Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: enterprise-resource-planning
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) market, covering market dynamics, size, segmentation, regional insights, and future trends for the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
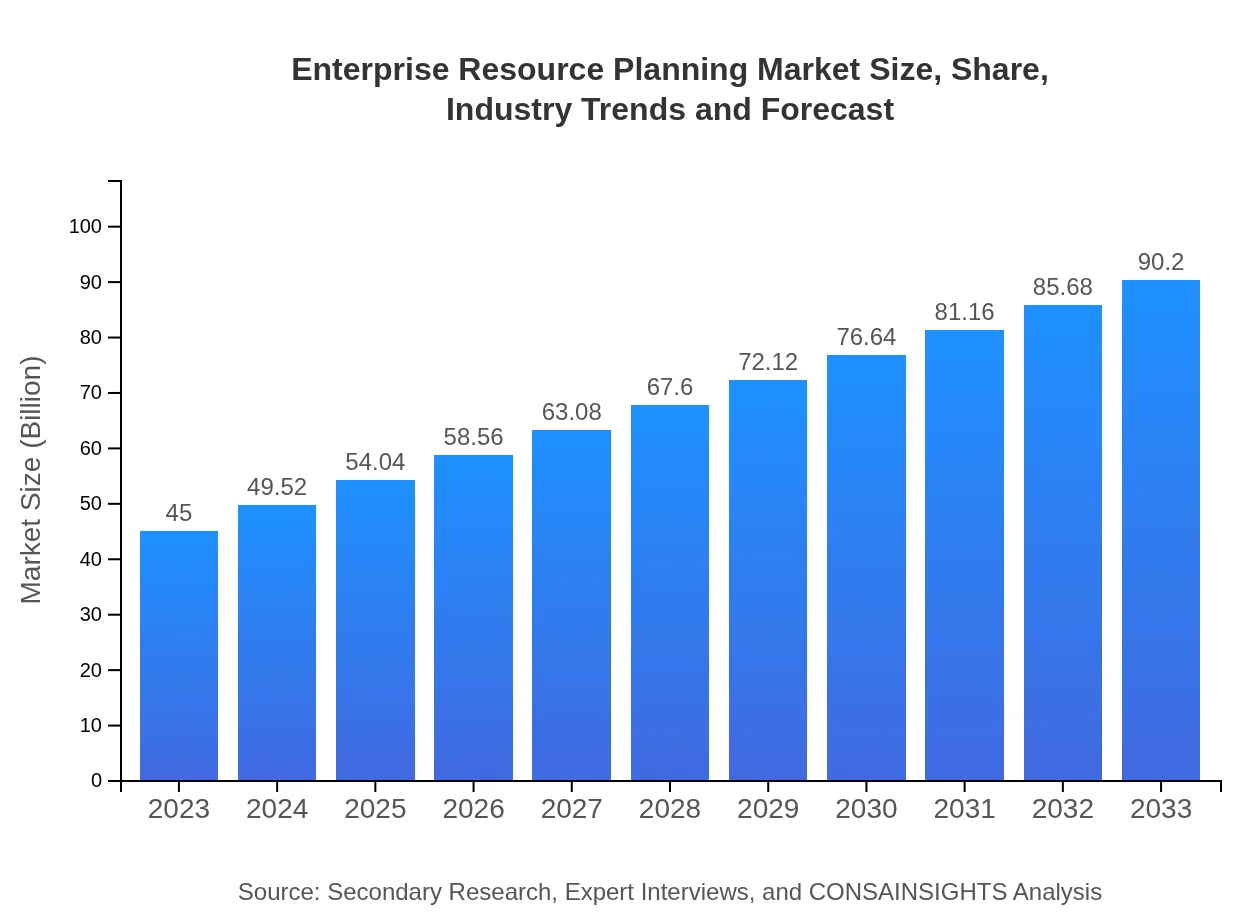
| 2023 Market Size | $45.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $90.20 Billion |
| Top Companies | SAP SE, Oracle Corporation, Microsoft Dynamics, Infor, Workday, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Overview
Customize Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Enterprise Resource Planning market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Enterprise Resource Planning's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Enterprise Resource Planning
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Enterprise Resource Planning market in 2023?
Enterprise Resource Planning Industry Analysis
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report:
Europe's ERP market will grow from $14.30 billion in 2023 to $28.66 billion by 2033. Increasing compliance requirements and the demand for industry-specific solutions in countries such as Germany and the UK significantly drive this growth.Asia Pacific Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the ERP market is expected to grow significantly from $8.96 billion in 2023 to $17.95 billion by 2033. The shift towards digital transformation across various sectors and increasing governmental support for technology adoption are key growth factors.North America Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report:
North America's ERP market was valued at $14.72 billion in 2023, with expectations to reach $29.50 billion by 2033. Dominated by major software companies, this region is seeing a rise in public cloud ERP adoption and integrated solutions that appeal to both large organizations and SMEs.South America Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report:
In South America, the ERP market is projected to expand from $2.36 billion in 2023 to approximately $4.73 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising demand for cloud ERP solutions and improvements in internet infrastructure.Middle East & Africa Enterprise Resource Planning Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are anticipated to see the ERP market grow from $4.67 billion in 2023 to $9.36 billion by 2033. Economic diversification initiatives in the region and a rising emphasis on digital transformation across enterprises contribute positively to market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
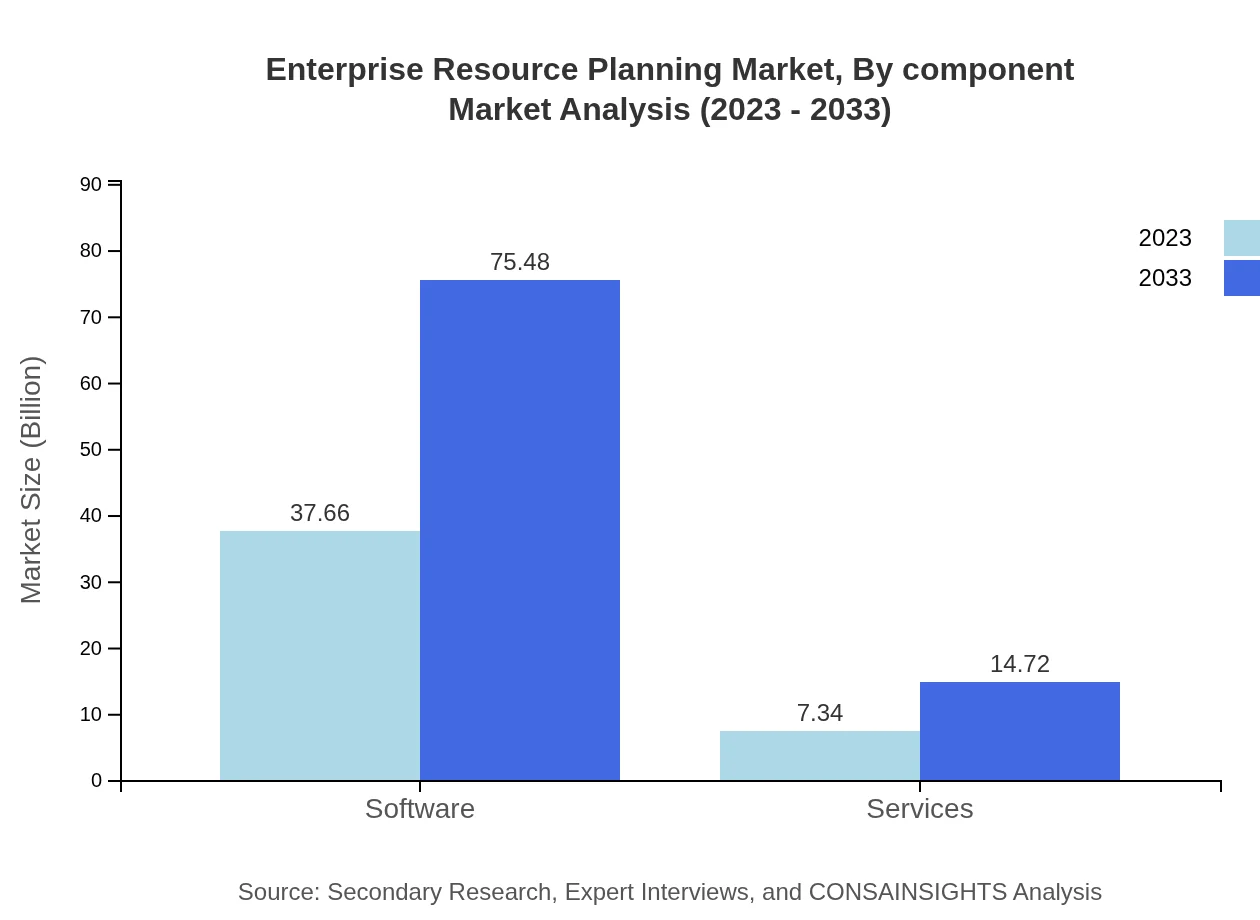
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis By Component
In 2023, the ERP market is composed predominantly of software, which captures around $37.66 billion, projected to grow to $75.48 billion by 2033, representing a significant demand surge for software solutions amidst growing complexities in business operations.
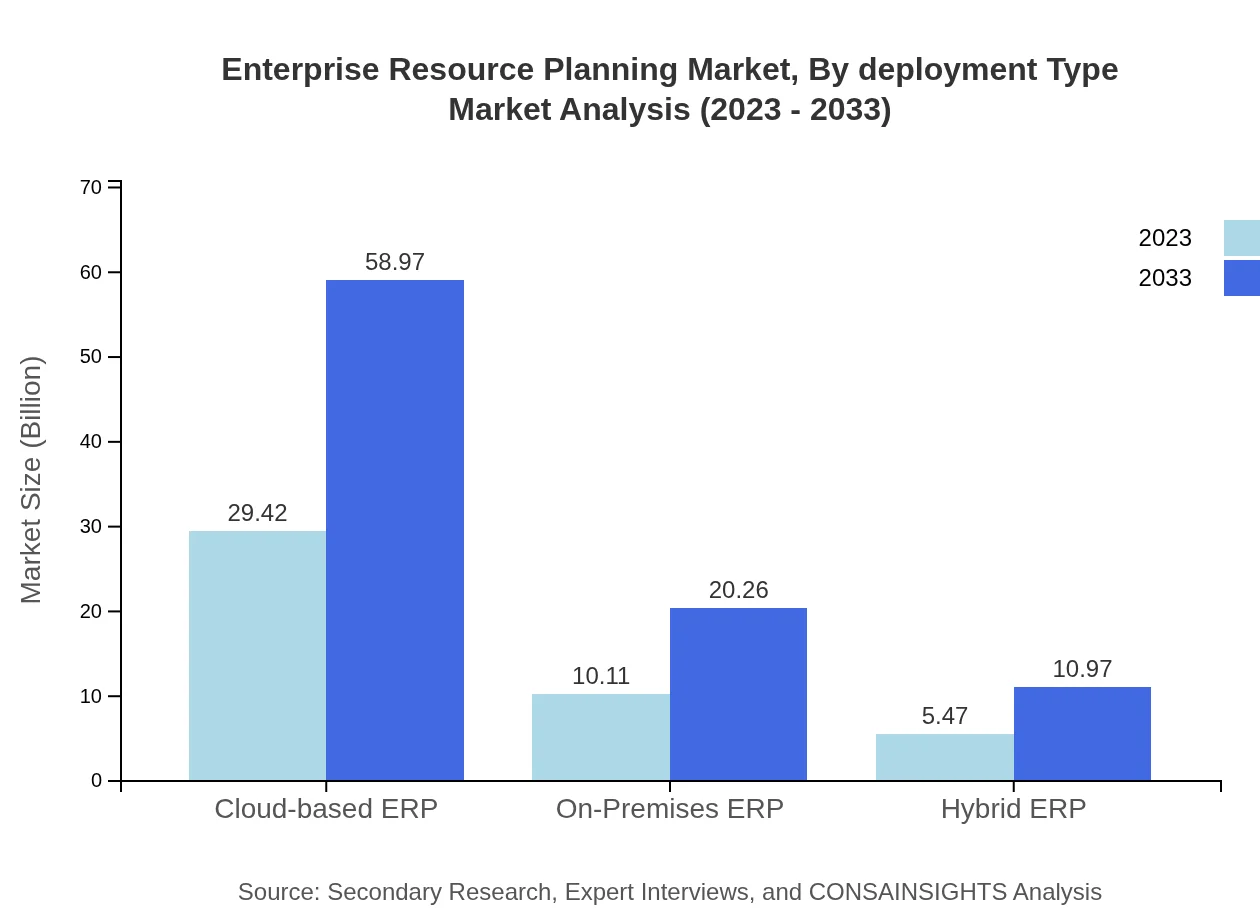
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Cloud-based ERP accounted for approximately $29.42 billion in 2023 and is expected to swell to $58.97 billion by 2033, reflecting a consumer preference shift towards more flexible, lower-cost solutions. In contrast, on-premises solutions are projected to gradually decline in favor of cloud solutions.
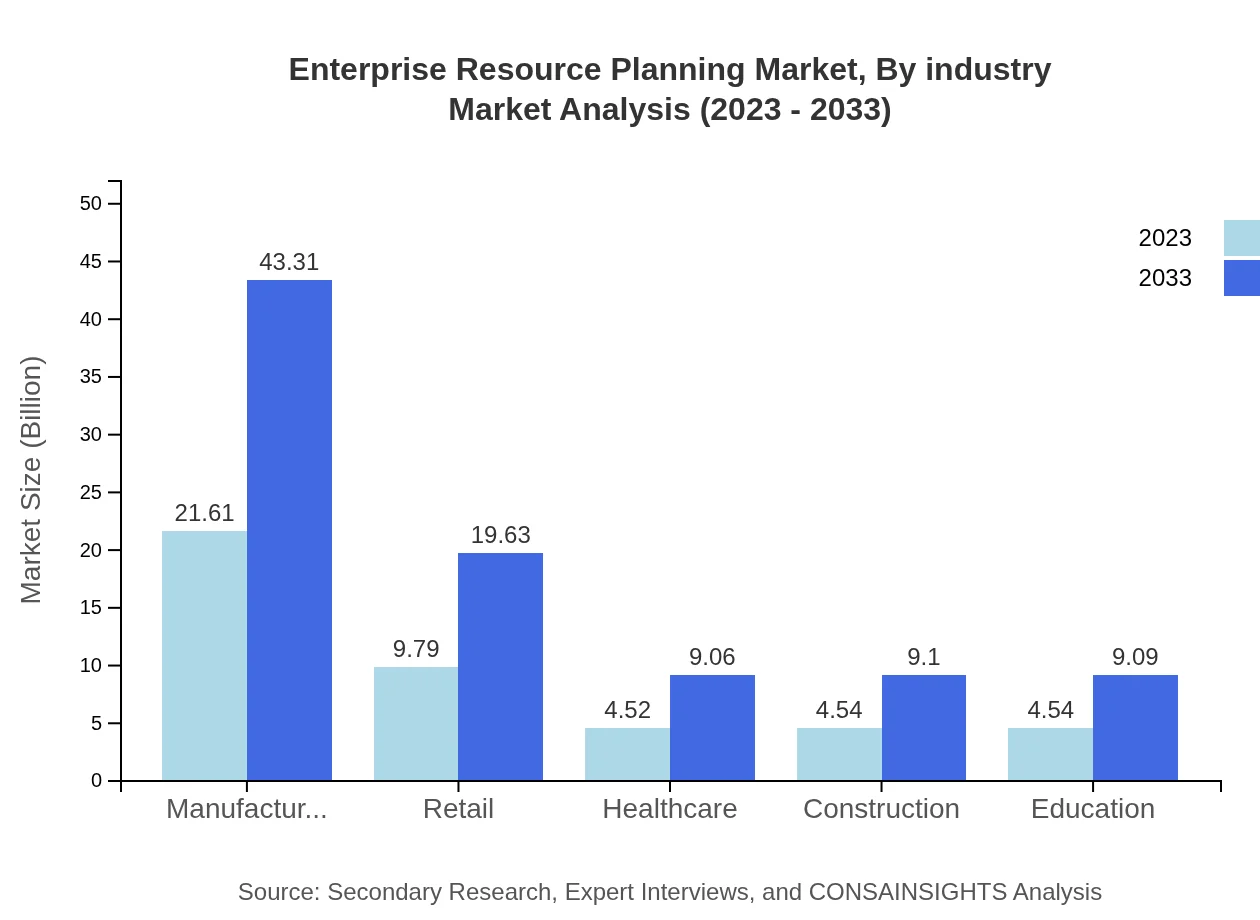
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis By Industry
The manufacturing sector forms the largest share of the ERP market, contributing approximately $21.61 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $43.31 billion by 2033. Manufacturing's continuous push towards automation and efficiency drives this demand.
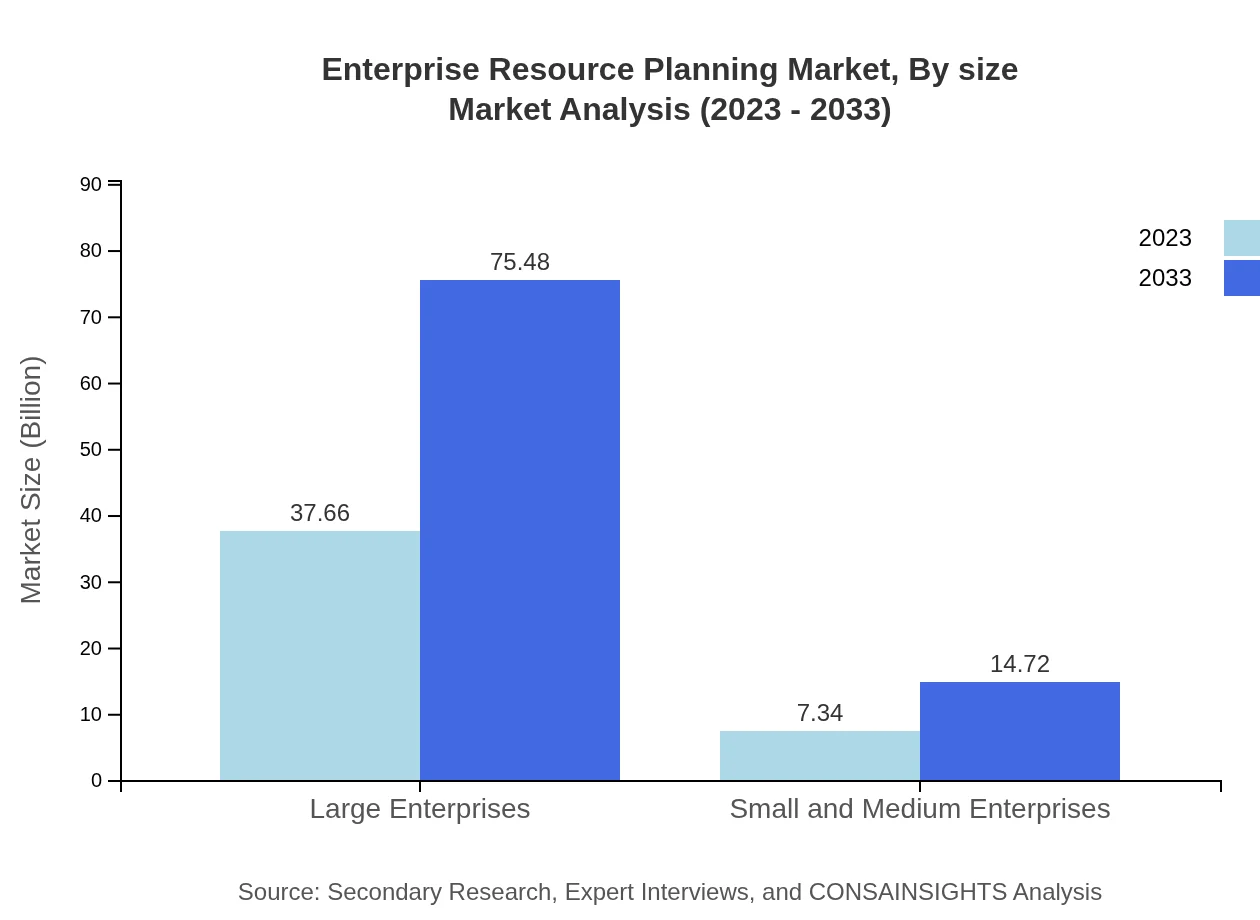
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis By Size
Large enterprises dominate the ERP market with a market size of $37.66 billion in 2023 and a share of 83.68%. However, SMEs are increasingly becoming significant players with a market growth from $7.34 billion in 2023 to $14.72 billion by 2033.
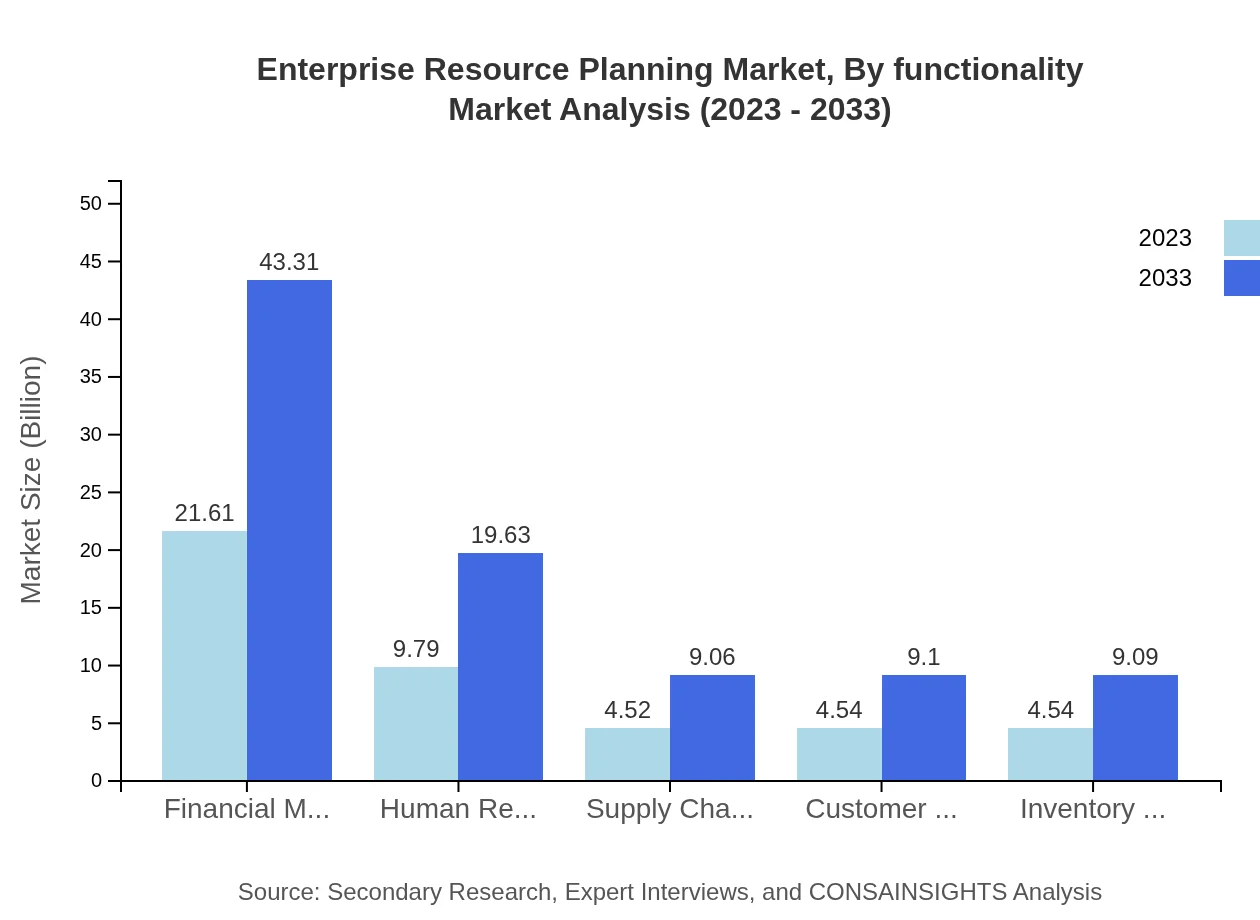
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Analysis By Functionality
Financial Management remains a pivotal segment within the ERP framework, valued at $21.61 billion in 2023 and anticipated to grow to $43.31 billion by 2033. Other functionalities like Human Resource Management, Supply Chain Management, and Customer Relationship Management also show robust growth trajectories.
Enterprise Resource Planning Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Enterprise Resource Planning Industry
SAP SE:
A pioneer in ERP software, SAP has consistently dominated the market with its comprehensive suite that covers end-to-end business management solutions.Oracle Corporation:
Oracle offers a broad range of cloud applications and is renowned for its advanced database solutions that integrate seamlessly with its ERP systems.Microsoft Dynamics:
Known for its flexible and scalable ERP solutions, Microsoft Dynamics assists businesses of all sizes with their diverse management needs.Infor:
Specializing in industry-specific ERP applications, Infor focuses on providing tailored solutions for manufacturing, healthcare, and distribution sectors.Workday, Inc.:
Focused primarily on human capital management and financial management, Workday offers robust cloud-based solutions that support workforce management.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of enterprise Resource Planning?
The enterprise resource planning market is currently valued at $45 billion. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7%, it is projected to expand significantly, increasing its footprint in various sectors by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the enterprise Resource Planning industry?
Key players in the enterprise resource planning industry include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Salesforce, and Infor. These companies are known for providing comprehensive solutions and have a significant market share, contributing to the sector's growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the enterprise resource planning industry?
Factors driving growth in the enterprise resource planning industry include digital transformation, the need for operational efficiency, advancements in cloud technology, and increasing demand for integrated systems among businesses looking to streamline their operations.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the enterprise Resource Planning?
The fastest-growing region in the enterprise resource planning market is North America, projected to grow from $14.72 billion in 2023 to $29.50 billion by 2033. Other regions showing strong growth are Europe and Asia Pacific.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the enterprise Resource Planning industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific customer requirements for the enterprise resource planning industry. This service helps businesses obtain relevant insights suited to their strategic needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this enterprise Resource Planning market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports detailing market size, segment analysis, key players, growth trends, regional insights, and actionable strategies tailored for your business needs in the enterprise resource planning market.
What are the market trends of enterprise Resource Planning?
Current trends in the enterprise resource planning market include a shift towards cloud-based solutions, the integration of AI and machine learning, increased customization options, and a focus on data analytics and business intelligence.