors:
Offers a wide range of semiconductor solutions and software tools for creating advanced embedded systems across several sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of embedded Software And Tools?
The embedded software and tools market is valued at approximately $15.6 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8%, reaching new heights by 2033. This growth reflects the increasing dependence on embedded technologies across various industries.
What are the key market players or companies in the embedded Software And Tools industry?
Key players in the embedded software and tools industry include major technology companies and specialized firms that focus on firmware development, software tools, platform solutions, and integration services. These entities are critical in driving innovation and meeting market demands.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the embedded Software And Tools industry?
Growth in this industry is primarily driven by the increasing demand for IoT devices, the rising penetration of AI in embedded systems, and advancements in communication technologies. Additionally, automation across various sectors boosts adoption rates of these tools.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the embedded Software And Tools market?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the embedded software and tools market, projected to grow from $5.74 billion in 2023 to $11.27 billion by 2033. This growth is spurred by significant technological advancements and high investment levels in R&D.
Does Consainsights provide customized market report data for the embedded Software And Tools industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs in the embedded software and tools industry. This service includes detailed insights and analyses relevant to particular segments, regions, or competitive landscapes.
What deliverables can I expect from this embedded Software And Tools market research project?
Deliverables from this market research project include comprehensive reports, detailed market forecasts, segmentation analyses by application and region, competitive landscape profiles, and strategic recommendations based on the latest trends and insights in the industry.
What are the market trends of embedded Software And Tools?
Current market trends in the embedded software and tools sector include the increasing adoption of cloud solutions, advancements in AI integrations, and a growing focus on security innovations. Moreover, IoT integration remains a key area of growth with significant implications for various industries.